3.5 Population and Ecosystem
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Biotic
A part of the environment of an organism that is living
Birth rate
The reproductive capaticty of a population: the number of new individuals derived from reproduction per unit time.
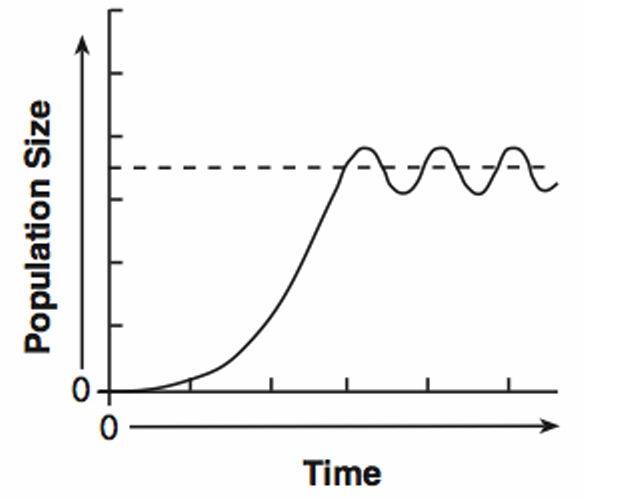
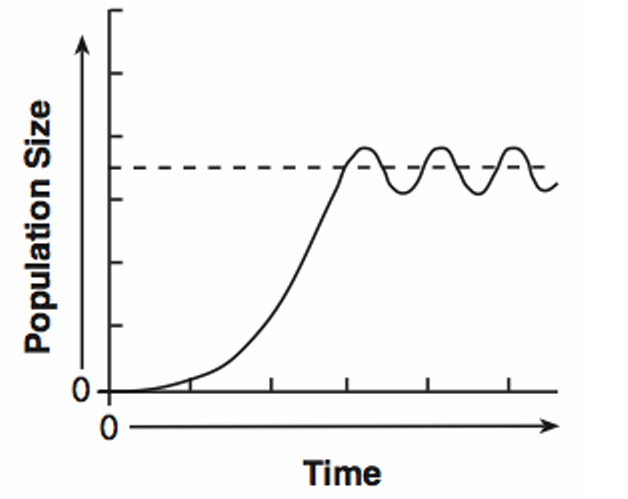
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number around which a population fluctuates in a given environment.
Community
Interacting populations of two or more species in the same habitat at the same time
Climax Community
a stable end point where there are no further successional stages
Equilibrium Species
Species that control their population by competition rather than by reproduction and dispersal
Fugitive species
Poor at competition and rely on a large capacity for reproduction and dispersal to increase their numbers
generation time
when cell numbers double at discrete time intervals
Ecology
The branch of biology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physicak surroundings
Ecosystem
A characteristic community of independent species interacting with the abiotic components of their habitat
Environmental Resistance
Refers to the environmental factors that sow down population growth
Immigration
The movement of individuals into a population of the same species
Limiting Factor
A factor that limits the rate of a physical process by being in short supply. An increase in a limiting factor increases the rate of the process
Niche
The role and position of a species in its habitat
Population
An interbreeding group of organisms of the same species and occupying a particular habitat.
