STI's
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chlamydia, Genital Herpes, HPV
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
STI vs STD
STI - infections that have not yet developed into diseases; transmitted during sexual activities or exchange of bodily fluids
STD - diseases that result from STI’s; all STD’s start as STI’s
Chlamydia
Causative agents;
Chlamydia trachomatis
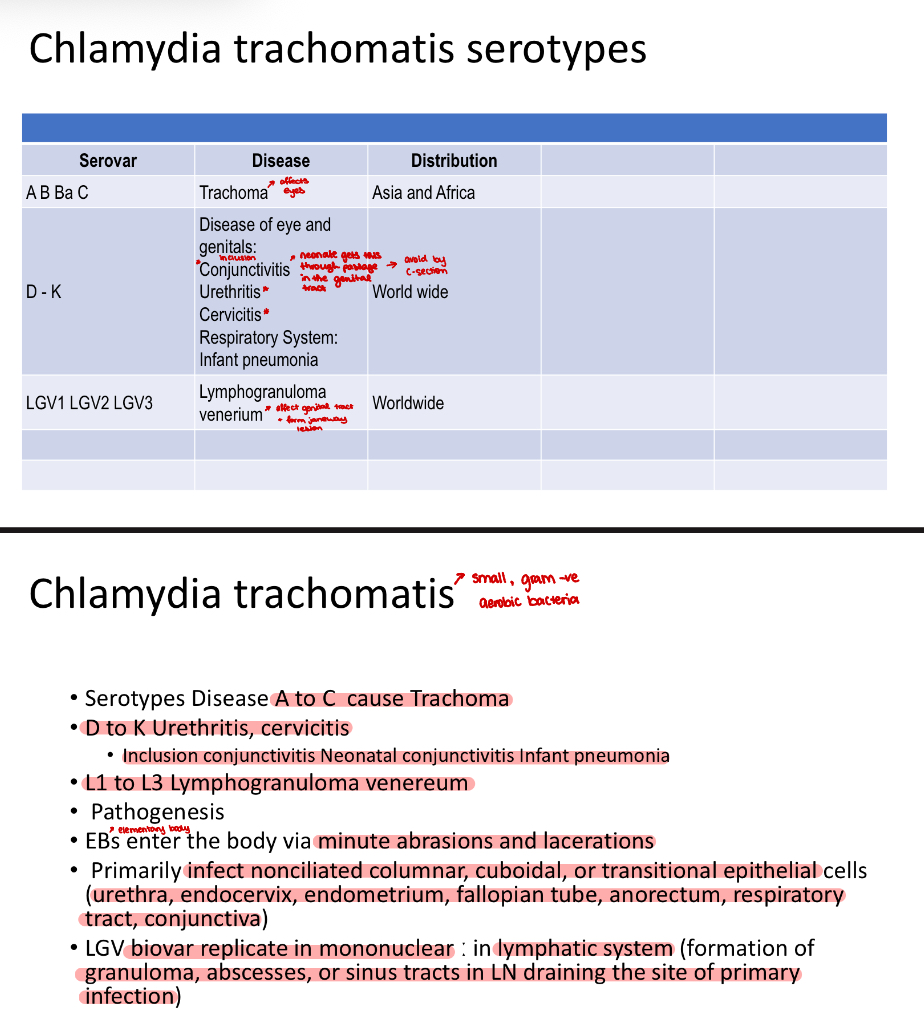
Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
.
