[A-LEVEL MATHS] Set Notation
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
is an element of
∈
is not an element of
∉
is a subset of
⊆
is a proper subset of
⊂
the set with elements x₁, x₂, ...
{x₁, x₂, ...}
the set of all x such that ...
{ x : ...}
the number of elements in set A
n(A)
the empty set
∅
the universal set
ε
the complement of the set A
A′
the set of natural numbers, {1, 2, 3, ...}
ℕ
the set of integers, {0, ±1, ±2, ±3, ...}
ℤ
the set of positive integers, {1, 2, 3, ...}
ℤ+
the set of non-negative integers, {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
ℤ⁺₀
the set of real numbers
ℝ
ℚ
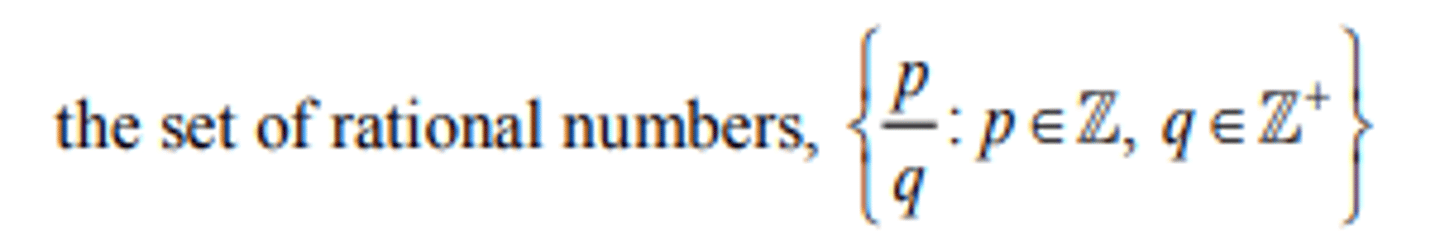
union
∪
intersection
∩
the ordered pair x, y
(x, y)
the closed interval {x ∈ ℝ: a ≤ x ≤ b}
[a, b]
the interval {x ∈ ℝ: a ≤ x < b}
[a, b)
the interval {{x ∈ ℝ: a < x ≤ b}
(a, b]
the open interval {x ∈ ℝ: a < x < b}
(a, b)
is proportional to
∝
p implies q (if p then q)
p⇒q
p is implied by q (if q then p)
p⇐q
p implies and is implied by q (p is equivalent to q)
