week 2 lecture 3 resting membrane potential
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
ionic environment inside a typical neuron
higher concentration of K+, low concentrations of Na+ and Cl-
resting membrane potential components
Na± and K± are key players, ionic driving force, nernst equation
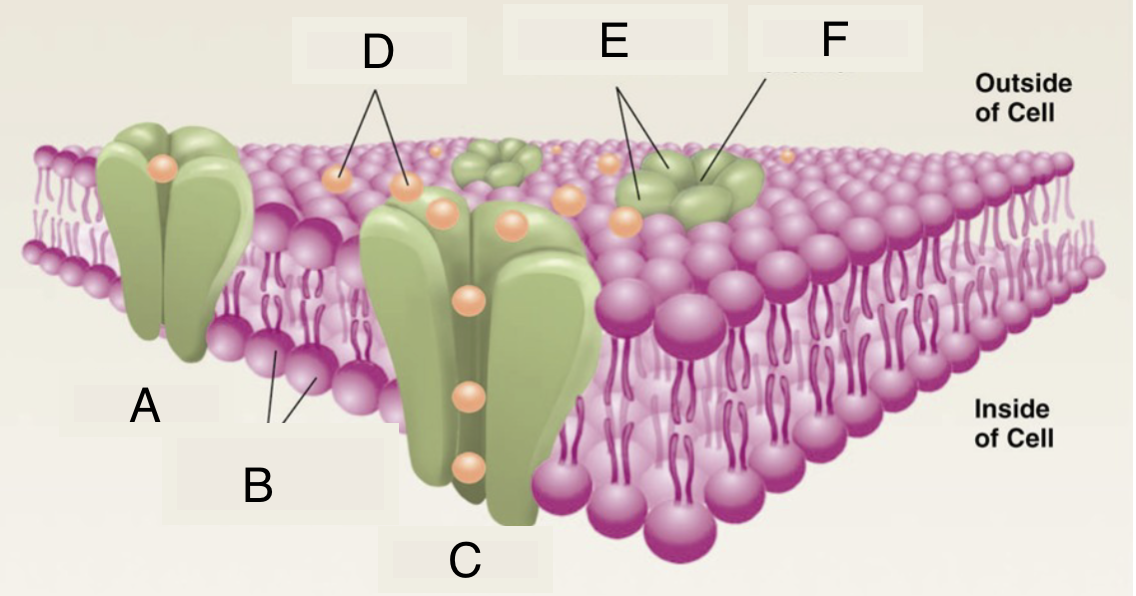
A
closed ion channel
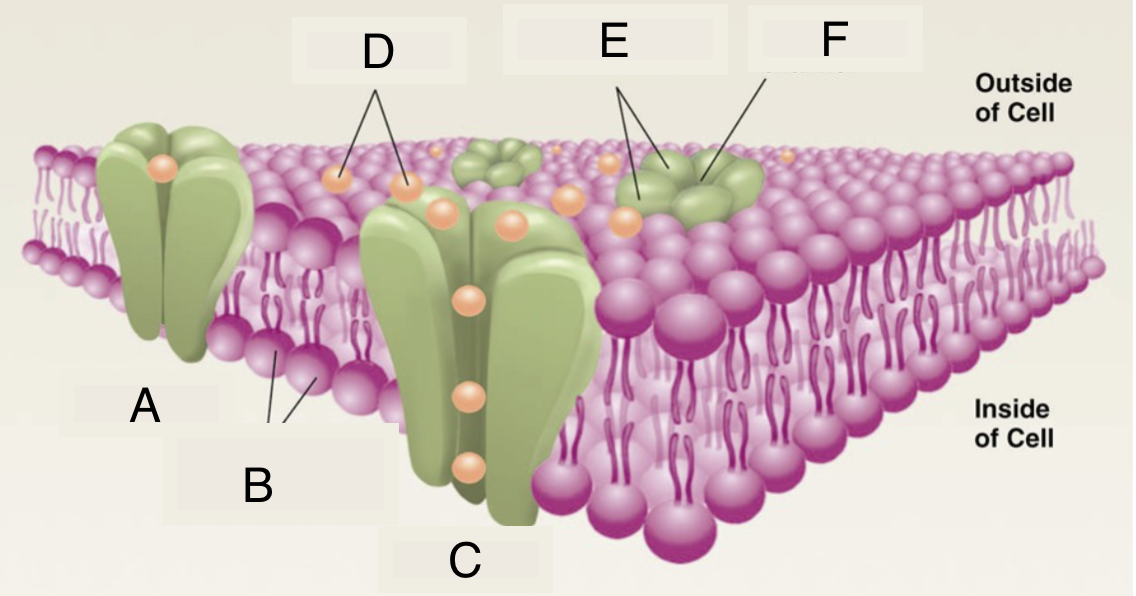