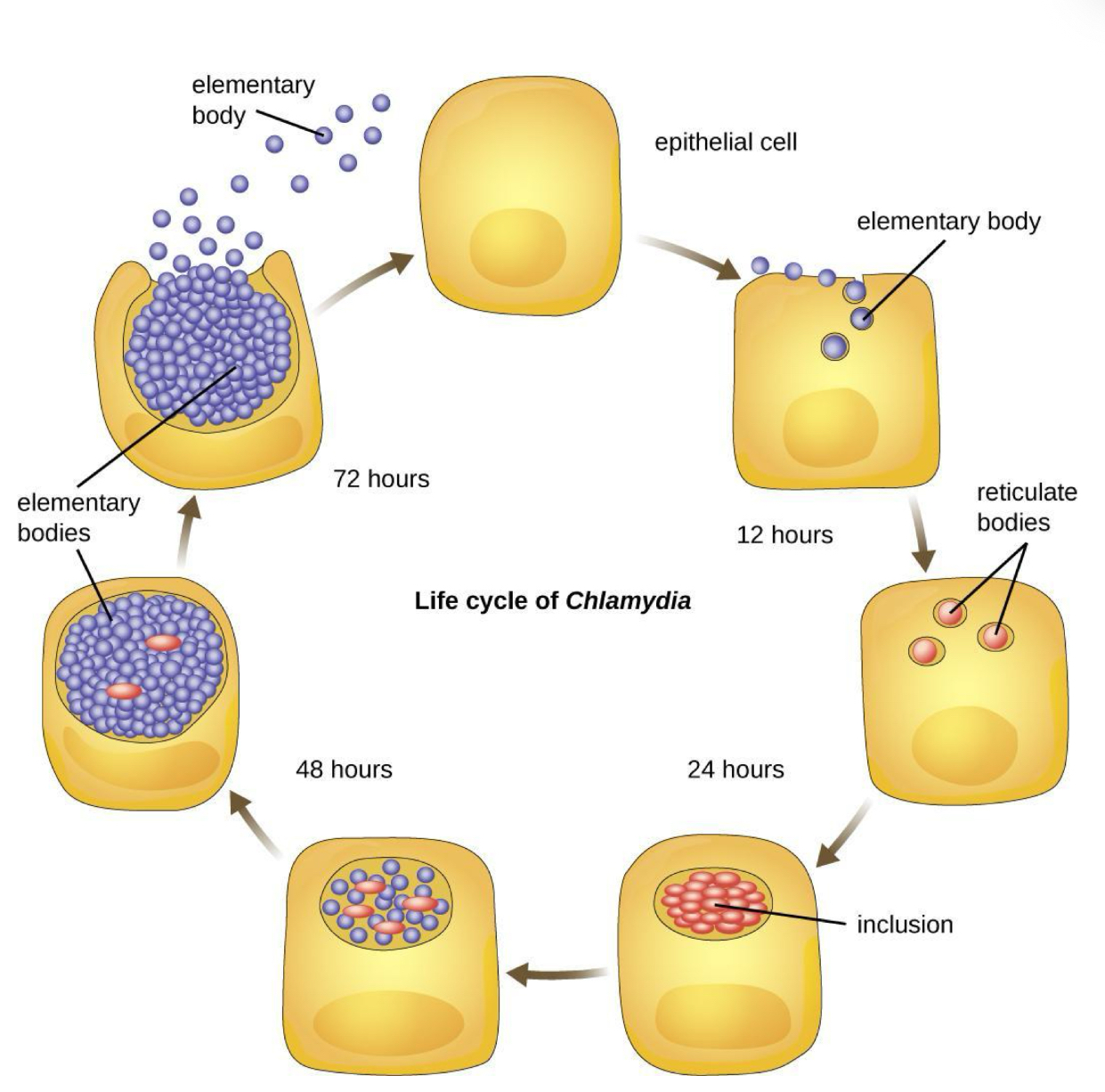
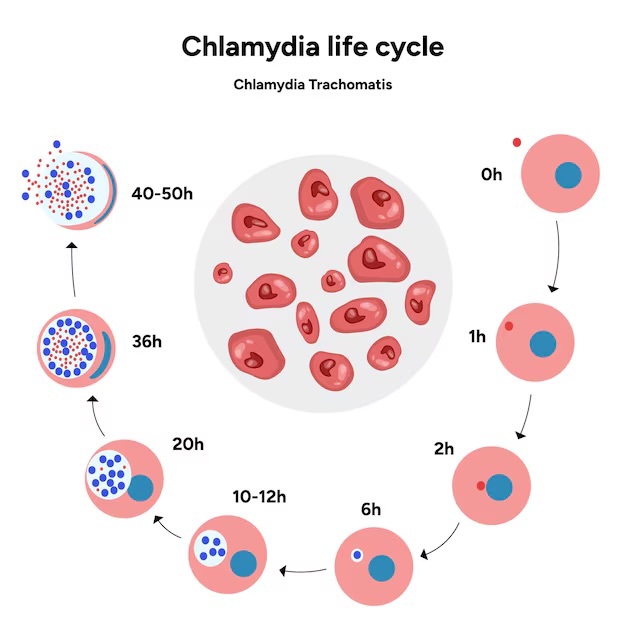
Chlamydia Trachomatis - Life Cycle
Chlamydia begins infection of a host when the metabolically inactive elementary bodies enter an epithelial cell.