p⇔ q
first term for an arithmetic or geometric sequence
a
last term for an arithmetic sequence
l
common difference for an arithmetic sequence
d
common ratio for a geometric sequence
r
sum to n terms of a sequence
Sₙ
sum to infinity of a sequence
S∞
a multiplied by b
a ⋅ b
a₁ + a₂ + ... + aₙ (definition)
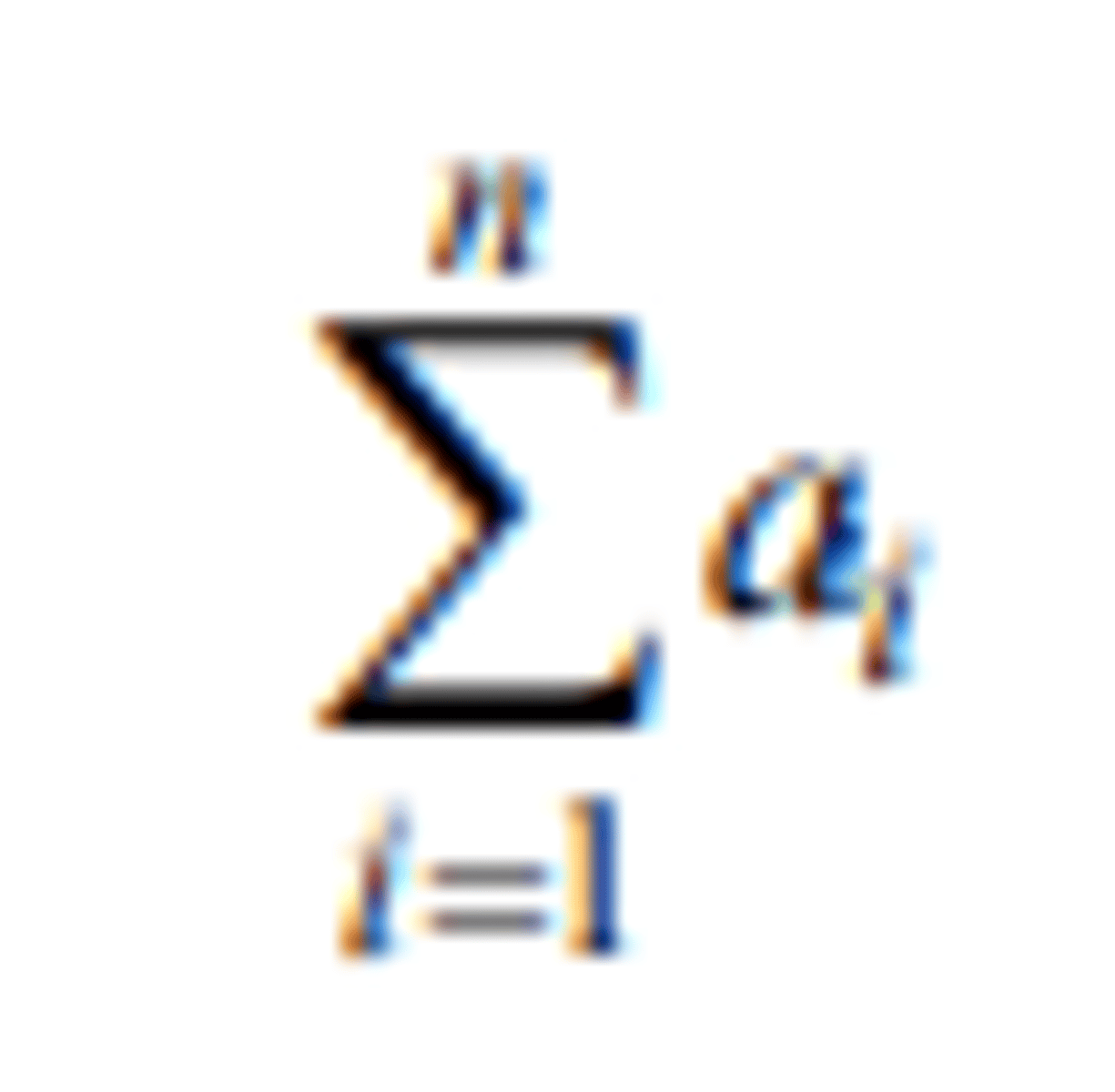
a₁ x a₂ x ... x aₙ (definition)
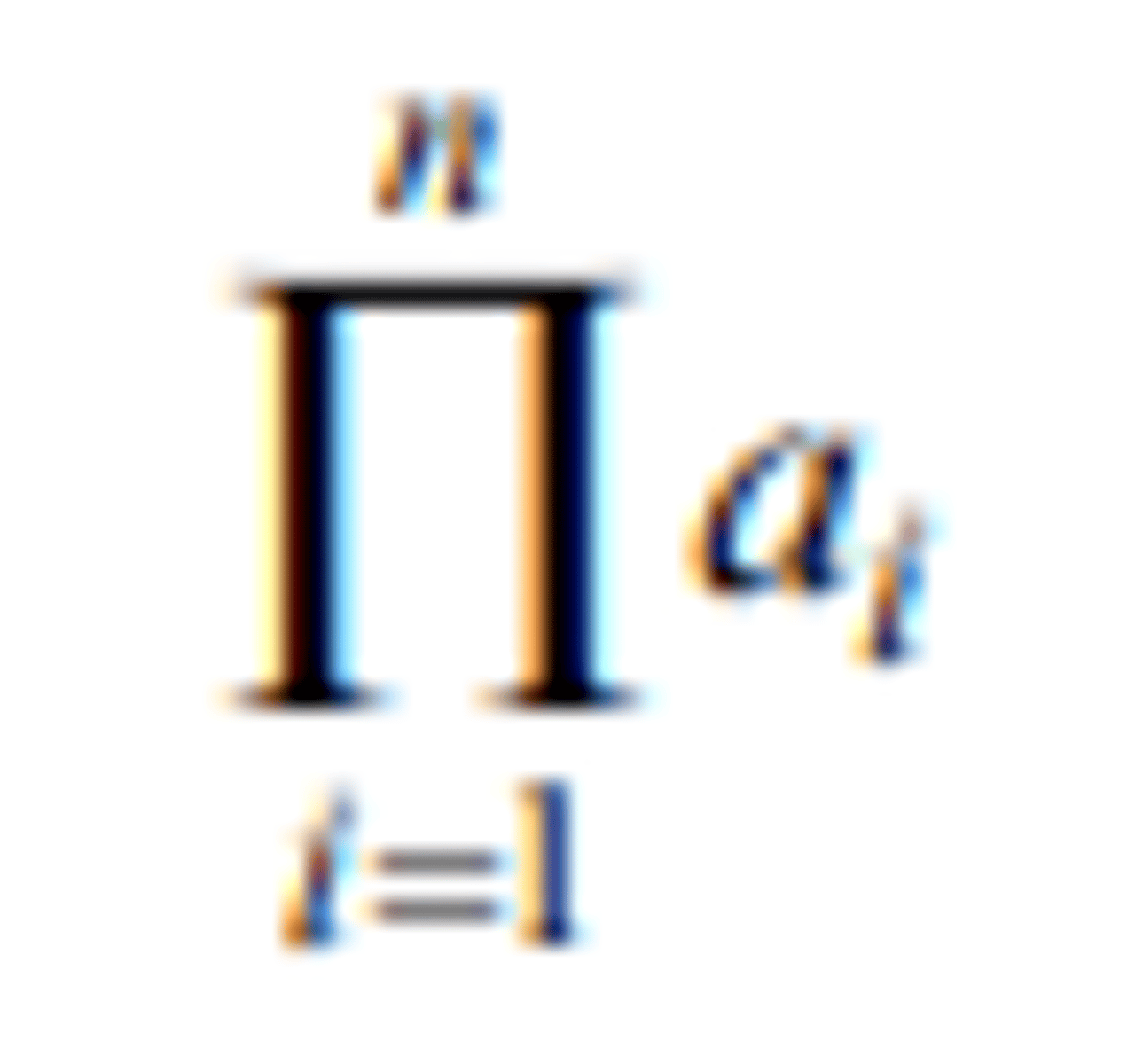
the modulus of a
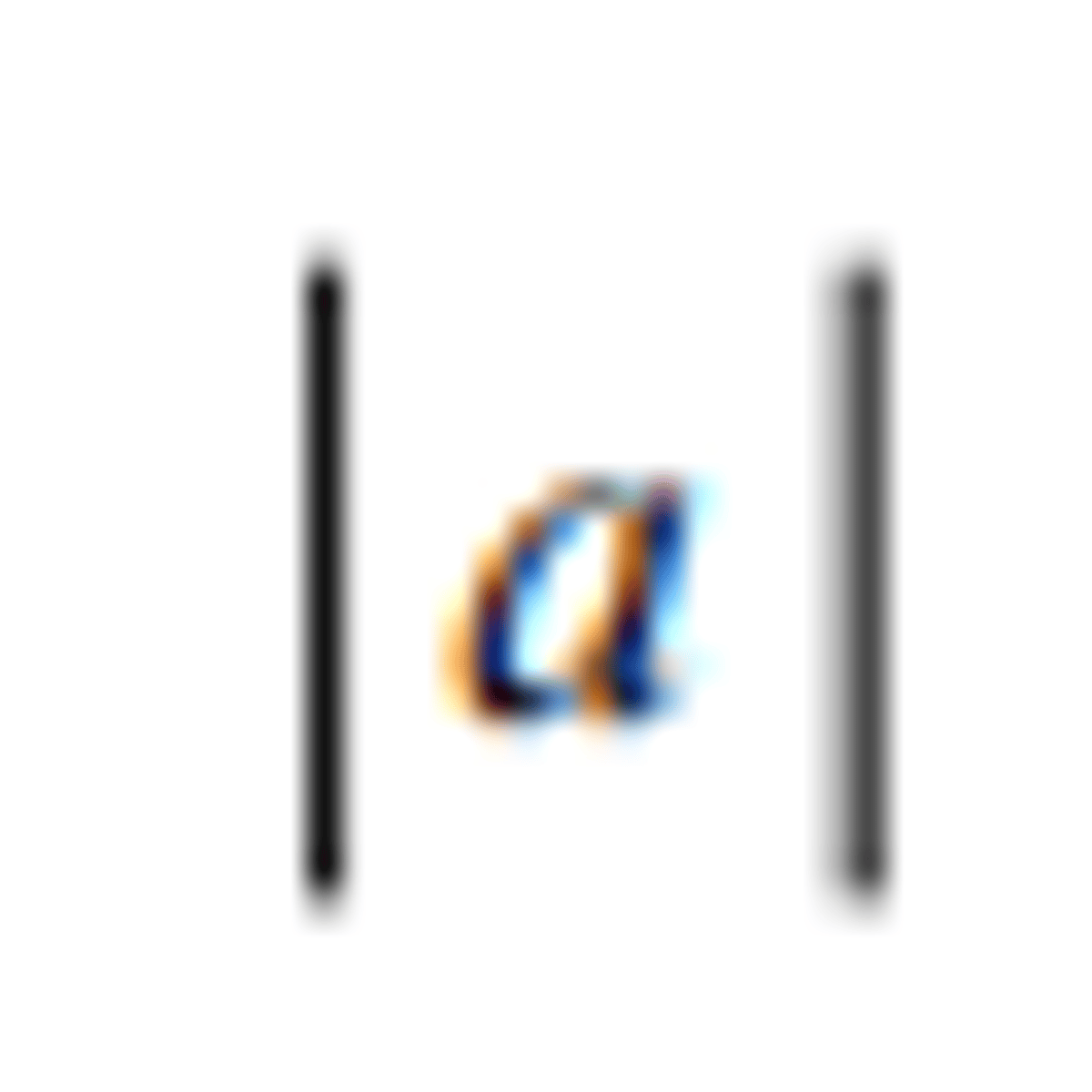
