1.06 Opthalmic prisms
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Why do we prescribe prisms

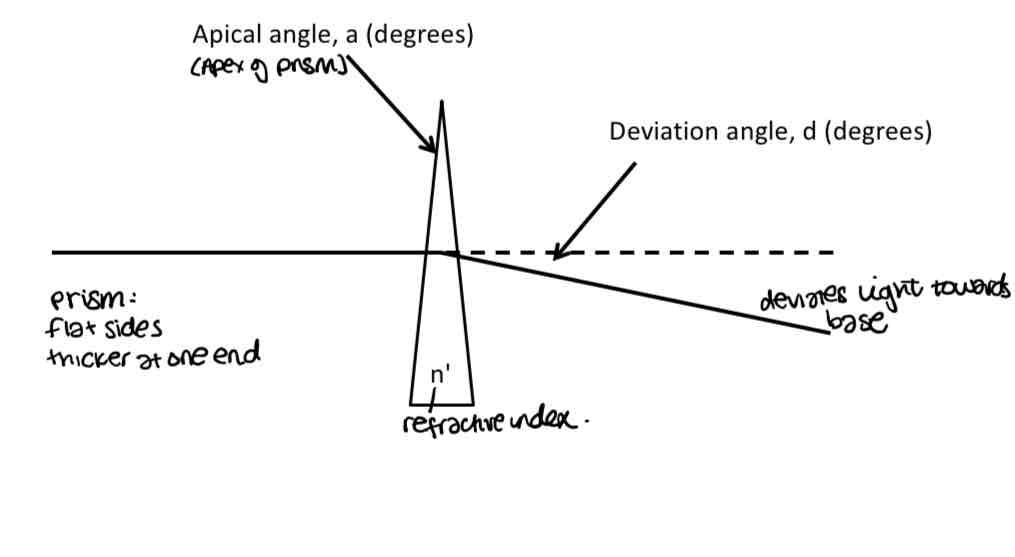
Diagram of prism
Prism effect on image position
Prisms deviate light towards the base
The image appears to move towards the apex (top)
How to calculate approximate deviation angle
