1 Exam ISP 205 CH 1-5
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
As objects move apart:
Gravity weakens rapidly and becomes incredibly small over vast distances.
When a rotating system's radius increases:
Its linear speed increases.
Why were Galileo’s observations inconsistent with the Greek geocentric model?
His telescopic discoveries showed that Venus orbited the Sun and proved not everything orbited Earth.
Hubble’s Law
Galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance
Why does earth's orbit cause small shifts in stars position?
Parallax makes nearby stars seem to shift against distant backgrounds as Earth moves around the Sun.
Blueshift
The decrease in a light wave's wavelength, indicating a source is moving towards an observer
Redshift
Stretching of light waves from a distant source, causing them to shift toward the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum
What color are the hottest stars?
Blue
What color are the coolest stars?
Red
Gamma Rays
Shortest wavelength with the highest frequency.
Radio Waves
Longest wavelength with the lowest frequency.
How is the Universe expanding?
Space-time itself is stretching and carrying galaxies away from each other
Observable Universe
The part of the Universe that could be observed in principle, including things that may require future technology.
You are on the north pole, which way is Polaris, the north star?
Directly Overhead, Zenith
You are on the south pole, which way is Polaris, the north star?
Below the southern horizon, you can’t see it.
It is Autumn in Michigan. What season is it in Australia?
Spring.
When does a Waxing Crescent Moon set?
After sunset.
Doppler Effect
Perceived difference in frequency of sound or light due to the sources movement.

Newtons 1st Law
An object at rest stays at rest. An Object in motion stays in motion, unless affected by an outside force.

Newtons 2nd Law
The force acting on an object is equal the mass of the object times it's acceleration, F=ma

Newtons 3rd law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.

Keplers 1st laws
Planets orbit in Ellipses.

Keplers 2nd Law
Planets sweep out equal areas in equal times.

