PULM 4: Eicosanoids
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
All eicosanoids are chemically diverse ________ derived from __________
autacoids (short-lived local hormones)
derived from arachidonic acid
eicosanoids are chemically diverse autocoids that allow for local communication and signaling acting in a _______ or _______ fashion by stimulating _____ receptors
paracrine or autocrine
g protein
what are the six different subtypes of eicosanoids?
prostaglandins (thromboxane, prostacyclin)
leukotrienes
lipoxins
hepoxolins
epoxyeicosatreionic acids
hydroxyperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids
Ecosanoids are synthesized from ____ carbon long ___________ ______ ________ (__________)
you can get ecosanoids in ur diet from _____ and _______
which organ systems are ecosanoids essential for?
20 carbon PolyUnsaturated Fatty Acids
plants and fish
cardiovascular, reproductive, and inflammation
Biochemical Effects of Exosanoids:
________, __________, ____________
_______ heart rate
vision
increase/decrease in
neuronal ________ ______
_____ _______
______ ________
gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, glycogenolysis
increased
increased/decreased
electrical activity
muscle contraction
blood pressure
arachidonic aids are synthesized from ______ _____
they are esterified to membrane phospholipipids such as __________ , __________, and ___________
rate limiting step: their release from membrane using __________ which can be secretory or cytosolic
release is stimulated by _______ and _______ ________
inhibited by ___________
linoleic acid
phosphatidylCHOLINE
phosphatidylETHANOLAMINE
phosphatidylLINOSITOL
'
cytokines and growth factors
lipocortins
what allows for the release of membrane bound archadonic acids that are esterified to membrane phospholipids?
what inhibits this release?
phospholipase A2 (stimulated by cytokines and growth factors)
lipocortins
once a stimulus such as a growth factor or cytokine binds to the receptor arachidonic acid is released from
phosphatidyl choline using ____________
OR
phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate using ___________ which turns it into __________ which is then converted to ___________ _______ and ________________ which can further be converted to arachidonic acid
released from phosphatidylcholine using phopholipase A2
released from phosphatidylbiphosphate using phospholipase C turning it into 1,2 diacylclycerol which is turned into arachadonoc acid and monoacylglycerol using diacylglycewrol lipase which is further broken down into arachidonic acid using monoacylglycerol lipase
What are three examples of prostanoids?
prostaglandins
prostacyclin
thromboxane
Prostanoids:
modulators of ________ ______ activity
controls _______ _________ and inhibits the effect of _________-______ hormone
plays a role in
_________ responses
________
pregnancy (dont take NSAIDs!)
which organ systems?
adenyl cyclase activity
control platelet agression
inhibit anti-diuretic
inflammatory
pain
cardiovascular and renal
Prostanoids (thromboxane, prostaglandin, prostacyclin) play a significant in modulating adenylate cyclase activity which includes…
renal and cardiovascular system
inhibit anti-dieruretic
control platelet aggression
inflammation
pain
pregnancy
how are prostanoids synthesized?
cyclooxygenase pathways
what are the three COX enzymes involved in the sythesis of prostanoids? what is the significance of each?
COX1 = housekeeping (maintain homeostasis)
COX 2= pain receptor
is COX 1 or COX 2 consituitive?
(expressed regardless of external stimulus)
COX1 - required for housekeeping - constitutive
COX2- mostly induced by pain but IS constitutive in parts of the Nervous System
COX 1 vs COX 2
where is each enzyme located in terms of tissues?
1= ubiquitous expression (found almost everywhere)
2= found in tissues that are under stress (inflamed and activated tissues)
COX 1 vs COX 2
where are the enzymes located within cells?
1= endoplasmic reticulum
2= endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear membrane (so if you stain for COX 2 you will find that both the ER and nuclear membrane will have color)
COX 1 vs COX 2: Substrate Selectivity
which substrates bind to COX 1?
which substrates bind to COX 2?
Cox 1 = arachidonic acid and eicosatetraenoic acids
Cox 2 = arachadinoic acid, eicosatetraenoic acids AND y-linolenate, a-linolenate, linolenate
COX 1 vs COX 2: Substrate Selectivity:
what typically happens when arachadoic acid or eicosatetrenoic acid binds to COX 1 enzyme?
what happens when aracadoic acid, eicosaterenoic acid, a-, g-linolenate bind to COX 2?
cox 1 = protection/maintenance
cox 2= proinflamatory and mitogenic functions
how are COX 1 enzymes induced?
they don’t have to be INDUCED they are naturally expressed EVERYWHERE (ubiquitously)
how are COX 2 enzymes induced?
