7.0 carbon monoxide poisoning
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
carbon monoxide poisoning
A life-threatening condition caused by exposure to carbon monoxide, characterised by:
tissue hypoxia,
impaired cellular respiration,
and direct cellular toxicity.
Carbon monoxide poisoning can arise from exposure to various sources.
Symptoms may be acute or chronic, depending on the dose and duration of exposure, and are often non-specific.
mild symptoms range from
headaches,
nausea,
and dizziness
severe symptoms range from
severe cardiovascular
and neurological effects.
Individuals at greatest risk of adverse outcomes include those with:
coronary heart disease,
vascular disorders,
asthma,
or anaemia,
as well as pregnant women and their foetuses,
children, and older adults.
Approximately one-third of severe cases result in death.
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is a serious and potentially fatal condition caused by the inhalation of carbon monoxide gas.
Often referred to as a "silent killer," carbon monoxide is colourless, odourless, and tasteless, making it difficult to detect without specialised equipment.
This gas is produced during the incomplete combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline, wood, coal, and propane.
Common sources of CO exposure include:
malfunctioning household appliances
, vehicle exhaust,
and improper use of generators in enclosed spaces.
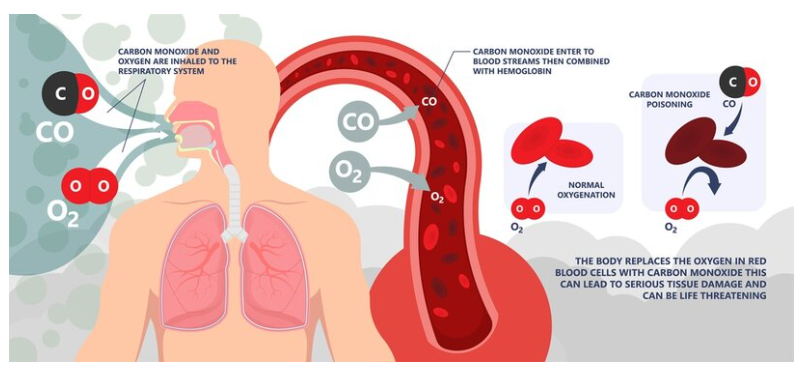
The primary mechanism through which CO exerts its toxic effects is by binding to haemoglobin in the blood to form carboxyhaemoglobin.
Carbon monoxide has an affinity for haemoglobin over 200 times greater than that of oxygen,
effectively displacing oxygen and preventing its transport to vital tissues.
This results in tissue hypoxia, impairing cellular respiration and energy production.
Furthermore, CO interferes directly with mitochondrial function and other cellular processes, amplifying its toxic effects.
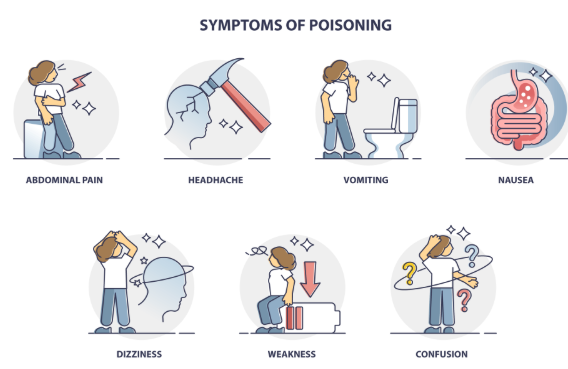
Symptoms of CO poisoning can vary depending on the level and duration of exposure. Initial symptoms are often nonspecific and may include
headache,
nausea,
dizziness,
and fatigue.
Prolonged or high-level exposure can lead to
confusion,
chest pain,
shortness of breath,
and loss of consciousness.
Severe cases may result in
permanent neurological damage,
cardiovascular complications,
or death.
particularly vulnerable groups
Children,
pregnant women,
the elderly,
and individuals with pre-existing health conditions such as coronary artery disease or respiratory disorders