poisson distribution [5]
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:15 AM on 9/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
1
New cards
compare and differentiate between binomial and poisson distribution
* both the binomial distribution and the poisson distribution are used to model/describe count data
* the binomial variable is the total number of successes in n trials where the trials are independent with a constant probability of success denoted by p for each of them
* the poisson distribution is the number of successes/responses in a defined time period or space where the rate per space unit or time unit is denoted by (λ)
* the binomial variable has a maximum value which is the number of trials (n), while the poisson variable, in theory, does not have that upper limit
* both binomial and poisson variables are example of
discrete variables
* the binomial variable is the total number of successes in n trials where the trials are independent with a constant probability of success denoted by p for each of them
* the poisson distribution is the number of successes/responses in a defined time period or space where the rate per space unit or time unit is denoted by (λ)
* the binomial variable has a maximum value which is the number of trials (n), while the poisson variable, in theory, does not have that upper limit
* both binomial and poisson variables are example of
discrete variables
2
New cards
what is the type of graph (left skewed, right skewed or symmetric) is the poisson distribution?
mostly right-skewed except for large λ, then it becomes symmetric
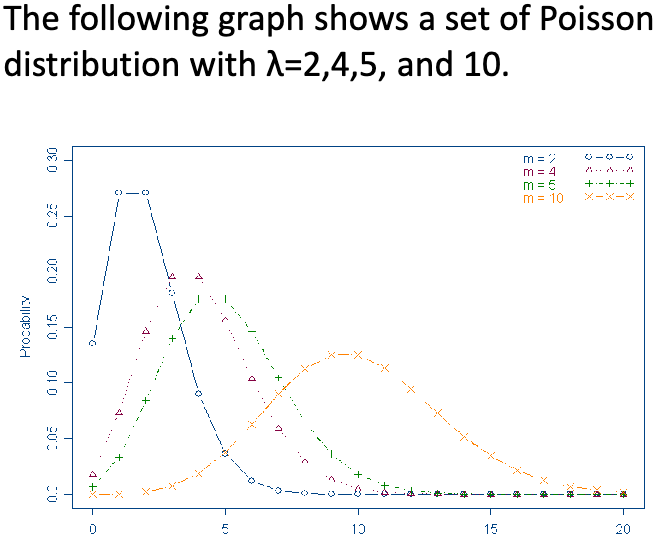
3
New cards
if Y has a poisson distribution with average rate λ \n (that is Y \~ Poisson(λ)) then what is the:
* mean of y
* variance of y
* standard deviation of y
* mean of y
* variance of y
* standard deviation of y
* λ
* λ
* √λ
* λ
* √λ
4
New cards
how to compute poisson probabilities in excel for point and cumulative probabilities
* point probability → =POISSON.DIST (k, λ, 0)
* cumulative probability → =POISSON.DIST (k, λ, 1)
* cumulative probability → =POISSON.DIST (k, λ, 1)