B
lipid molecules in membrane
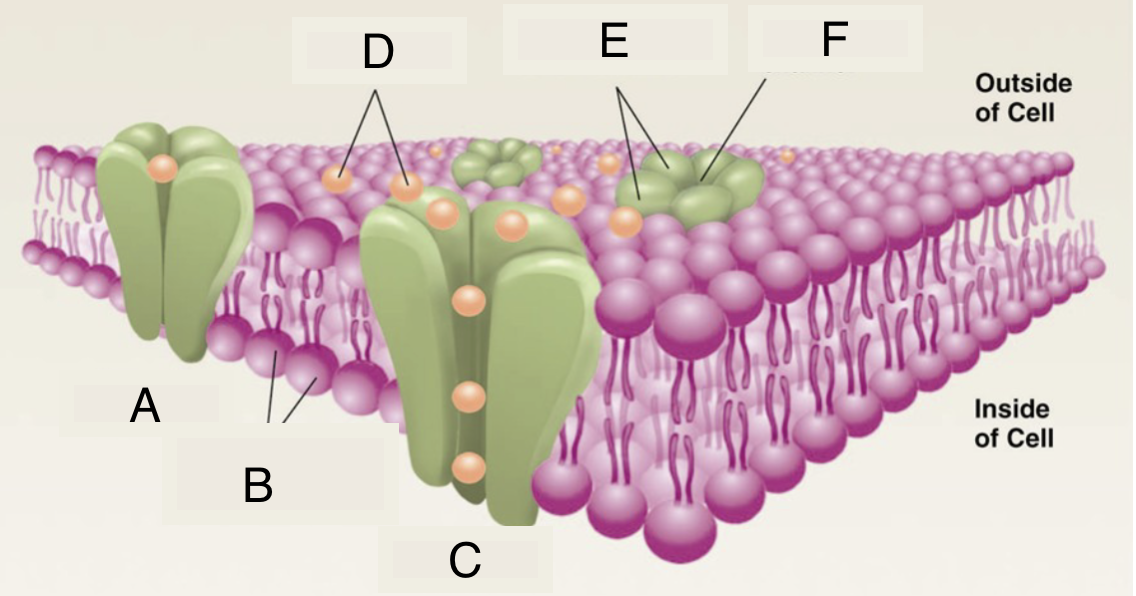
C
open ion channel
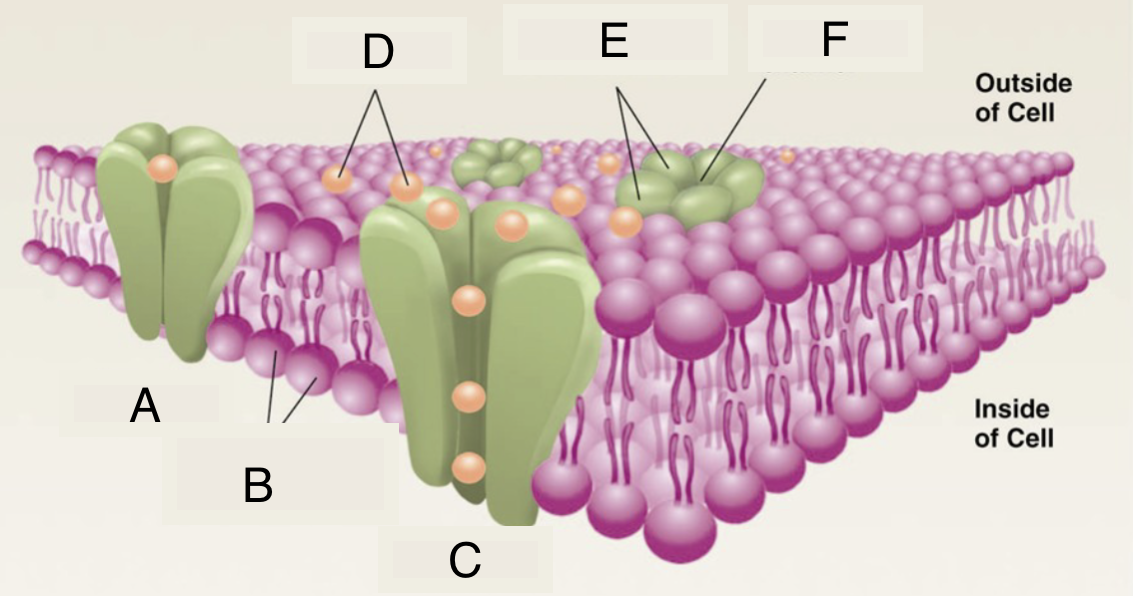
D
ions
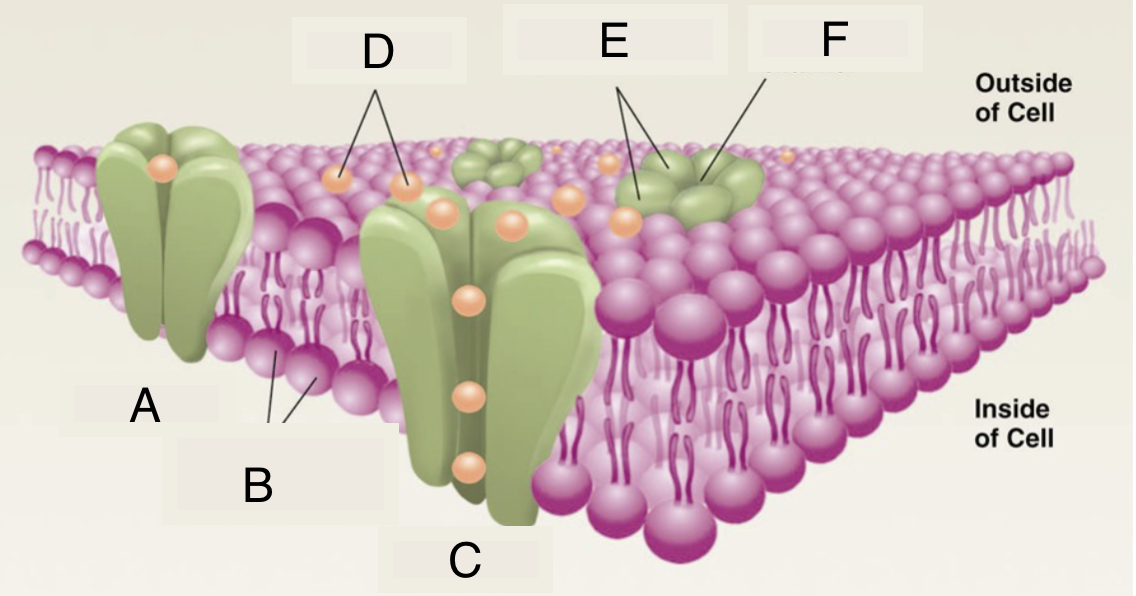
E
protein subunits of ion channel
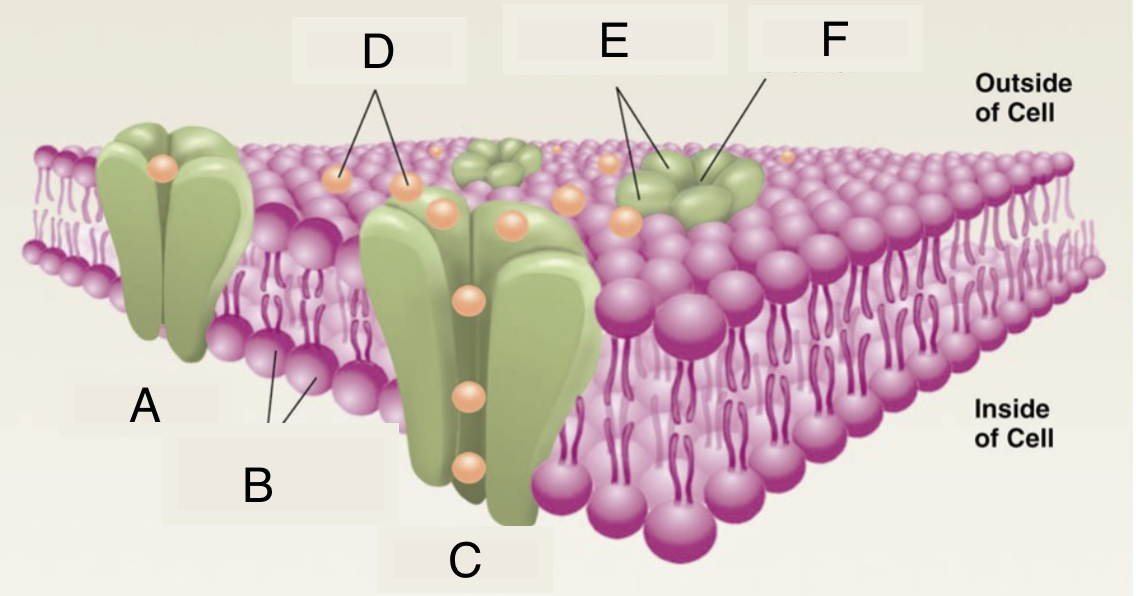
F
pore of ion channel
passive transport
sodium channels (Na+), potassium channels (K+)
active transport
