Behavioral Adaptations for Survival
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
finding prey
Predators that are good at ____________ are favored by natural selection
selection pressure
any cause of reduced reproduction in some portion of a population
escape predation
Prey are selected for their ability to ____________
evolutionary arms race
what is the evolution of a predator driving the adaption of a prey and vice versa an example of?
adaptive trade offs
most behaviors where animals must make decisions come with ___________
mobbing behavior
many adults cooperate to fend off a much larger/stronger predator
no
Should we expect perfectly effective mobbing behavior?
lack of appropriate mutation, pleiotropy, coevolution
what are constraints on perfect adaption?
relatively better
Genes for phenotypes that are _____________ than other phenotypes become more frequent in a population
a heredity trait that is spread bc of natural selection from past to present and is currently spreading relative to alternative traits due to natural selection
what is an adaptation?
cost-benefit
Testing whether one phenotype is better than alternative phenotypes has involved a ___________ approach
benefits must be greater than costs and the benefit to cost ratio must be greater than all alternative traits
what must happen for a trait to be an adaptation?
parasite infestation, less predation risk
potential cost of a high density gull/skua population? benefit?
predation, offspring develop faster due to less parasites
potential cost of low density gull/skua population? benefit?
selective pressures
If a given trait is adaptive for one species, then it should be adaptive for another species subject to the same _______________
divergent evolution
what type of shift resulted in ground nesting behavior?
no
If mobbing behavior in black-headed gulls is an evolved response to predation on gull eggs and chicks, then should other gull species whose eggs and young are at low risk of predation exhibit mobbing behavior?
the simplest explanation with the fewest undocumented assumptions is preferred
what does the principle of parsimony state
no
does the principle of parsimony mean that simpler explanations are correct?
fewest
base on the principle of parcimony: The best estimate of character evolution is the one that requires us to postulate the _________ evolutionary changes
convergent evolution
distant ancestry with a shared inepentently evolved behavior
divergent evolution
shared ancestry with different behaviors
masting
reproductive strategy that takes advantage of safety in numbers
safety in numbers principle
why do butterflies sun themself in large groups?
blending into background
what is crypsis?
the background
what is the effectiveness of crypsis dependent upon?
yes
can conspicuousness be an adaptation for prey animals?
aposematic coloration
bright coloration broken up with dark colors, often warns of poison
secondary defense mechanisms
defense mechanisms that come into play at the time of an attack
stotting
series of jumps or hops performed int he presence of potential predators
alarm signal hypothesis
hypothesis that stotting has evolved to warn other conspecifics especially close relatives that there is a predator near
social cohesion hypothesis
stotting behavior developed to get individuals to join a group for safety in numbers
confusion effect hypothesis
stotting behavior breaks focus on individuals making it harder to target
sign of unprofitability hypothesis
stotting is advertising that it is young, agile ect to a predator so it would be a waste to pursue it over easier prey
sign of unprofitability
which hypothesis for stotting has the most support?
fear screams
loud vocalizations that animals engage in at the time of capture
optimality theory
states that: among alternative behavioral phenotypes, the one with highest benefit to cost ratio should be favored by NS
X
which phenotype is the adaptation?
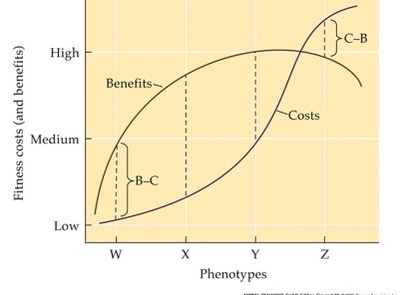
different fitness units
why is measuring B and C difficult?