Edexcel Global Politics: Theories of Global Politics
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Global Governance
Attempts to bring government structures and authority to world politics in order to deal with common interests and challenges, such as climate change or terrorism
National Politics
- Government with clear mandate
- Clear national laws that apply to all citizens
- Laws are enforceable
Global Politics
- No single government with clear mandate
- Laws often only applies to states who have ratified
- International laws are hard to enforce
Realism
States are the most important and authoritative actors in global politics. Their primary goal is to protect their own national interests.
Liberalism
States' interests in global politics are linked and interdependent. They are best advanced through states working closely with each other and with non-state actors in order to achieve common political objectives.
Security Dilemma
Realist idea that as one state builds up its defences, others will respond by building up theirs. This increases tensions between the two states and can provoke conflict.
Anarchical Society
Realist idea from Hedley Bull. Global politics is in a state of disorder because there is no higher authority than nation states with the power to control global politics.
Society of States
Global politics is a system in which states attempt to establish order by forming alliances, creating international institutions and laws
(Realist Thinker) Kenneth Waltz
- Defensive realist
- Bipolarity is more stable than multipolarity
- Two major powers can negotiate their way to stability more easily than many powers
- The international system is in a state of anarchy
- There is no central authority above nation state level
Realist Thinker: Hedley Bull
- Anarchical Society
- Society of States operates in spite of anarchy
- Society of States is formed when states realise they have common interests and will benefit from working together
(Realist Thinker:) Hans Morgenthau
- Classical realist
- Human nature is naturally selfish and will always try to dominate others
- In global politics, moral considerations are less important than national interest
(Realist Thinker:) John Mearsheimer
- Offensive realist
- Conflict and competition between the great powers will continue
- States are trying to secure hegemony and want to dominate all other states within a region
Realism: Human Nature
- Naturally selfish and egotistical
- Human nature is fixed
- Motivated by desire to dominate others
- Motivated by need to survive
Liberalism: Human Nature
- Optimistic view
- Human nature is not fixed so states can improve and develop
- Committed to individual freedom
- Prefer to cooperate with others
- Conflict is avoided and is only a last resort
International Anarchy
Im a world system where there is no authority as legitimate, powerful or authoritative as nation states, nations frequently clash with each other.
Realism: likelihood of conflict
- Conflict is unavoidable
- Conflict is sometimes necessary to defend and increase national interest
- Defending national security is crucial. This is best achieved through well defended borders and clear & enforced laws
- Every state is potentially a threat to other states
Liberalism: likelihood of conflict
- Conflict is avoidable
- IGOs offer a forum for conflict resolution
- Economic interdependence reduces the likelihood of conflict
Realism: power
- Powerful states will always overcome weaker states
- Hard power is particularly important in the global self-help system
- The primary motivation of states is to gain power
Liberalism: power
- Military power is often counterproductive
- Economic interdependence is powerful, and makes the global system more stable
- Soft and Smart power are important means by which states can achieve their intended outcomes
- Hard power is only a last resort
(Liberal Thinker:) Robert Keohane
- Complex interdependence
- It is more rational and in states' interests to cooperate
- States are inherently egotistical
- International laws and Institutions can still be successful
(Liberal Thinker:) Francis Fukuyama
- Defeat of communist Soviet Union makes Liberal democracy the undisputed form of government
- 'End of History'
(Liberal Thinker:) Kenichi Ohmae
- Globalisation has brought about deep and revolutionary shifts that have dramatic implications for state sovereignty
- States are losing economic power
- States are no longer the main participants in the global economy
Complex Interdependence
States are inextricably linked
John Dalton's Billiard Ball Model
