economic problem + Demand, supply, consumer and producer surplus, elasticity (micro)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
what is a characteristic of a free good
what about an economic good
-free goods have no opportunity cost
-economic goods are scarce
What is the basic economic problem?
What questions would economists ask to decide how to allocate resources?
-the basic economic problem is how we go about allocating scarce resources where wants are unlimited and resources are finite
-to do this, economists ask three questions:
what should be produced?
how should it be produced?
for whom should it be produced?
define what a positive statement is
define what a normative statement is
positive statements are factual and be tested
normative statements are opinion-basaed
What are the 3 economic agents?
what is rationality?
-the three economic agents: governments, firms, households
-rationality is the assumption that each economic agent acts in their own best interest
name and describe the three types of economies
planned economy - the government controls the factors of production and decides on the allocation of resources
mixed economy - a combination of market forces and government policies that controls the allocation of resources
market economy - allocation of resources is decided by the interaction of supply and demand (market forces)
what is economic efficiency?
economic efficiency is when an economic system achieves both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency
define allocative efficiecy
what point on graphs does it occur?
Allocative efficiency - occurs when resources are distributed in such a way that maximises overall welfare in an economy.
achieved when supply = demand AND when P = MC
define productive efficiency
what point on graphs does it occur?
productive efficiency occurs when a firm produces at the lowest possible cost, meaning it is operating at maximum capacity
occurs on the lowest point on the AC curve or any point on the PPF
what is opportunity cost?
what is a trade-off?
-Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative foregone when a decision is made
-trade-off is a sacrifice that is made in order to gain something
what is specialisation?
- specialisation is focusing on one activity to be able to produce more efficiently
- each of the factors of production can be specialised to make it more efficient
define division of labour
division of labour refers to the process where the production of goods or services is broken down into several distinct tasks, and each worker or group of workers focuses on one specific task
adv and disadv of division of labour and specialisation
advantages:
-quicker production process
-able to produce more goods and services
-lower average cost of production
disadvantages:
-demotivating for workers focusing on one small task
-A single worker absent or a piece of capital equipment missing can stop the whole production process
-may be a barrier to entry for smaller firms that cannot afford the investment
what is a barter system?
-The barter system is a system of exchanging one product for another without the use of money as a medium of exchange
what are the 4 types of demand?
define all of them
derived demand - when the demand for one good is due to the demand for a related good
joint demand - when products are demanded together as they are complements for one another
competitive demand - the demand for substitutable goods
composite demand - when a product is demanded for multiple uses
shifts in demand are caused by PIRATES, what is each cause?
shifts in demand:
Population
Income
Related goods - substitutes or complements
Advertising
Tastes and fashions
Expectations - future price changes
Seasons
what are the three types of supply?
define each one
joint supply - when the production of one good automatically leads to the production of another good, as is often as a by-product
composite supply - when a good or service can be supplied for multiple purposes
competitive supply - when two or more goods compete for the same resources so an increase in the supply of one results in a decrease int eh supply of the other
shifts in supply is caused by PINTSWC, what is each cause?
