Lecture 9 - Thinking, Reasoning, and Language
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Any mental activity or processing of information (2 terms)
Thinking / cognition
The following activities are involved in what action?
learning, remembering, perceiving, attention, language, believing, and deciding
Thinking / cognition
Thinking about something in a logical way
Reasoning
Our brains are __ misers.
Instead of thinking everything through carefully and logically, we often take mental shortcuts
cognitive
T or F
We have unlimited capacity to process info
False
Mental shortcuts or rules of thumb used in problem solving or making decisions.
Heuristics
When you see a person with their hood up in a dark alley and you decide to subtly walk past a bit faster, your brain has probably used a __ to evaluate the situation instead of a full thought-out deliberation process.
heuristic
A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total.
The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball.
How much does the ball cost?
You are a __ if you said $0.10.
Cognitive Miser
Who conducted the following experiment
A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total.
The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball.
How much does the ball cost?
Kahneman
im learning about addition + subtraction on khanacademy
People often substitute difficult problems with simpler ones to __ them
quickly solve
Who asked participants to make snap personality judgments about students based on their dorm rooms
Gosling
I judged Ryan Gosling in Barbie as strange based on his pink room
Who studied the 2 modes of thinking
Kahneman
i THINK there are 2 MODES (light and dark) on KHAN academy, right MAN?
What are the 2 modes/systems of thinking
Intuitive and Analytical
This mode of thinking is fast and takes no effort
intuitive
These are examples of what mode of thinking?
Forming first impressions, stereotypes, getting out of dangerous situations
Intuitive thinking
This mode of thinking is slow and requires effort. Used to override the other mode of thinking.
Analytical
These are examples of what mode of thinking?
reasoning, problem solving.
Analytical thinking
__ Heuristic: Involves judging the probability of an event by its superficial similarity to a prototype or stereotype
Representativeness
Generalized beliefs about a particular category of people
Stereotypes
Stereotypes ignore __ rate
a statistic used to describe the percentage of a population that demonstrates some characteristic
base
We need to consider similarity to the category, but also how __ the category is
prevalent
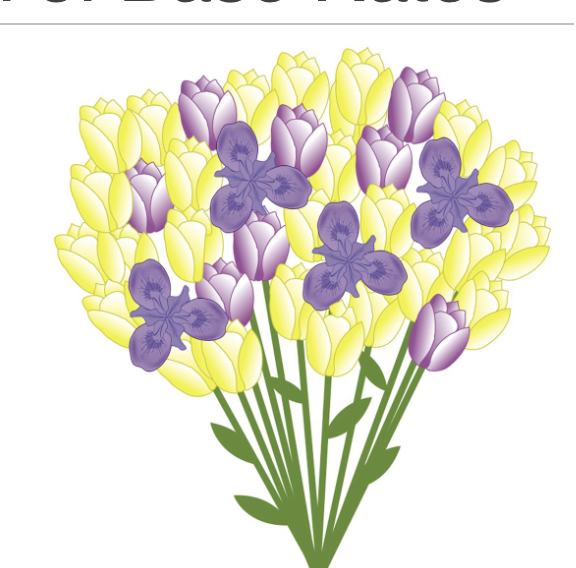

in the demo below, we need to consider the __ of each type of purple flower
Even though irises might look more distinct or attention-grabbing (they're shaped differently and more colorful), there are way more purple tulips in the bouquet than irises.
So, even if irises stand out, statistically it’s more likely you'll grab a tulip — because there are more of them.
base rate

For the below examples, what are our brains doing to make quick decisions.
Blue shirt = best buy employee?
Suit + carrying a briefcase = lawyer?
categorize things

__ Heuristic: Involves estimating the likelihood of an occurrence based on the ease with which it comes to our minds
Availability

Being more afraid of flying vs. being in a car crash is an example of __ heuristic
availability
What are the 2 key factors in Availability Heuristics?
The availability heuristic is also called availability bias because it indirectly affects our decision-making. For example, when shopping for laundry detergents, you may choose Tide over other brands because it comes to mind first and faster than any other brand.
Recency: Did it happen recently?
Vividness: Was it dramatic or emotional?
Which has more calories: a pint of beer or a half-cup of dry-roasted peanuts?
Example of __ Heuristics
Availability
__ — : Our tendency to overestimate how well we could have predicted something after it has already occurred
Hindsight Bias
Example of what?

