Cells - Basic Units of the Body
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for cell biology review, focusing on vocabulary terms and definitions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Cell
Basic unit of structure and function in the body.
Differentiated Cells
Cells that have developed specialized characteristics.
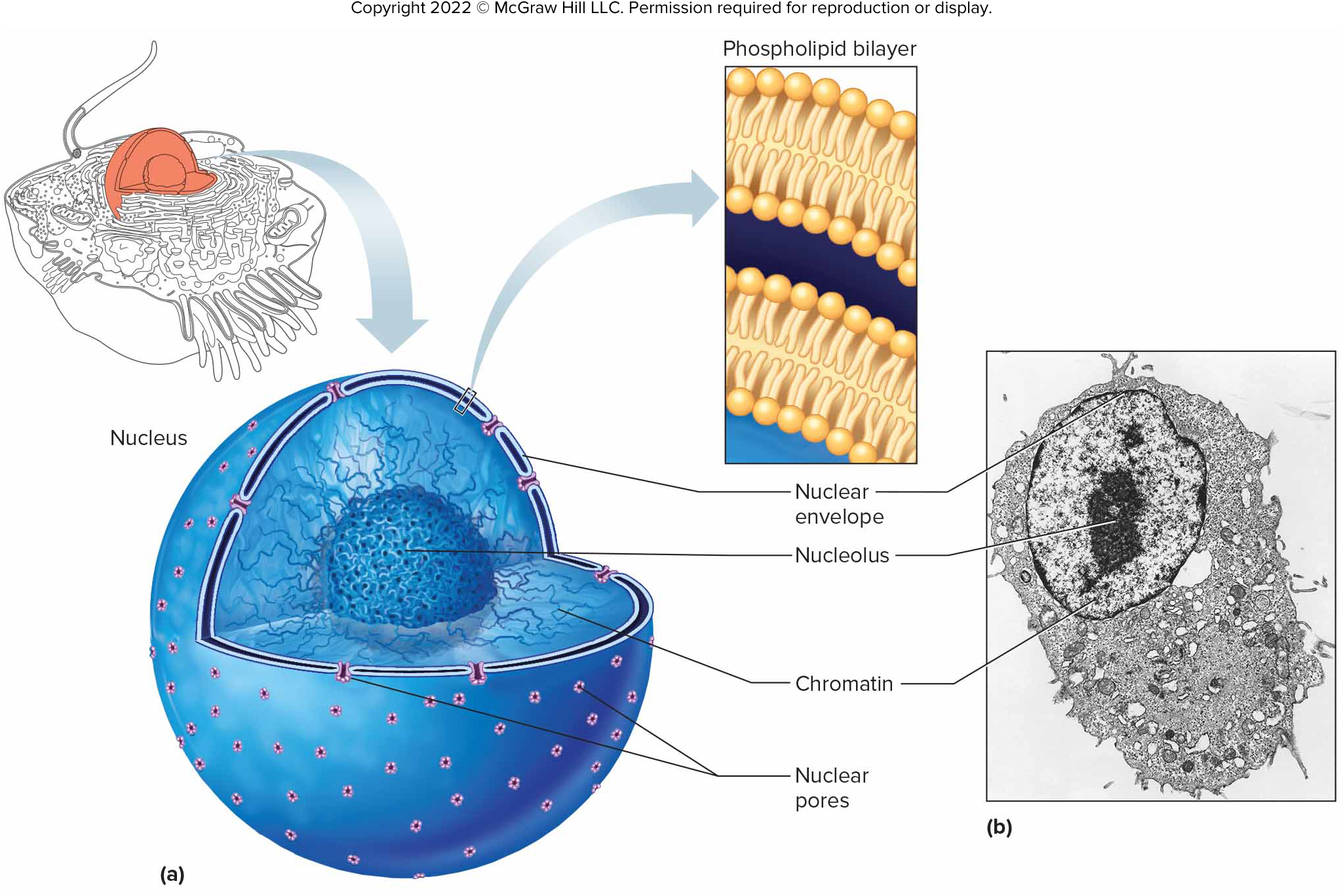
Nucleus
Contains genetic material and directs cell activities.
Cytoplasm
Consists of organelles suspended in cytosol.