Liposacharides (LPS)
TNF-a (tumor necrosis factor)
Interleukin 1 (IL-1)
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
IFN-y (interferon- family of cytokines)
what inhibits COX 1 enzyme from maintaining homeostasis?
NSAIDS
what inhibits COX2 enzymes from creating proinflammatory and mitogenic responses ?
NSAIDS
Acetaminophen (is a costrubstate that INDIRECTLY inhibits ecosanoids from binding to COX2)
antiinflammatory glucocorticoids
IL4, 10 (downregulate macrophages), 13
cox2 selective inhibitors
which interleukins INHIBIT COX 2?
which interleukins INDUCE COX 2?
what about COX 1?
IL-4, 10, 13inhibit COX 2
IL-1 and IL-2 induce COX2
COX 1 is only inhibited by NSAIDS and is not induced by interleukins
Prostanoid Synthesis:
arachidonic acid that is esterified to phospholipid on membrane is released by __________
the arachidonic acid is then converted to ________ using ___________ also known as __________ (CYCLOOXYGENASE REACTION)
_______ —→ ________ (PEROXIDASE REACTION) THIS IS THE PRECURSOR TO ALL PROSTOGLANDINS
phospholipase A2
arachadoic acid —> PGG2 (cyclooxygenase 1 and 2— PGH2 synthases)
PGG2—> PGH2 (cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 — PGH2 synthases)
what is the precursor to all prostaglandins?
how do we get there from arachidonic acid?
PGH2
aracadoic acid is esterified to phospolipid on membrane and detached by phospholipase A2
CYCLOOXYGENASE REACTION;
arachidonic acid is converted to PGG2 using cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (PGH2 synthase)
PEROXIDASE REACTION:
PGG2 —> PGH2 using cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (PGH2 synthase)
how do you get from PGH2 to
PGF2a
PGD2
PGE2
PGI2
TXA2
PGF synthase
PGD synthase
PGE synthase
Prostacyclin Synthase
thromboxane synthase
which prostanoids can you make from PGH2?
which enzyme doesnt have the most straightforward name?
PGD2
PDE (found in macrophages)
PGF2a
PDI2
thromboxane A2 (TXA2) - found in blood vessels
to make PDI2 from PHH2 you use prostacyclin synthase but for the rest of them its their name-synthase
Prostaglandins:
all have ________ ring
letter code is based on ring modifications such as ______ and ______ groups (F, D, I, E)