Community
Interacting populations of two or more species in the same habitat at the same time
Habitat
The place in which an organism lives
Abiotic
A part of the environment of an organism that is non living
Describe lag phase
Slow growth due to physiological adaption of cells to culture conditions. They are synthesising enzymes and replicating DNA
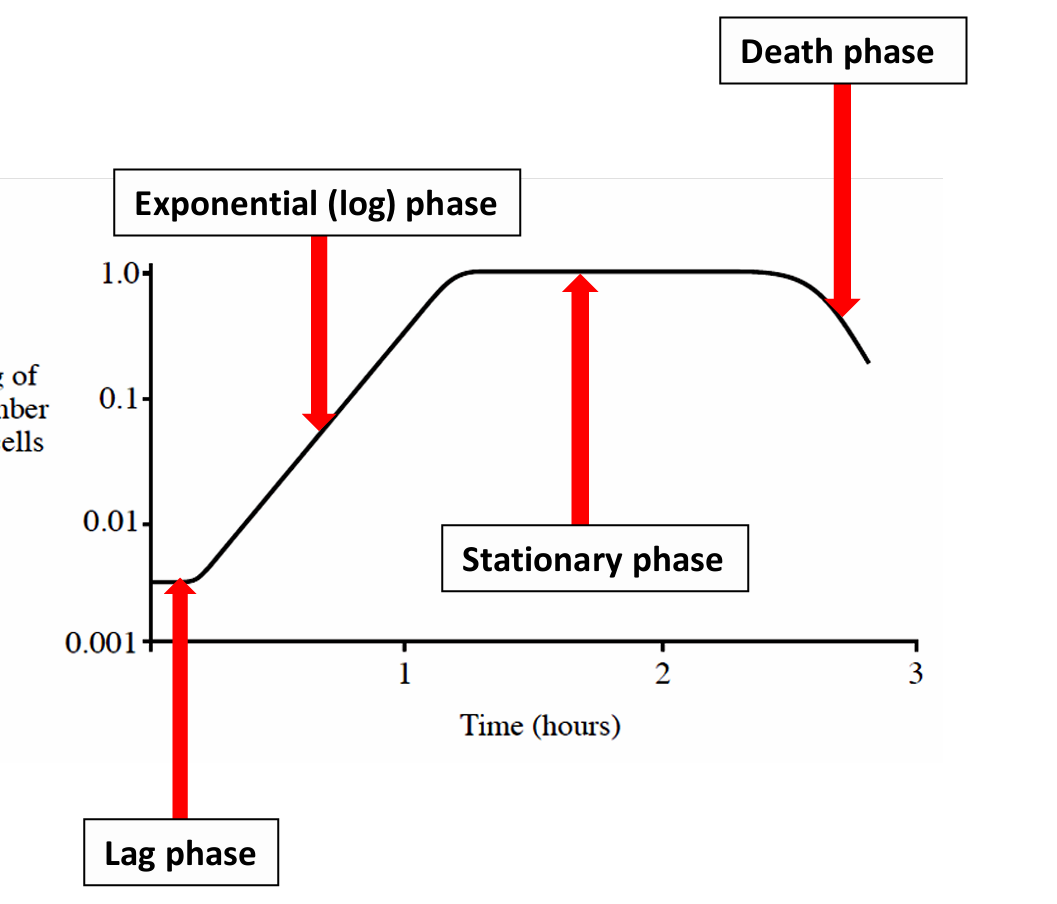
Describe log phase
As the nutrient availability is high, the growth becomes exponential.
Cells divide rapidly, reproduction exceeds death rate and population doubles for each unit of time
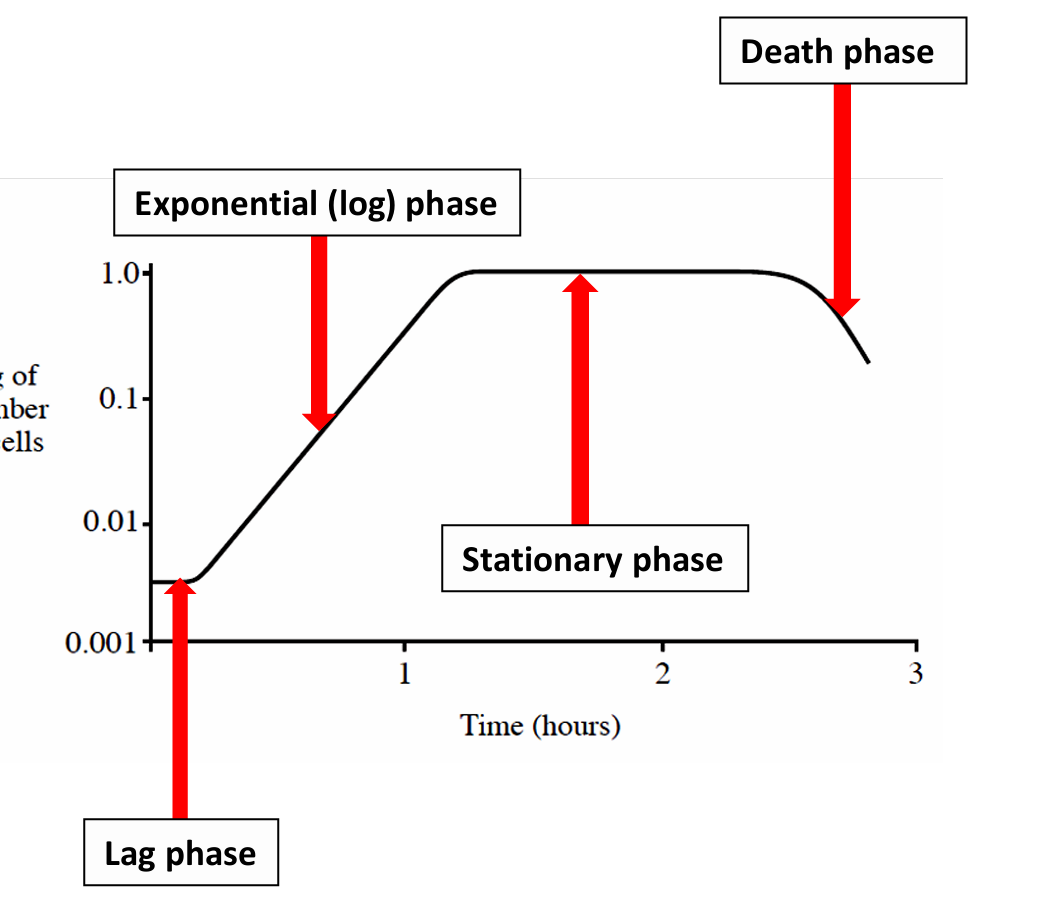
Describe stationary phase
Growth and death of cells counterbalance each other resulting in no net increase in cell numbers.
Population has reached its carrying capacity for that environment
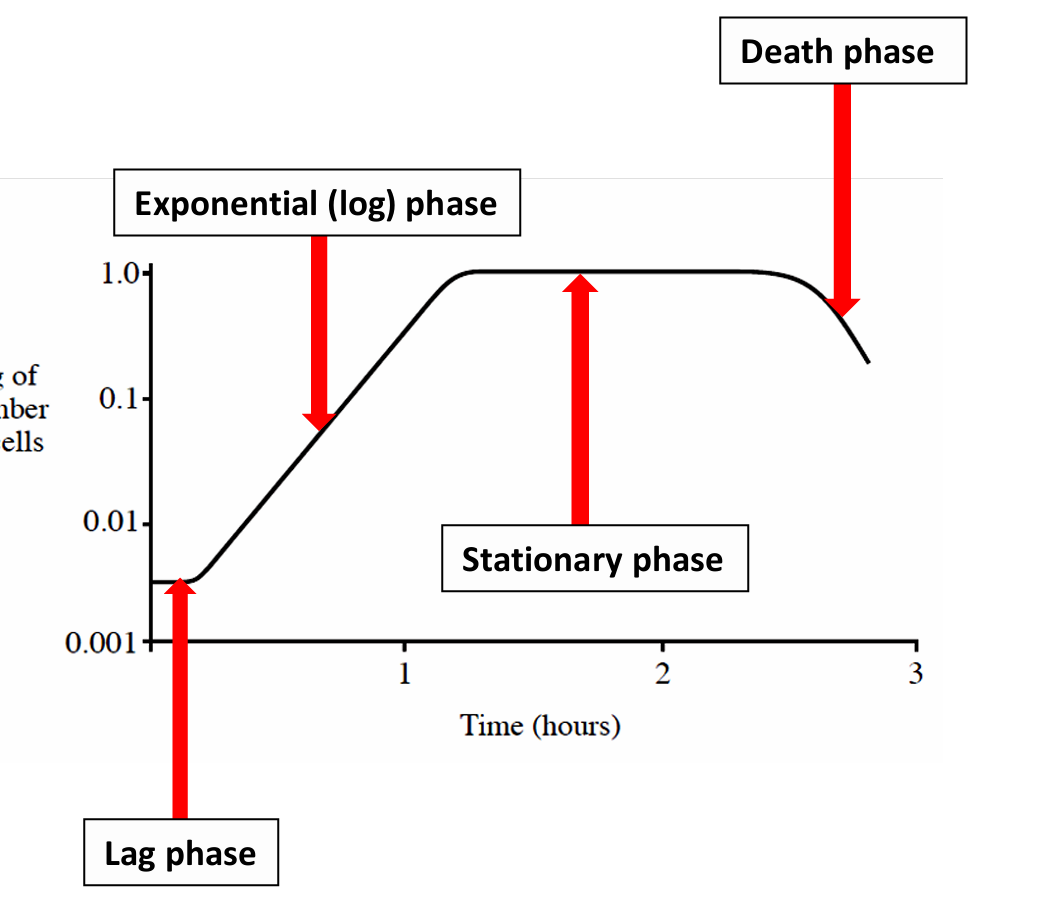
What causes a reduced growth rate in a population
depletion of nutrients
build up of toxic waste
Describe death phase
Death rate exceeds growth rate resulting in a net loss of viable cells
Examples of environmental resistance - biotic
Available food
Overcrowding
Competition
Accumulation of toxic waste
Predation
Disease
Examples of abiotic environmental resistance
Water
Temperature
Light intensity
Intraspecific competition
competition within a species
Interspecific competition
competition between species
Define density-dependent factor
These factors affect a greater proportion of the population if the population is denser. They are biotic factors
Examples of density dependent factors
disease, depletion of food supply, parasites
Define density-independent factor
The effect is the same regardless of the size of the population and is usually a sudden change in a abiotic factor
Example of density independent factor
Flood or fire
Describe how a population size is regulated by negative feedback