Kepler’s 3rd Law
The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major Axis
Spectra Lines
A dark or bright line in a continuous spectrum.
Thermal Radiation Spectrum
a continuous band of electromagnetic waves
Gamma Rays
This light form has the shortest waves and longest wavelengths. It is smaller than a nucleus. It is used in radiation therapy.
X Rays
This light form has high energy and is the size of a hydrogen atom. It can penetrate dense materials like bone.
Ultra Violet
This light form is shorter than blue light and is the size of a protein. It can cause skin damage.
Visible Light
This light form can be seen by the naked eye. It is the size of a bacterium and allows us to see color.
Infrared
This light form is longer than red light and is the size of a cell. It goes past red in the rainbow; it is used for heating and red light therapy.
Microwave
This light form ranges from the size of a pinhead to a baseball. It is used for observing radiation.
Radio
This light form has the longest wavelength. It is the size of a football field and is used for communication.
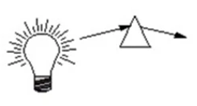
Continuous spectrum
Full rainbow of uninterrupted wavelengths. produced by dense, hot objects like light bulbs.
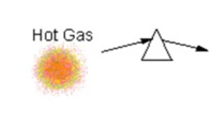
Emission Line Spectrum
Dark background with bright lines. Produced by hot gas.
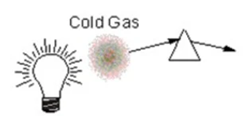
Absorbtion Line Spectrum
Continuous spectrum with dark lines at specific wavelengths. Made when hot light passes through cold gas.
How do we measure a planets mass?
By using Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
Conservation of Angular Momentum
A rotating system's total angular momentum stays constant if no net external twisting force acts on it
Potential Energy
The stored energy an object or system possesses due to its position or arrangement
What did Newton add to Kepler’s 3rd law?
The masses of the orbiting bodies and the universal gravitational constant (G)
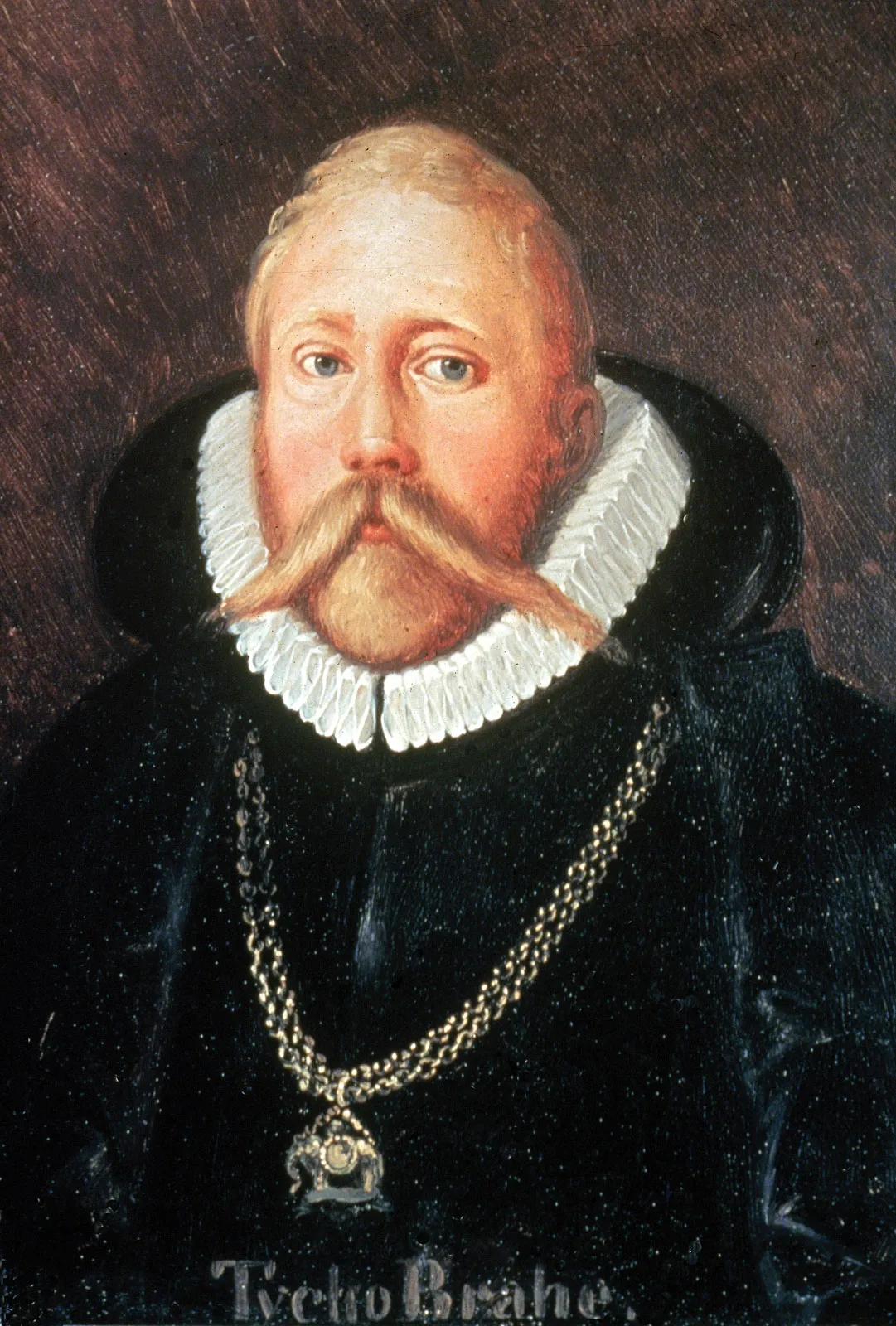

Tycho Brahe
A 16th-century Danish astronomer famous for his extremely precise naked-eye observations of the night sky, including the supernova of 1572
Gravitational Law
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that's stronger with more mass and weaker with more distance.
Copernican Sun model
Heliocentric model of the Solar System, where the Sun is at the center and the planets, including Earth, orbit it.
Greek Geocentric Model
An astronomical system with the Earth at the center of the universe, around which the Sun, Moon, and stars orbit.
Radio Waves are a form of _____ Light
Low Frequency
Why do smaller things spin faster, and what happens to its temperature?
Conservation of Angular Momentum. It Heats up. Potential energy transfers into kinetic energy.
Which is closer to Earth? A star on the Near side or Far side of Andromeda Galaxy
Near Side
Which is closer to Earth? A star on the Near side or Far side of the Milky Way Galaxy?
Near Side
Which is closer to Earth? Orion nebula or Alpha Centauri.
Alpha Centauri
Which is closer to Earth? A star in the Milky Way Galaxy or Alpha Centauri?
Alpha Centauri