n factorial: n! = n × (n −1) × ...× 2 × 1, n∈ℕ; 0! = 1
n!
the value of the function f at 𝑥
f(𝑥)
the function f maps the element x to the element y
f : x|→y
the inverse function of the function f
f⁻¹
the composite function of f and g which is defined by
gf(𝑥) g(f(𝑥))
gf
the limit of f( ) x as x tends to a (def)
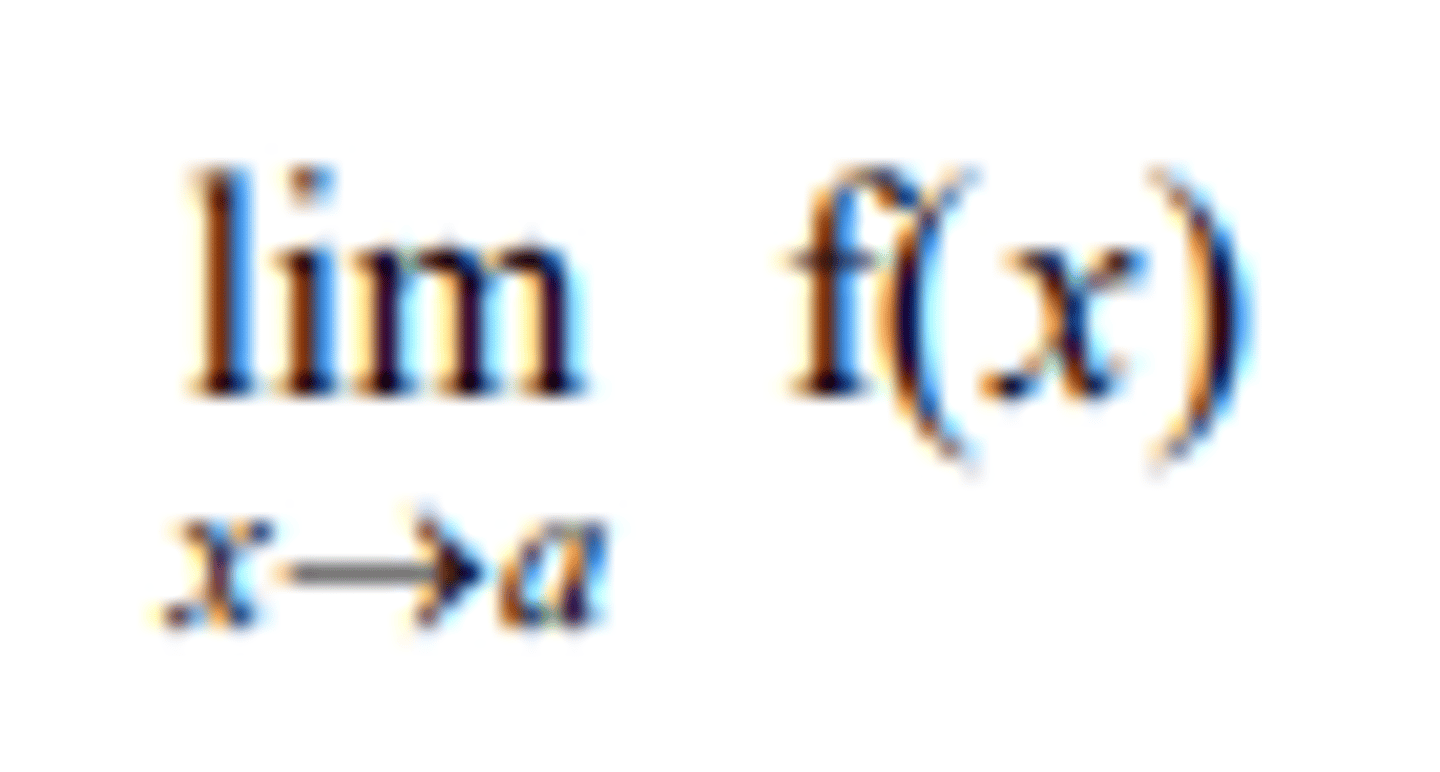
an increment of x
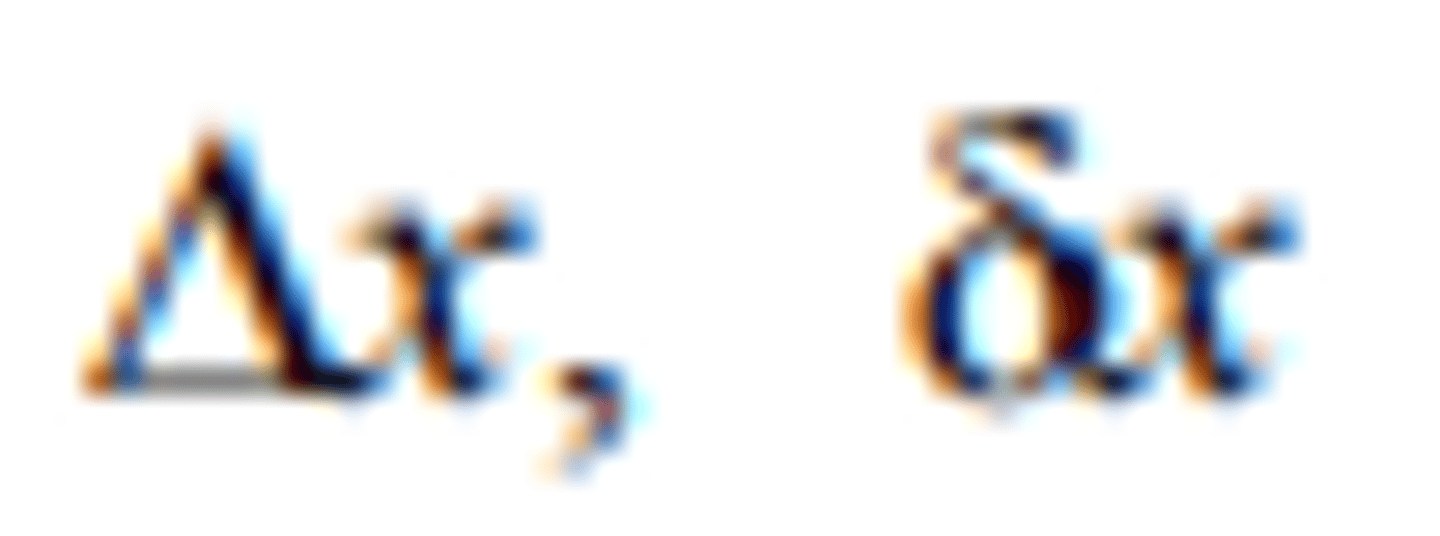
the nth derivative of y with respect to x
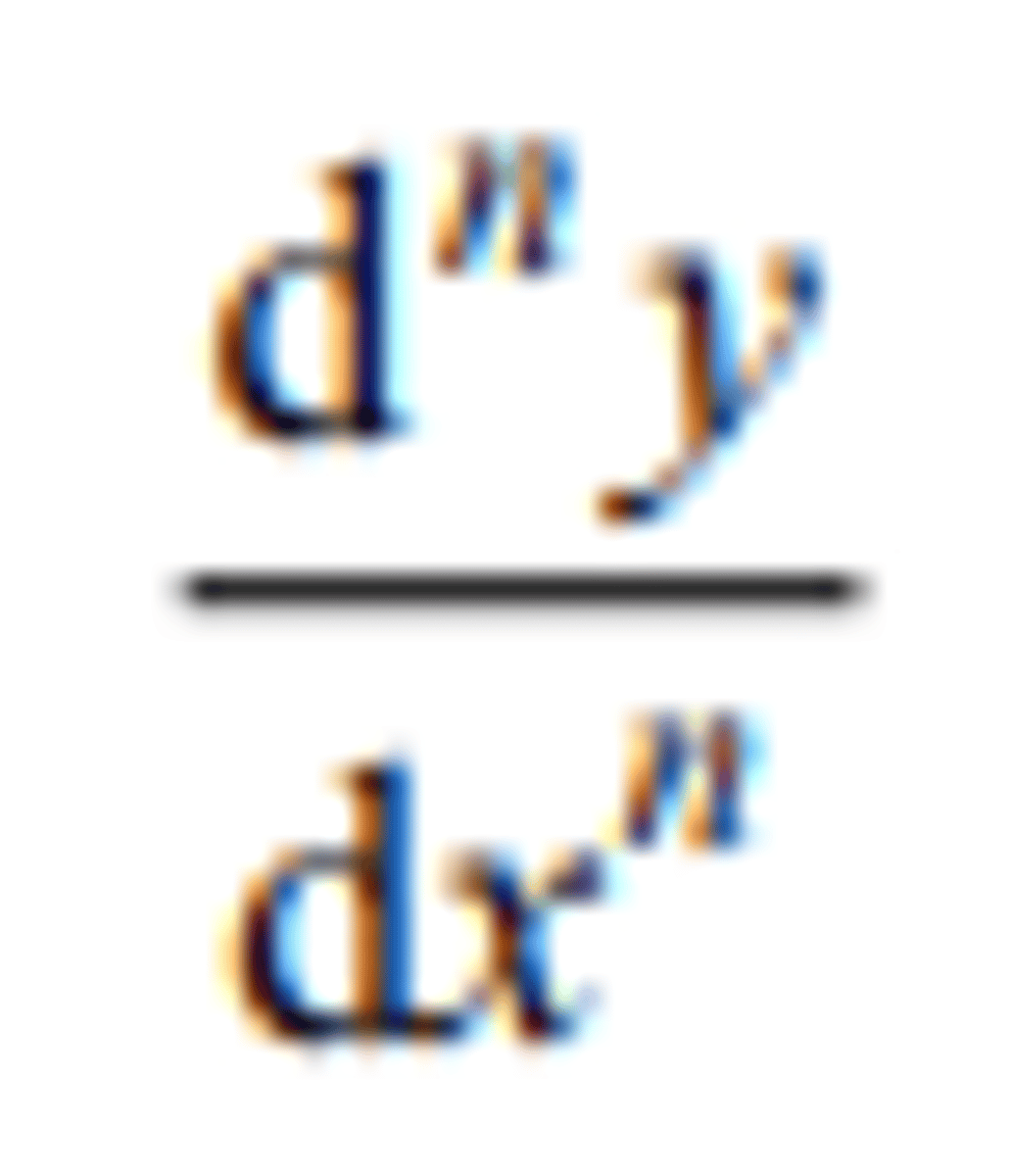
