Chapter 7 Medical Terminology Quick and Easy - Circulatory
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
cardi/o
heart
vascul/o
vessel
home/o
sameness
-stasis
controlling
Circulatory System
consists of the cardiovascular system (heart and blood vessels) and the lymphatic system, (structures involved in the conveyance of the fluid lymph)
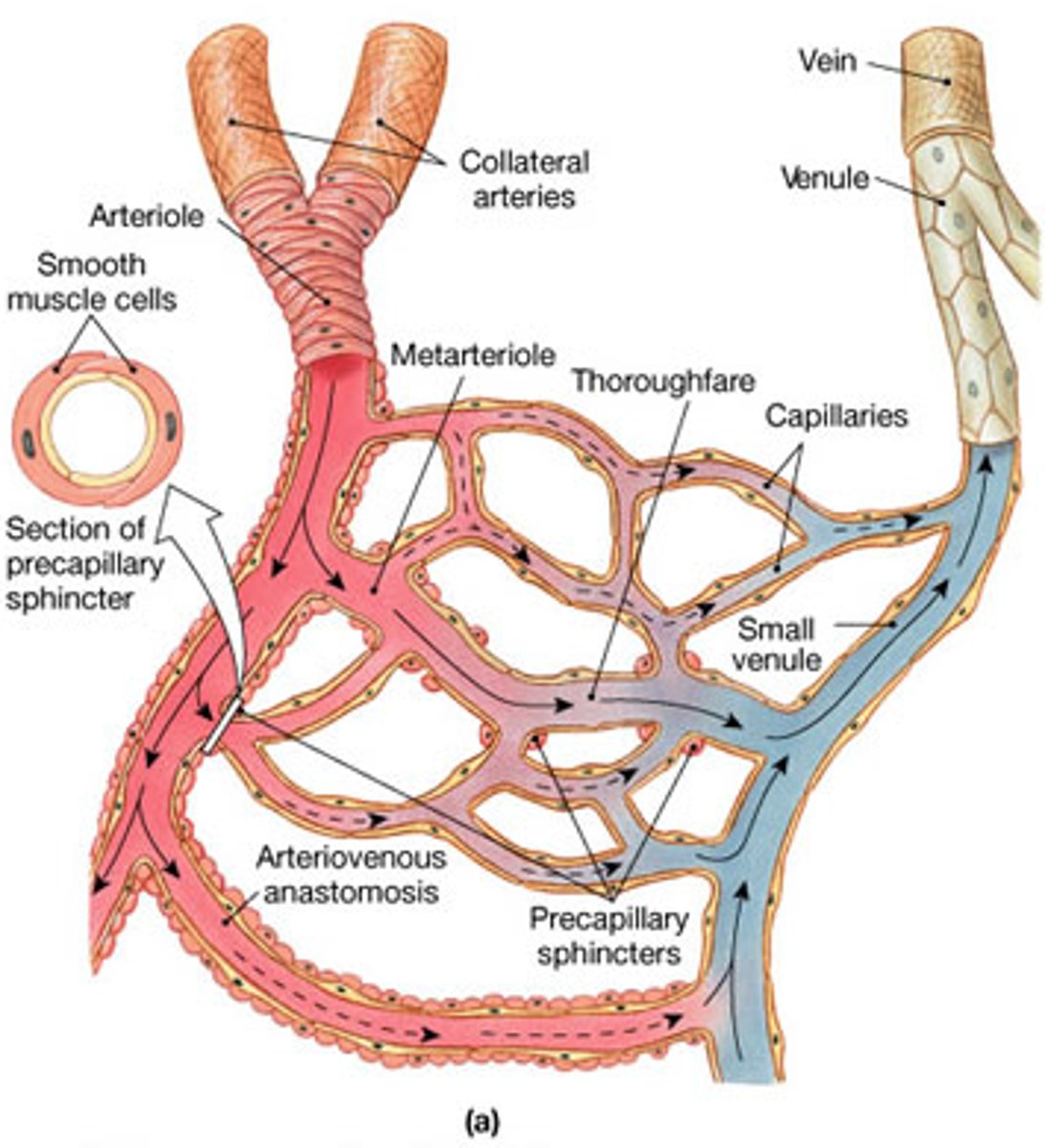
5 Anatomical Types of Blood Vessels
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, veins, and venules
