white dirty shoes on
1/381
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
382 Terms
Early evidence of viruses
Mayer found disease transmitted from rubbing sap of sick plants onto healthy ones, Ivanowsky showed this sap still caused disease even after passing through filter
Why are viruses difficult to study
-extremely small
-lack structures / metabolic system found in cells
-Cant grow without host ( no petri dish test)
-No tools to visualize until 1940s
How did Stanley contribute to knowledge of viruses
Crystallized tobacco mosaic virus, proving that viruses could behave like chemical molecules, not cells
What did Stanley’s crystallization of TMV reveal
No living cell can form crystal, only molecules can, revealed viruses were noncellular, simple in structure, capable of retaining infectivity even when crystalized
four forms of viral genomes
dsDNA
ssDNA
dsRNA
ssRNA
What is a capsid
protein shell that protects viral genome
What are capsomeres
protein subunits that assemble to form capsid
What are the different shapes of capsids
Helical
Icosahedral
Complex
Phospholipid bilayer
outer membrane surrounding capsid, derived from host cell
Host membrane proteins
provides envelope basic membrane structure, derived from host cell
Viral glycoproteins
proteins encoded by viral genome and inserted into host derived membrane before viral budding, allows virus to bind to specific receptors, derived from virus
What is the role of an envelope in animal viruses?
Bind to receptors using viral glycoproteins (spikes)
Fuse viral membrane with host cell membrane
Deliver capsid and genome into cytoplasm
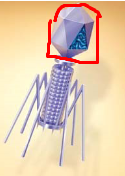
Structure circled in red
Head / Capsid
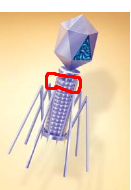
Structure circled in red
Tail sheath

Structure circled in red
Tail fibers
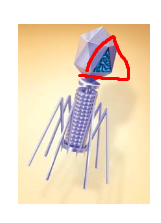
Structure circled in red
Genome / Dna

What type of virus
Bacteriophage, specifically t-even phage (t2 t4 t6)
What does bacteriophage mean?
Bacteria Eater