the first, second, ..., nth derivatives of f(𝑥) with
respect to x
f' (𝑥), fⁿ(𝑥), , f ⁽ⁿ⁾ (𝑥)
the first, second, ... derivatives of x with respect to t
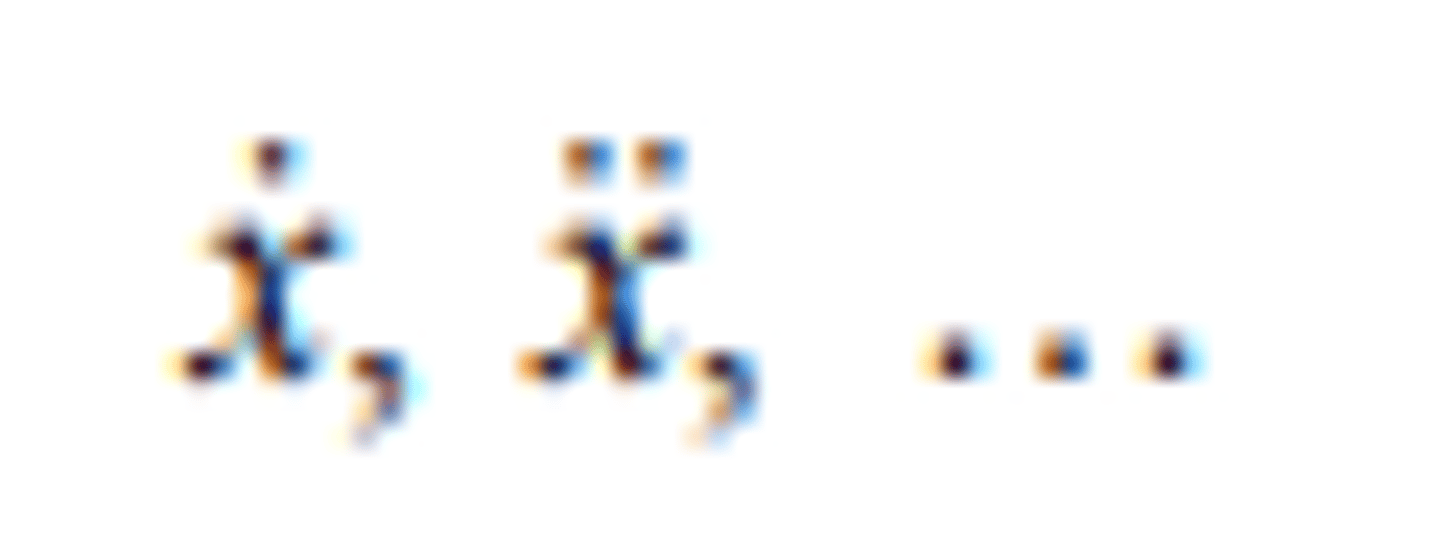
the indefinite integral of y with respect to x
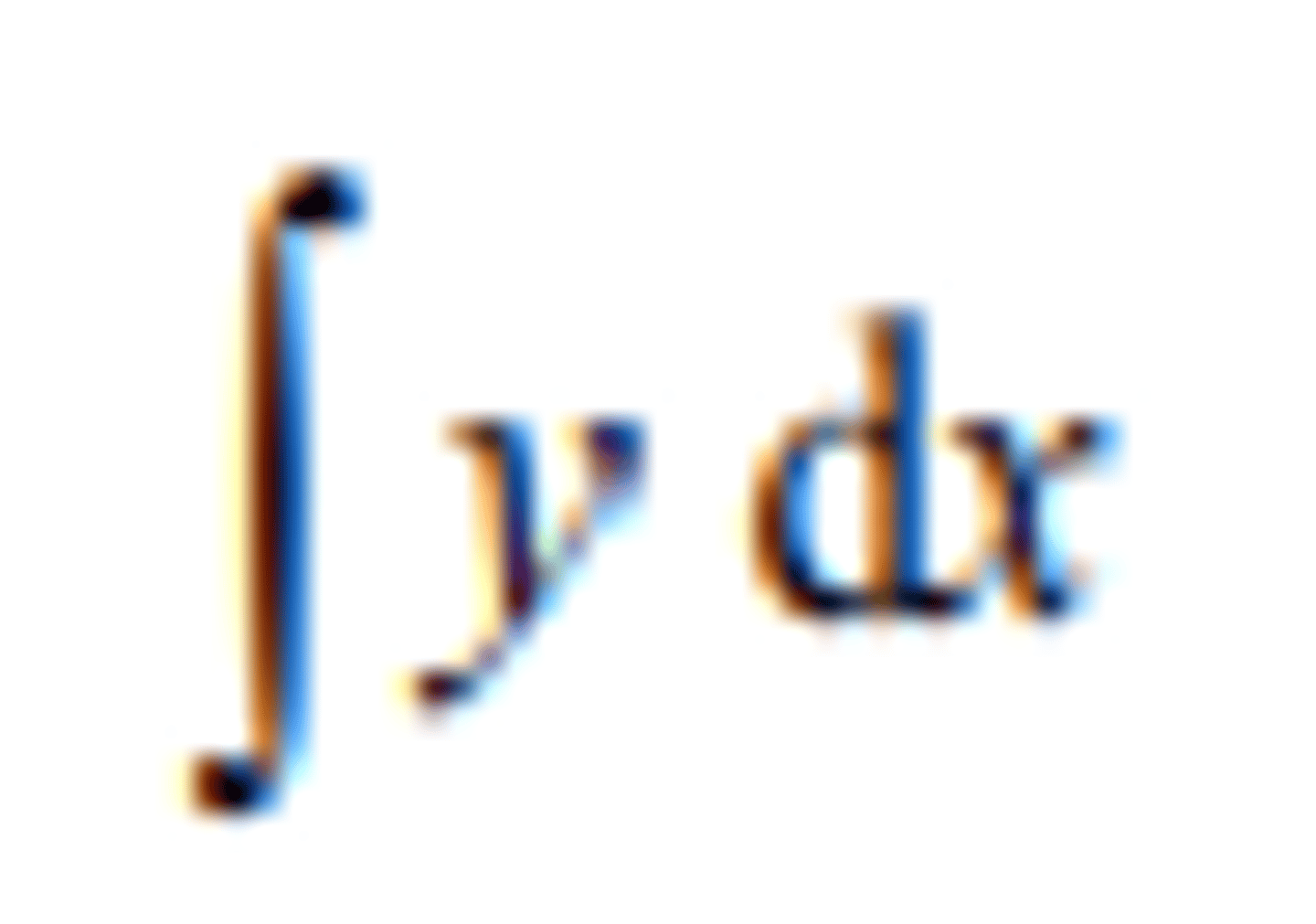
the definite integral of y with respect to x between the
limits x = a and x = b
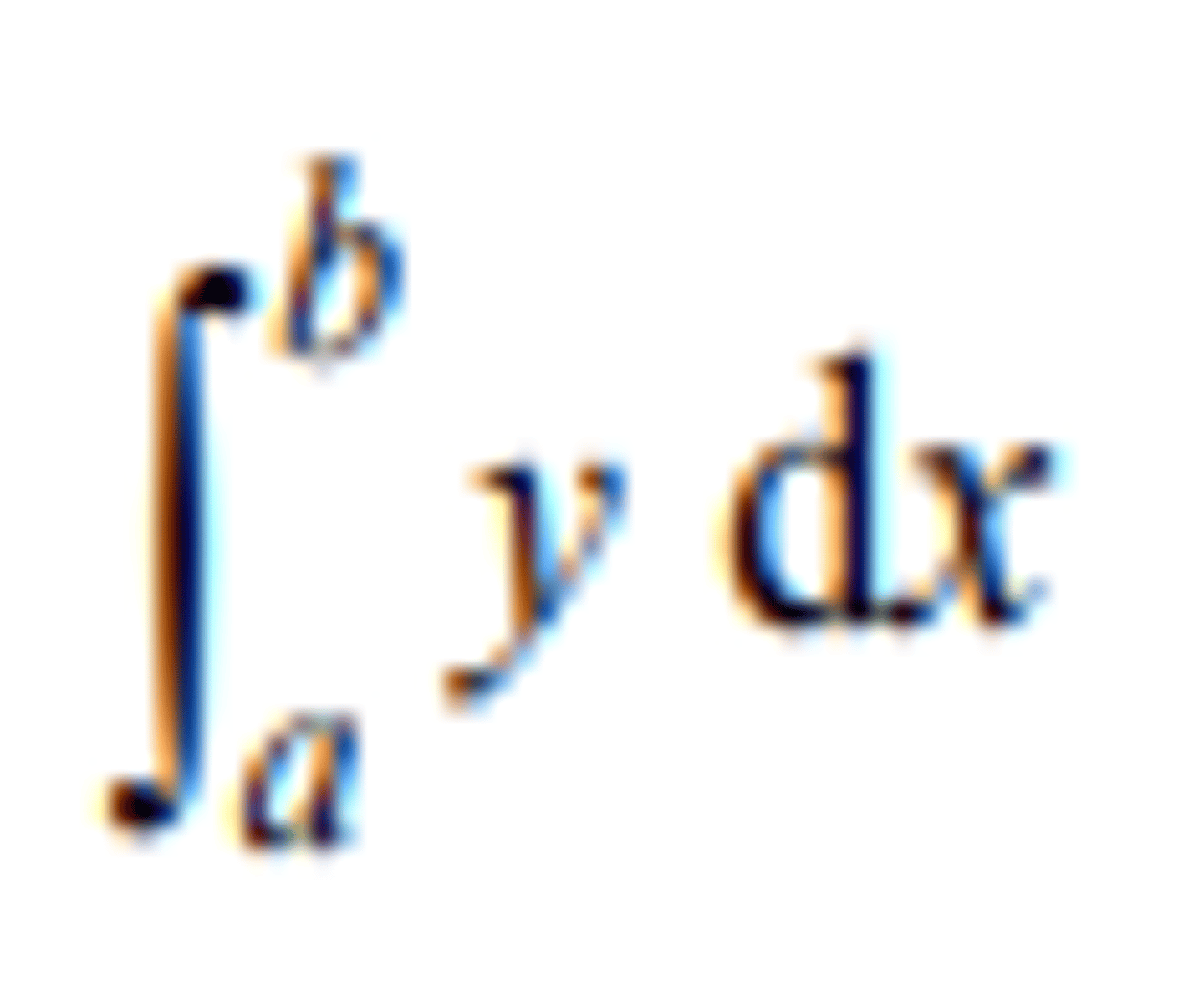
base of natural logarithms
e
exponential function of x
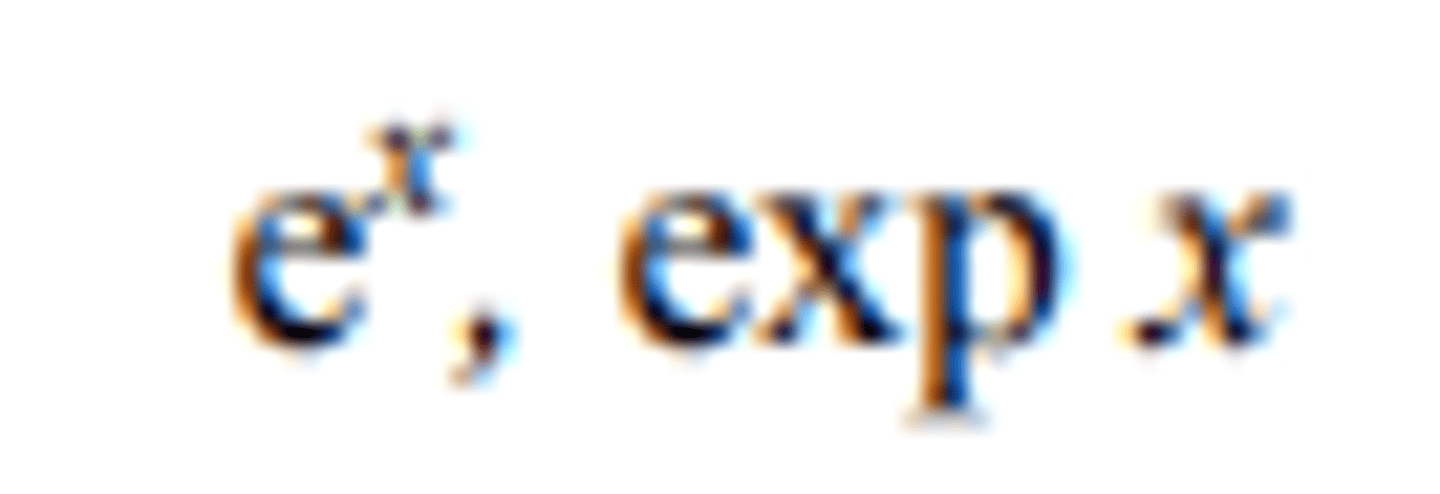
logarithm to the base a of x