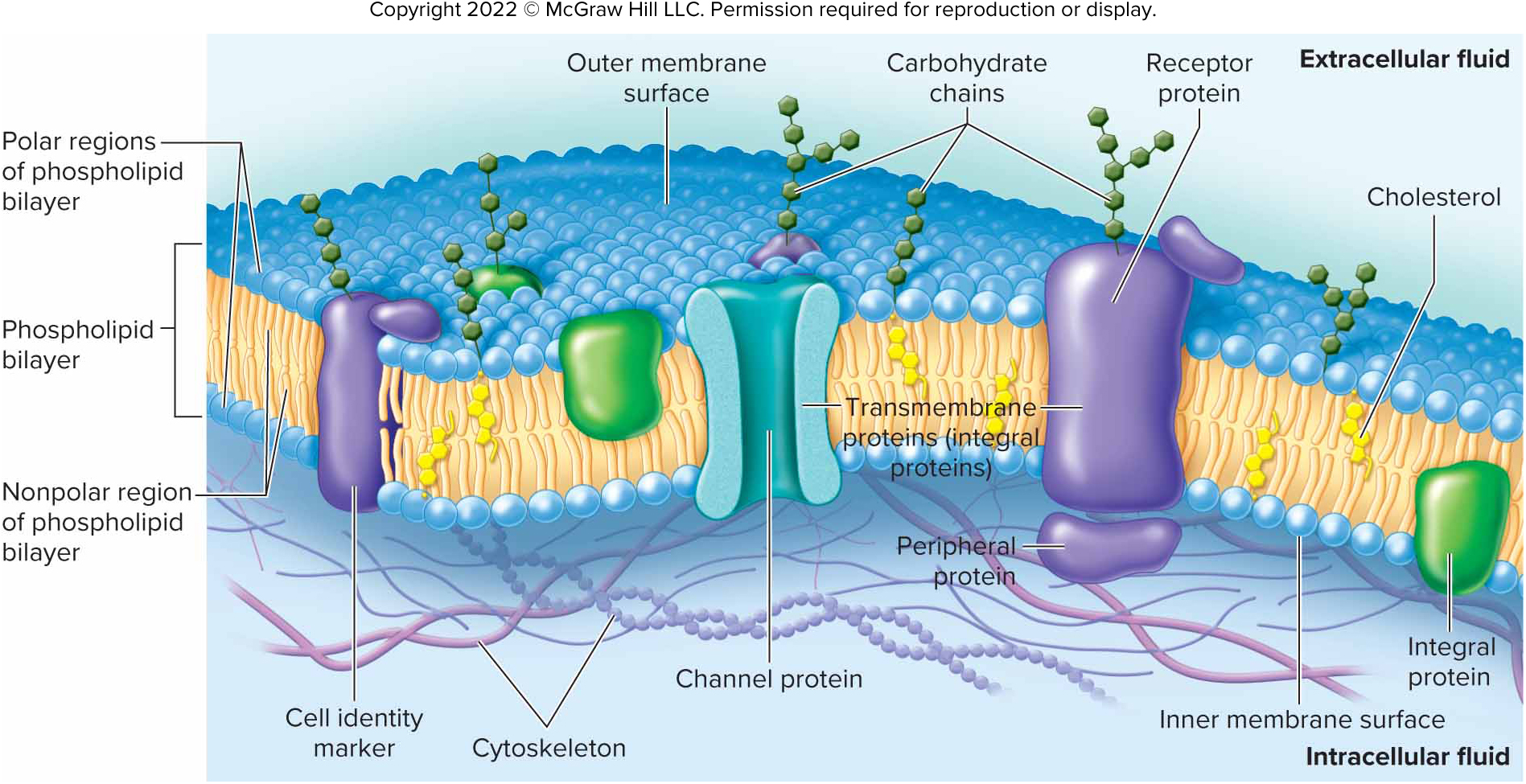
Cell Membrane
Outer boundary of a cell; maintains integrity and regulates substance passage.
Selectively Permeable
Selectively regulates the entry and exit of substances in a cell.
Signal Transduction
Permits cell to receive and respond to messages.
Hydrophilic Heads
Water-soluble heads that form the surfaces of the cell membrane.
Hydrophobic Tails
Water-insoluble tails that form the interior of the cell membrane.
Cholesterol
Stabilizes membrane and helps keep it impermeable to water-soluble substances.
Cytosol
Fluid portion of the cytoplasm.
Organelles
Tiny solid structures with specific functions in the cell.
