Chem 101
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1 Pre Midterm 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Daltons Atomic Theory
Atoms from one element can’t be converted to atoms of another element but they form specific ratios with other atoms to form compounds
Proton (p+)
Relative charge (+1)
Mass (AMU) = 1.0073
Neutron
Relative charge is 0
Mass (AMU) = 1.0087
Electrons e-
Relative charge -1
Mass (AMU) = 0.0005486
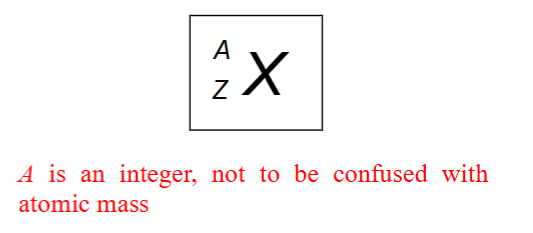
X value is atomic symbol
A value is mass number = protons + neutrons
Z value is the atomic number = number of protons
Number of neutrons
Is calculated by A - Z
Isotopes
Same number of protons (Z) but different mass number (A) b/c they have different number of neutrons
Average Atomic Mass
Atomic mass = sum of isotope mass x fractional abundance
sum of (m1)(x1)
Mass is in AMU
When do radioactive elements start
Starting with palladium (Pd)
Ion types
Cations - positive ion - e- removed
Anions - negative ion - e- added
11p 12n 10e
Sodium (Na+) ion
17p 18n 18e
Chloride (Cl-)
How to identify species
Use neutrons to find element and find difference in e and p to find ionic charge
Ionic compounds (Binary)
Metal and nonmental - cation first then anion
Add -ide to end of anion (CO2)
Meaning of roman numerals in Copper (ll) telluride
Means copper has a 2+ charge
What roman numerals go in FeCl3
Iron (lll) Chloride
NaClO
Sodium hyopchlorite

Polyatomic naming table
Strontium Iodate
Sr(IO3)2
Binary Compounds
Non metal + non metal and are written in order of increasing electronegativity
add -ide to the end of second element
N2O
dinitrogen monoxide
Dichlorine heptoxide
Cl2O7
SF6
Sulfur hexafluoride
Dihydrogen monoxide
H2O
Binary acids
Contains no Oxygen
HCN(aq)
Hydrocyanic acid
HF(aq)
Hydrofluoric acid
Hydrosulfuric acid
H2S(aq) - sulfur has -2 charge - need 2 H
Oxyacids
Contain H + O + nonmetal
Oxyacids increase in O
Hypo_ous acid - hypo_ite
_ite - _ous acid
_ate - _ic acid
per_ate - per_ic acid
HClO2
Chlorous acid
HClO3
Chloric acid
HClO4
perchloric acid
Nitric acid
HNO3
Periodic acid
HIO4
hypobromous acid
HBrO
sulfurous acid
H2SO3
units of frequency
s^-1 or Hz
Amplitude
height of crest or trough and is related to the intensity of the radiation
Equation for speed of wave
c= lamda multiped by v
Blackbody radiation
EM radiation emerging from a blackbody (smoldering coal) gives a spectrum that cannot be explained by treating light as a wave

Change in energy of an atom equation
Physical explanation of blackbody
each atom emits only certain quantities
Quanta
Absorbed or emitted by an atom when there is a change in energy which is = hv
Energy of a photon
= hv = hc/wavelength
Spectral lines
are produced when an electron moves from one energy level to another
Work function
minimum energy required to remove an electron from the surface of a material in a vacuum
1/wavelength = R(1/(n1² - 1/n2²)
Rydberg equation where R = 1.097 × 10^7 m^-1
En = -RH(Z²/n²)
Different version of Rydberg equation but finds energy rather than wavelength