- Realist Model of global politics
- States are billiard balls that collide with each other
- Sovereignty is the hard impenetrable outer shell of the ball which enables it to withstand the impact of the collision.
- Not all balls are the same size, which is why international politics gives attention to the interests and behaviour of 'great powers'.
Cobweb Model
- Liberal Model of Global Politics
- A global web of relationships has created a situation of 'complex interdependence', in which state are forced to co-operate.
Realism: state sovereignty
- States = primary and most powerful actors in global politics
- Sovereignty is an absolute concept; it should not be violated unless a nation's national interest and security requires it
Liberalism: state sovereignty
- States are important actors within a complex web of interdependence with other states, IGOs and NGOs
- Pooling Sovereignty is the most effective use of sovereignty
- Another state's sovereignty may be infringed upon in order to uphold values of the international community (ie. Human Rights)
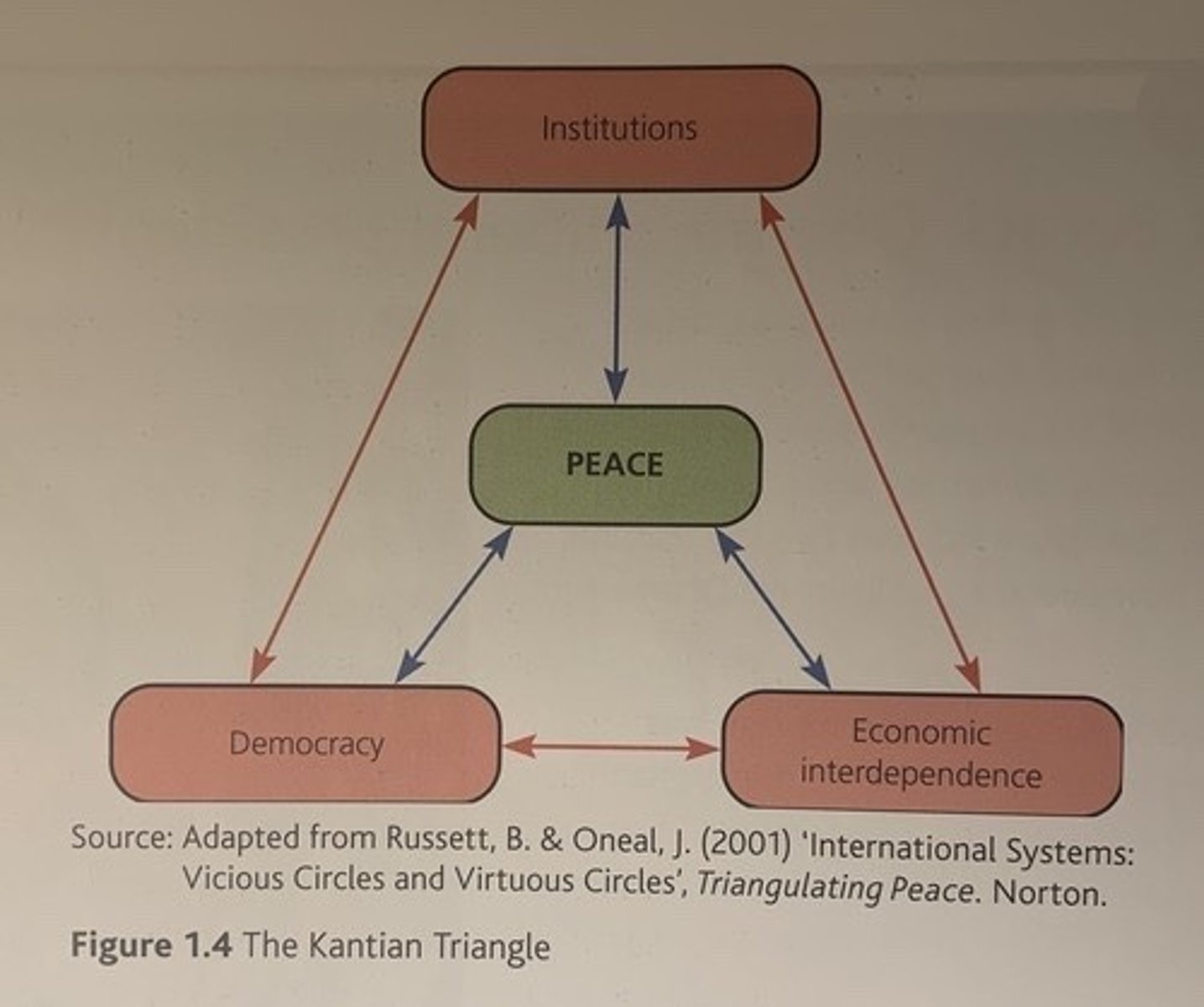
Kantian Triangle (Democratic Peace Theory)
- DEMOCRACY: Conflict between democratic states is very rare
- IGOs: Act as a powerful way to resolve disputes peacefully
- ECONOMIC INTERDEPENDENCE: Conflict would be mutually harmful, making it less likely
= PEACE
Realism: IGOs
- Tools for enhancing state power
- If they're only used to enhance national interest, they are not useful and can be dangerous
- States should be able to veto IGO decisions
Liberalism: IGOs
- Key part of world order
- Most powerful and authoritative source of international law
- Forums for discussions and negotiations
- Allow for the pooling of sovereignty
Ideology
Set of political ideas agreed by a group within society
Civilisation
Group of humans organised into a settled, urban and literate community with a shared culture
Huntington's 'Clash of Civilisations'
- C21st source of conflict is cultural
- Identified 9 major civilisations:
1. Western (Australasia, USA, W.Europe)
2. Orthodox (Russia, former USSR)
3. Islamic (N.Africa, Middle East)
4. African (Sub-Saharan Africa)
5. Latin America (Central & South America)
6. Sinic (China)
7. Hindu (India)
8. Japanese
9. Buddhist (Tibet, SE. Asia, Mongolia)
What couldn't be explained by realism
-decline of interstate conflict and rise of intrastate conflict
-rise in democracy
-growth of world trade
-growth of IGOs
Examples of realism
-Iraq War, 2003
-Chinese activity in South China sea
-Russian annexation of Crimea, 2014
Iraq War (2003)
The US invaded Iraq (2003) on the basis that Saddam Hussein had weapons of mass destruction (September Dossier), without UNSC approval. Hussein executed.
Why is the US invasion of Iraq an example of realism
- US did not have international support
- legality was highly questionable
- USA and allies acted in what they perceived to be their best interests
Chinese activity in South China Sea
Border conflict; nation states want the region as it has valuable materials. China has been increasing ports and naval patrols in area while US has carried out Freedom of Navigation patrols in 'international waters' which China claims as its own.
Why is the Chinese activity in the South China sea an example of realism
-states wish to gain / maintain control over key strategic regions
Russian Annexation of Crimea (2014)
Russian militia enter Crimea, which is declared independent. Ukraine split over West and East.
Why is the annexation of Crimea an example of realism
-Russia put military forces into Ukraine unilaterally
-Russia argued they were acting in their national interest
-The primary objective was to regain territorial control over Crimea
Implication of international anarchy
-IGOs are limited in impact and effectiveness as states determine success of international efforts
-international law is non-binding
-international courts can be ignored
Implications of international anarchy
-decreased impact and effectiveness of IGOS
-unbinding international law
-international courts may be ignored
Realism: superiority of states
-IGOs exist as they were created by states
-IGOs fail/succeed based on member-state actions
-States often act outside of IGOs
-free trade exists only as states agree to it
-states still have the ability to act unilaterally
Key Liberal Thinkers:
-Robert Keohane
-Francis Fukuyama
-Kenichi Ohmae
Key Realist Thinkers
- Hans Morgenthau
- Kenneth waltz
- Hedley Bull
- John Mearsheimer
Constraints on conflict
developed by immanuel kant (see kantian triangle)