D = (n’ - 1) x a
N’ = refractive index
A = apical angle
A prism power of 1∆ will deviate light by
By 1 unit at a distance of 100 units
Eg 1cm deviation at 1 metre
How to convert from deviation angle to prism power
Prism power (∆) = 100 x tan (deviation angle)
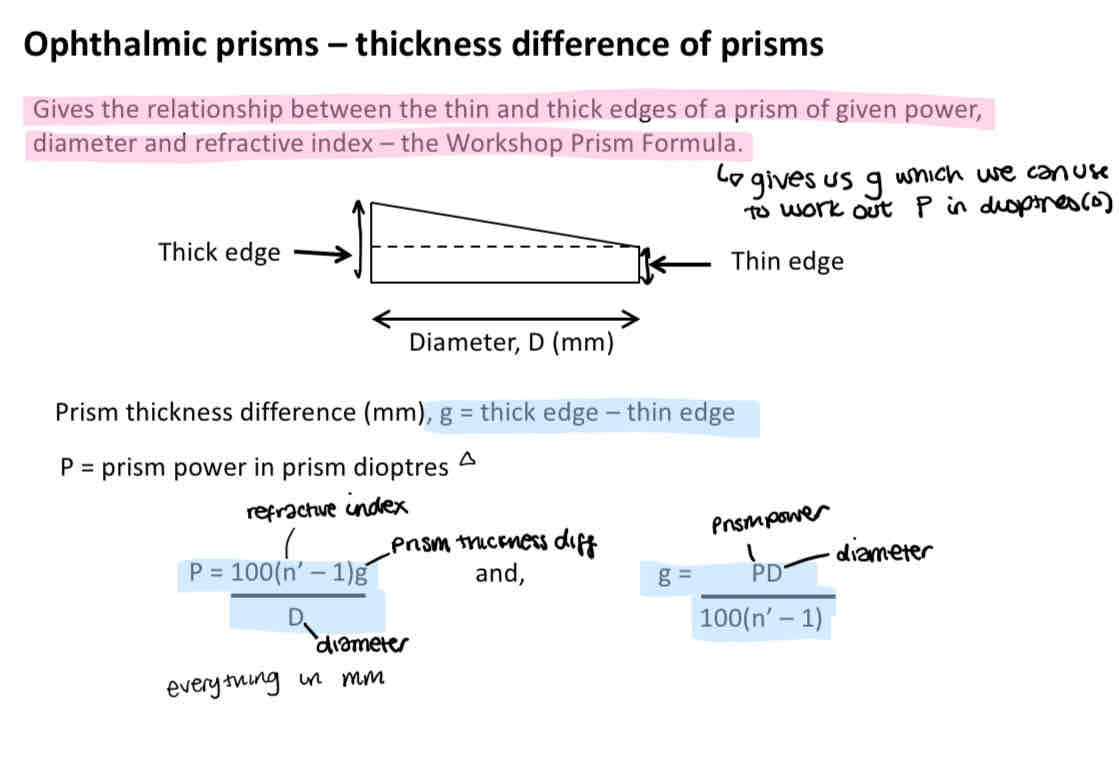