Hindsight Bias
Process of selecting among a set of possible alternatives
Decision making
Does decision making involve system 1 (intuitive) or system 2 (analytical) thinking or both?
both!
system 1 of thinking: __
system 2 of thinking: __
intuitive - ONE-IN
analytical - TWO-AN
Cognitive __ means your brain tries to be efficient, not perfect.
It trades accuracy for speed, which works most of the time, but can lead to biases and mistakes too.
Many daily decisions are made on the basis of this
economy
Who conducted this study
Students got to choose a poster to take home.
Half were told to just go with their gut feeling.
Half were told to carefully analyze the options and write down their reasons.
Wilson
i got to take home a poster of a wilson volleyball
For __, personal choices (like picking art or a favorite snack), your intuition can be more satisfying than overthinking it
low-stakes
When people overthink a problem or situation and can't make a decision.
Analysis Paralysis
The more __ available, the longer it takes to make the decision
options

Individuals' tendency to choose intermediate options
By introducing extreme proposals that are less favourable to the opposing party, negotiators can make a middle option appear more appealing and increase the likelihood of agreement
Compromise effect
The way a question is presented can influence decisions
“5% chance of winning” vs. “95% chance of losing”
Framing
Generating a cognitive strategy to accomplish a specific goal.
Problem solving
Step-by-step learned procedure
Algorithms
Algorithms depend on the same __ every time to find a solution
E.g., Fixing a car, filling a cavity, making a peanut-butter-and-jelly sandwich
basic steps
Problem solving strategy:
breaking a big problem into smaller, manageable goals
subgoals
Problem solving strategy:
Replacing a difficult part of the problem with something simpler or easier to work with.
Substitutions
Problem solving strategy:
Means solving a new problem by using a similar past situation as a guide
Analogical Approaches
Eg. George de Mestral invented Velcro after noticing how burrs stuck to his dog’s fur. He connected nature's solution (burrs hooking to fur) to an idea for clothing fasteners
An obstacle to problem solving where u become stuck in a specific strategy, inhibiting our ability to generate alternatives
It’s like your brain is on autopilot, and you can’t easily think outside the box to try something new
mental sets
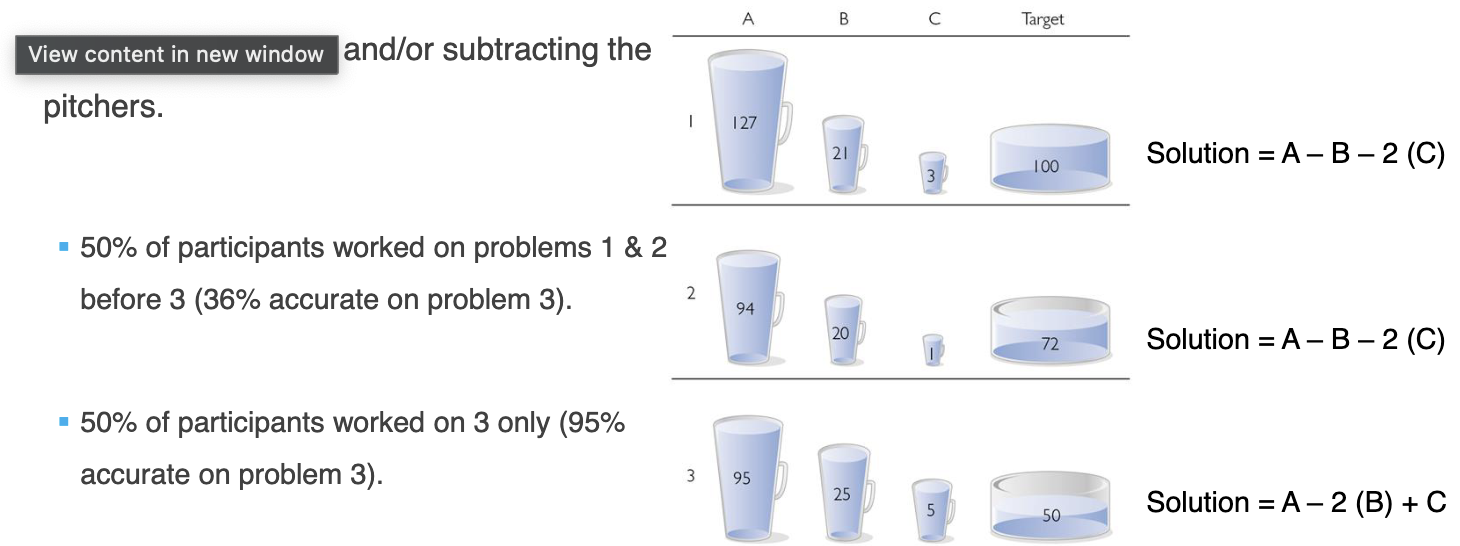
The water jug task is an example of what?
Mental sets - past success can actually lead to future mistakes if we don’t adapt our thinking
Difficulty conceptualizing that an object typically used for one purpose can be used for another.
Functional fixedness