shifts in the supply curve:
Population
Indirect taxes
Number of firms
Technology
Subsidies
Weather - usually for agricultural produce
Costs of production
define demand
define supply
demand - a consumer's ability and willingness to purchase goods and services at a specific price
supply - ability and willingness of a firm to sell products at a given price
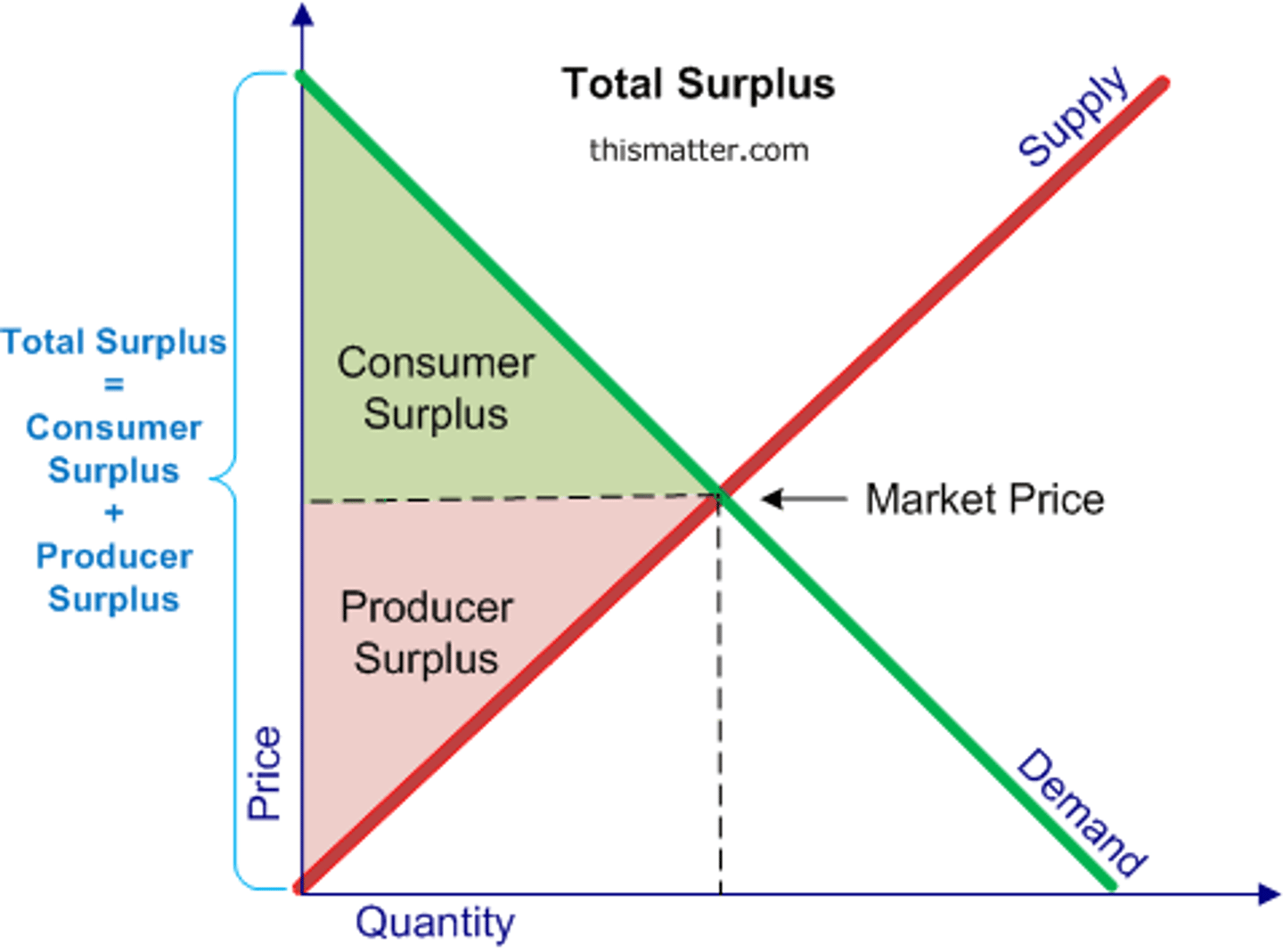
define consumer surplus
define producer surplus
where are they on a graph?
consumer surplus - the difference between the price consumers are willing and able to pay and the market price
producer surplus - the difference at which producers are willing and able to supply a product and the market price
what does PED represent?
formula?
PED =
- 0?
- ∞?
- 0-1?
- >1?
PED shows the degree to which demand responds to a change in price
percentage change in demand/percentage change in price
PED=0 - perfectly inelastic
PED = ∞ - perfectly elastic
0
determinants of PED (SPLAT)?
determinants of PED (SPLAT):
Substitutes (no.)