How to calculate prism power (in prism dioptres)
P = (100 (n’ -1) g) / D
N’ = refractive index A
G = prism thickness difference
D = diameter
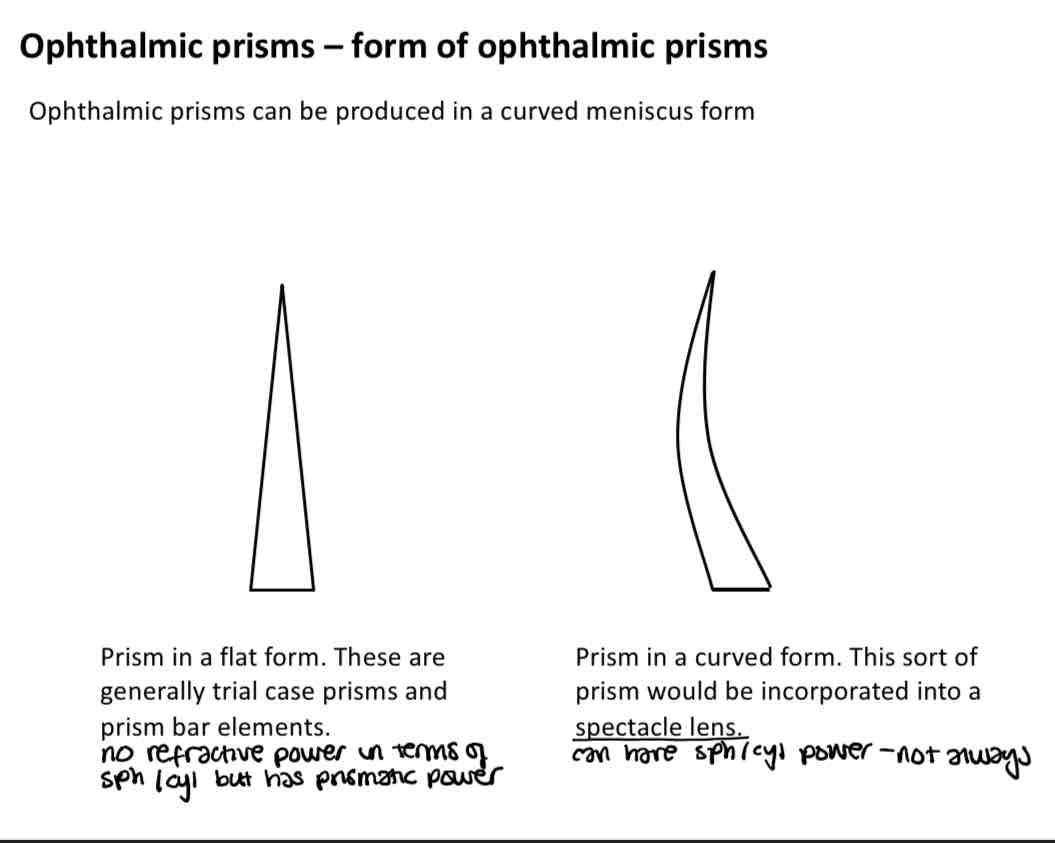
Forms of opthalmic prisms
Measuring prism power on focimeter
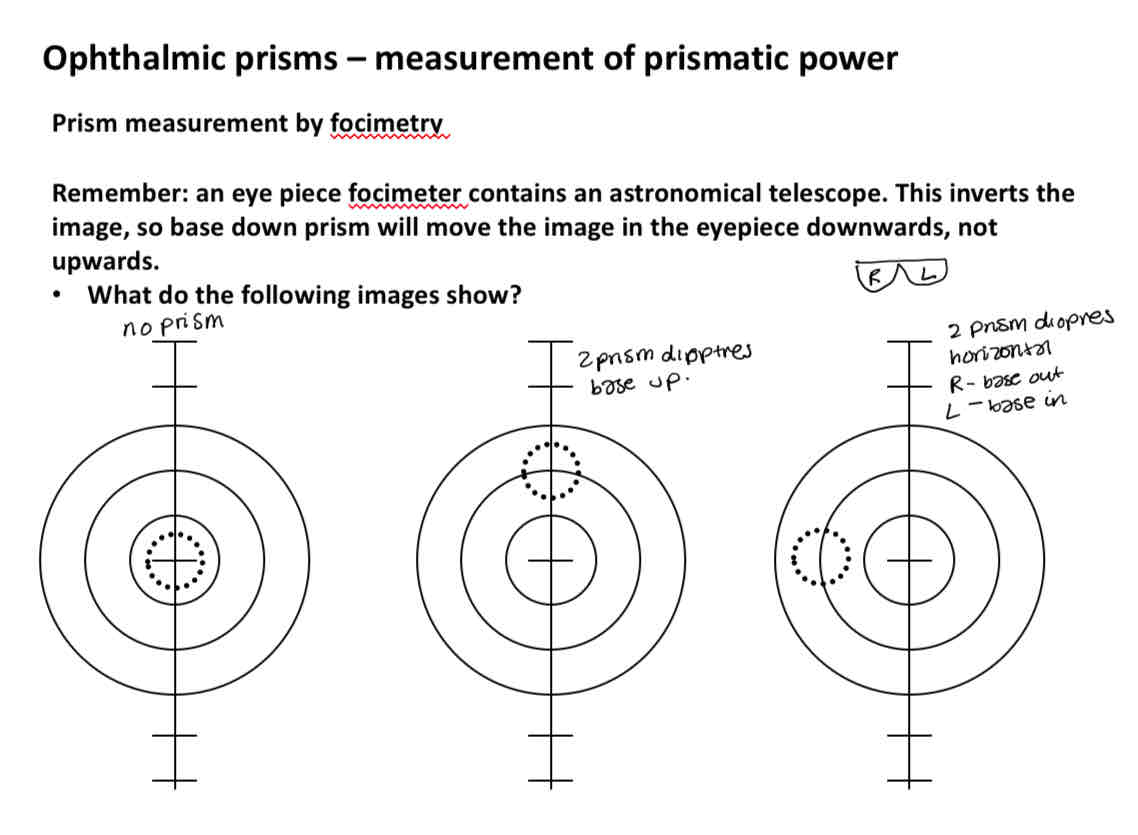
Prims displacing cross
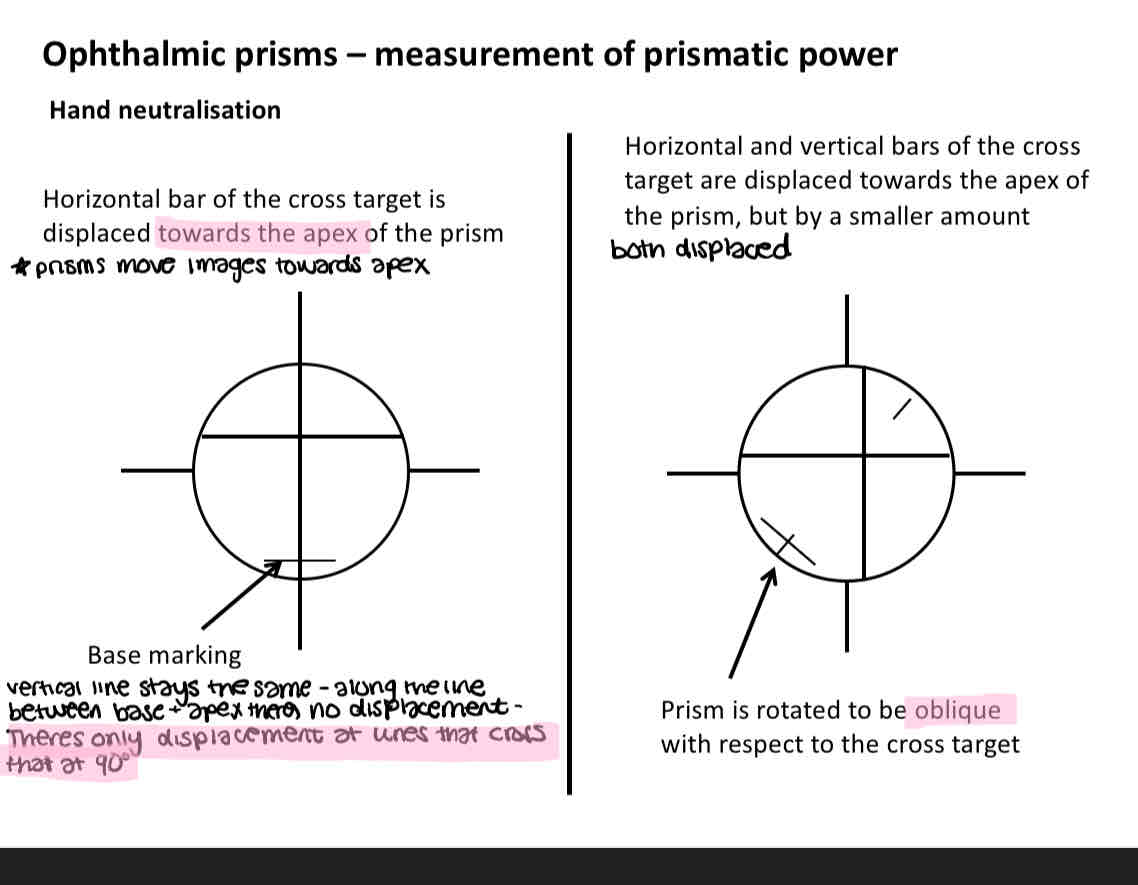