Once inside the host cell, the elementary bodies turn into active reticulate bodies.
The reticulate bodies multiply and release more elementary bodies when the cell dies after the Chlamydia uses all of the host cell’s ATP.
Chlamydia Trachomatis - Pathogenesis
Only infects human non-ciliated columnar epithelial cells (Except Biovar mouse)
Stimulates the infiltration of polymorphonuclear cells and lymphocytes leading to lymphoid follicle formation and fibrotic changes,
Cell wall prevents phagosome from fusing with lysosome in phagocytosis
Cell destruction/host inflammatory response
Does not stimulate long-lasting immunity
Reinfection results in an inflammatory response and subsequent tissue damage
Chlamydia - Treatment & Prevention
Azithromycin (!)
Tetracycline
Erythromycin (Macrolides)
Vaccines are of little value and are not used.
Condom use
Treatment, coupled with improved sanitation to prevent reinfection, is the best way to control infection.
Chlamydia - Lab Diagnosis
Cytology
Examination of stained cell scrapings for the presence of inclusion bodies
Culture
most specific method for diagnosis
cultures of susceptible cells
iodine-staining inclusion bodies
The McCoy cell line originally derived from human synovial fluid in 1955, has been later found useful for cultivation of Chlamydia trachomatis
HeLa
Serology
Detection of high titer IgM antibodies is indicative of a recent infection
Use IgG because of recurrence
Chlamydia - Clinical Features
Male - Non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU - mimics gonorrhea, discharge, painful urination)
Female - Urethritis, Cervicitis, Bartholinitis, Discharge