This is an example of over coming what problem solving obstacle
Functional fixedness

Who conducted the candle, thumb tack, box experiment?
Duncker
no duct tape was given
What is the solution to overcome functional fixedness?
Try to think outside the box!
What matters in order for the following sentences to make sense
“Jake saw her duck.”
“Include your children when baking cookies”
Context
Arbitrary system of communication that combines symbols, (such as words or gestural signs), in rule-based ways to create meaning
Language
words and gestural signs are examples of what?
symbols

certain speech sounds seem to be associated with particular meanings to us
Sound symbolism
Communication of __
▪ What time is the exam?
Information
Social and __ Functions
▪ It’s nice to meet you.
▪ “I thought you were mad at me.”
▪ I really like this music.
Emotional
Who preformed the following study:
Russian has two separate words for blue:
"Goluboy" = lighter blue
"Siniy" = darker blue
English just uses the single word "blue" for both shades.
Russian vs. English speakers showed an advantage in colour discrimination
Winawer
i was never going to WIN a WAR at colours with aurora and Sveva
View that all thought is represented verbally and language defines our thinking. In other words, if you don’t have a word for something, you can’t really think about it.
Example: Labeling someone as “hysterical” vs. “distressed.”
Linguistic Determinism
Evidence against linguistic —-:
Children can perform complex cognitive tasks b4 they can talk about them.
Language areas are not especially active during spatial tests or visual imagery
determinism
The idea that the language you speak can influence how you think.
It doesn’t control your thoughts (like linguistic determinism says), but it can shape:
what you notice,
how you describe things,
how you categorize the world.
Linguistic Relativity
Language is highly practiced and __ cognitive process
automatic
The delay in reaction time between neutral and incongruent stimuli. Naming the color of a word not the word itself
Stroop effect
Shown a picture of a brown STROOPwafel but asked to say blue