Z is the number of protons in the nucleus
Ground state
electron is in its first orbit - lowest possible energy
excited state
any orbit further from the nucleus - n>1
n=2 first excited state
n=3 second excited state
…
In the rydberg equation if n = infinity what is the approximate energy of the photon
About 0 because n is on the denominator in the equation and all answers will approach closer to 0
Infrared series
Starts at n= 4 or higher and goes to n=3 (second excited state)
Visible series
When electrons drop from outer orbits (n=3 or higher) to the n= 2 orbit (first excited state)
Ultraviolet series
When electrons drop to n= 1 (ground state)
H-like species
Hydrogen like species - one electron species
X+(Z-1)
n
any positive integer and is the size of the orbital
L (angular momentum)
0 to n-1 and is the shape of the orbital
one or more sublevels denoted by L
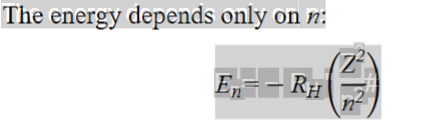
Equation for energy level
orbitals
s p d f
mL
limited by values of L and is spatial orientation of orbital
-L thru 0 to +L
-L, (-L+1)… 0, … L
total number of mL values is calculated by 2L+1
L = 2
d orbital
L = 1
p orbital
L = 0
s orbital
L = 3
f orbital
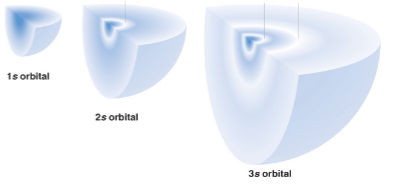
s orbitals
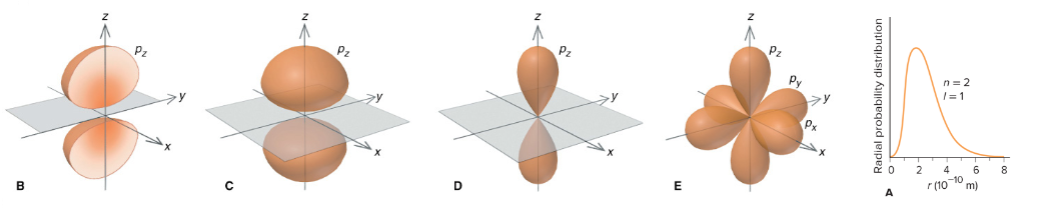
p orbitals
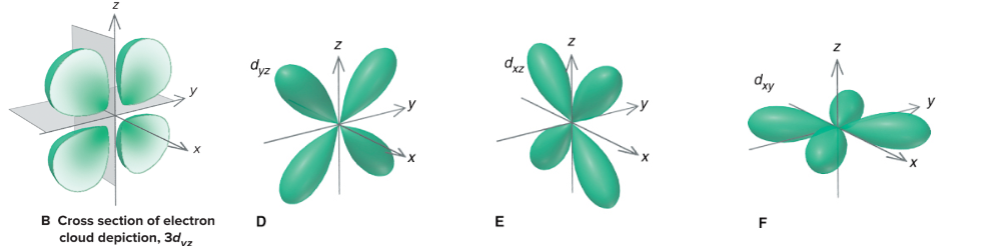
d orbitals
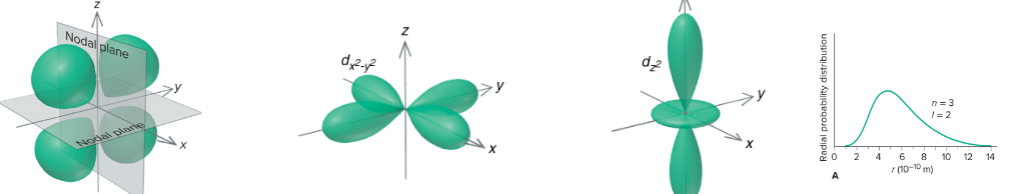
d orbitals
2pz orbital
mL = 0
L = 2 mL = 0
3dz²
number of radial nodes
n - L - 1
to change from 1s to 2s orbital
add + sign in first shell and - sign in second
not charges just notation for radial node
paramagnetic species
unpaired electrons
diamagnetic species
all electrons are paired
Zeff in cations
Increases as there is a net positive charge
Smaller than atoms
Radius decreases
Zeff in anions
Larger than atoms
Decreases as there is a net negative charge
Radius Increases
Down a group
Ionic size increases because n increases
Across a period
Ionic size decreases with increased positive charge
How to define size of an atom
Atomic radius is half the distance between 2 centers
extent of the spherical contour (90% probability of finding an electron)
What happens when Zeff increases
the outer electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus which decreases atomic size
Ionization Energy
Energy that must be added to remove an electron
First Ionization energy
outermost electron removed
If an electron is removed what happens to Zeff
Zeff increases
More energy is required to to remove next electron because it is tighter together
IE increases
Across a perid IE ….
increase
down a group IE …
decreases
Exceptions to IE increasing
O and Be
Have slightly different electron configurations
electron affinity
energy change when a GASEOUS atom or ion gains an electron
across a period EA ..
increases with some exceptions
N EA1 is positive instead of negative because it starts very stable and you add an electron
Be too
down a group EA …
decreases with some exceptions
unlike alkali metals…
hydrogen shares its electrons with nonmetals instead of transferring it
H-
Hydride - not common and very reactive