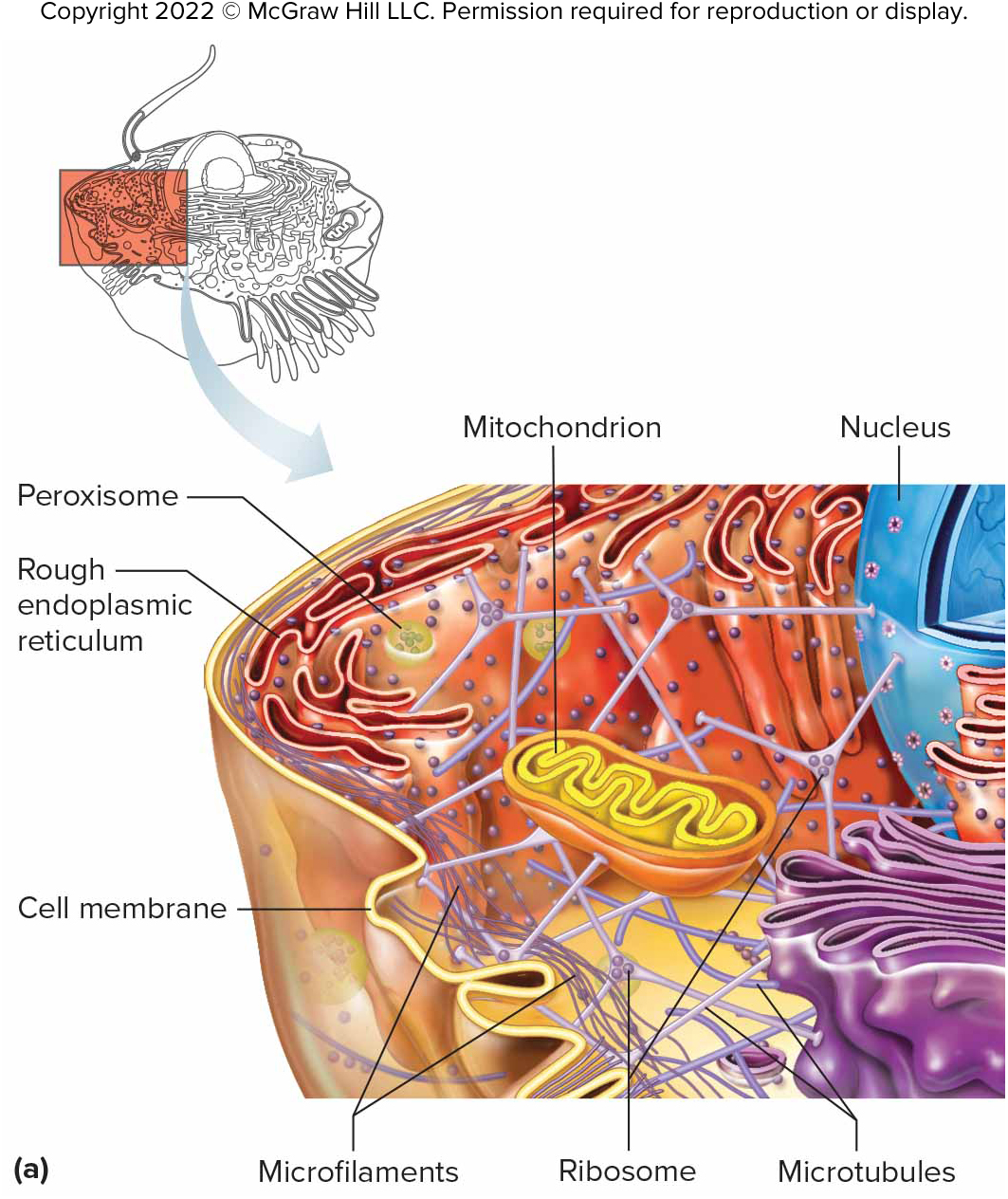
Cytoskeleton
Supporting framework of protein rods and tubules within the cytoplasm.
Ribosomes
Composed of protein and RNA; provides structural support and enzyme activity for protein synthesis.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Membrane-bound sacs, canals and vesicles that function as a tubular transport system.
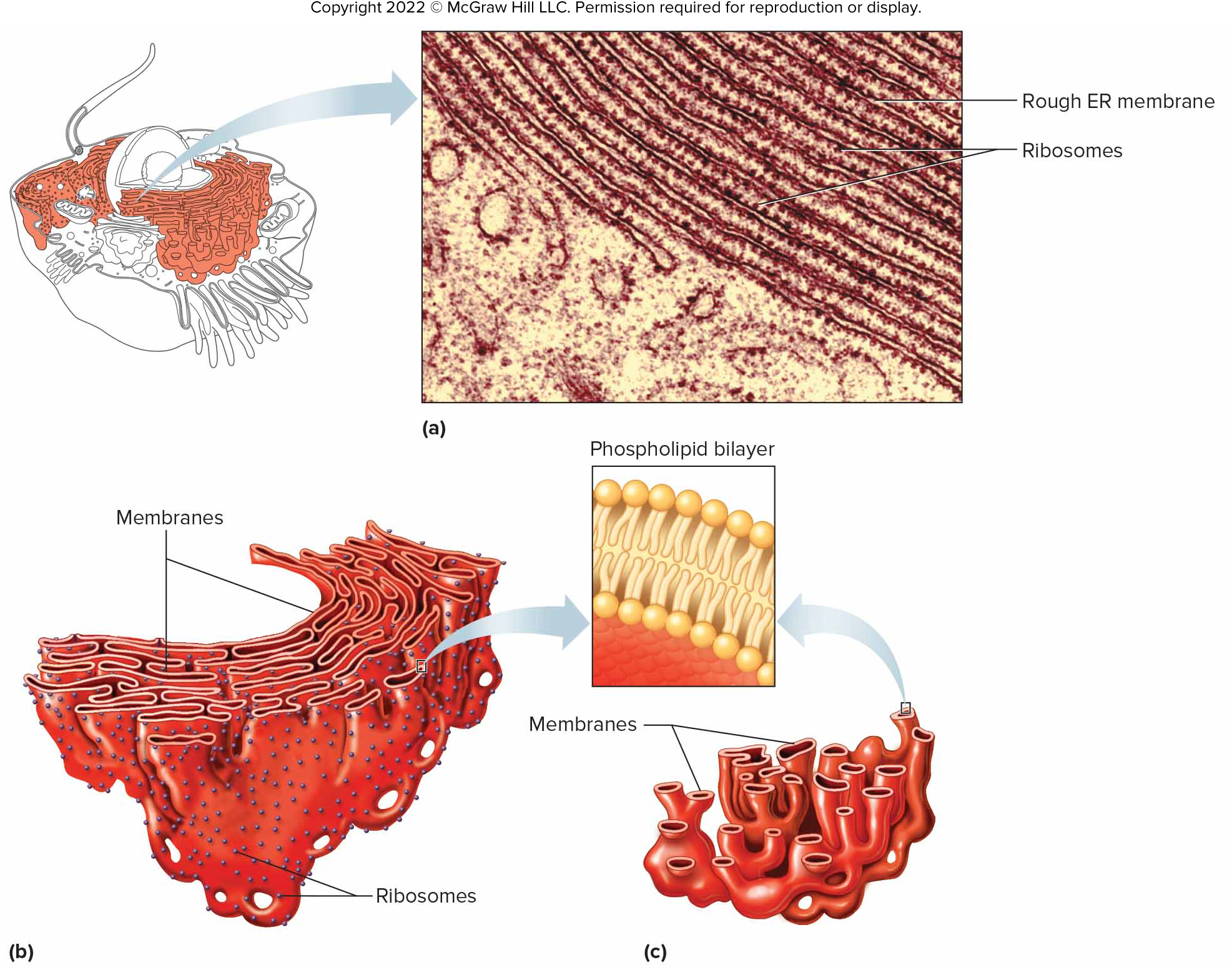