If the population rises above the set point, a density dependent factor increases and mortality or reduces breeding to such an extent that the population decreases
If the population falls below the set point, environmental resistance is temporarily relieved so that the population rises again
Define abundance
The number of individuals in a species in a given area or volume
How can animal abundance be measured
capture-mark-recapture experiments
Kick sampling in a stream
How can the abundance of a plant species be measured
Using a quadrant to calculate the mean number of individuals in several quadrants of known area
Estimating percentage cover
Estimating percentage frequency
Define distribution
The area or volume in which the organisms of a species are found
State two sources of error in collecting data for pyramids of biomass
Roots not collected
Water is included in the measurement of biomass
What is the source of energy in food chains
sunlight
How do some animals occupy more than one trophic level
They feed in different levels at different times of the year
Describe the role of detritivores
Feed on small fragments of organic debris which is called detritus
Describe the role of decomposers
Obtain nutrients from dead organisms and animal waste
Define trophic level
Feeding level
The number of times that energy has been transferred between the sun and successive organisms along a food chain
Define biomass
The mass of biological material in living, or recently living organisms
Summarise a detritus food chain
detritus -> detritivore -> decomposer
State the factors that affect the factors of the food chain
-The more energy fixed in photosynthesis
If energy is transferred more efficiently
Larger ecosystems can support longer food chains
Three dimensional environments have longer food chains than two dimensional habitats
