M1-1 Cells and Tissues Vocab
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Superior
“above,” “upper”
Adipose (fat) tissue
A type of connective tissue that stores fat, provides insulation, cushioning, and support for the body.
Adipocytes
Specialized fat cells that make up the adipose tissue and store energy in the form of lipid (fat) droplets.
Apical membrane
The surface of an epithelial cell that faces the lumen or external environment, often involved in absorption or secretion.
has tiny finger-like projections (microvilli) that increase S.A. available for transport
Basal lamina/basement membrane
A thin layer of extracellular matrix that separates epithelial cells from underlying connective tissue, providing support and influencing cell behavior.
ECM epithelial cells that make up this layer
proteins that are secrete by epithelial cells and depostied on the basolateral surface
a thin, protein‑rich layer of extracellular matrix that underlies the basal side of epithelial cells.
Basolateral membrane
The surface of an epithelial cell on the cell membrane that faces the extracellular fluid playing a role in cell communication and transport.
may also have folds that increase the cell’s surface area
Caudal
“waist line”
Cell-cell junctions
Protein complexes which connect and hold cells together; connections of different cells in the body
Cell-matrix adhesions
Protein complexes which connect cells to the ECM
Ciliated epithelium
Simple cuboidal/columnar
apical surface (tissue surface facing lumen) covered with cilia that beats in coordinated rhythmic motion, moving fluid and particles across the tissue surface
ex. nose, trachea, upper airways
Chondrocytes
Specialized cells that produce and maintain the firm but flexible matrix of the cartilage in the body.
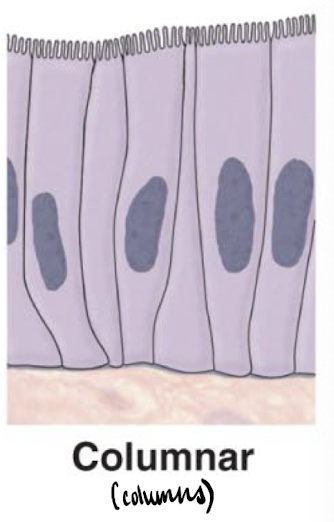
Columnar epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue characterized by high, column-like cells that are primarily involved in absorption and secretion, often found in the digestive tract and respiratory system.
found in transporting, ciliated, and secretory epithelia
Connective tissue
The diverse, second major tissue type that supports, binds together, and protects tissues and organs of the body
contains a loose widely scattered mesenchymal cells in the extensive ECM
includes blood, support tissues for the skin and internal organs, cartilage and bone
Types of Connective Tissues
Loose connective tissue
Dense/Fibrous connective tissue
Supporting connective tissue
Blood
Cranial cavity
relative term to describe the location of the “head of the body”
Cuboidal epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue characterized by cube-shaped cells that are involved in secretion and absorption, commonly found in glandular tissues and the lining of kidney tubules.
found in protective, transporting and ciliated epithelia
Dense connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that is characterized by a high density of collagen fibers, providing strength and flexibility
includes fibroblasts and densely packed ECM
It is commonly found in tendons, ligaments, and the dermis of the skin.
Distal
“far from the body in extremity"”
Dorsal
known as ‘posterior’
“Back of the body”
Elastin
A coiled, wavy protein fiber found in connective tissues that provides elasticity and resilience
protein return to its original shape after stretching.
Endocrine gland
A ductless gland that secretes products/hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate various body functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood.
ex. pituitary, thymus, thyroid, pineal
Endothelium
most common type of epithelium
simple squamous epithelium lining the heart and blood vessels
Epithelial tissues
lines the external and internal surfaces of most organs
any substance crossing the internal/external boundary crosses an epithelium
organized by structure and function!!