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
ER that contains ribosomes and conducts protein synthesis.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
ER that lacks ribosomes and conducts lipid synthesis.
Vesicles
Membranous sacs that store or transport substances.
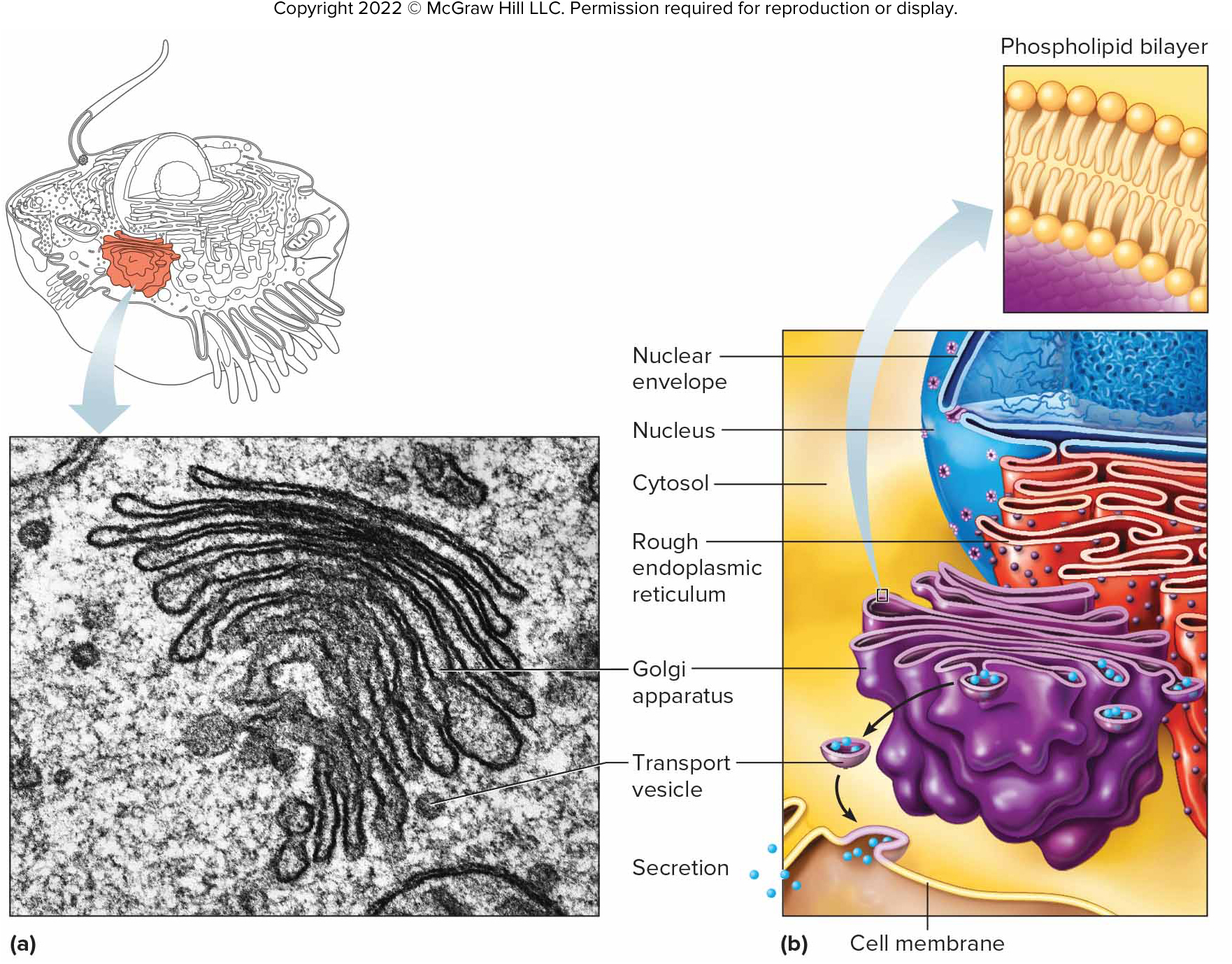
Golgi Apparatus
Refines, packages, and delivers proteins made on the RER.