State what a transect is
A useful technique that displays the variation in organisms and its correlation with a changing abiotic factor
What is a belt transect
Shows abundance data for a given area at measured distances along a transect. A quadrant is placed at each co-ordinate along the transect.
State how energy lost limits the number of steps in a food chain
The amount of remaining energy in the food chain may not be great enough to support viable populations at higher trophic levels
Why can not all light energy hitting the leaf be used in photosynthesis
Some energy is reflected by the waxy cuticle
Some energy is the wrong wavelength
Some energy is transmitted through the leaf as it does not strike a chloroplast
How is energy lost in a food chain
as heat in respiration
energy in molecules are egested and excretion
How is biomass lost in a food chain
some of its food will not be digestible and will be egested as faeces
Excess amino acids will be converted to nitrogenous waste and will be excreted as uric acid
Some of it will be used in respiration and will be lost as heat
Gross primary productivity
The rate of production of organic molecules by photosynthesis in a given area per unit time
Units of GPP
kJ m-2 y-1
Define net primary productivity
The organic molecules assimilated
Primary productivity
The rate at which energy is converted by producers into biomass
Secondary productivity
The rate at which consumers convert the chemical energy of their food into biomass
Trophic efficiency
The percentage of energy at one trophic level which is passed on to the next trophic level
How do farmers increase productivity of their livestock
Keeping animals in barns during winter will reduce the heat loss by respiration. The energy saved can be used to increase biomass instead.