the subscript refers to the number of _______ ______in the two side chains (F2a, D2, I2)
cyclopentane
ketone hydroxy
double bonds
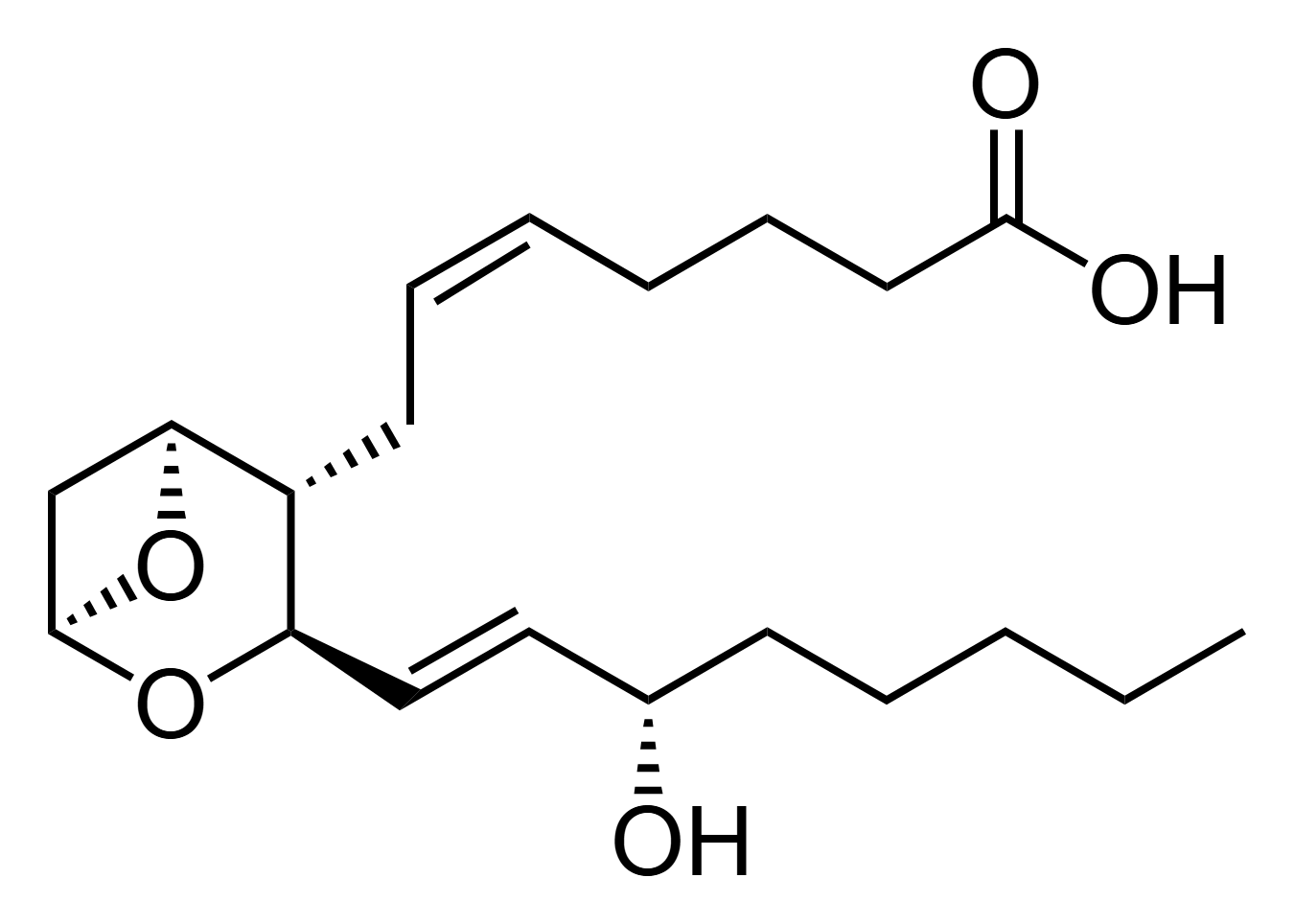
which prostanoid is shown
thromboxane A2
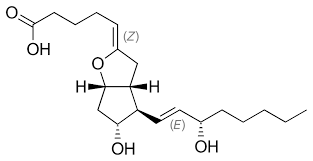
which prostanoid is shown?
prostacyclin (PGI2)
Prostanoid Receptors:
where are they located
the specificity of their receptor (what binds to them) is determined by _____ _________ and _______ on different cells
all prostanoids are _________ coupled
there are multiple isoforms of receptors identified due to ________ ______ _________ (ex. EP3= 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, e, f)
cell membrane
receptor density and type
g-protein coupled
differential mRNA splicing
which prostanoid is the precursor to all other prostaglandins?
prostaglandin H2
which prostoglandin when bound to g-coupled receptor leads to
broncoconstriction
sleep control
inhibits platelett agression
Prostaglandin D2
*sounds like a man that has a D
sleeps, agression, bronco
which prostoglandin when bound to g-coupled receptor leads to
vasodilation
bronchodilation
hyperalgesia (more responsive to pain)
fever
diuresis (excess urine)
immunomodulation
Prostaglandin E2 (just like IgE during allergic reaction)
which prostaglandin when bound to g-coupled receptor leads to
smooth muscle contraction
bronchocontriction
abortion (allow to give birth)
Prostoglandin F2a
think female—abortion, smooth muscle contraction, also a broncoconstrictor with the male
which prostaglandin when bound to g-coupled receptor leads to
vasoconstriction
control of vascular tone
platelet activation
thromboxane
you want to make a clot so you would wanna restrict the blood vessel first and then begin activating the platelets which is controlling the vascular tone
which prostaglandin when bound to g-coupled receptor leads to
vasodilation
control of vascular tone
platelet aggregation inhibition
Prostaglandin I2 = prostacyclin
I2 is thromboxanes OP - does complete oposite, does NOT want aggregation to prevent embolism so will dilate blood vessel which is vascular tone control
which prostaglandin has both anti-inflammatory AND inflammatory responses?
what happens once it binds to receptor?