What is it’s host
Bacteria

Is the genome of this virus DNA or RNA
dsDNA
What property of a virus determines its attachment to a host cell membrane?
Attachment proteins must match specific receptor molecules on host cell surface
Obligate intracellular parasites meaning
Must infect and live inside host cell to replicate
What is a host range
range off organisms a virus is capable of infection
broad host range vs limited host range
broad can infect multiple species whereas narrow host range can only infect one species
broad host range example
rabies / influenza
limited host range example
HIV
host range of rabies vs host range of human cold virus
rabies is more broad, infects many mammal species
hcv is more narrow, infects only humans
what components of a host cell does virus use to reproduce itself
enzymes ribosomes nucleotides amino acids atp and membranes
How does a DNA virus reproduce its genome
-Capsid delivers viral DNA into host nucleus
-Viral DNA acts as a template, host enzymes (pol, hel, prim) replicate the viral genome
-Copies of viral DNA are produced
How does a RNA virus reproduce its genome
-Viral genome enters host cell
_Viral RdRp makes new RNA genomes and mRNA for protein synthesis
-new viral proteins + new genomes = self assembly
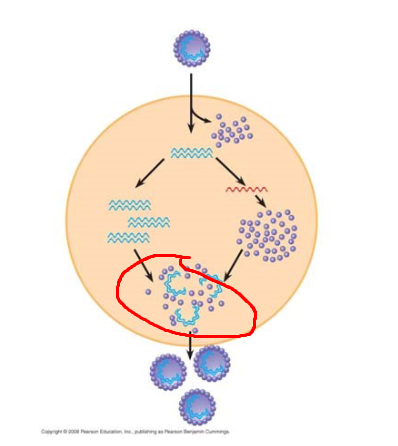
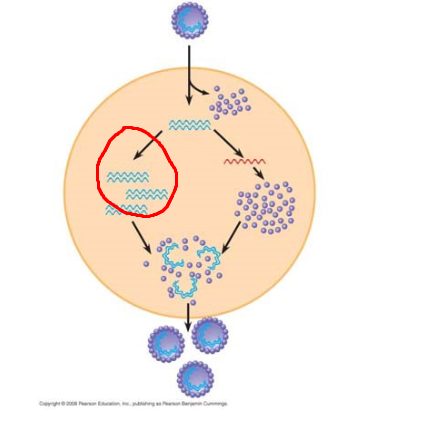
Process circled in red
Self assembly, capsid proteins assemble around genomes to form complete viral particles
Process circled in red
Transcription, genome is used as template to make mRNA
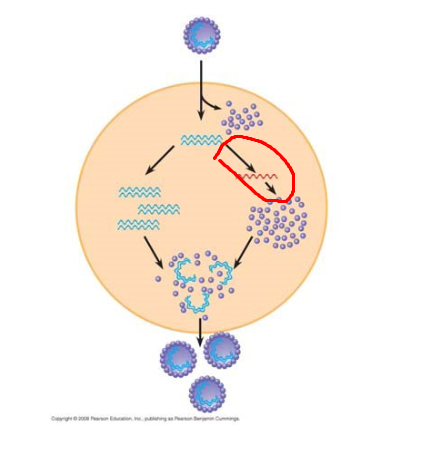
Process circled in red
Replication, Viral genome is replicated to produce many copies for packing into new virions. DNA viruses use host DNA pol
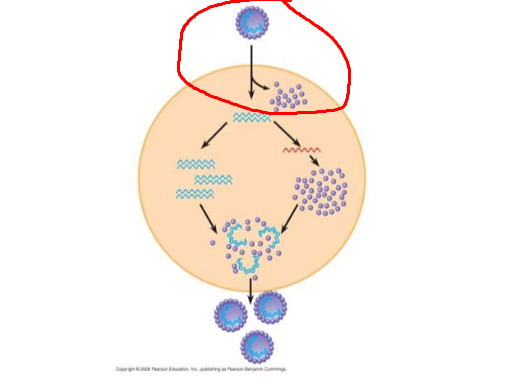
Process circled in red
infection, virus binds to host cell receptors and enters cell.
What are bacteriophages?
Viruses that infect bacteria
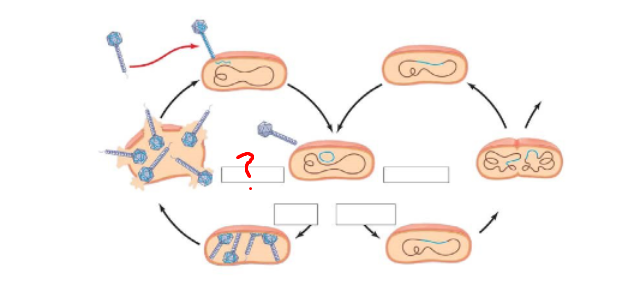
Distinguish between virulent and temperate phages.
Virulent phages reproduce only by lytic cycle, killing host cell
Temperate phages use either lytic or lysogenic cycle, allowing DNA to integrate in host genome and remain dormant
What portion of a phage enters the host cell?
only the viral genome enters, usually dsDNA
how does a phage enter bacteria
tail fibers recognize specific receptors on bacterial cell wall, tail sheath contracts like a spring loaded syringe, contraction forces tail tube through bacterial envelope, viral genome is injected
what are restriction enzymes, what is there role in bacteria
bacterial enzymes that cut dna at specific sequences, protect bacteria by cutting foreign DNA.
Why don’t restriction enzymes destroy the DNA of the bacterial cells that produce them?
Bacteria methylates their own DNA at restriction enzyme recognition sites, methylation blocks enzyme from cutting so only foreign DNA gets destroyed
What are three ways bacteria may win the battle against the phages
-mutating surface receptors so phages cant attach
-restriction enzymes cutting injected phage DNA
-CRISPR can recognize phage DNA
What is a prophage?
phage DNA that has been integrated into bacterial chromosome during lysogenic cycle and is copied along with host DNA
What might trigger the switchover from lysogenic to lytic mode
when a host is in danger, prophage bails out and activates lytic cycle
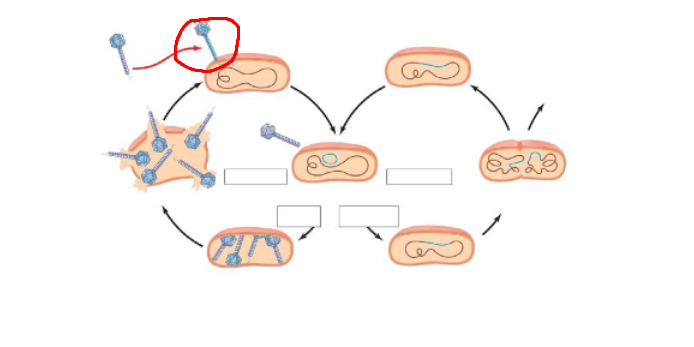
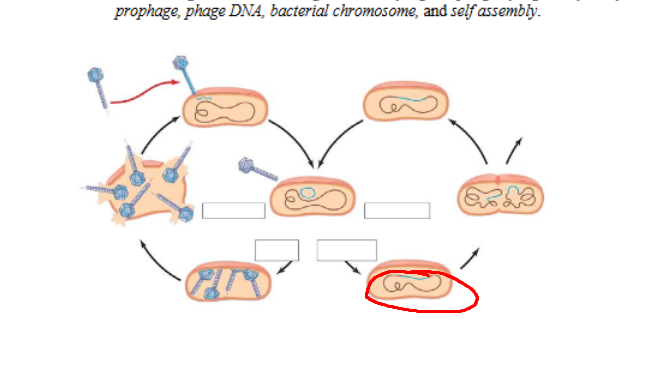
Structure circled in red
Phage DNA
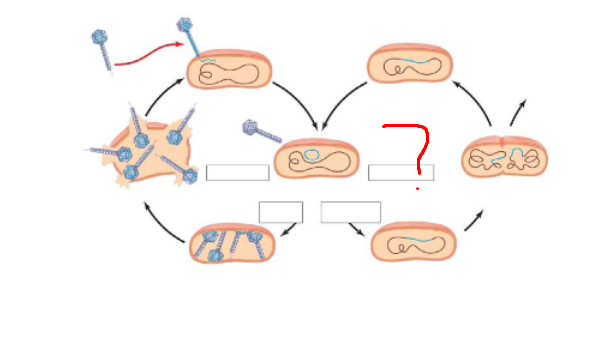
Which cycle?
Lycitic
What structure
Prophage,
Which cycle
Lysogenic
How does the lytic cycle work
-attaches to bacterial surface receptor
-injects phage DNA
-viral DNA shuts down host cell machinery
-host ribosomes synthesize viral proteins and replicate viral genome
-self assembly assembles capsids into new phage genomes
-lysis, host cell membrane wall breaks open releasing many new phages.
How does the lysogenic cycle work
-attaches to bacterial surface receptor
-injects phage DNA