Feed animals more digestible food
Why do herbivores have a lower secondary productivity than carnivores
The protein rich diet of carnivores is more readily and efficiently digested
Why do aquatic food chains tend to be longer than terrestrial ones
The do not use as much energy to move as there is buoyancy from water
Why do cold blooded organisms lose less energy
Cold blooded organisms aren't losing energy to heat from respiration
Why do smaller animals lose more energy
Have a high sa:vol ratio so will lose more heat and will have to respire at a higher rate to keep warm
What do pyramids of biomass measure
The amount of energy converted into living tissue at the different trophic levels
Why might a pyramids of numbers by inverted
A large organism can sustain many smaller organisms
A low biomass of organisms can sustain a larger biomass at the next trophic level because the organisms reproduce rapidly and thus supply continuous nourishment
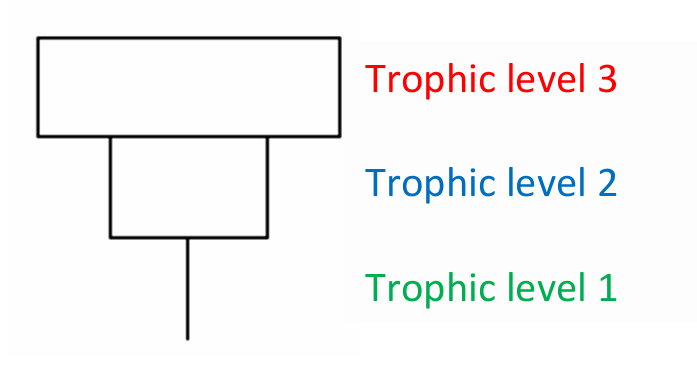
Why must pyramids of energy by up-right
energy cannot be created or destroyed
During the transfer of energy, some energy is always lost as heat
Pioneer species
First organism to colonise a new area in an ecological succession
Succession
A change in species composition and communities over time
Primary succession
The change in structure and species composition of a community over time in an area that has not previously been colonised
What are the stages of succession called
seres
Describe an example of primary succession
Lichens arrive on the rock as spores blown in by the wind or carried by animals
Lichens erode the rock and as they decompose a little soil builds up
mosses appear
Soil formed will eventually be deep enough to allow grasses to take root, from seeds being blown in or carried by animals
The grass is replaced by herbaceous plants which is then replaced by shrubs
The woodland in the climax community
Does biodiversity increase or decrease because of succession
increase
equation for NPP
NPP = GPP - R
Secondary succession
The changes in a community following the disturbance of damage to a colonised habitat
Where does secondary succession start
Where there is seeds or spores available in the soil
Mutualism
An interaction between organisms of two species from which both derive benefit
Name factors affecting succession
immigration
Competition
Facilitation
Commensalim
An interaction between organisms of two species from which one benefits but the other is not affected.
Describe ammonification
1) Detritivores consume dead organisms and animal waste products and saprophytic bacteria and decomposers secrete enzymes
2) Proteases digest proteins into amino acids
3) Deaminases remove amino groups from amino acids and reduce them to ammonium ions
4) Digestion products are absorbed by decomposers
Describe nitrification
The ammonium ions in decomposition are converted to nitrites and then nitrates
Nitrosomonas
ammonium to nitrite
Nitrobacter
converts nitrite to nitrate
Why do Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter require aerobic conditions?