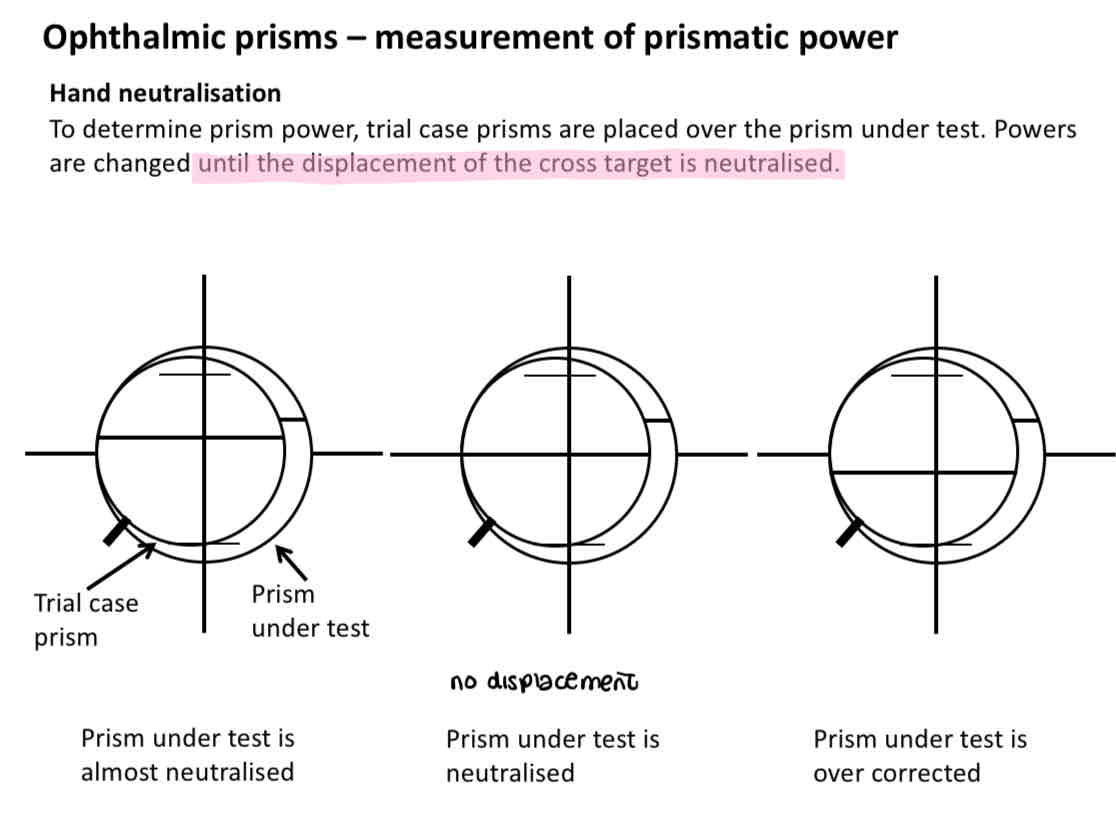
Hand neutralisation
Cross is in the middle of the lens in the middle image
Prism compensators
Used to centre the image
How to provide prism in a spectacle lens

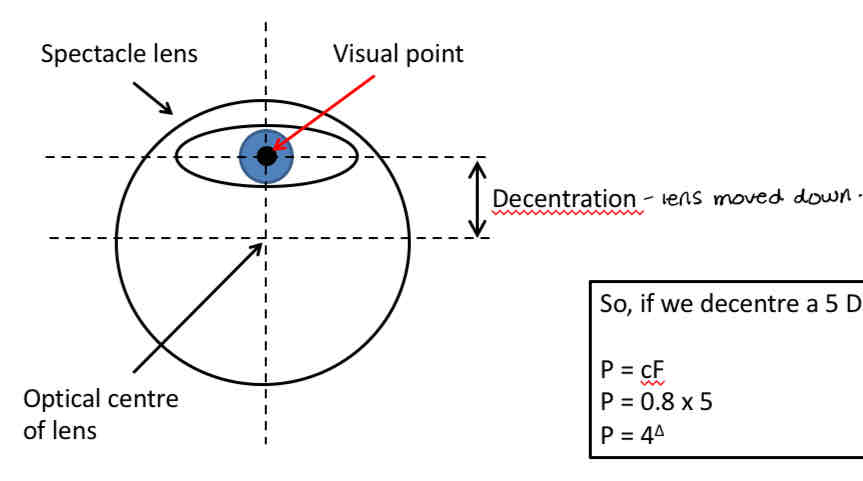
Pretices rule
Used to calculate the degree of prismatic power