-Viral DNA integrates into bacterial chromosome, becoming a prophage
-Every time bacterium divides, prophage is copied
-No phages are produced, virus is dormant
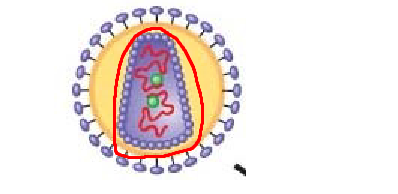
Two elements that nearly all animal viruses have
Envelope/outer membrane and glycoproteins
What is a retrovirus
RNA virus that uses reverse transcriptase to convert RNA to DNA
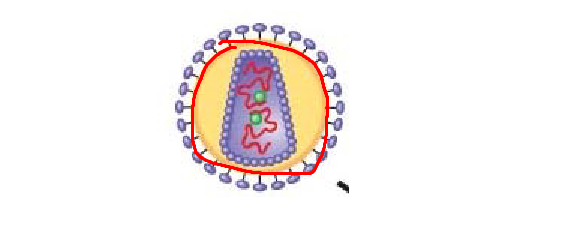
structure circled in red
HIV envelope
structure circled in red
HIV capsid
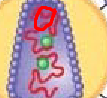
structure circled in red
RNA
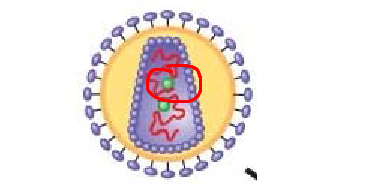
structure circled in red
reverse transcriptase
prophage vs provirus
prophage is a DNA integrated into bacterial chromosome
provirus is a viral DNA integrated into eukaryotic host chromosome
how does HIV work
HIV enters a helper T cell by fusing its envelope with the plasma membrane,
reverse-transcribes its RNA genome into DNA, integrates that DNA as a provirus into the host chromosome, uses the host to transcribe and translate viral RNA and proteins, assembles new virions, and buds from the cell with a host-derived envelope studded with viral glycoproteins
plasmids
small circular dsDNA molecules that replicate independently of main chromosome
Transposons
Segments of DNA that can move from one location to another within a cell genome (jumping gene)
Why do we recover completely from a cold but not from polio?
cold virus infects surface cells of upper respiratory tract, those cells divide and are easily replaced
polio infects and destroys motor neurons in spinal cord, cns neurons don’t regenerate
What tools are in the medical arsenal against human viral diseases?
vaccines train immune system
antiviral drugs stop steps in replication
public health- sanitation condoms masks
Emerging viruses such as HIV, Ebola, and SARS seem to burst upon the human scene. What
are three processes that contribute to this sudden emergence
-high mutation rates = more transmissible
-spread=travel lets viruses transmit easy
-transmission from animal to human
The current flu pandemic is H1N1. What does this name mean?
h1=hemagglutinin, helps attach virus to host cell
n1=neuraminidase, helps virus exit infected cell
horizontal transmission in plants
virus comes from outside plant (nearby infected plant, soil, sap)
Vertical transmission in plants
virus is inherited from parent
two ways viruses spread throughout plant bodies?
-Cell to cell through plasmodesmata
-systemic spread through vascular system,
What is a viroid? What important lesson do they teach?
Short circular ssRNA
highlights how RNA alone can be an infectious agent
Viroid disease example
potato spindle tuber viroid
what are prions
infectious misfolded protein that contains no DNA or RNA
how are prions transmitted
eating infected nervous tissue, contaminated surgical instruments, inherited
what do prions do
convert normal brain proteins into misfolded prion form, causing brain damage.
four diseases caused by prions
scrapie
mad cow disease
CJD
Kuru
Two alarming characteristics of prions
slow acting but always fatal
virtually indestructible
stage 1 origin of life
abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules
-simple molecules (amino acid nucleotide sugar) forms from lightning uv radiation volcanic activity
stage 2 origin of life
small organic molecules link together to form polymers such as proteins, rna, polysaccharides
stage 3 of life
Polymers become enclosed in lipid membranes or vesicles, forming protocells capable of maintaining internal environment
stage 4 origin of life
rna molecules can self replicate, allowing inheritance and evolution
what gas was missing from early earth mix
oxygen, earth had no plants to photosynthesize
how old is earth
4.6 bil years
oldest evidence of life
microorganism fossils 3.5 bil years ago
Oparin and Haldane hypothesized that early atmosphere was a reducing environment. What did they suggest as a source of energy for early organic synthesis
Lightning and UV radiation