The nitrogen atom in the ammonium ion progressively loses hydrogen atoms and gains oxygen atoms and so the reactions are oxidations
What is the energy released in the oxidation reactions in nitrification used for
to synthesise organic compounds in a process called chemosynthesis
Describe denitrification
Anaerobic bacteria converts nitrate ions to nitrogen gas
What do denitrifying bacteria use nitrates for
as a source of oxygen for respiration
What is a common cause for anaerobic conditions in nature
water logging
Name some nitrogen fixing bacteria
Azotobacter and Rhizobium
Describe nitrogen fixation
The conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonium by nitrogen fixing bacteria
What enzyme do nitrogen fixing bacteria have
nitrogenase
Where does nitrogen fixation by Rhizobium occur
in the root nodules of legumes
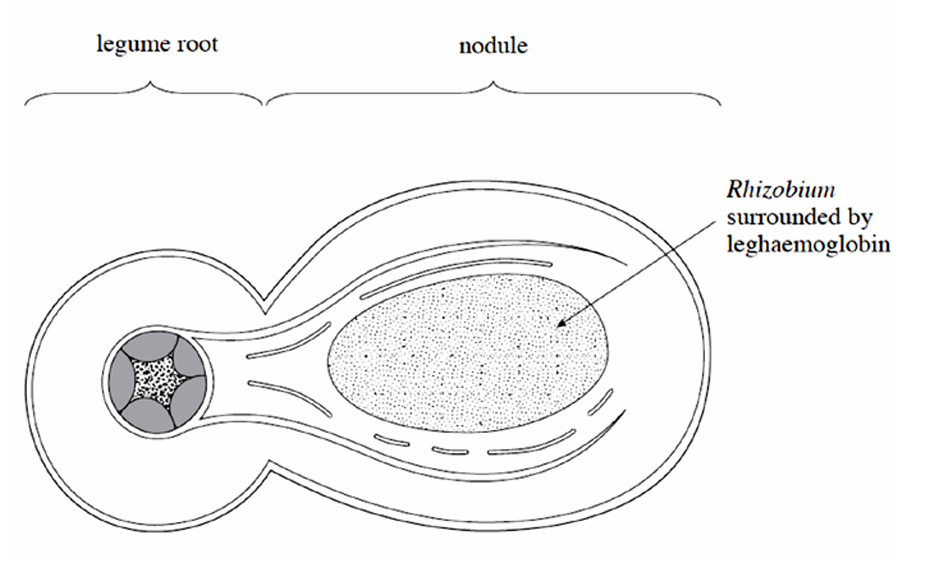
Describe the mutualistic relationship between rhizobium and legumes
Nitrogen fixation requires much ATP and the Rhizobium gains the sugars for respiration from the plants photosynthetic product.
Plant provides a pigment called leghaemoglobin which binds to oxygen in the root nodule to create anaerobic conditions
Excess ammonium and amino acids are exported to the plant for protein synthesis
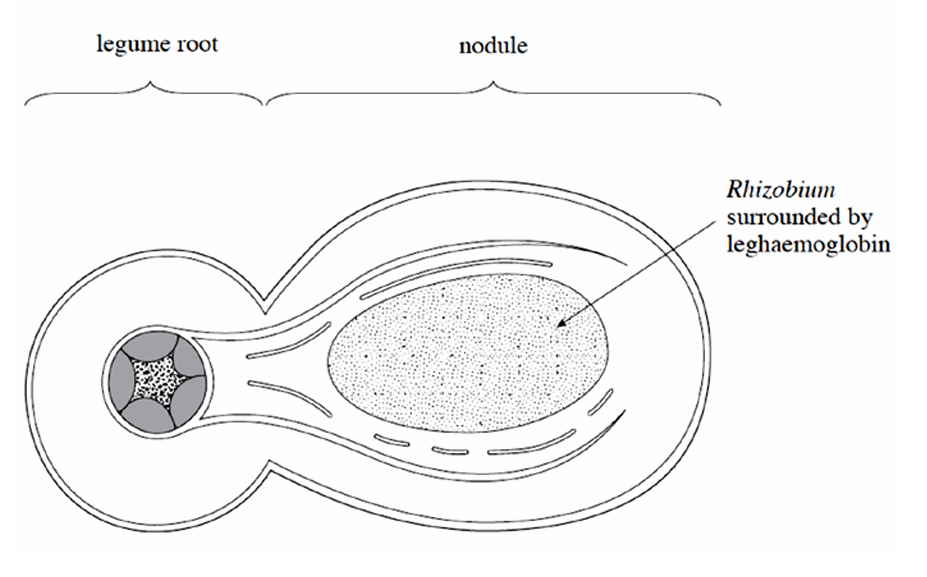
Why does nitrogen fixation require anaerobic bacteria
nitrogenase activity is inhibited by high oxygen concentrations
State human activities that can improve the circulation of nitrogen in agricultural soils
Ploughing fields to improve soil aeration
Draining land so it reduces anaerobic conditions
Artificial nitrogen fixation
Large amounts of animal waste
Planting fields of legumes
What will increase atmospheric carbon dioxide lead to
increased greenhouses effect