when a patient looks through a point other than the optical centre of a lens
P = cF
P = prismatic effect (prism dioptres)
C = decentration of the optical centre of lens (cm)
F = the power of the lens (D)
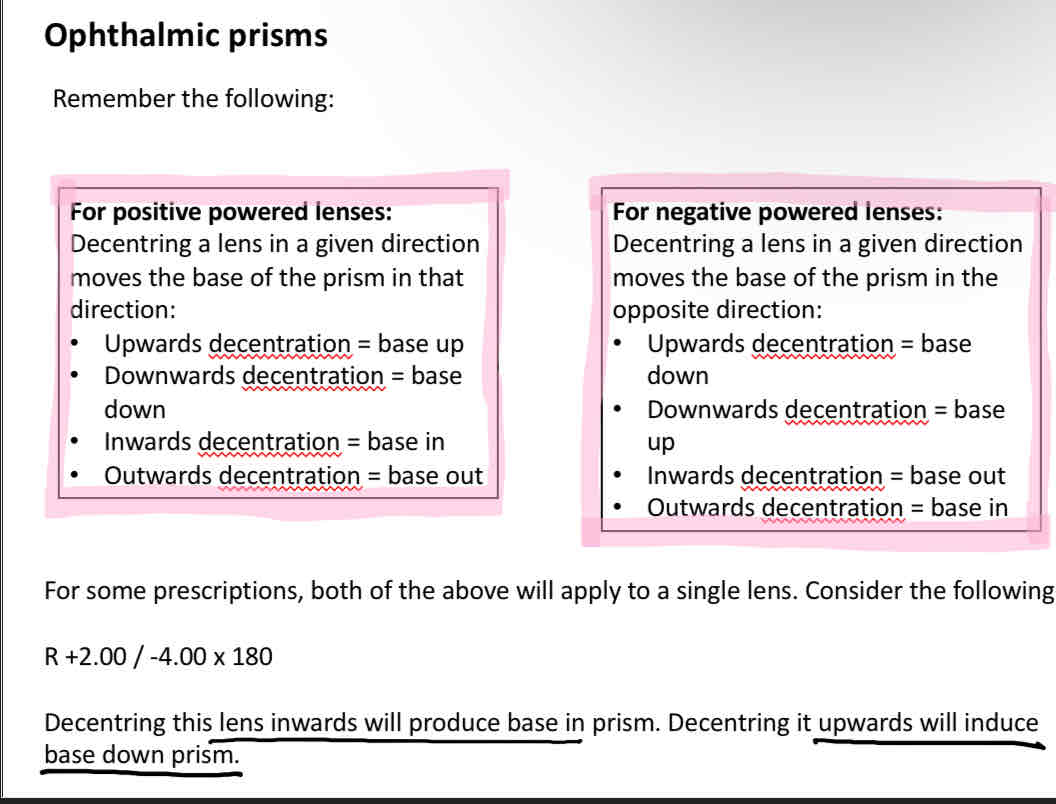
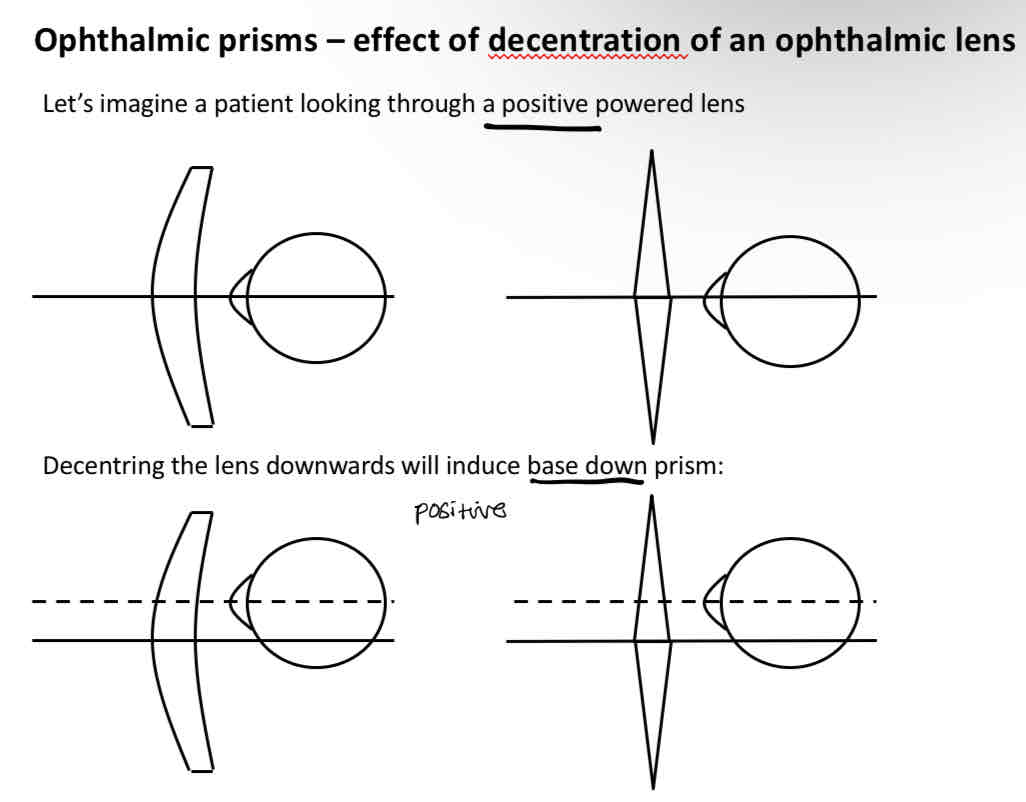
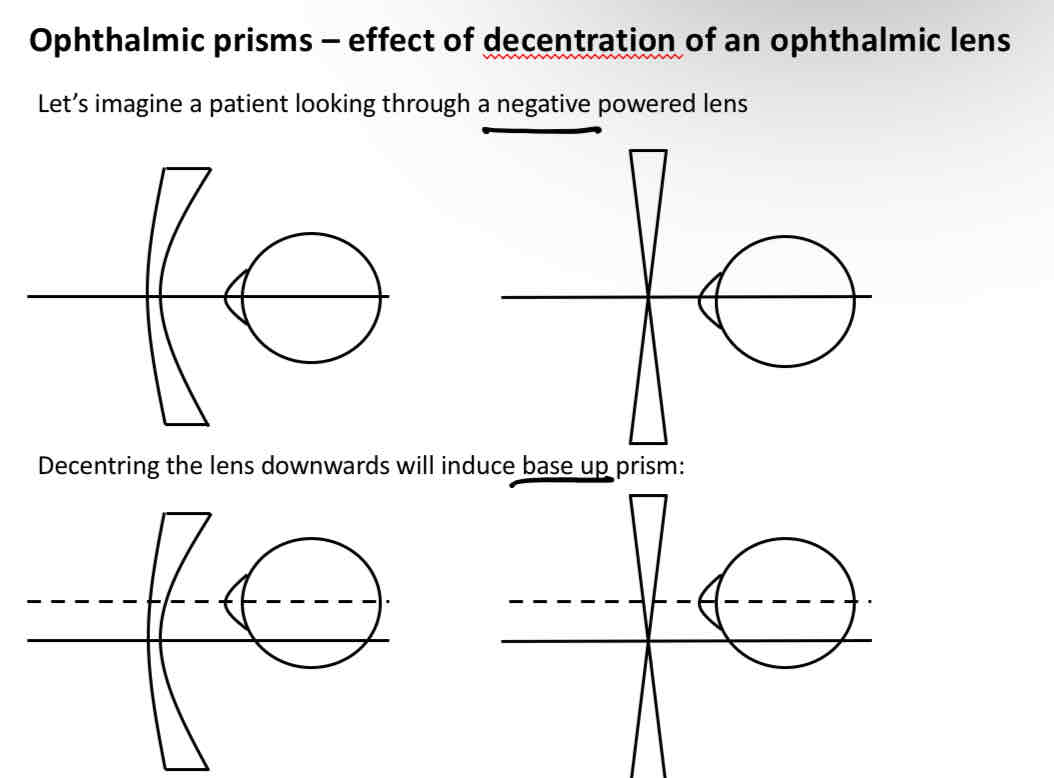