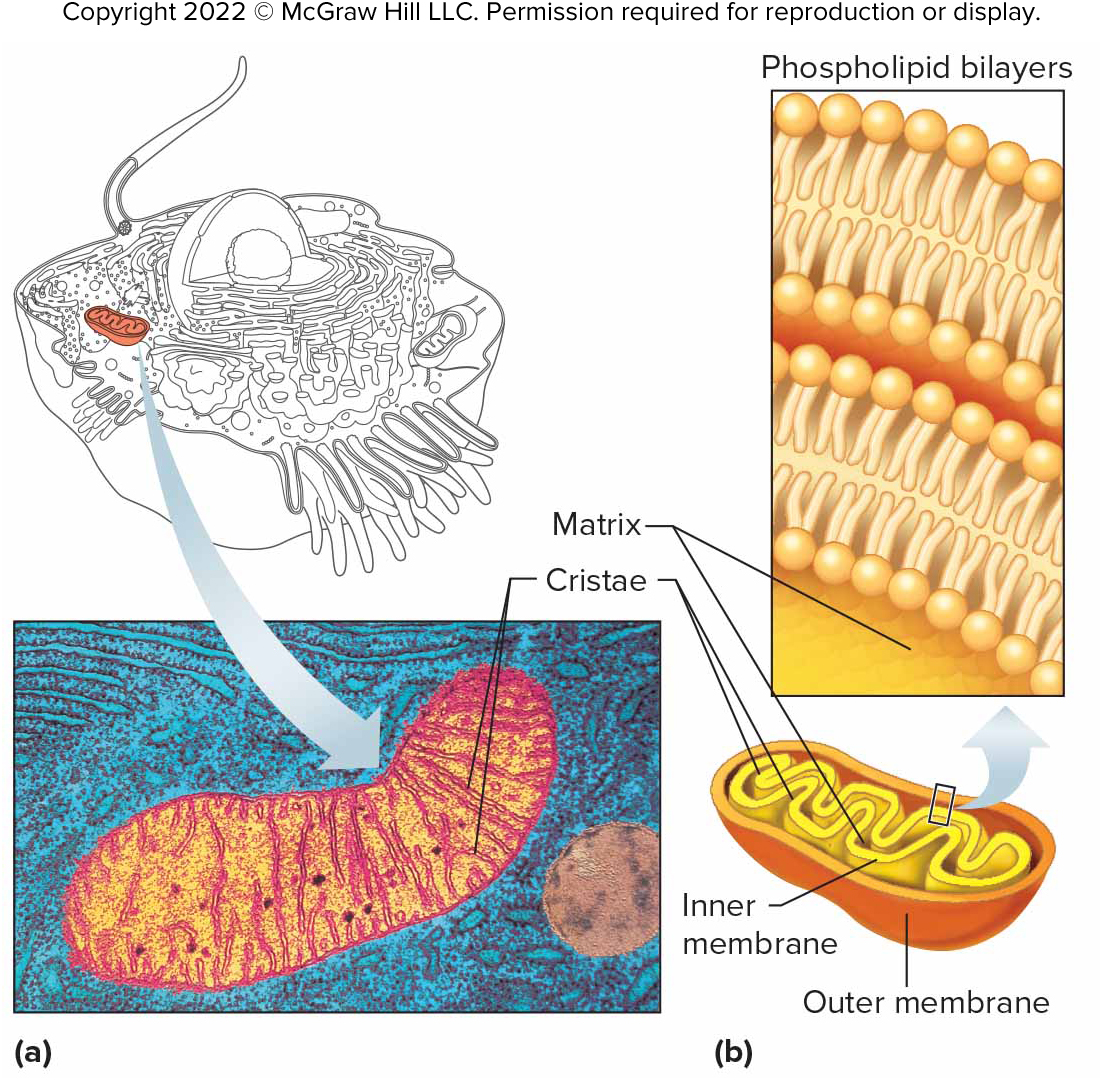
Mitochondria
Membrane-bound, fluid-filled sacs that house chemical reactions extracting energy from nutrients.
