Cog Neuro - Txb C6 Object Recognition (6.3, 6.7)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what are the three types of visual agnosia
apperceptive
integrative
associative
apperceptive visual agnosia?
problem seeing the shape
patients may be able to recognize an object from a typical viewpoint, but it if it is in a different view point or distorted with shadows, recognition deteriorates
they have acuity, colour vision, and brightness discrimination intact, but cannot verbally recognize objects based on limited stimulus information like a line drawing
impaired object constancy

object constancy
ability to understand that even though something is moving or, the object is not changing. Ex. if a car is going off in the distance, we can discern that the car is staying the same size
integrative visual agnosia
problem combining parts into wholes
can identify parts of an objects, but not recognize that the parts make up a coherent whole
ex. can identify a door, window, or walls, but not a house
cannot identify an object it there is overlap. ex. a chair covered by a table, cannot identify the chair unless they see the entire chair
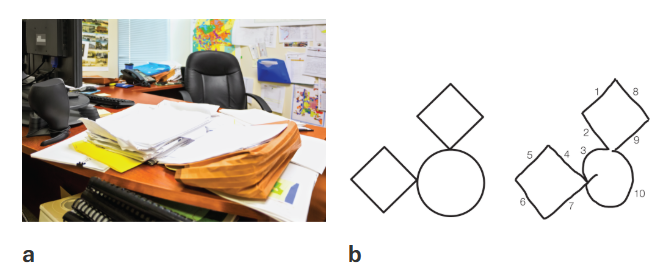
associative visual agnosia
problem linking perception to meaning
perception occurs without recognition; inability to access conceptual knowledge from visual input
ex. can see a house and draw a house but cannot tell its a house or describe what a house is for
ex. can be shown a picture of a mice and dog and asked which is bigger, cannot do it, but when told that they are a mouse and a dog, he knows which is bigger verbally
prosopagnosia
term used to describe an impairment in face recognition
where is the most common area where patients with prosopagnosia have lesions?
ventral pathway, especially regions associated with face perception such as the FFA and are usually bilateral due to 2 strokes involved with the Posterior Cerebral Artery
developmental prosopagnosia (DP)
people with no known history of brain injury that have deficits in face perception and in particular the ability to recognize faces.
due to gene mutation presumably arising from impaired information transmission between the FFA and other face-processing regions
can people with developmental prosopagnosia (DP) identify an intact face from a scrambled face?
no, the FFA activation patters from these individuals could not distinguish between intact and scrambled faces
what is the link between autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and face recognition
reduced connectivity between the FFA and other core and extended face-processing regions.
observed hypoactivity in response to faces
fewer neurons and less neuronal density in the fusiform gyrus layers
have lower facial recognition maybe because they don’t look at faces for a long time
acquired dyslexia
loss of reading ability
visual word form area
area of the left fusiform gyrus important for recognizing written words and letter strings and turning them into meaningful language
holistic processing
perceptual analysis that emphasized the overall shape of an object.
important for face recognition to analyze peoples facial features to identify them
can you have typical object recognition but have prosopagnosia and dyslexia at the same time
what happens if the analysis-by-parts system is damaged but the holistic system is ok or visa versa
object recognition can still occur, but will be suboptimal because its relying on the other system to take over
what is the analysis-by parts system
a form of perceptual analysis that emphasizes the component parts of an object
ex. recognizing someone’s nose alone
important for reading
Individuals with developmental prosopagnosia typically have _____ activation patterns of the FFA, but _____ connectivity with other face-processing regions.
normal; decreased