AP Human Geography Unit 3: Culture
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Culture
complex system of learned beliefs, practices, and material creations that shape a society’s way of life
Material Culture
physical objects, artifacts, items that hold significance to a group
Non-material Culture
non-physical components of culture like ideas, beliefs, values, languages
Artifact
any object made, used, or modified by humans that serves as a material representation of culture
Mentifact
non-material component of culture consisting of the core ideas, values, and beliefs that shape a society’s identity
Sociofact
a social institution and the norms and customs that structure how a culture’s members interact and organize their society
Cultural Relativism
the principle that a person’s beliefs, values, and practices should be understood based on their own culture and not judged against the standards of another
Ethnocentrism
the belief that one’s own culture is superior to others, leading to the evaluation of other cultures based on standards and values of one’s own culture
Individualism
a cultural perspective that values personal independence, self-expression, and individual success
Collectivism
a cultural perspective that prioritizes the needs and goals of the group over individual desires
Cultural Landscape
the visible modifications of the natural environment shaped by human culture, practices, beliefs, and values (architecture, land use patterns, agricultural methods, and toponyms
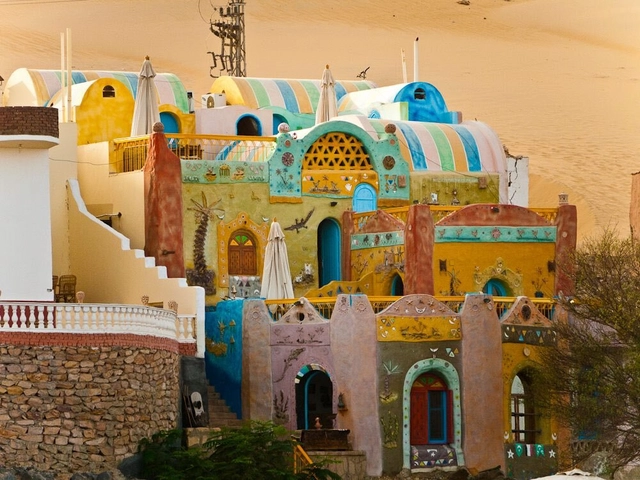
Traditional Architecture
style of architecture deeply rooted in a specific region’s ethnic culture, usually constructed from locally sourced materials and techniques passed down through generations, embodies the adaptation of a community’s built environment to the climate, social conditions, and history of the region, reflect a deep sense of cultural identity

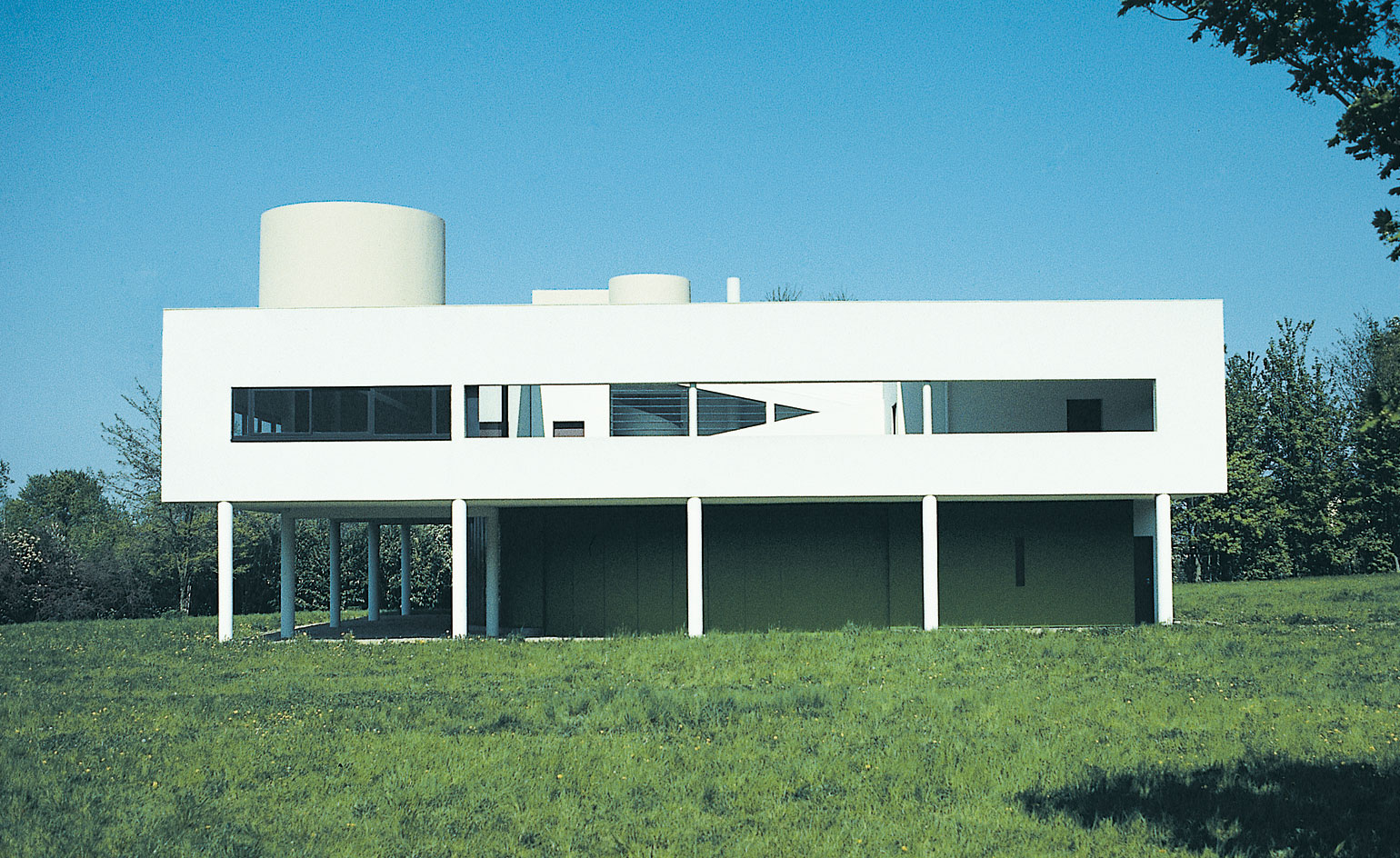
Modernist Architecture
rejection of historical ornamentation in favor of functionality, clean lines, and minimalist aesthetic, emphasizes the rational and efficient use of space, and incorporates modern materials like glass, steel, and concrete to create open floor plans and large windows, (function over form)

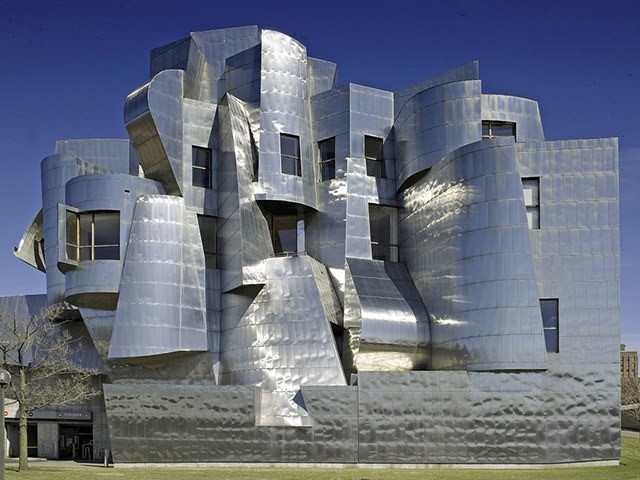
Post-modern Architecture
style that emerged in the late 1970s as a reaction against the minimalist and functionalist principles of modernism, characterized by its use of humor, irony, and eclecticism, incorporating a variety of shapes, colors, form and function (often wavy and bright colors)

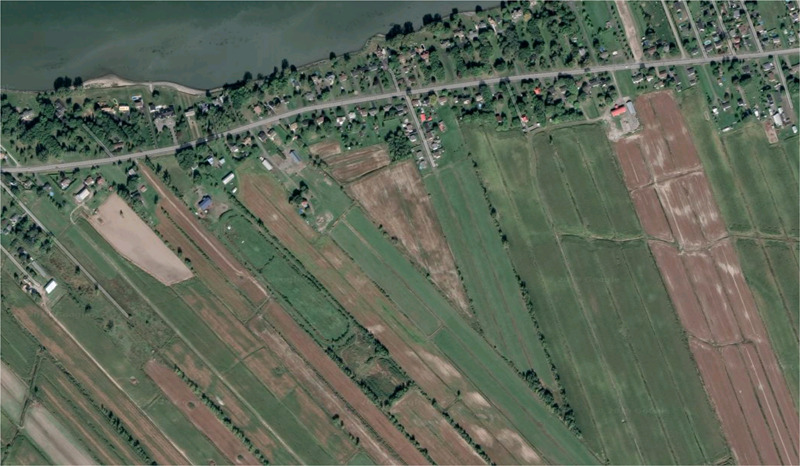
Long-lot Settlement
a linear settlement where land is divided into narrow, rectangular lots that extend back from a river or road, giving each person equal access to the resource

Township and Range
a method for subdividing land in the US, creates a grid by dividing land into six mile square townships which are further divided into 36 square-mile sections
Ethnic Enclave