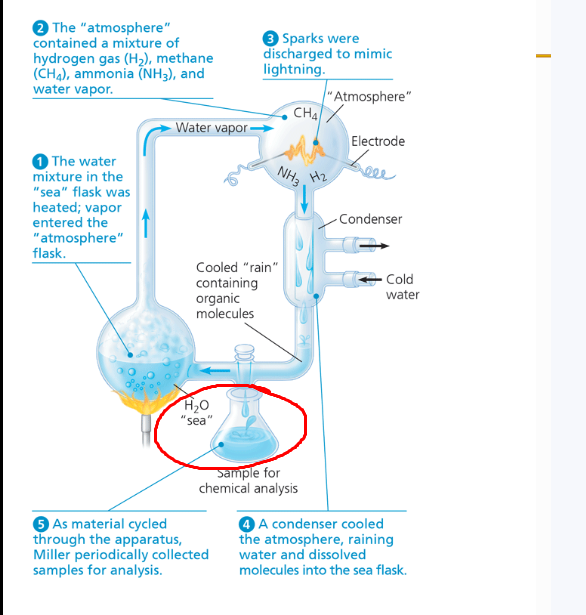
Identify process circled in red
Sparks to mimic lightning

Identify process circled in red
Water to mimic sea

Identify process circled in red
atmosphere containing mixture of h2 ch4 nh to mimic early earth atmosphere
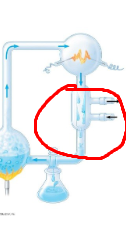
identify process circled in red
condenser, cooled atmosphere = raining water, dissolved molecules go into flask
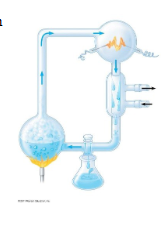
What was collected
organic molecules that are common in organisms
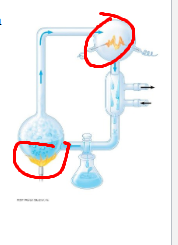
what are the two processes circled
heating and sparking to provide energy
what would happen if o2 was introduced
oxygen would oxidize and break down organic molecules before they can accumalate
List all molecules that appeared in the sample collection of Miller-Urey experiment
amino acids
simple organic acids
hydrocarbons
small organic molecules (aldehydes + hydrogen cyanide)
what did miller-urey experiment reveal
organic molecules can form spontaneously from inorganic molecules under conditions that simulate early earth
what was concluded from results of miller-urey
simple inorganic molecules can be converted into biologically important organic molecules in a reducing atmosphere
what does the miller-urey results imply about origins of life
life may have begun through natural and chemical processes on early earth
What other hypotheses explain abiotic organic synthesis besides Miller–Urey?
Volcanic atmosphere, hydrothermal vents, and meteorite delivery.
what are protocells
abiotically formed membrane bound droplets containing organic molecules and show properties of living cells.
what properties of life to protocells demonstrate
growth, reproduction, metabolism, selective permeability, compartmentalization (membrane boundary separating inside / outside environment)
What was most likely the first genetic material, DNA or RNA, why
RNA, rna can catalyze chemical reactions including making copies of itself, dna needs enzymes proteins etc to copy.
what are ribozymes
rna molecules that act like enzymes
Explain the evidence for an early “RNA world.
rna contains nucleotide sequences just like dna
how do tectonic plates move
heat from earth interior raises mantle, dragging plates above them
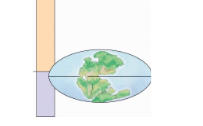
What continent / era
Pangea in the Paleozoic era