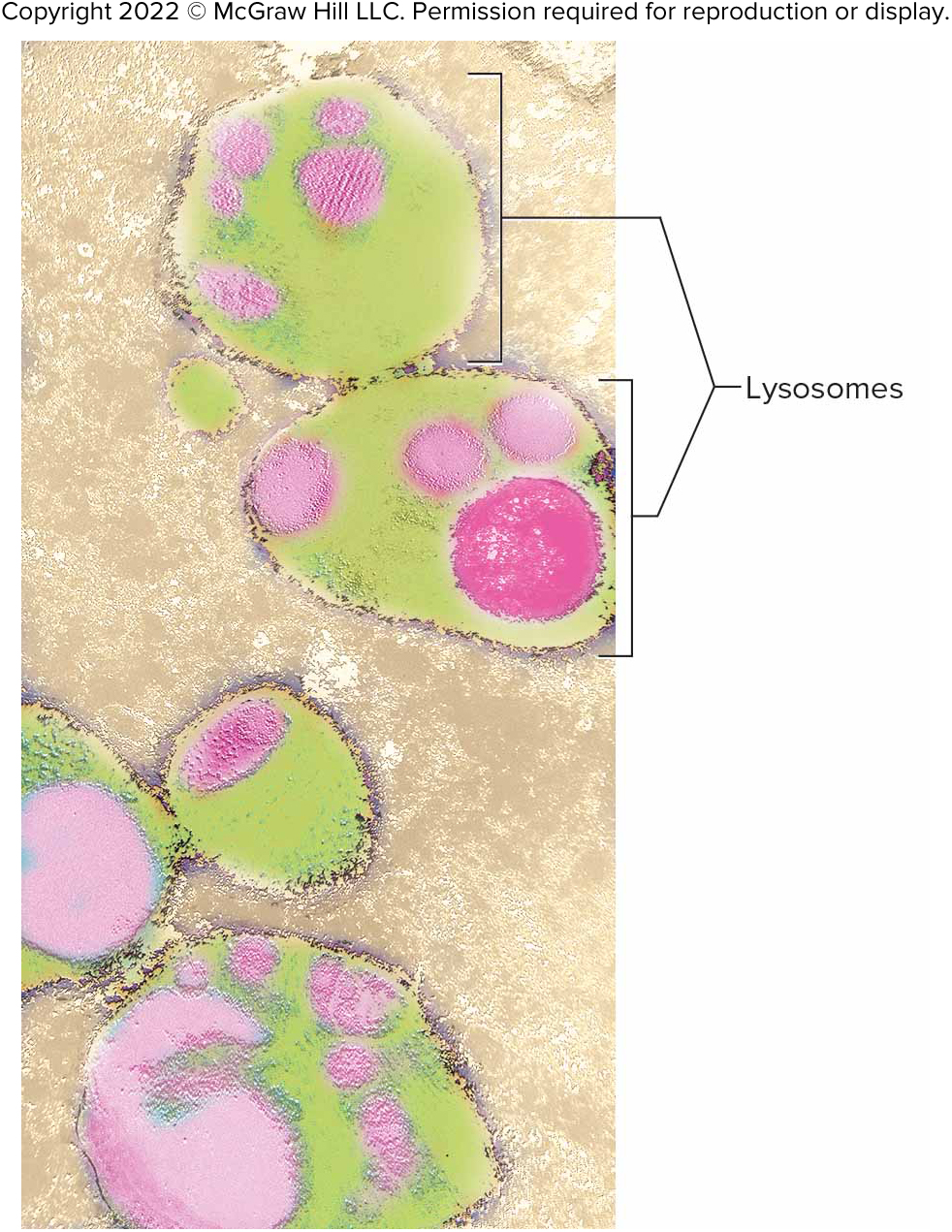
Lysosomes
Small membranous sacs that contain enzymes to digest proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, etc.
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs similar to lysosomes, containing enzymes that digest lipids, alcohol, and hydrogen peroxide.
Microfilaments
Tiny rods of actin that provide cellular movement like muscle contraction.
Microtubules
Larger tubes of tubulin that maintain cell shape, and comprise cilia, flagella, and centrioles.
Intermediate Filaments
Composed of several proteins and support the nuclear envelope of the cell.
Centrosome
Central body consisting of two centrioles near the nucleus.