what are the 2 conditions of each column of words?
L: Control condition
R: Stroop Interference Condiition
the smallest unit of sound that carries meaning in a particular language
eg. k / a / t = cat
phonemes
phonemes are categories of sounds our vocal __ produces.
apparatus
how many distinct phonemes across all languages and how many in english (range)
100
40-45
All the body parts and structures that work together to let us produce speech sounds.
vocal apparatus
Smallest units of meaning in a language
Morphemes
Are morphemes full words (“dog”) or modifiers (“re-”: recall, rewrite)?
can be either
Set of rules of a language by which we construct sentences (ie the arrangement of words and phrases in a specific order)
I ate pizza for dinner. vs. Pizza ate I for dinner.
Syntax (Yoda lived on the Syntax starship)
if you take the morpheme cookie and add the suffix –s, you create a new word—cookies
the suffix -s is an example of a ___ modifier
morphological
Elements of communication that are not part of the content of language, but are critical to interpreting its meaning
Extralinguistic Information
Give a couple examples of Extralinguistic Information
Facial expressions, tone of voice
eg. “nice job”
Which month of pregnancy when auditory system is developed enough to:
▪ Recognize mothers’ voices.
▪ Melody and rhythm of native language.
▪ Specific songs or stories heard repeatedly
5th
Which study measured how often a two-day old infant sucked on a pacifier in response to hearing their native language vs foreign language.
__ — procedure
High-amplitude sucking procedure
refers to intentional vocalization that lacks meaning
a stage of early language development when baby makes consonant-vowel or vowel-consonant sounds, such as “ma”, “da” or “um”
Babbling
When does babbling and Phoneme recognition emerge in babies
before 1 year old
babbling allows babies to develop control over what part of their bodies?
vocal tracts
Initially all babies share the same basic __ categories
phoneme
Babies must learn which sets of sounds are __
relevant
Comprehension precedes __
production
u need to be able to comprehend words before producing them
Begin to produce words around __ year(s) of age, with a rapid rate of increase.
1 year of age
12-18 months know __ words.
24 months know __ words.
By kindergarten, __ words
20-100
several hundred
several thousand
young children often make vocabulary mistakes when learning:
__ = using a word too broadly
calling all flying things “bird” (including planes or butterflies)
__ = using a word too narrowly
thinking “cat” only means their pet, not other cats
Overextension
Underextension
The process by which individuals learn to structure sentences and arrange words meaningfully
Syntax Development
At 1yo, infants are in the __ stage of Syntactic Development and move to —- stage by 2 years old
one-word
two-word
At what age do children begin by saying single words like:
“doggie” — which could mean:
"There's a dog"
"I want the dog"
"Where's the dog?"
one
At what age do children begin combining words in simple but meaningful ways:
“Read book”
“More juice”
“My shoe”
“Eat cookie”
2 yo
Children can comprehend basic syntax rules before they can __ them.
display
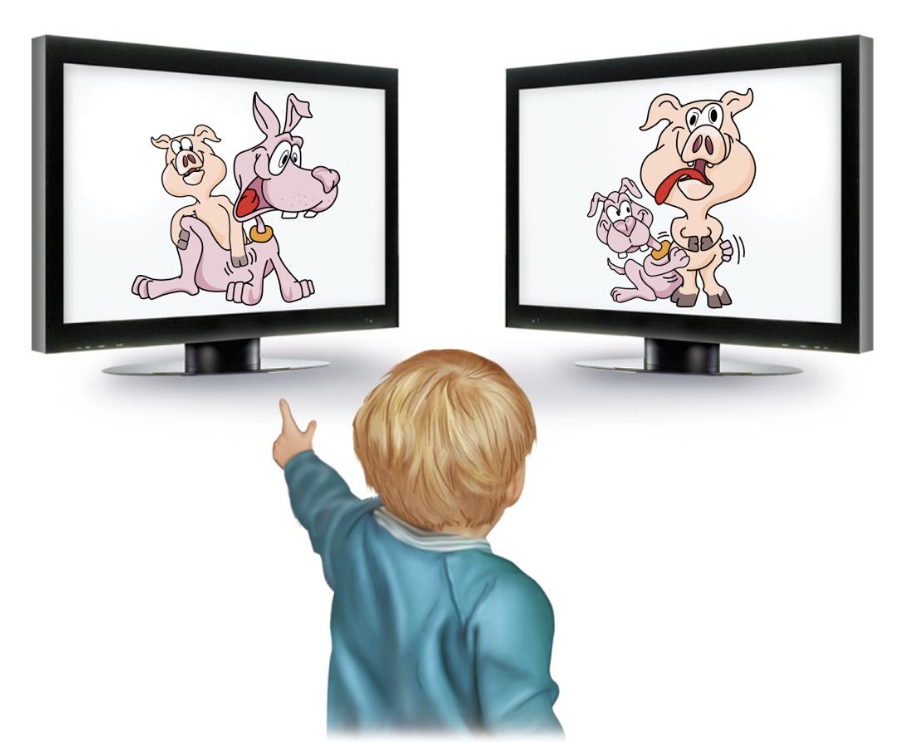

At __ (age) can point to a video displaying their comprehension of the sentence, “The pig is tickling the dog.”
17-months
Sign language exhibits same __ of spoken language
features
sign language activates __ areas + areas involved in —processing.
language
visual/spatial
sign language has the same __ stages
eg Deaf babies “babble” with their hands.
developmental
Bilinguals usually have 1 dominant language but __ in both
proficient
Bilingual learning passes through the same stages as monolinguals, although __ is slowed.
syntax development
a window of time when the brain is especially ready to learn language, and missing that window can make it much harder later on.
critical period
The earlier immigrants arrived in the U.S, the better their __ in English
grammar
Age matters more for __ and — than for —.
So even older learners can learn new words, but sounding fluent and using correct grammar is harder after childhood.
syntax (grammar)
pronunciation
vocabulary
__ Theory
Babies learn language by copying what they hear.
They listen to adults and imitate the sounds, words, and grammar.
Example: A baby hears “Hi” and learns to say “Hi.”
Imitation