Prostaglandin E2
bronchodilation
vasodilation
hyperalgesia
fever
diuresis (excessive pee)
immunomodulation
Prostanoid Inactivation:
what is the half-life or prostanoids and where are they usually found?
seconds to minutes
lungs and liver
how are prostanoids excreted once they are inactivated?
excreted through urine
What are the five different ways that prostanoids can be inactivated?
hydroxylation by 15-a-hydroxy prostaglandin hydroxylase (PGH) followed by reduction by 13 prostaglandin reductase
oxidation of hydroxy group at C15 to keto group
reduction of C13 and C14 to dihydroxy derivatives
B-oxidation - resulting in the loss of 2 carbons
w-hydroxylation to dicarboxylic acid derivatives
Prostanoid Inactivation:
___________by 15-a-hydroxy PGH followed by ________ by 13-PG reductase
oxidation of hydroxy group at carbon 15 to ______ group
reduction of C13 and C14 to _______ derivatives
____-_______ resulting in loss of 2 carbons
w-hydroxylation to ______________ ____ derivatives
hydroxylation followed by reduction
hydroxy→keto at 13th carbon
dihydroxy
b-oxidation
dicarboxylic acid
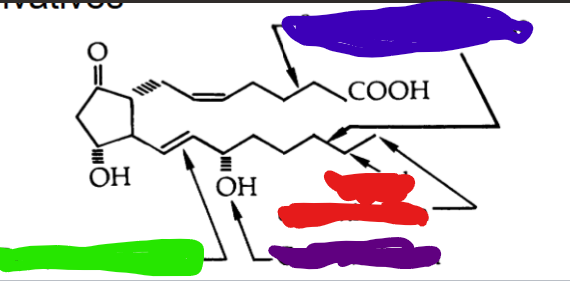
Prostanoid Inactivation:
hydroxylation by 15-a-hydroxy prostaglandin hydroxylase (PGH) followed by reduction by 13 prostaglandin reductase
oxidation of hydroxy group at C15 to keto group
reduction of C13 and C14 to dihydroxy derivatives
B-oxidation - resulting in the loss of 2 carbons
w-hydroxylation to dicarboxylic acid derivatives
COLOR CODE THE WHERE THE FOLLOWING INACTIVATION ROUTES WOULD OCCUR
blue= beta oxidation (loss of 2 carbons)
green= reduction of C13 and C14 to dihydroxy
red= w-hydroxylation
purple = C15 oxidation to keto
Leukotrienes:
produced by _________
100-10000 more potent than ______ in causing __________
component of slow reacting substance of ______ ( )
produced via ________ pathway
leukocytes
histamines bronchoCONSTRICTION
anaphylaxis (SRS-A)
5-lipoxegenase
Leukotriene Synthesis:
arachadoic acid is released from esterified lipoprotein from membrane using _________
Arachadoic acid is then converted to ________ using ___________
which is then converted to __________ using ________
which is then converted to PARENT leukotriene (_____) using ______
Once the parent compound _______ the cell it is able to convert into different leukotrienes
you can use ________ to convert the parent compound into _________ by removing ______
you can further convert it using _________ which removes a ________ turning it into
phospholipase 2
5-HPETE using 5-lipoxygenase
LTA4 using 5-lipoxygenase
LTC4 using LTC4 synthase
LEAVES
gamma glutamyl transferase turn LTC4 into LTD4 by removing glutamate
LTE4 using dipeptidase by removing glycine
SEQ Leukotriene Synthesis
arachadonic acid is released from esterified phospholipid in membrane using phospholipase A2
arachadonic acid converted to 5-HPETE using 5- lipoxygenase
then converted to LTA4 using 5-lipoxxygenase
then converted to parent compound LTC4 using LTC4 synthase
LEAVING cell glutamate can be released by gamma glutamyl transferase leaving LTD4
further remove glycine using dipeptidase turning LTD4 —> LTE4
which prostoglandins are most likely to bind to the DP1 receptor found in
platelets
vascular smooth muscle
nervous tissue
retina
lung
uterus
stomach
small intestines
illum
macrophages
D
E2
F2a
I2 and TXA2
which prostoglandins are most likely to bind to the DP2 receptor found in
esinophils
basiphils
T helper cells
macrophages
D
E2 and F2a
I2 and TXA2
which prostoglandins are most likely to bind to the EP1 receptor found in
kidney
lung
spleen
skeletal muscle
testis
uterus
E2
F2a and I2
D2 and TXA2
which prostaglandins are most likely to bind to the EP2 receptor found in
lung
placenta
heart
macrophages
bone marrow
E2
F2a and I2
D2 and TXA2
which prostaglandins are most likely to bind to the EP3 receptor found in
kidney
stomach
uterus
pancreas
adrenal
testis
ovary
small intestine
brain
spleen
colon
heart
liver
skeletal muscle
lung
thymus
ileum
E2
F2a and I2
D2 and TXA
which prostaglandins are most likely to bind to the EP4 receptor found in
small intestine
lung
thymus
kidney
uterus
pancreas
spleen
heart
stomach
brain
ileum
PBMC
macrophages
E2
F2a and I2
D2 and TXA
which prostaglandins are most likely to bind to the FP receptor found in
corpus luteum (f for female!)