Nearly 75% infections are asymptomatic - puts women at risk for PID
Neonates - Inclusion conjunctivitis
Infants - Infant Pneumonia

Herpes
sexually transmitted disease
virus infection - Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1 & HSV-2)
spreads via sexual intercourse, kissing someone w/ Herpes, skin to skin contact
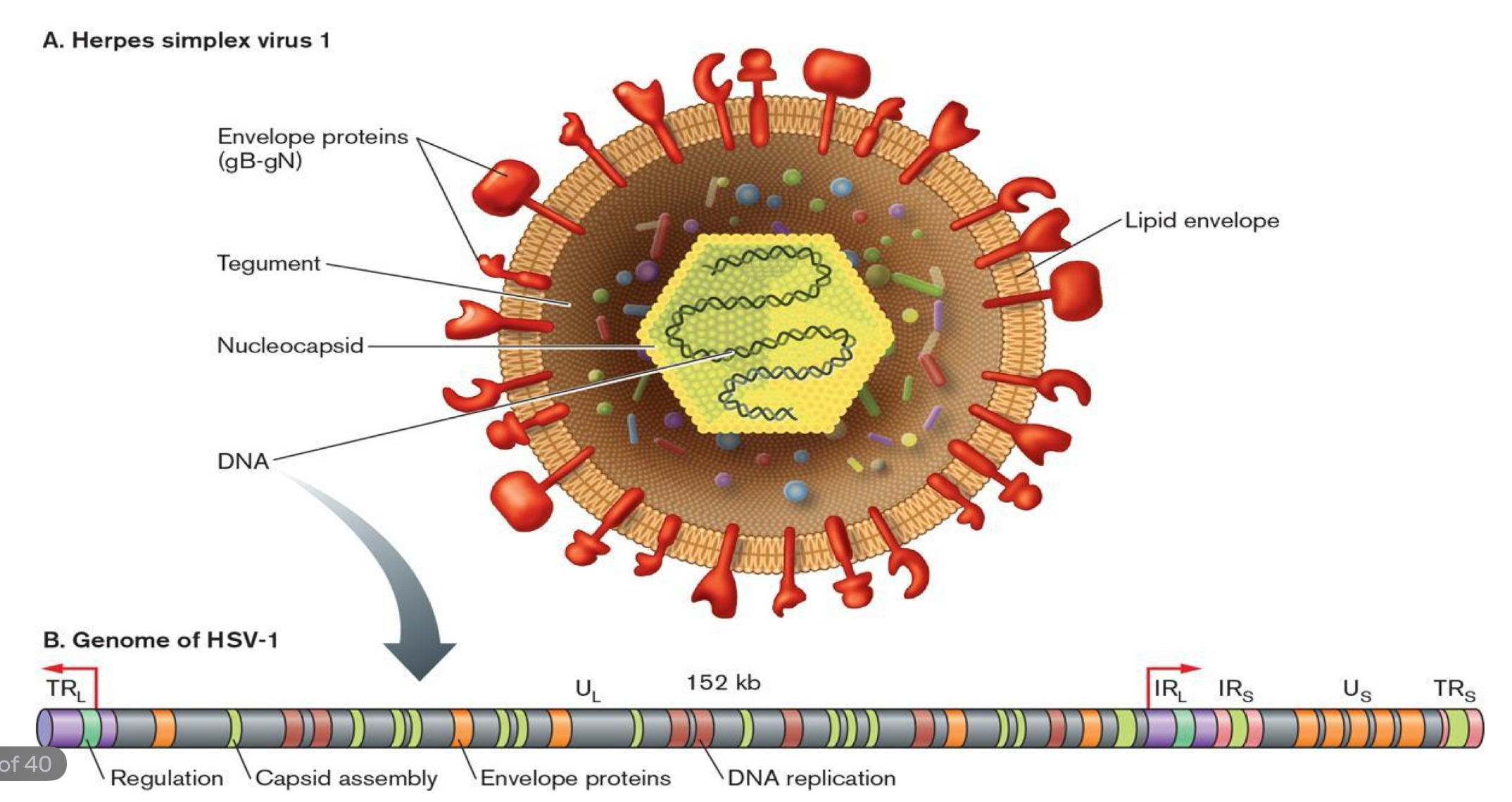
HSV Structure
relatively large
double stranded linear DNA encased in an icosahedral protein cage (capsid)
capsid is wrapped in a lipid bilayer called the envelope which is joined to the capsid by a tegument
the complete particle is a VIRION
HSV-1
primarily oral to oral contact (kissing)
typically causes cold sores (oral herpes)
cold sores around/on mouth
white, creamy colour - ooze clear liquid when popped
controlled by creams
HSV-2
