Chemistry Exam 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
gigameter
1 Billion Meters
kilometer
1 Thousand Meters
decimeter
1 Tenth of a Meter (0.1)
millimeter
1 Thousandth of a Meter (.0001)
centimeter
1 Hundredth of a Meter (.01)
micrometer
1 Millionth of a Meter (0.000001)
nanometer
1 Billionth of a Meter (0.000000001)
picometer
1 Trillionth of a Meter (0.000000000001)
What is the scientific unit for mass
Kilograms (1000 grams)
Scientific Unit for length
meters
scientific unit for temp
Kelvin (Celsius + 273.15)
Scientific Unit for time
seconds
what is density
mass/volume
What is Kelvin in terms of Celsius
Celsius + 273.15
I milligram = how many grams
0.001 grams
Cm³ = ?
1 mL
Precision
How close the measurements are to each other in a series
Accuracy
How close measurements are to actual value
systematic error
Measurements either being too high or too low
Random error
Measurements being both high and low
atomic number
number of protons in 1 atom
mass number
number of protons plus neutrons
Isotope
element with a different number of neutrons and therefor different mass number
element
the most basic kind of substance
atom
individual unit of an element (building block)
two or more atoms bounded together
molecule
pure substance
has properties that do not very between samples (i.e, element and compound)
mixture
physical combination of two or more pure substances; can be hetero or homogeneous
chemical combining of two or more pure substances
compound
Dalton’s 1st Atomic Theory
Each element is composed of individual units called atoms
Dalton’s 2nd Atomic Theory
In a sample of a given element all atoms are identical
Dalton’s 3rd Atomic Theory
Two different elements will have different atoms
Dalton’s 4th Atomic Theory
Compounds are made by combining different elements. A given compound will always have the same type or ratio of atoms
Dalton’s 5th Atomic Theory
Atoms of 1 element cannot be changed into atoms of a different element. They can not be created or destroyed
Law of Constant Composition
in a chemical compound, the relative number of different atoms is constant throughout
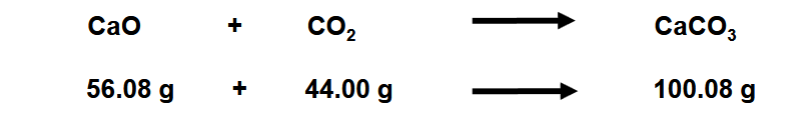
Law of Mass Conservation
Total mass of substances present does not change during chemical reaction
Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
discovered that atoms have electrons, and that electrons have mass
Oil Drop Experiment
discovered the magnitude/measured an electrons charge, and was used to calculate the electrons mass
Rurtherford Gold Foil Experiment
discovered that the mass of an atom is in the nucleus in the center of the atom, and that an atom is mostly empty space
AMU
1/12 mass of Carbon 12
which two particles in an atom have relatively the same mass
Protons and Neutrons
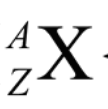
A
mass number (P + N)
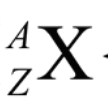
Z
atomic number (P)
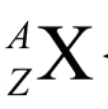
X
atomic symbol
How do you find average atomic mass?
%1(AMU1) + %2(AMU2) = Average Mass (%1+%2=100)

Group 1A (Red)
soft, reactive (alkali) METALS
Group 2A (Orange)
alkaline earth metals
Group 7A (Purple)
halogens

Group 8A (Pink)
noble gasses
Where does the main group elements STOP on the right side of the periodic table?
Diagonally from Boron (B) to Astatine (At)
Empirical Formula
the smallest ratio of different elements in a formula (can represent many different compounds)
ways to draw molecules
structural, perspective, ball and stick, space filling
Ion
an atom that has become electrically charged
Poly-atomic Ion
a molecule that has become an Ion
which comes first in naming ionic compounds
cation
how do you dictate the charge of transitional metals?
Roman Numerals
NH4+
Ammonium
H3O+
Hydronium
Molecular Mass
sum of compounds atomic mass’
Molecular Formula
Gives you the actual number of atom in each element (i.e O2, O3, H2O)
Molecular Compound
the sharing of electrons between two nonmetals
Ionic Compound
the transfer of electrons between a metal and nonmetal
Name diatomic molecules
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
Two or more nonmetals that form a compound
Molecular Compound
how do you name an non oxygenated anion in a ionic compound
by adding the suffix ‘ide’ to the root of the nonmetal
cation is to metal as anion is to
nonmetal
amu also equals
grams (g)/ mol (mole)
mole
number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of Carbon-12
Binary Acid Solutions produce what
H+ when dissolved in water
for an oxoacid, the suffix ‘ate’ and ‘ite’ become
‘ic’ and ‘ous’
true of false: Formula mass is found differently than molecular mass
false
Avagadro’s # (Na)
6.0221421 × 1023 (items/mol)
mass %
(mass of element in a compound/mass of the full compound) x 100
what is the difference between a physical and chemical change
physical alters appearance but NOT chemical composition while chemical change creates new substances
how to extensive properties differ from intensive
the value of extensive properties are dependent on the amount while the value of intensive stay the same regardless of amount.
chemistry
study of materials and their transformations
matter
anything that occupies space
homogeneous mixture
uniform throughout (same proportions and composition) and only 1 phase
heterogeneous mixture
not uniform throughout (can see different substances and phases)
examples of physical properties
color, density, hardness, boiling point, etc
what are physical properties
properties observable without changing the substance
examples of chemical properties
reactivity and flammability
chemical properties
observable by transforming the substance into another substance (chemical change)
Law of multiple proportions
ratio of different atoms in a compound can be expressed as a ratio of small #’s
percent composition
the mass percent of each element in a compound
molarity
mol of solute/Liters of solution
how do you get the molecular formula from the empirical formula
divide molecular mass by empirical mass, then multiply subscripts by that number
solutions are homo or hetero mixtures
homogeneous mixtures
solute
substance that gets dissolved (lesser amount)
solvent
substance that is doing the dissolving
solution
the mixture of solvent and solute (final product)
diluted
small amount of solute
concentrated
large amount of solute
mass percentage, volume percentage, mass-volume percentage
(mass of solute/mass of solution, volume of solute/volume of solution, mass of solute/volume of solution) x 100 percent
Why are all atoms in an element NOT identical?
Each version of an element will have the same amount of protons but can very in neutrons and electrons, making them not identical.
electrostatic attraction
the force that attracts opposite electric charges