Exchange epithelium
contains simple squamous for efficient gas exchanges between cells and across the epithelium
weak tight junctions
lines lumen of blood vessels/capillaries
can be fenestrated (pores in capillaries to allow smaller molecules than proteins to pass between two adjacent epithelial cells
Exocrine duct/gland
A gland that releases products through ducts into the external environment (outside of the body)
ex. sweat, sebaceous, salivary, liver, pancreas, mammary, and mucous
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
The network of extracellular proteins surrounding the cells in tissues
synthesized and secreted by the cells of a tissue
these proteins provide cell attachment and resistance to compression
associated with all cell types, but most abundant in connective tissue
Fenestrated capillaries
large pores that allow high volumes of fluid to pass rapidly between the plasma and interstitial fluid
primarily found in the kidney and the intestine
Fibroblasts
A type of cell in connective tissue that secretes collagen-rich matrix, playing a crucial role in wound healing and maintaining the extracellular matrix.
cells that secrete matrix proteins
-blast: on a connective tissue name often indicates a cell that is either growing or actively secreting extracellular matrix
Frontal/coronal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (ventral, front ) and posterior (dorsal, back)) sections.
Histology
Study of tissue structure and function
Homeostasis
Maintaining the internal body’s regulation within an finite range of normal values in response to a changing environment
Variables under homeostatic control: temp, pH, osmolarity, water/oxygen levels, ions, hormones
ALWAYS CHANGING AND AT DISEQUILIBRIUM; NOT STATIC
Inferior
“below”; “lower part of the body”
Lateral
“Side of the body”
Ligaments
Connect one bone to another bone
contain elastic fibers
limited ability to stretch and provide stability to joints.
elastin allow for shock absorbant
Loose connective tissue
elastic tissues that underlie the skin and provide support for small glands
very flexible with multiple cell types and fibers
contains fibroblasts and loose ECM
attaches epithelia to underlying tissues
provides shape and structure to organs
Lumen
interior of any hollow organ that may be wholly or partially filled with air or fluid
ex. heart, lung, blood vessels, intestines
Medial
“Center of the body”
Mesenchymal cells
widely scattered (loose unstructured) cells that secrete and modify the extensive ECM in connective tissues
Negative feedback
the response opposes or removes the stimulus, shutting off the response loop
stabilize the regulated variable and helps the system maintain homeostasis
Osteoblasts
Specialized cells synthesize and deposit matrix, stimulating bone formation
Pelvic cavity
apart of one of the 3 main body cavities: abdominopelvic cavity
beneath the abdominal cavity and bounded by the pelvic bones
contains organs such as the female reproductive systems, urinary bladder, and the lower digestive tract/the terminal portion of the large intestine
Positive feedback
the response further amplifies the stimulus rather decreasing or removing it, sending the variable farther from the set point
response increases in the same direction as the stimulus
Posterior
Dorsal; “Back of the body”
Proximal
“Close to the central body in proximity”
Protective epithelium
found on the outer skin/integumentary system
Stratified bottom cuboidal layers to stratified top squamous
outer skin cells are constantly being replaced
prevent exchange between internal and external environments and provide protection
strong tight junctions to keep water in and pathogens out
found on the skin, lining of cavities that open to the environment (digestive/respiratory tract)
Sagittal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into left and right sections.
Secretory epithelium
composed of epithelial cells that produce a substance and secrete it into the internal/external environment
contains to types of glands: exocrine and endocrine glands
Simple Epithelium
A single layer of cells
It is typically found lining internal organs and body cavities.
Squamous epithelium
A type of epithelium made up of flat, squashed cells that allow for rapid diffusion and filtration.
It is commonly found in areas such as the alveoli of the lungs and the lining of blood vessels.
Stratified epithelium
many epithelial layers
It is commonly found in areas subject to abrasion, such as the skin and the lining of the mouth.
Tendons
Connective tissues that attach muscles to bones.
They are strong and resistant to pulling force
lack elastin so cannot stretch
not stretchy so muscles can contract → move bones
transporting epithelium
actively and selectively import/export solutes (nongaseous materials; ions and nutrients) between the internal and external environment
lines the hollow tubes of digestive system and kidney (where lumens open into the external environment)
simple cuboidal/columnar NOT STRATIFIED
No free exchange; strong tight junctions
contains microvilli - increase surface area for absorption
transverse/cross-sectional plane
A hortizonal division section providing a view of internal organs or structures
superior vs inferior
Ventral
known as the anterior
“front of the body”