sexually transmitted disease (sexual intercourse)
causes genital herpes around the genitals in the form of warts
very painful to urinate and have sexual intercourse
antivirals - acyclovir, valcyclovir (Zovirax, Valtrex)
condoms are protective
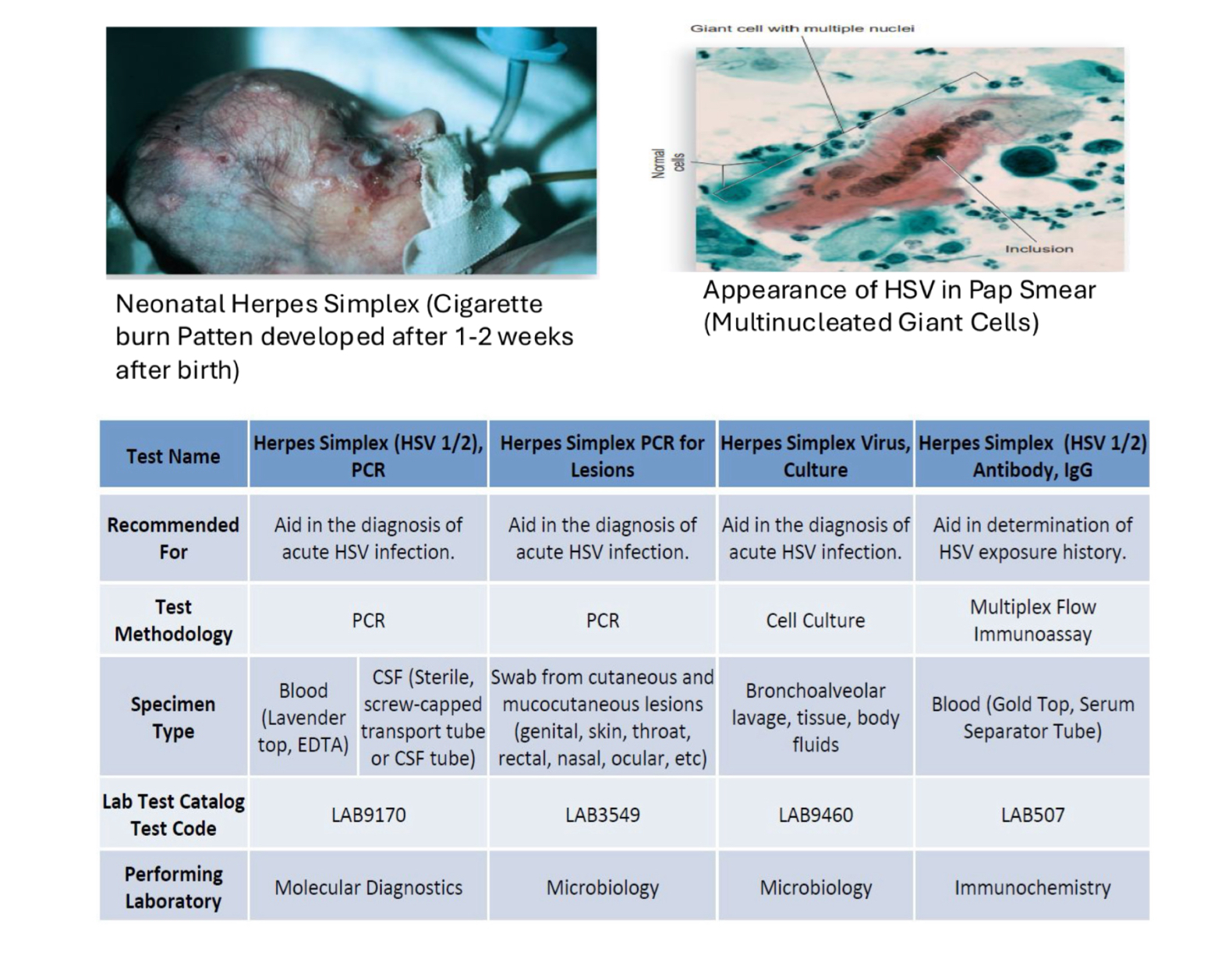
Herpes - Lab Diagnosis
scrape of vesicle/genital vesicle fluid/ulcer swab
Pap smear
Culture: Primary cell cultures
Serology: CFT, TORCH
Herpes - Clinical Features & Complications
single/multiple vesicles on genitalia, perineum, thigh, buttocks
vesicles are small and filled with clear fluid
painful to touch
accompanied by malaise, anorexia, fever, bilateral swelling, tenderness in groin
Complications
Meningitis or encephalitis
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
group of 150 different kinds of viruses; some strains are high-risk and can lead to cancers, like cervical, vulvar and vaginal cancers