Decentration general rule
Down + out = positive
Up + in = negative
Different types of lenses
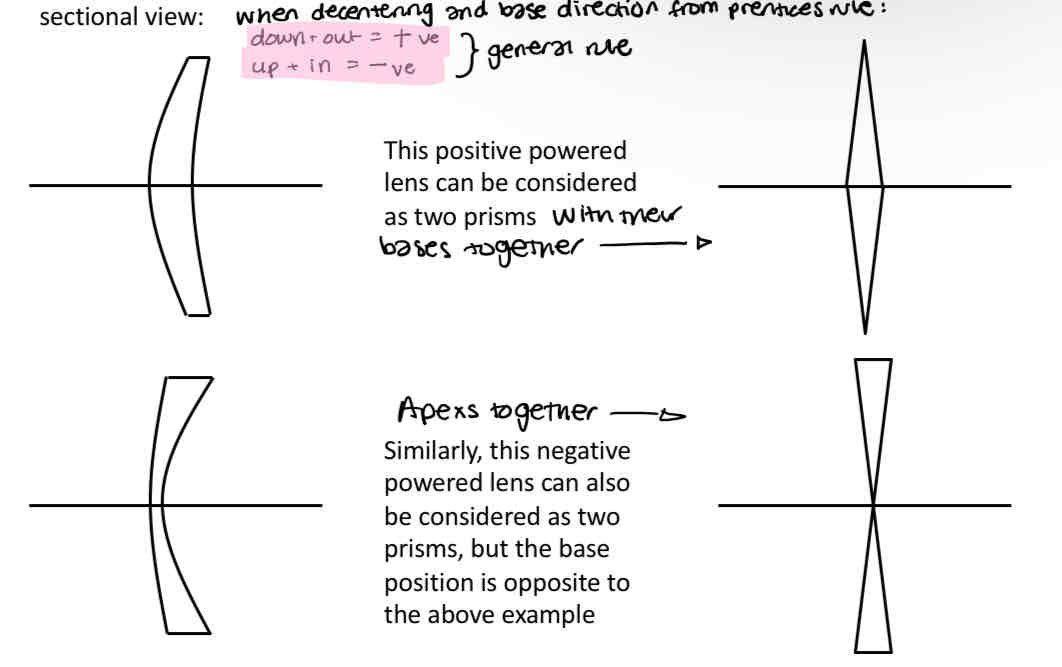
Decentering a positive powered lens
Decentering a negative powered lens
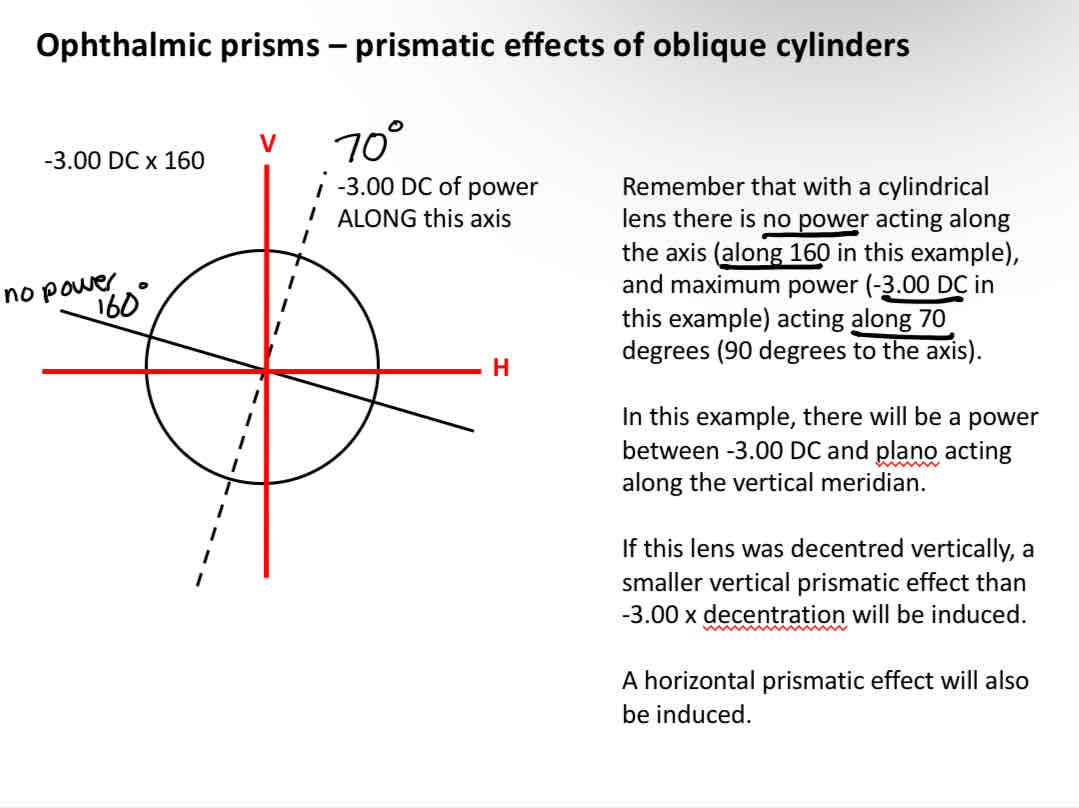
Prismaatic effect of oblique cylinders
Decentering sphero cylindrical lens