sodium-potassium pump
sodium-potassium pump
required ATP and moves 3 Na+ and 2 K+
ionic driving force
diffusion: concentration gradient, electrical gradient
concentration gradient
which way the ions want to move
electrical gradient
which way the charge pulls the ion
nernst equation
equilibrium potential for a given ion: Ex=-RT/zF ln([X+]i/[X+]o) or Ex=-RT/zF ln([X-]o/[X-]i)
action potential
rapid, temporary reversal of electric polarization across a neuron or muscle cell membrane, functioning as an electrical impulse for communication
Does the sodium-potassium pump set the resting membrane potential of a neuron
Yes
for a neuron at rest what must be true
membrane voltage at -65 mV, ion channels are closed, Na/K pump is moving ions, membrane is alittle leaky
equilibrium potential
specific electrical voltage across a cell membrane of a particular ion
membrane potential
electrical voltage difference across a cell's plasma membrane
permeability
capacity of a membrane to allow specific ions, molecules, or substances to pass through
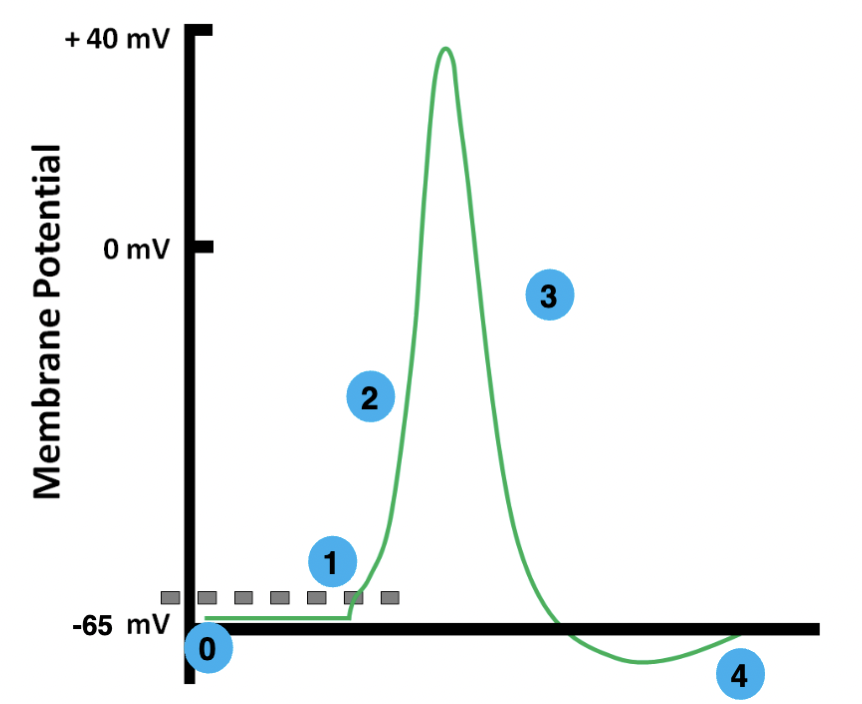
0
resting
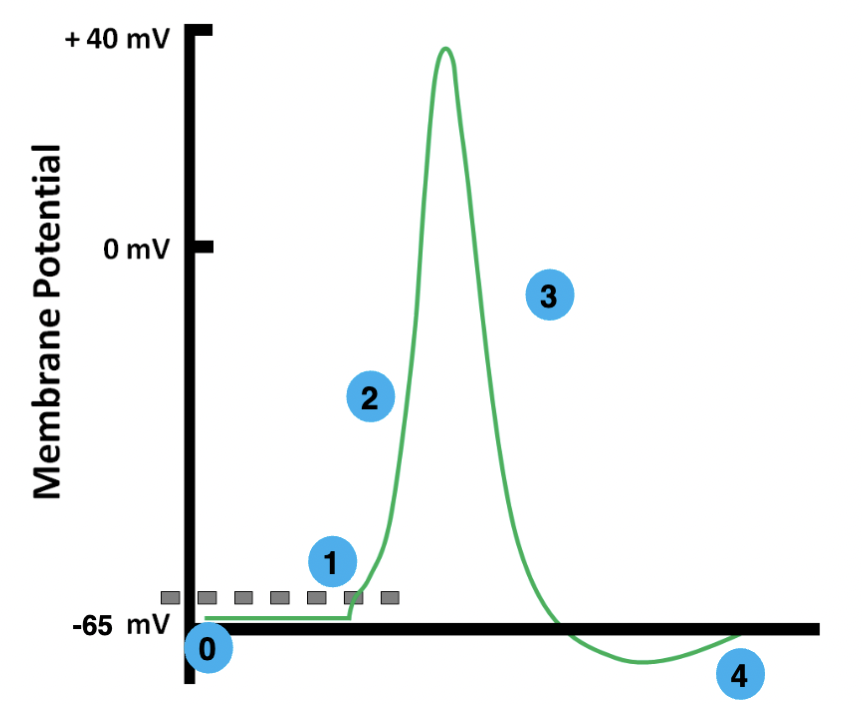
1
threshold
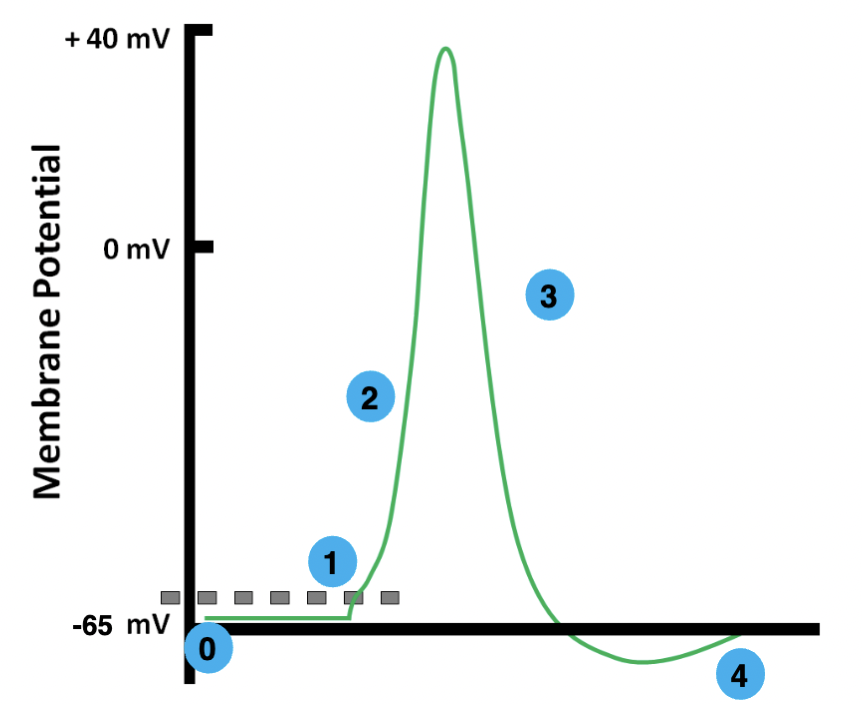