logₐ x
natural logarithm of x
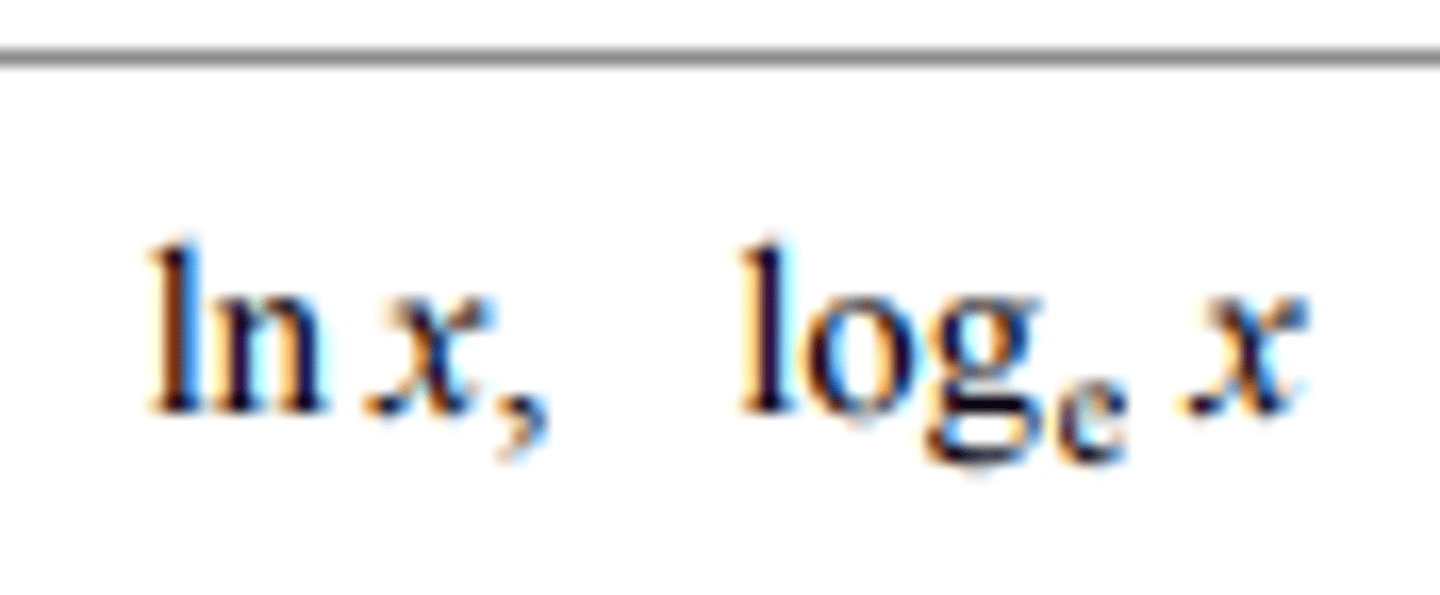
the trigonometric functions
sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, cot
the inverse trigonometric functions

radians
rad
the vector a
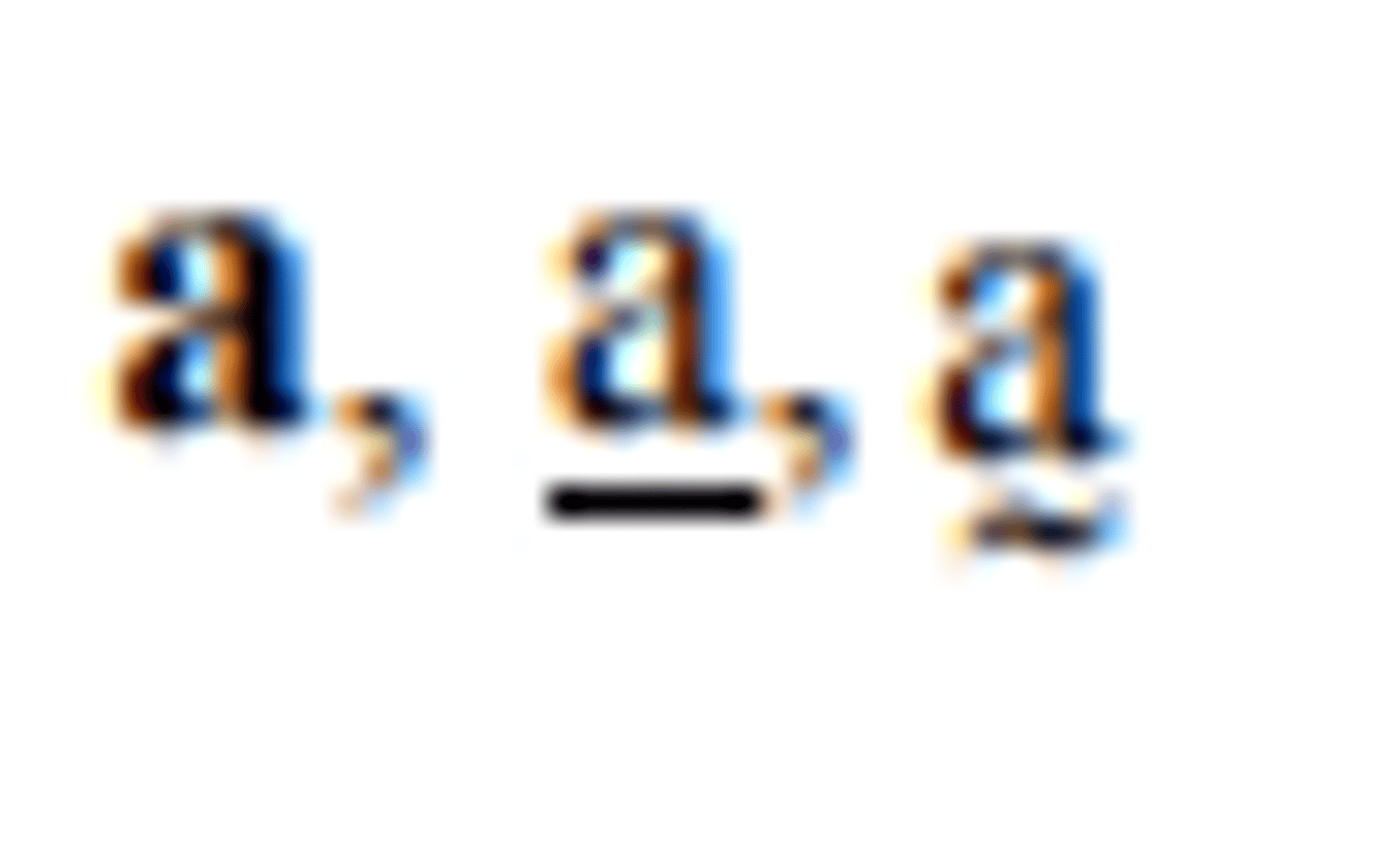
the vector represented in magnitude and direction by
the directed line segment AB
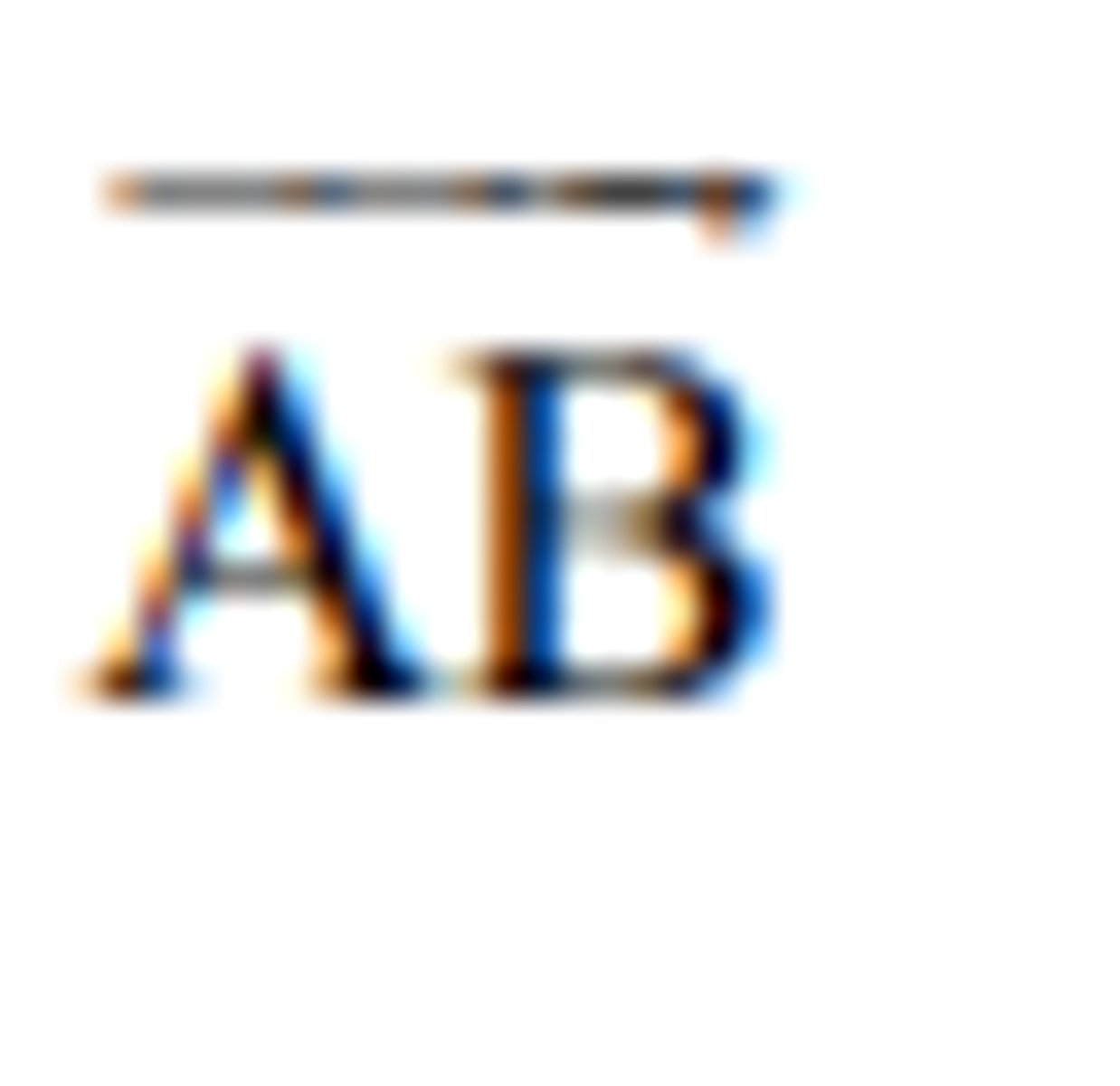
a unit vector in the direction of a
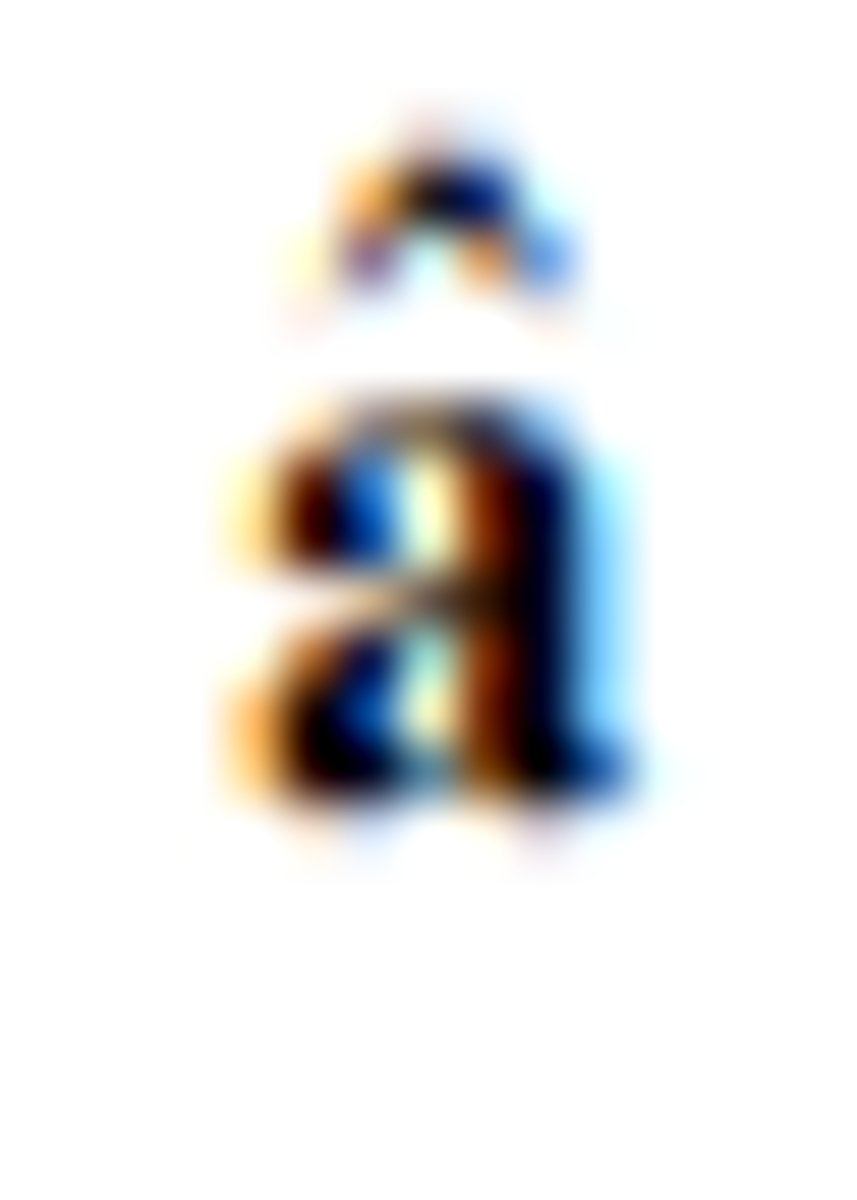
unit vectors in the directions of the cartesian