Prismatic effect of a decentrered sphero cylinderical lens
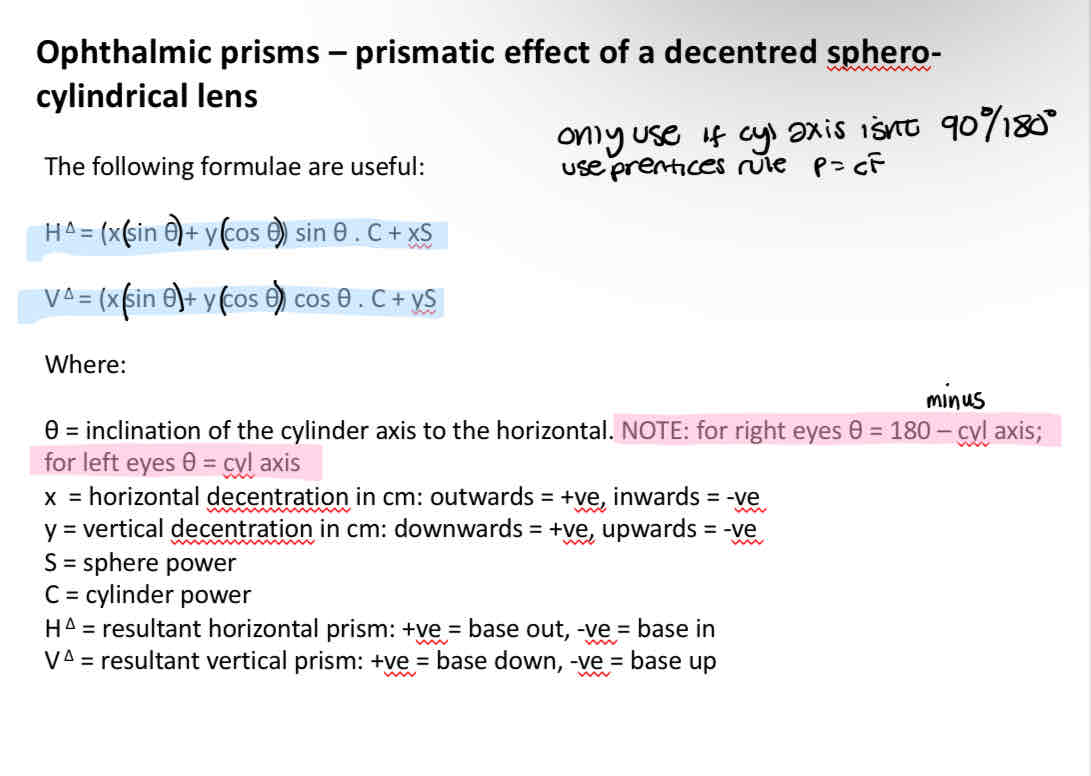
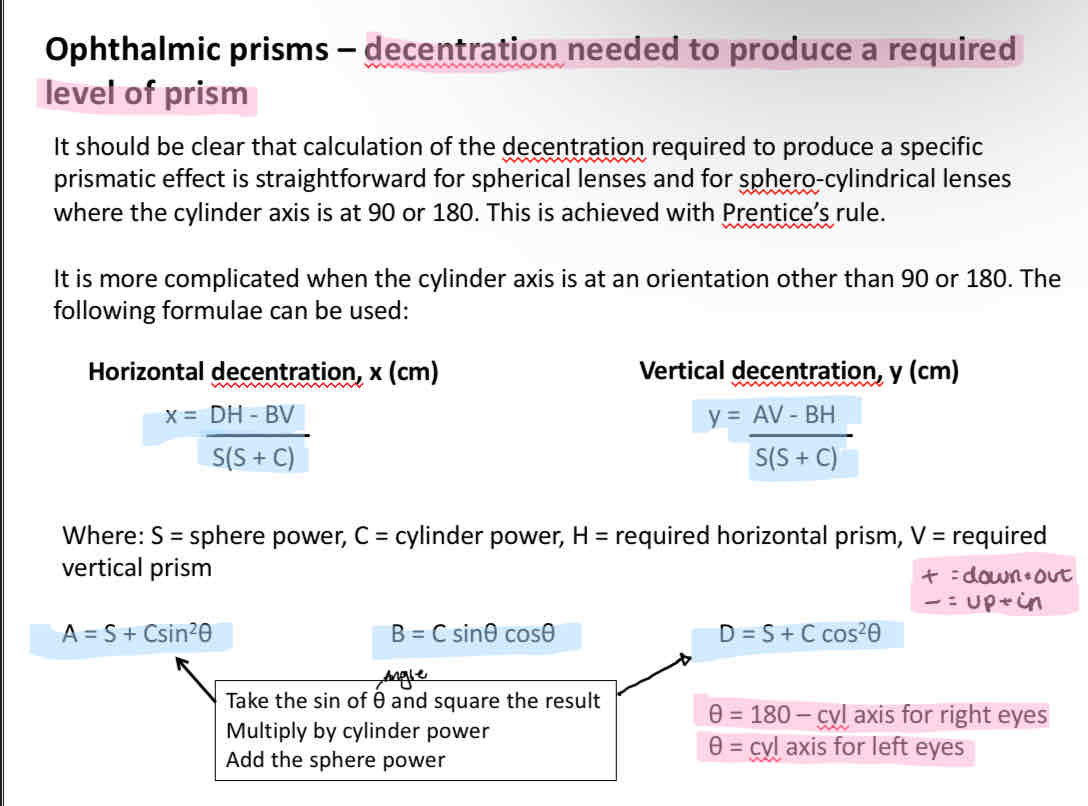
Decentration needed to produce a required level of prism
horizontal decentration
Vertical decentration
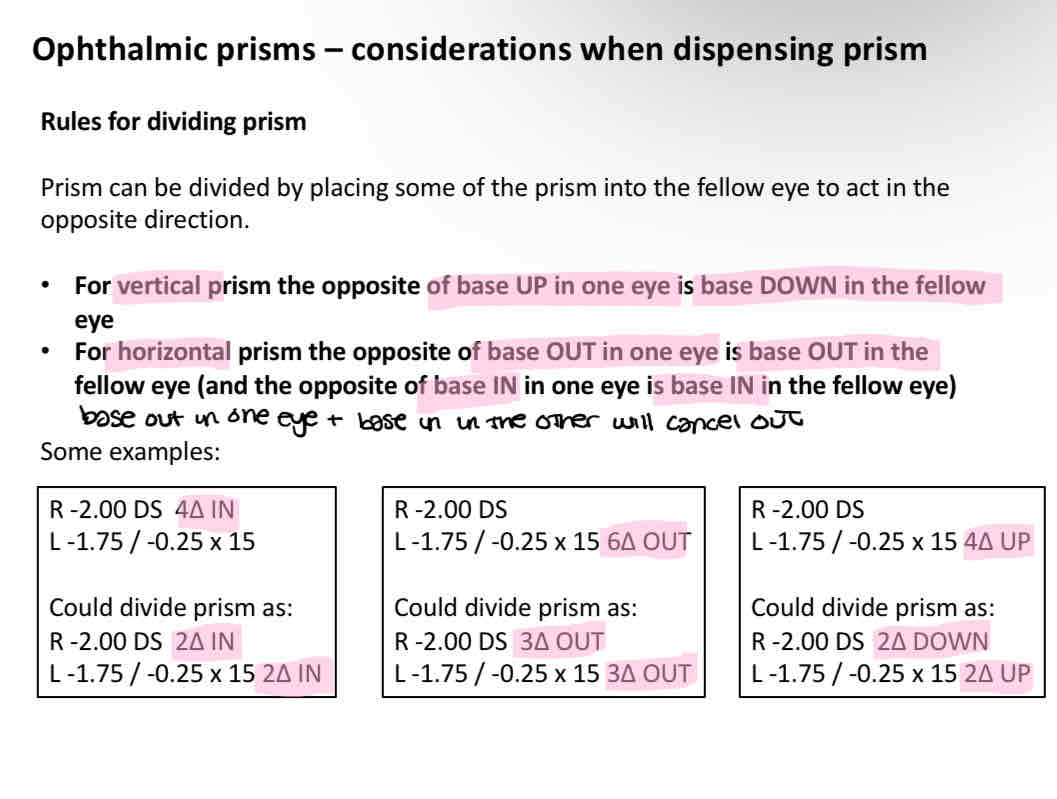
How to improve cosmetic appearance of prisms