a geographic area (usually smaller like a neighborhood) with a high connection of a distinct ethnic group, maintaining its cultural identity through shared language, customs, and social practices, providing support for immigrants, creating a sense of community
Culture Region
a geographic area (usually bigger, can span over countries) with a shared set of cultural traits like language, religion, and customs, which create a distinct identity
Cultural Divergence
the process where different cultures become increasingly distinct over time due to factors like geographic, social, or political isolation
Cultural Convergence
when different cultures become more similar due to interaction, a process driven by globalization through increased communication, trade, and travel
Centripetal Force
forces that pull people together and unify groups in a society
Centrifugal Force
forces that push people apart and create different groups and interests in society
Cultural Hearth
the starting point of a cultural phenomenon
Cultural Diffusion
the process of a cultural trait, idea, or phenomenon spreading from its point of origin (cultural hearth) to other places
Relocation Diffusion
culture and ideas spread through people physically moving and bringing cultural phenomena, innovations, diseases and more, weakens cultural hearth because people leave
Expansion Diffusion
culture and ideas spread from person to person, ideas spread without the people actually moving
Contagious Diffusion
the cultural phenomenon spreads rapidly to almost everyone regardless of age, gender, race
Hierarchical Diffusion
culture and ideas spread hierarchically—starting with someone of power in society and spreading down the social hierarchy
Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
culture and ideas spread from less populated areas and smaller towns up to larger cities and people of power
Stimulus Diffusion
the full idea does not spread, but the main or underlying idea spreads, new but related
Creolization
the process of cultural blending that results in new hybrid cultural identities, particularly through the interaction of different groups in contexts like colonization and migration, creating new languages, food, music, and other cultural practices by mixing elements from multiple original cultures
Diaspora
a group of people who have dispersed from their original homeland but maintain cultural ties to it
Acculturation
the exchange of cultural traits while both cultures remain distinct
Assimilation
the process where a minority group or individual completely adopts the cultural traits of a dominant group, often leading to the loss of their original culture, most often forcefully
Folk culture
traditionally practiced by small, homogenous, and often isolated groups
Pop culture
widespread, rapidly diffused cultural traits in large, diverse, societies
Subculture
a group within a larger culture that has its own distinct set of values, beliefs, norms, and practices, groups often emerge around shared interests like music or lifestyle, ethnicity, religion, or age, and maintain a unique identity while still being influenced by the mainstream culture