Percentage of income taken up
Luxury/neccessity
Addictive
Time Period
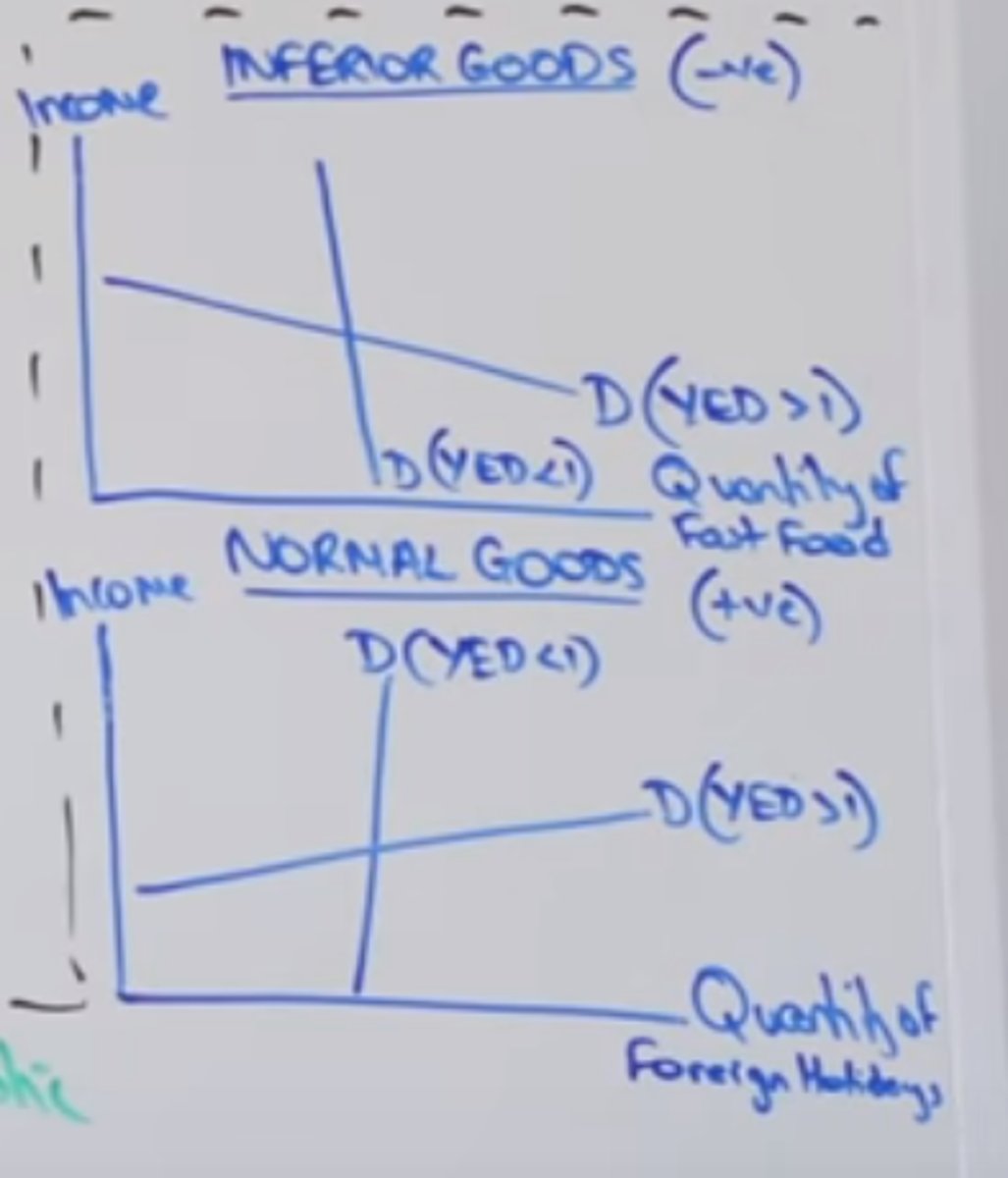
what is YED representing?
formula?
YED shows the degree to which demand responds to a change in income
%change in demand/ %change in income
if YED +ve then what type of good?
if YED -ve?