2
depolarization
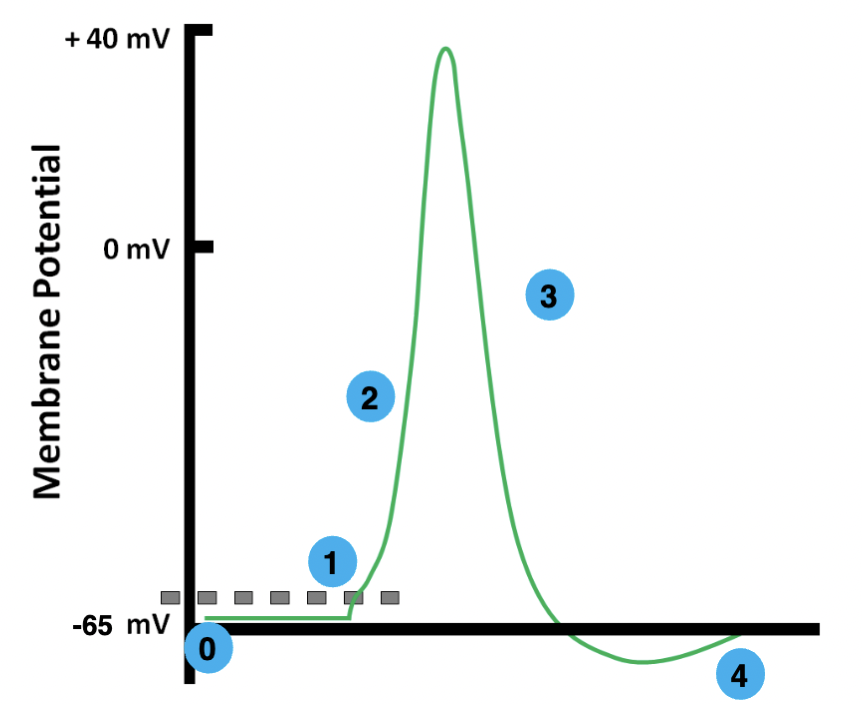
3
repolarization
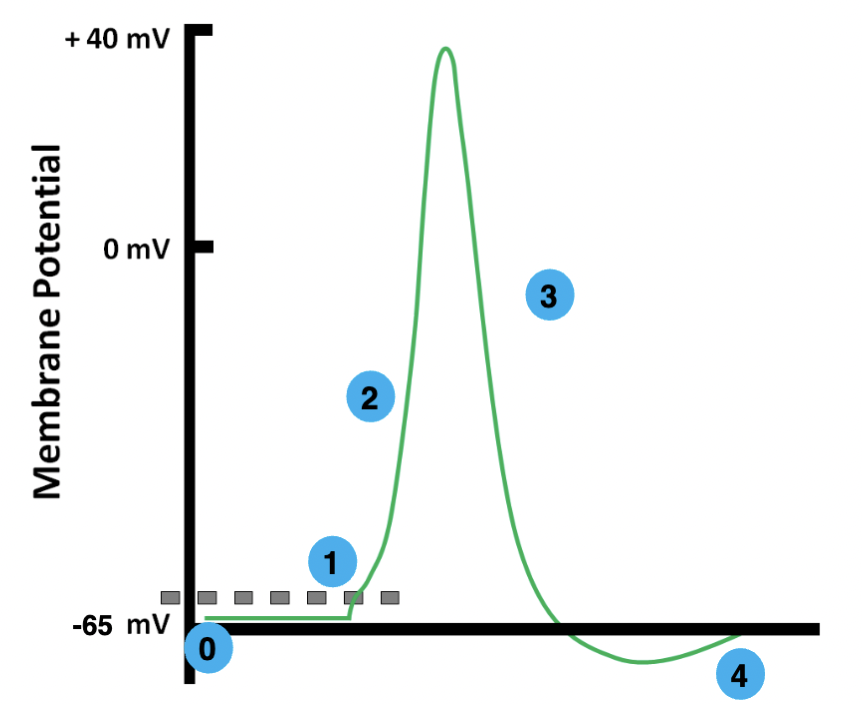
4
hyperpolarization
resting membrane potential
the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in a non-excited state
cell membrane properties
closed ion channel, lipids, opened ion channel, ions, protein subunits of ion channel, pore of ion channel,