uterus
stomach
kidney
liver
heart
lung
eye
liver
F2a
D2
E2
I2 and TXA2
which prostaglandins are most likely to bind to the IP receptor found in
platelets
vascular smooth muscle
kidney
thymus
liver
lung
spleen
kidney
heart
uterus
I2
D2
E2 and F2a
TXA2
which prostaglandins are most likely to bind to the TP receptor found in
platelets
vascular smooth muscle
thymus
spleen
lung
kidney
heart
uterus
TXA2 and H2 (parent compound need thromboxane synthase to get)
D2, E2, F2a, I2
mostly thromboxane and H2 but fair game for anyone else
Leukotriene Singnalling:
Which leukotrienes are signal to Gai/aq proteins?
which leukotrienes signal Gaq/Ga11?
Gai/aq = BLT1, BLT2, GPR17
Gaq/Ga11= CysLTR1, CysLTR2, and CysLTRE (GPR99)
which receptors signal Gai/Gaq subunits?
what effect does leukotriene binding to these receptors have?
BLT1
BLT2
GPR17
decreased cAMP and increased Ca2+
which receptors signal Gaq/Ga11 subunits?
what effect does leukotriene binding to these receptors have?
CysLTR1
CysLTR2
CysLTRE (GPR99)
activation of PLC = increased DAG and IP3
which leukotriene binds to BLT 1?
which G protein is signaled?
what effect does this have?
B4
Gai/Gq
decreased cAMP and increased Ca2+
which leukotriene binds to BLT 2?
which G protein is signaled?
what effect does this have?
B4, 12(S)HETE, 12(S)HPETE
Gai/Gaq
decreased cAMP and increased Ca2+
which leukotriene binds to GPR17?
which G protein is signaled?
what effect does this have?
C4 more than D4
Gai/Gaq
decreased cAMP and increased Ca2+
which leukotriene binds to CysLTR1?
which G protein is signaled?
what effect does this have?
D4>C4>E4
Gaq/Ga11
increase PLC, DAG, and IP3
which leukotriene binds to CysLTR2?
which G protein is signaled?
what effect does this have?
C4 > D4 >E4
Gaq/Ga11
increased PLC, DAG, IP3
which leukotriene binds to CysLTRE?
which G protein is signaled?
what effect does this have?
E4> D4> C4
Gaq/ Ga11
increased PLC, DAG, IP3
which leukotriene gives rise to all other leukotrienes?
A4
which leukotriene allows for
neutrophil activation
chemotatic
plasma exudation (plasma filled with proteins rushes to scene)
B4
which leukotriene allows for
bronchoconstriction
vasoconstriction
decreased coronary blood flow
decreased cardiac contractility
plasma exudation
promote endothelial and mesangial cell proliferation
activation of transcription factors
cytokine release
C4 and D4
which leukotriene allows for
mucin release
this leukotriene can cause issues in _____ patients who already deal with an array of secretions
E4
issue in asthma patients
which leukotriene
releases Ca2+ stores
promotes cell proliferation
HETEs
Leukotrienes are metabolized in the _______ and excreted in the ________
metabolized in liver
excreted in urine
Leukotriene Inactivation:
LTE4 —→ __________ using ____________
—> _________ using _____________
—> _________using __________________
LTE4—> 20-COOH-LTE4 (acylcoA oxidase) —>
18-COOH-dinor-LTE4 (hydratase/dehydrogenase) → 16-COOH-tetranor-LTE3 (B-oxidation 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase) —→ 14-COOH-hexanor-LTE4 (B-oxidation by CoA thiolase)
What are the five structures in order of leukotriene inactivation?
