Chapter 5: Electric Circuits
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It comprises an energy source typically a battery, one or more conducting materials, and circuit components such as resistors and capacitors
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
Current
The continuous flow of charge
2
New cards
Average current
***Iavg = change in charge/ change in time***
3
New cards
Battery
A battery is a device that maintains an electric potential difference between the two terminals.
4
New cards
Direct current
The flow is from higher potential to lower potential. The electricity also flows in that direction called direct current.
5
New cards
Resistance
It is the impedance to the flow of electricity through a material. Asa charge moves through a material, it eventually hits a non-moving nucleus in the material.
6
New cards
Resistivity
It can be thought of as the density of nuclei the electrons may strike.
***R = ρ l / A***
* R = resistance of the circuit
* ρ = resistivity
* l = length
* A = cross-sectional area
***R = ρ l / A***
* R = resistance of the circuit
* ρ = resistivity
* l = length
* A = cross-sectional area
7
New cards
low resistivity
conductors
8
New cards
high resistivity
insulators
9
New cards
resistors in series
***R eq = R1 + R2***
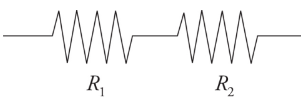
10
New cards
resistors in parallel
***1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2***
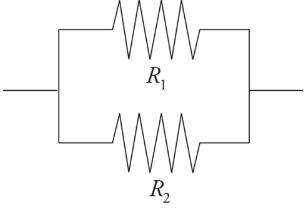
11
New cards
Ammeter
An ammeter is a device with a very low resistance that measures the current.
12
New cards
Voltmeter
It measures the electric potential called potential drop.
13
New cards
Ohm’s Law
***V = IR***
* R is the resistance in the circuit.
* V is the potential difference in the circuit
* I is the electric current
* R is the resistance in the circuit.
* V is the potential difference in the circuit
* I is the electric current
14
New cards
Power dissipation
* ***P = VI***
* ***P = I^2 R***
* ***P = V^2 IR***
* P is the power
* V is the potential difference in the circuit.
* I is the electric current.
* ***P = I^2 R***
* ***P = V^2 IR***
* P is the power
* V is the potential difference in the circuit.
* I is the electric current.
15
New cards
Kirchhoff’s rules
The loop rule states that the voltage drop across any complete loop in the circuit is 0V. This statement follows from the conservation of energy when applied to circuits.The junction rule states that the sum of all current flowing into any junction is equal to the current flowing out of the junction. This statement follows from the conservation of charge.
16
New cards
Capacitance
***C = QV***
* C = refers to the capacitance that we measure in farads
* Q = refers to the equal charge that we measure in coulombs
* V = refers to the voltage that we measure in volts
Besides, there is another formula that appears like this:
***C = kε0Ad***
* C = refers to the capacitance
* K = refers to the relative permittivity
* ε0 = refers to the permittivity of free space
* A = refers to the surface area of the plates
* d = refers to the distance between places measured
* C = refers to the capacitance that we measure in farads
* Q = refers to the equal charge that we measure in coulombs
* V = refers to the voltage that we measure in volts
Besides, there is another formula that appears like this:
***C = kε0Ad***
* C = refers to the capacitance
* K = refers to the relative permittivity
* ε0 = refers to the permittivity of free space
* A = refers to the surface area of the plates
* d = refers to the distance between places measured
17
New cards
Capacitors in parallel
***Cp = C1 + C2***
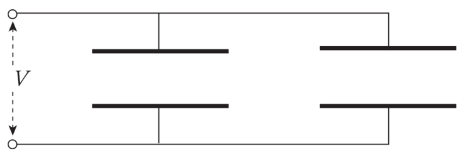
18
New cards
Capacitors in series
***1/Cs = 1/C1 + 1/C2***
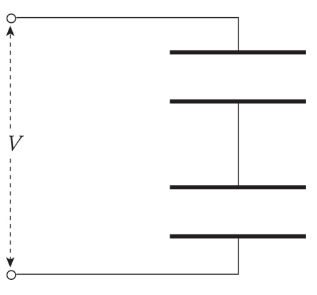
19
New cards
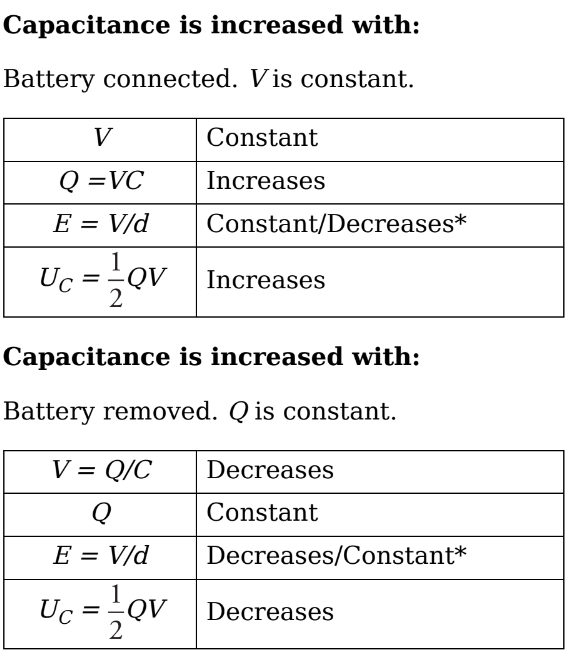
Altering the capacitance of capacitor
20
New cards
Name four possible energy sources for a circuit
Battery \n Photocell \n Electric Generator \n Thermocouple
21
New cards
A circuit is opened and closed using a:
Switch
22
New cards
What will happen to the charges in a circuit when a switch is closed?
The charges will flow through the circuit.
23
New cards
What will happen to the charges in a circuit when a switch is open?
The circuit is broken and the charges stop flowing through the circuit.
24
New cards
What is the standard voltage per branch in a home in the United States?
120 V
25
New cards
A switch that automatically opens if the current is too high is a ________________
Circuit Breaker
26
New cards
The symbol used to represent resistance in a schematic diagram is
a zigzag line
27
New cards
A closed circuit is a circuit in which charge
can flow
28
New cards
When two light bulbs are connected in series, the
same amount of current always flows through each bulb
29
New cards
When resistors are put in parallel with each other their overall resistance is
smaller than the resistance of any of the resistors
30
New cards
As more lamps are put into a series circuit, the overall current in the circuit
decreases
31
New cards
As more lamps are put into a parallel circuit, the overall current in the circuit
increases
32
New cards
When one light bulb in a parallel circuit containing several light bulbs burns out, the other light bulbs
burn the same as before
33
New cards
Electrical devices in our homes are connected in
parallel