sexually transmitted disease - vaginal/oral/anal sex or by skin-to-skin touching during sex
virus infection - Human Papillomavirus
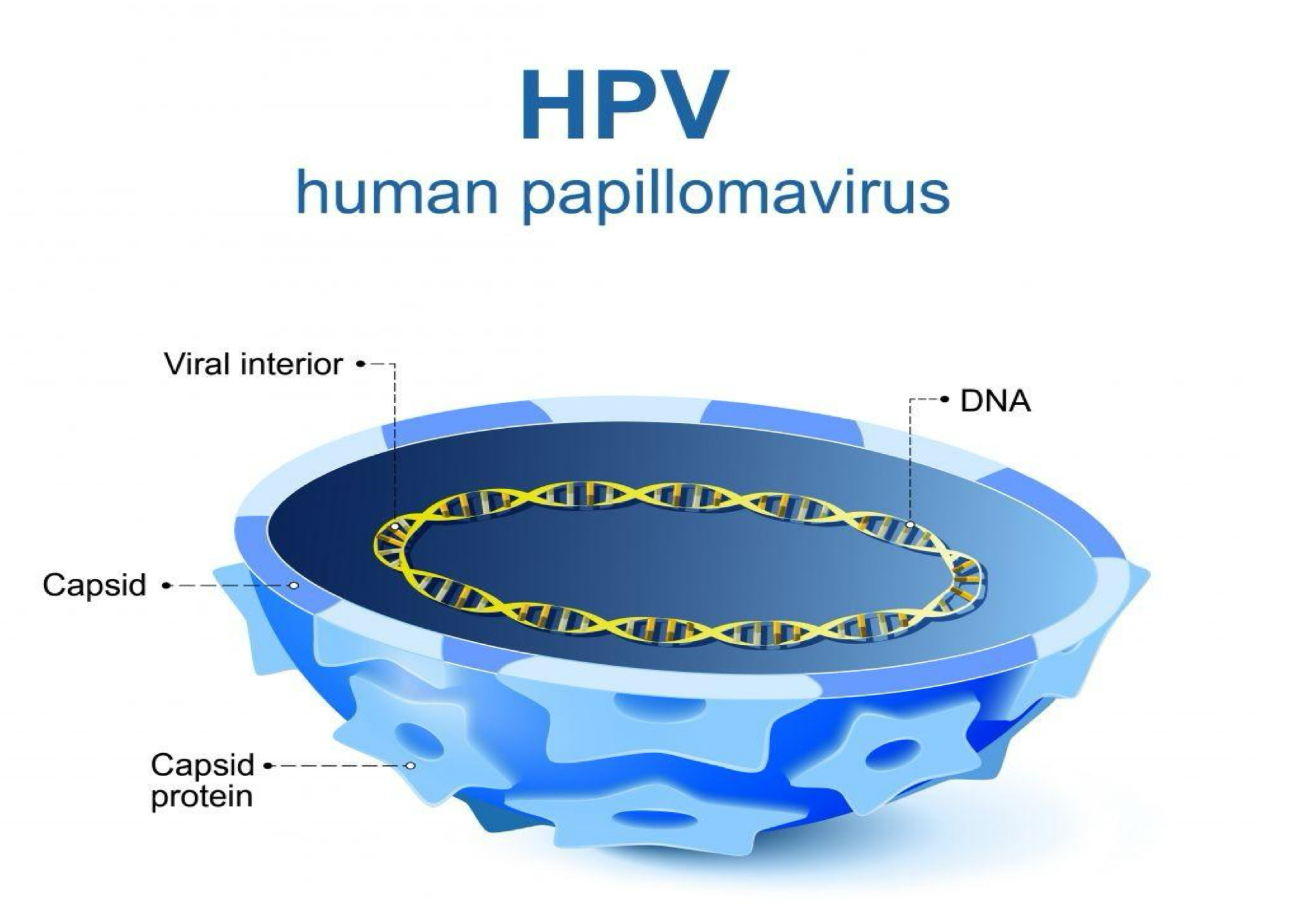
HPV Structure & Types
non-enveloped virus - more virulent
high risk HPV types; HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 56, 59, 66, 68
HPV16 & HPV18 - responsible for most HPV-related cancers
HPV6 & HPV1 - cause 90% of genital warts which barely develop into cancer
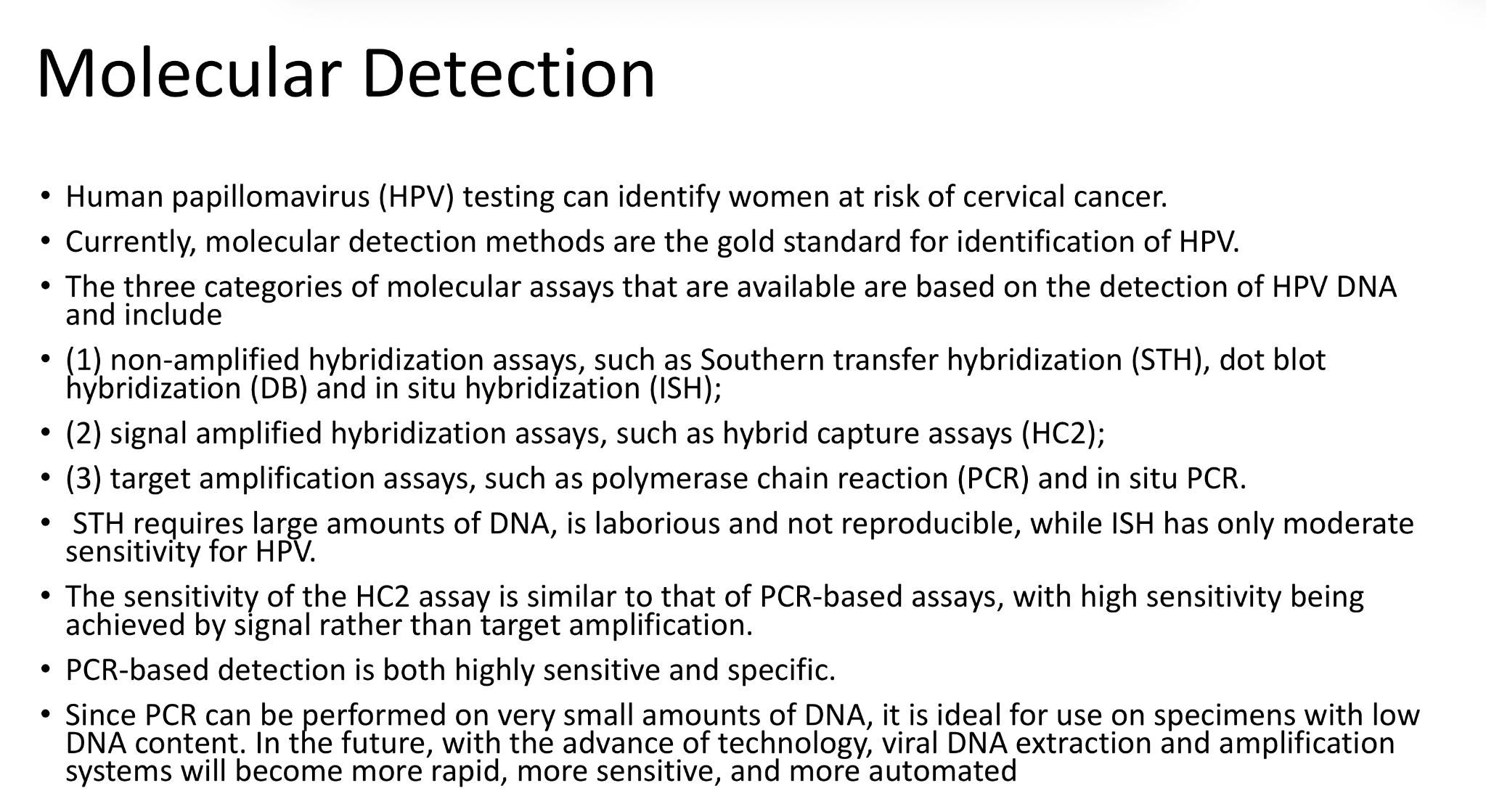
HPV - Molecular Detection
gold standard for HPV detection - can identify women at risk or cervical cancer
three categories of molecular assays for detection of HPV DNA:
Non-amplified hybridization assays
Signal amplified hybridization assays
Target amplification assays