coordinate axes
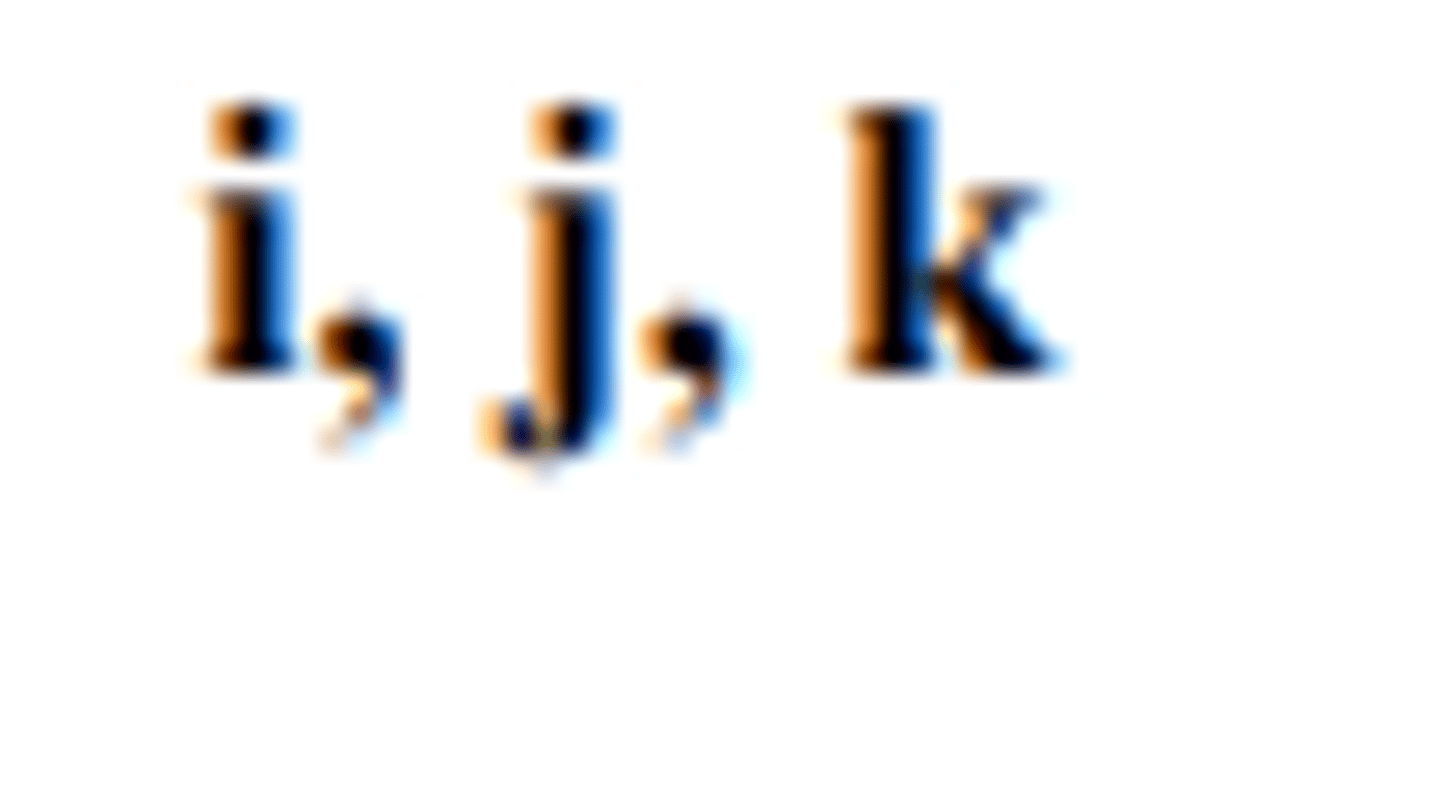
the magnitude of a
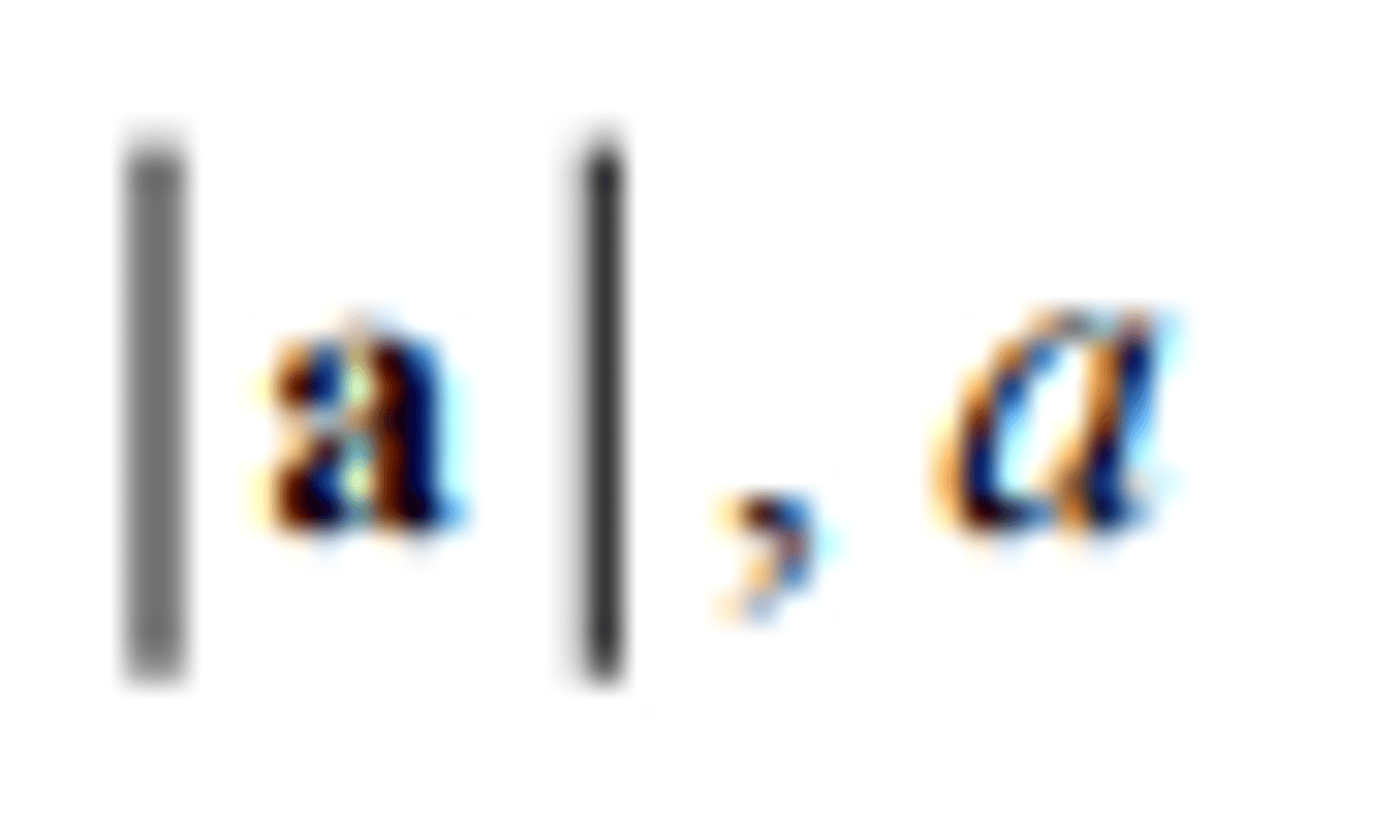
column vector and corresponding unit vector notation
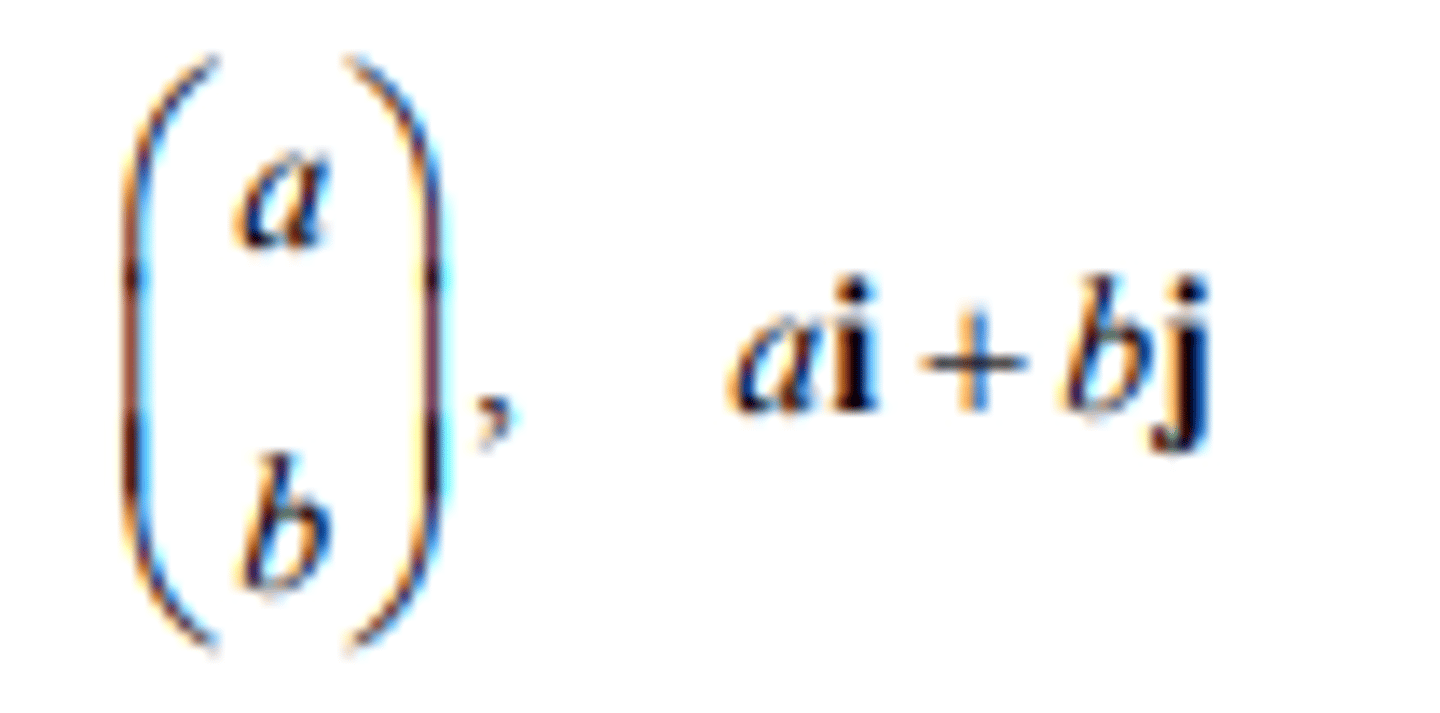
the magnitude of AB
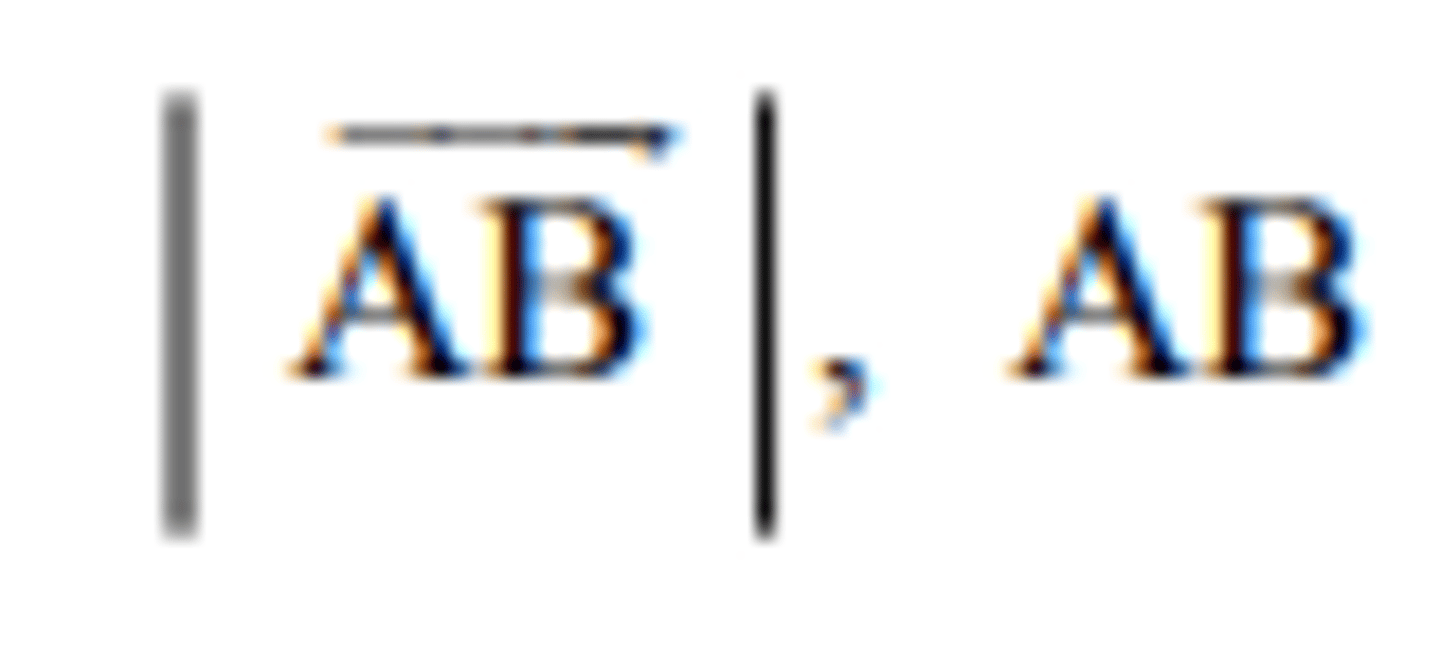
position vector
r
displacement vector
s
velocity vector
v
acceleration vector
a
events
A,B,C, etc
complement of the event A
A′
probability of the event A conditional on the
event B
P(A | B)
random variables
X, Y, R, etc.