Built Environment
all human-made surroundings providing settings for human activity, representing tangible cultural elements that shape society, health, and daily life, and reflecting cultural values and needs
Dialect
a regional or social variety of a language that is distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation, often reflecting a specific cultural identity, variations of a single language, can be influenced by factors like migration
Language Branch
subdivisions of a language family, contain languages that share a common ancestor confirmed by archeological evidence
Language Family
a group of languages that share a common, ancient ancestor language called a proto-language
Lingua Franca
a common language used for communication between people with different native languages, often for trade, diplomacy, or cultural exchange
Glocalization
blending of the words “globalization” and “localization” describing how global forces are modified by local contexts
Isogloss
a geographic boundary that separates different linguistic features, such as a specific word, pronunciation, or grammar, used to map and understand dialectical differences, showing how languages evolve and vary across regions
Monotheism
religions that believe in one god
Polytheism
religions that believe in multiple gods
Multiculturalism
the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a single society, where each group maintains its unique identity, traditions, and practices
Orthography
the system of spelling and writing symbols for a language, how languages are written can be a source of identity
Placelessness
places that are homogenous, uniform, could be anywhere
Sense of Place
emotional connection or perception of a particular place, often based on what makes it unique
Sequent Occupance
the idea that successive cultures leave layers of their imprint on a place, creating a cumulative cultural landscape that shows history, conflict, and adaption over time
Syncretism
the blending of two or more cultural traits resulting in a new, hybrid culture
Universalizing Religion
a faith that seeks to appeal to and convert people from all cultures, locations, and ethnicities worldwide, actively spreading through missionaries and outreach
Ethnic Religion
a faith tied to a specific cultural or ethnic group, deeply rooted in traditions, customs, and the physical geography of a particular place, not seeking converts
Colonialism
the practice of a powerful country establishing control over a foreign territory, often through settlement and resource extraction, to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles
Triangular Trade
the transatlantic trade routes connecting Europe, Africa, and the Americas, fueled by the forced migration of enslaved people from Africa to the Americas
Pidgin
a simplified language that develops between groups with no common language, used primarily for communication in specific contexts like trade or colonization