LTE4
20-COOH- LTE4
18-COOH-dinor- LTE4
16-COOH- tetranor - LTE3
14- COOH -hexanor- LTE4
what are the five enzymes in order in leukotriene inactivation?
w- oxidation by acyl-coa oxidase
b-oxidation by hydratase/dehydrogenase
b-oxidation 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase
b-oxidation by CoA Thiolase
Are lipoxins antiinflammatory or proinfllamtory?
anti-inflammatory
lipoxins are produced via -___ alone or a compination of ___-____ pathway + ___-___ followed by conversion by __________
platelets convert LTA4 via ___-____ pathway
are lipoxins short-lived or long-lived?
either 5 LOX alone or 15LOX and 5 LOX followed by conversion by hydrolase
platelets convert LTA4 via 12-LOX pathway
short lived
Lipoxins:
Neutrophils convert Arachadoic acid into _____ using _________ enzyme which the platelets will convert to ______ or ________ using ______
Epithelial cells convert arachidonic acid into __________ using the ______ enzyme which neutrophils will convert to _____ or _______ using _________
In Epithelial Cells 15 LOX coverts Arachadoic Acid into __________ which is converted to ____ or ______ using neutrophilic ________
Arachidonic Acid —> LTA4 (5 LOX in neutrophil)—> LXA4 or LXB4 (12-LOX in platelets)
Arachidonic Acid —>15-H (p) -ETE (15 LOX in epithelial cells)—> LXA4 and LXB4 (5-LOX in neutrophil)
Arachidonic Acid—> 15R-H(p)-ETE (COX-2/ASA in epithelial/endothelial cells) —> 15-epi-LXA4 or 15-epi-LXB4 (5 LOX in neutrophil)
Lipoxin Functions:
act as negative/positive regulators of inflammation and leukotriene actions
which type of G protein is stimulated upon binding?
where are they found?
negative regulators
Gai
neutrophil
monocytes
T cells
Lung
spleen
blood vessels
Gi protein coupled receptor
Lipoxin Functions:
inhibit neutrophil __________, _________, ____________
inhibit eosinophil ______________________
stimulate ____________by stimulating production of ______ and ________
inhibit LTC4 and LTD4 stimulated ______________
inhibit _______ stimulated inflammatory effects
inhibit function of _____ cells and ___ cell secretion
chemotaxis, adhesion, transmigration
recruitment
STIMULATE vasodilation by stimulating PGI2 and PGE2
vasoconstriction (cause vasodilation)
LTB4
NK cells and T cell secretion
what is inhibited vs stimulated by lipotoxin?
Inhibited:
neutrophil
eosinophil
LTC4 and LTD4
LTB4
NK cell and T cell secretion
Stimulate:
PGI2 and PGE2 vasodilation
How does lipoxin mediate the resolution of inflammatory response?
stimulates _____ and ___________ of apoptotic _________ and ___________
increases ____-______ activation of monocyte
uptake and clearance neutrophils and macrophages
non-phlogistic (removal of dying cells)
Which eicosanoids play a role in asthma?
LTC4
D4
E4
Which eicosanoids play a role in inflammatory bowel disease?
LTB4
Which eicosanoids play a role in glomerulophritis?
LTB4
C4
D4
Which eicosanoids play a role in cancer?
COX2
PGE2
Which eicosanoids play a role in cardiovascular disease?
TxA2 mediated in thrombosis
Myocardial Infarction
Leukotriene Production
Which eicosanoids play a role in inflammation?
Leukotrienes
PGE2
LXA2
TxA2
PGI2
PGD2
involved in vasodilation, edema, chemotaxis, pain, vascular permeability, fever
Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EETs):
produced via _________
act as paracrine factors regulating ______ ______ and _____-___________
can act as ________ to increase/decrease blood pressure
cytochrome P450 epoxygenase
local vascular tone and anti-inflammation
vasodilators
where are Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EETs) located?
cardiovascular endothelium (lower blood pressure)
ascending loop of henle
vascular endothelium of kidney
brain astrocytes
airway and parenchymal lung tissue
ANY TISSUES LACKING CYCLOXEGENASE AND LIPOXYGENASE
Epoxyeicosatrataenoic Acids are found in any tissues that lack _________ and _________ as they are produced via ______________________
found in tissues that lack CYP450 epoxygenase
epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EETs)
which LOX enzyme is found in the
epithelial cells
neutrophils
platelets
for the
15-LOX
5-LOX
12-LOX