values of the random variables X, Y, R etc.
x, y, r, etc.
observations
x₁, x₂, ...
frequencies with which the observations x₁, x₂, ...
occur
f₁, f₂, ...
probability function of the discrete random
variable X
p(x), P(X = x)
probabilities of the values x₁, x₂, ... of the discrete
random variable X
p₁, p₂, ...
expectation of the random variable X
E(X)
variance of the random variable X
Var(X)
has the distribution
~
binomial distribution with parameters n and p, where n
is the number of trials and p is the probability of
success in a trial
B(n,p)
q =1− p for binomial distribution
q
Normal distribution with mean µ and variance σ2
N(µ, σ²)
standard Normal distribution
Z ~ N(0,1)
probability density function of the standardised Normal
variable with distribution N(0, 1)
φ
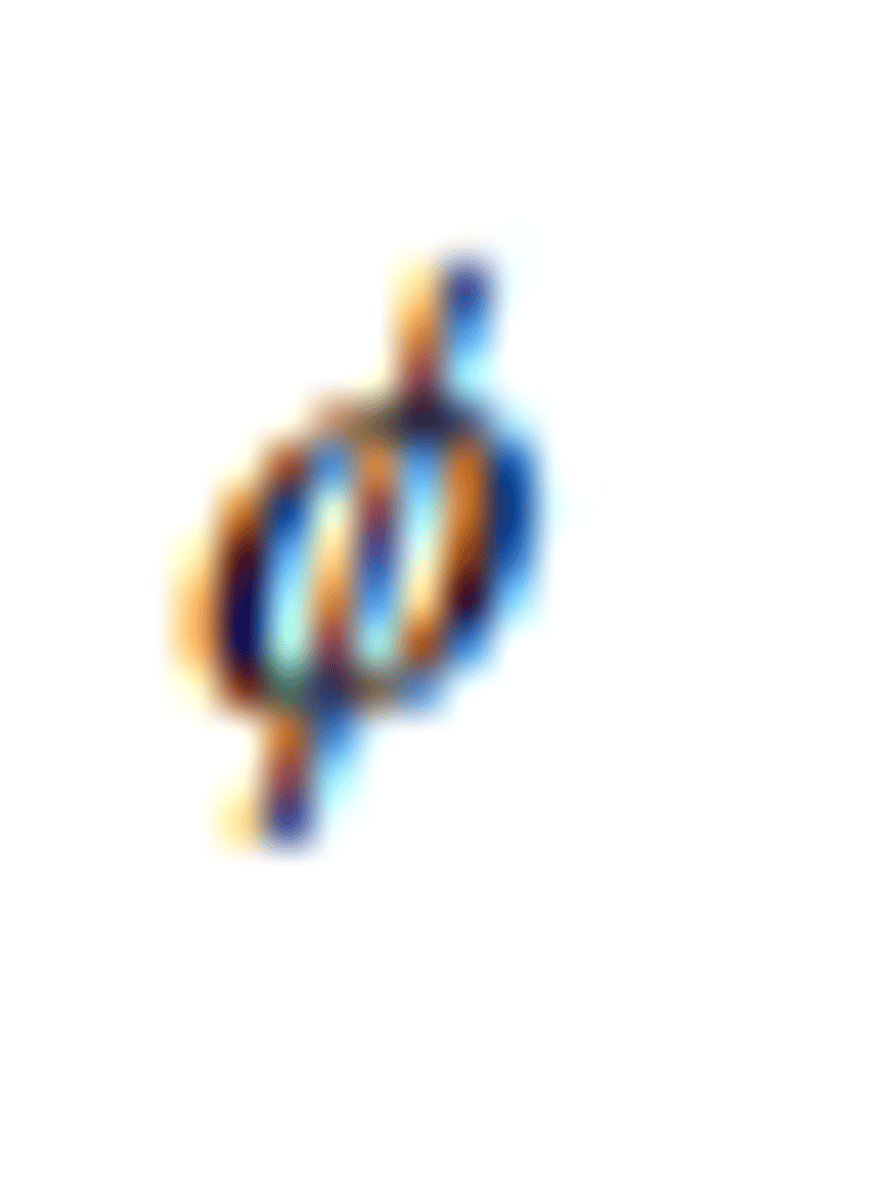
corresponding cumulative distribution function
Φ
population mean
µ
population variance
σ²
population standard deviation
σ
sample mean
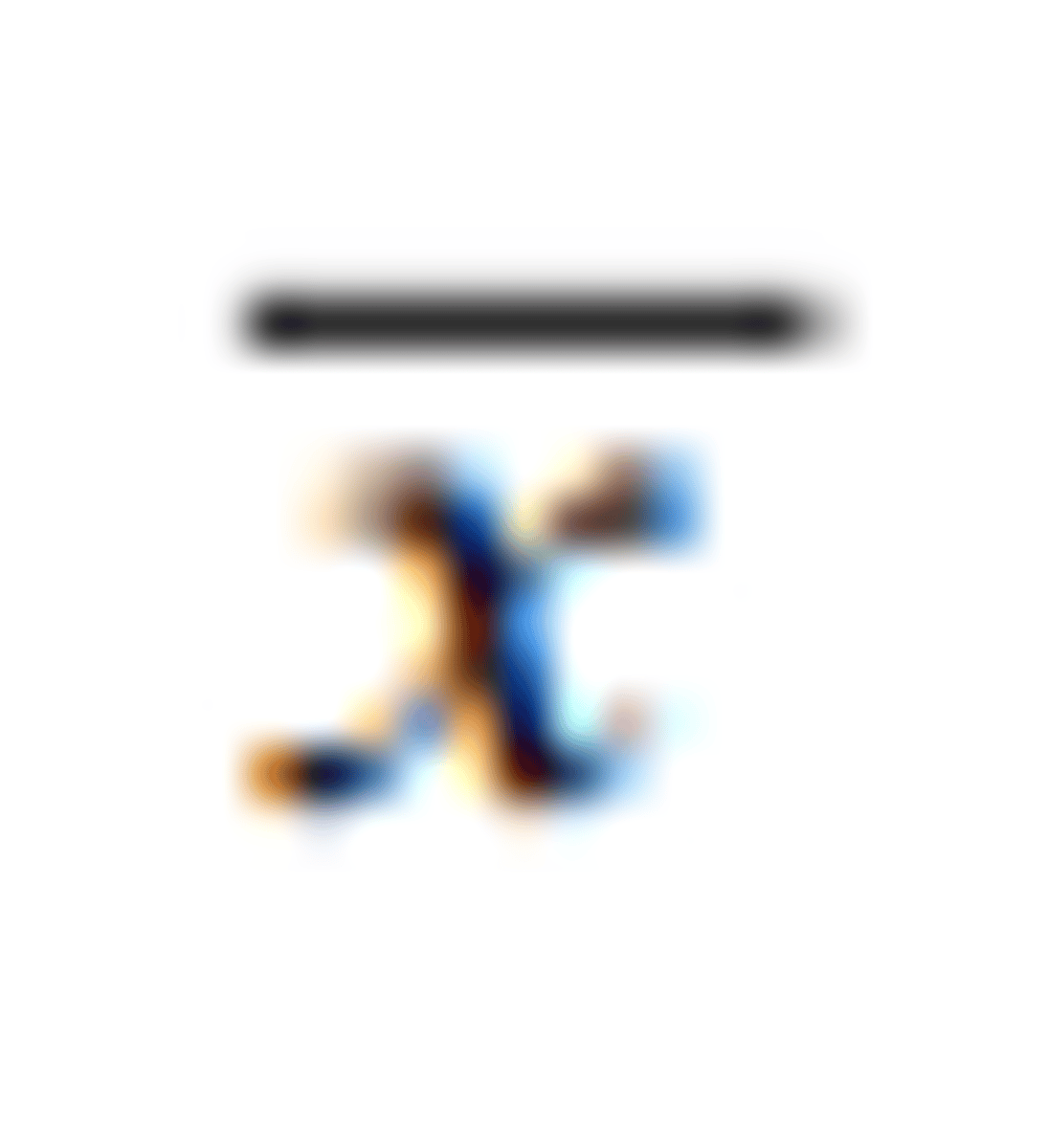
sample variance
s²
sample standard deviation
s
Null hypothesis
H₀
Alternative hypothesis
H₁
product moment correlation coefficient for a sample
r
product moment correlation coefficient for a population
ρ
coefficient of friction
µ