if 0
if -1
if YED = +ve then normal good
if YED = -ve then inferior good
normal goods:
- neccesities, 0
inferior goods:
- inelastic inferior goods, -1
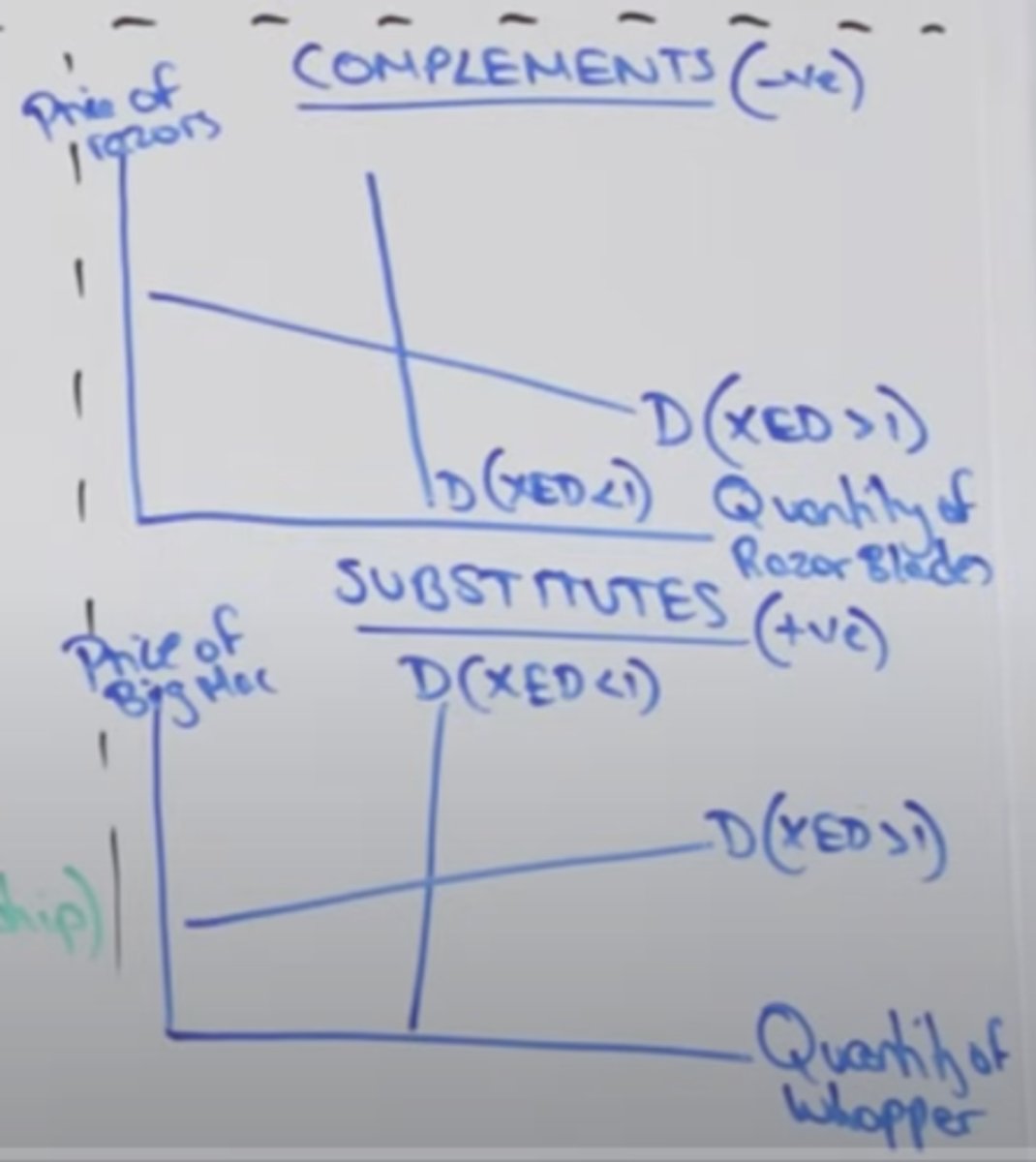
what does XED represent?
formula?
XED shows the degree to which demans responds to change in the price of another good
%change in demand of A / % change in price of B
if XED +ve then what type of good?
if XED -ve?
if 0
if -1
if XED = +ve then substitue
if XED = -ve then complement
substitute:
- 0
complement:
-1
what does PES represent?
formula?
PES shows the degree to which supply responds to a change in price
%change in supply / %change in price
PES = 0 ?
PES = ∞ ?
0
PES = 0 - perfecly price inelastic
PES = ∞ - perfectly price elastic
0
use and significance of PED
PED - allows for revenue forecasting and pricing strategy
use and significance of YED
YED - allows forecasting demand across different economic conditions in the business cycle
use and significance of XED
XED - can find the strength of relation between products, can signal merger and aquisition decisions if XED is high between 2 substitutes, they may merge
use and significance of PES
PES - helps firms assess how quickly they can increase or decrease production