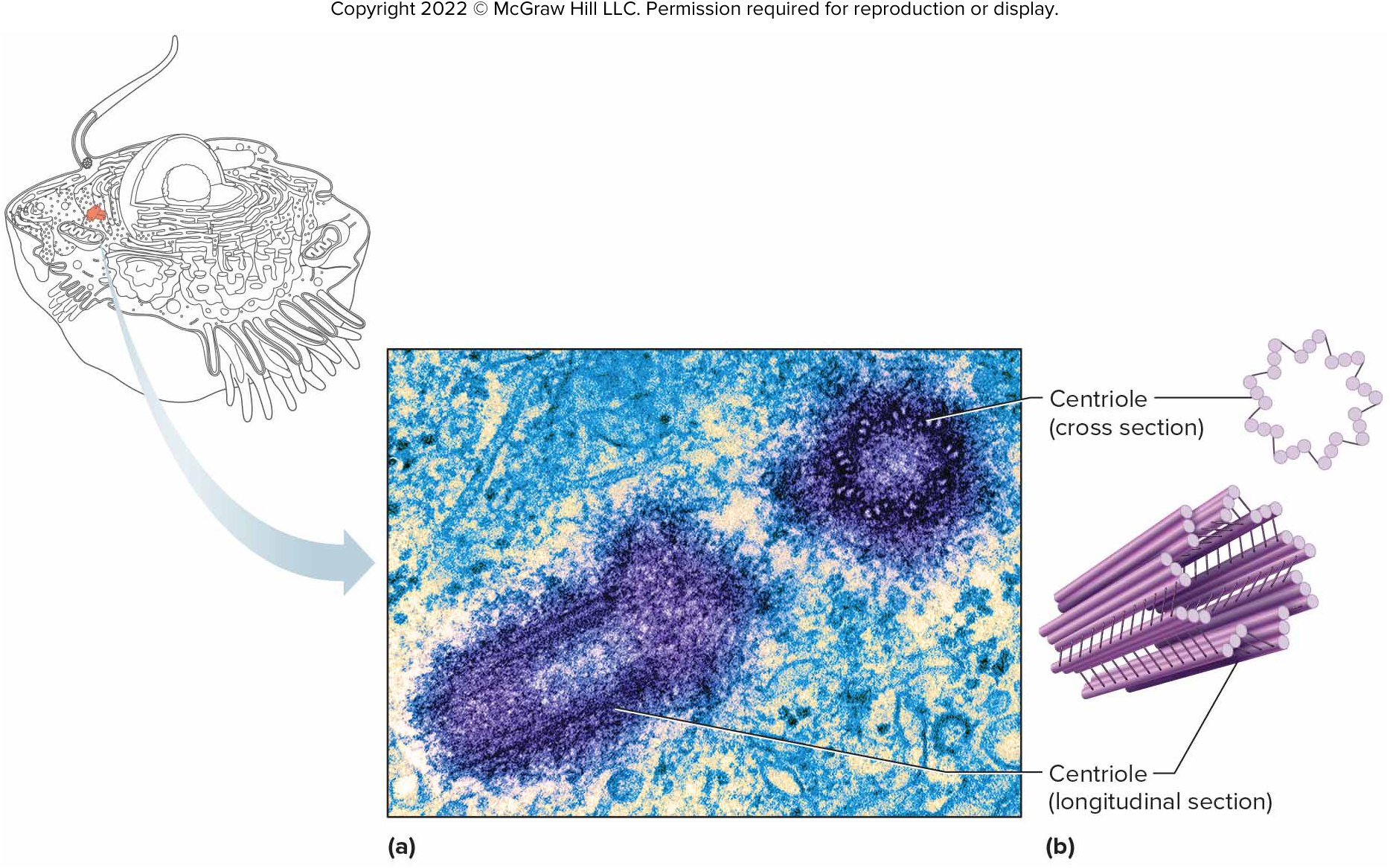
Centrioles
Cylindrical structures composed of microtubules; produce spindle fibers during cell division.
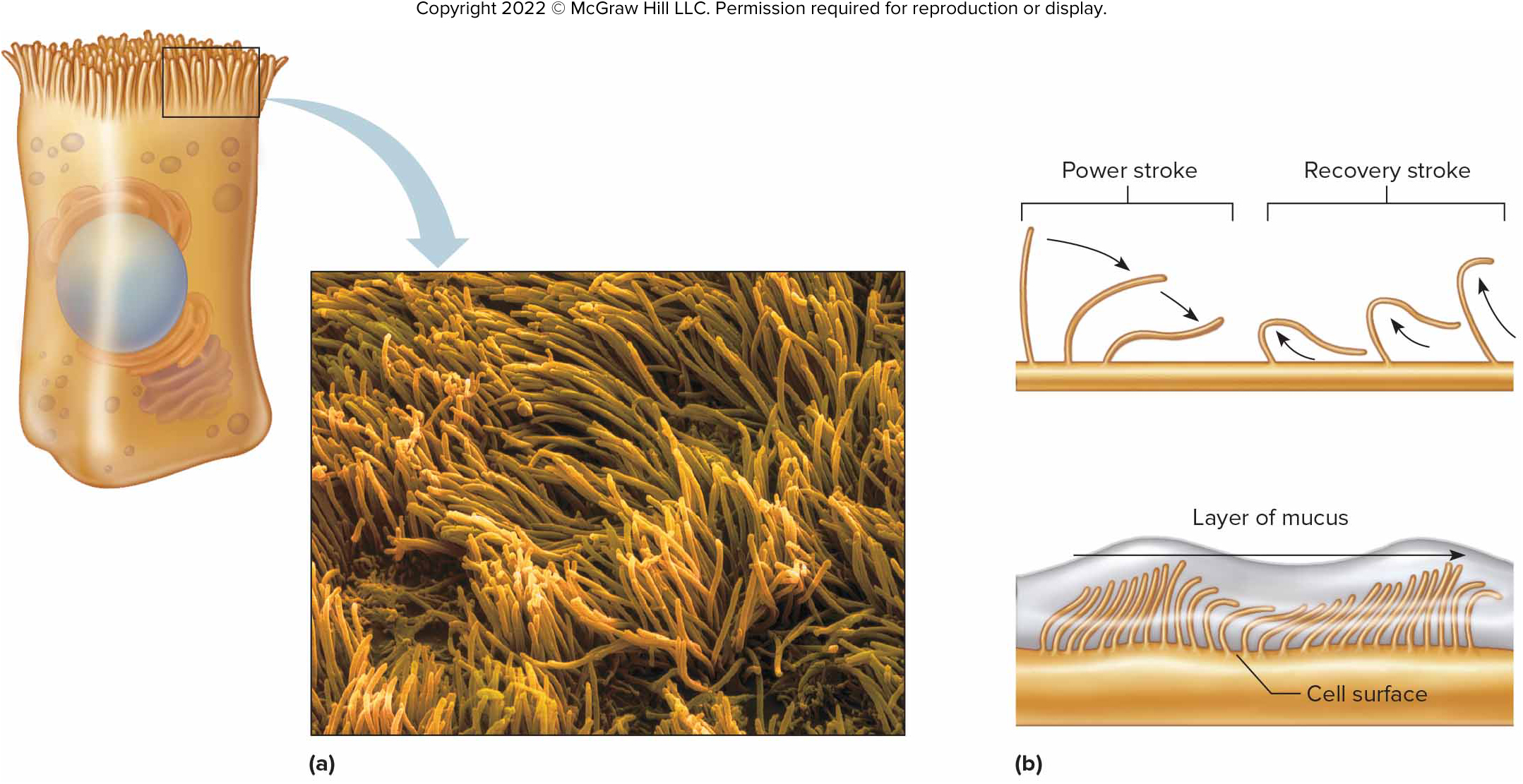
Cilia
Motile extensions of cell membrane consisting of microtubules, which beat back and forth in a coordinated manner.
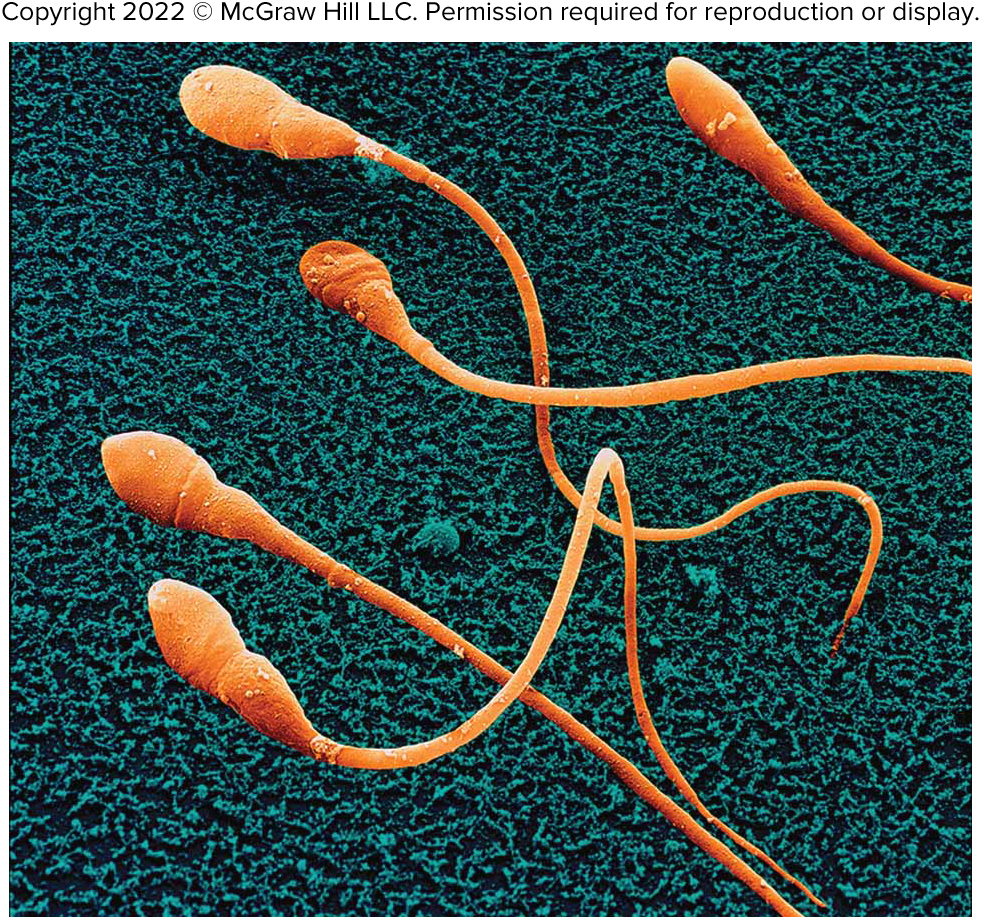
Flagella
Motile extension from cell membrane, similar to cilia but much longer, causing the entire cell to move.
Nuclear Envelope
Double-layered membrane surrounding the nucleus.
Nucleolus
Dense body of RNA and protein in the nucleus; site of ribosome production.
Chromatin
Consists of the cell’s chromosomes, containing DNA wound around proteins; stores information for protein synthesis.