The prism power can be divided between the eyes to even out the weight and cosmetic appearance
Rules for dividing prism
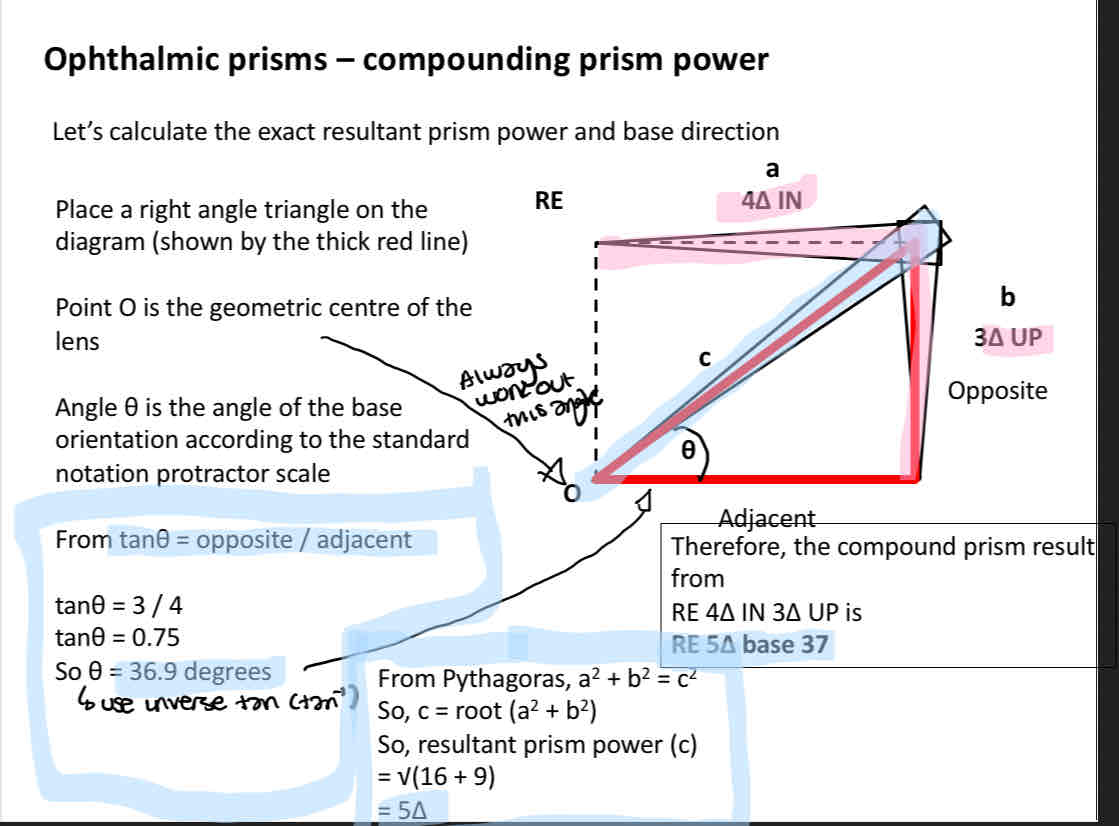
Compound prism power
Use pythagorus to get the resultant prism power
Use soh cah toa to get base orientation
Rotatory prism

Fresnel prisms