Arteries
leaves the heart with blood
Arterioles
branch out many times from the arteries
Capillaries
tiny vessels with one-cell thick walls that branched out even more from the arterioles
Venules
blood leaving the capillaries returns to the heart and through this
Veins
carry blood back to the heart
Relationship of Blood Vessels
arter/o
artery
-ole
little
lymphat/o
lymphatic
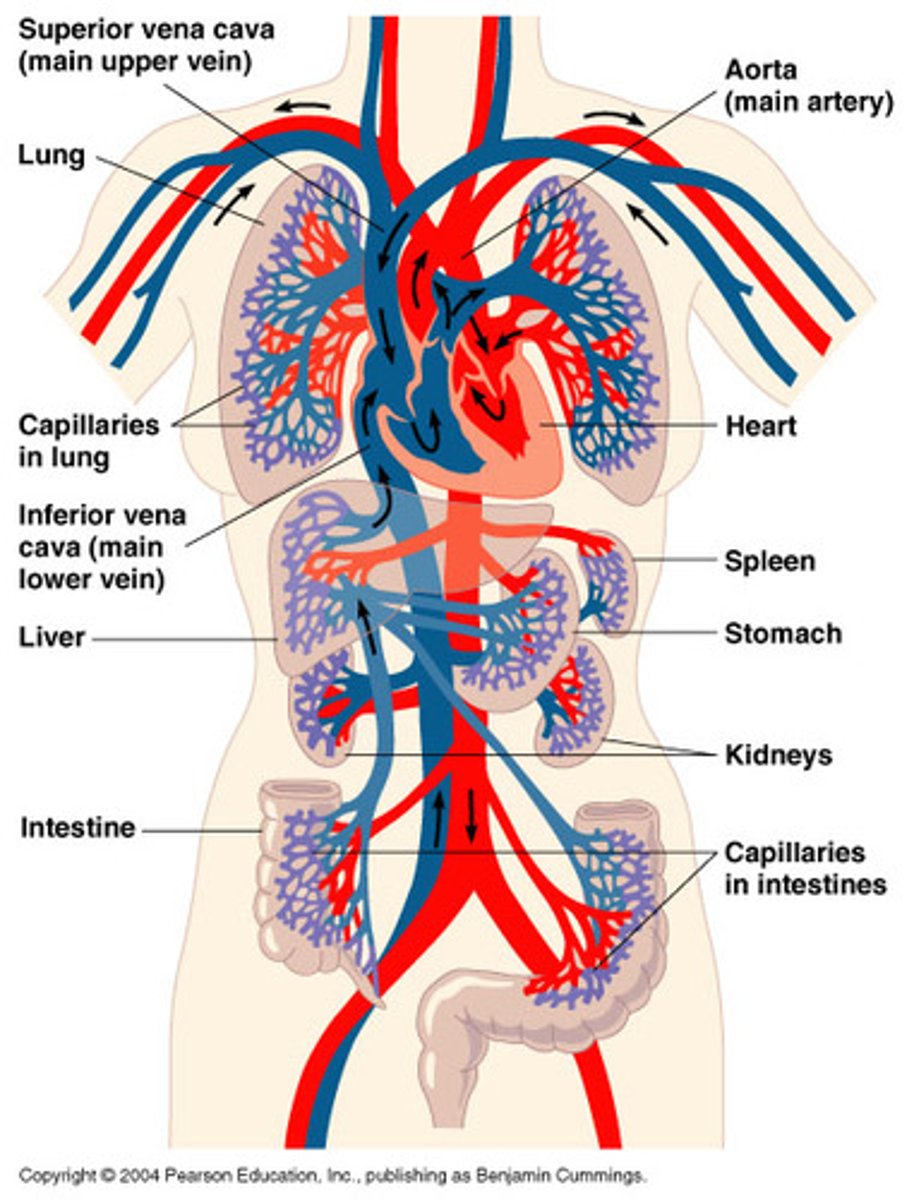
Cardiovascular System
coron/o
heart
sub-
below
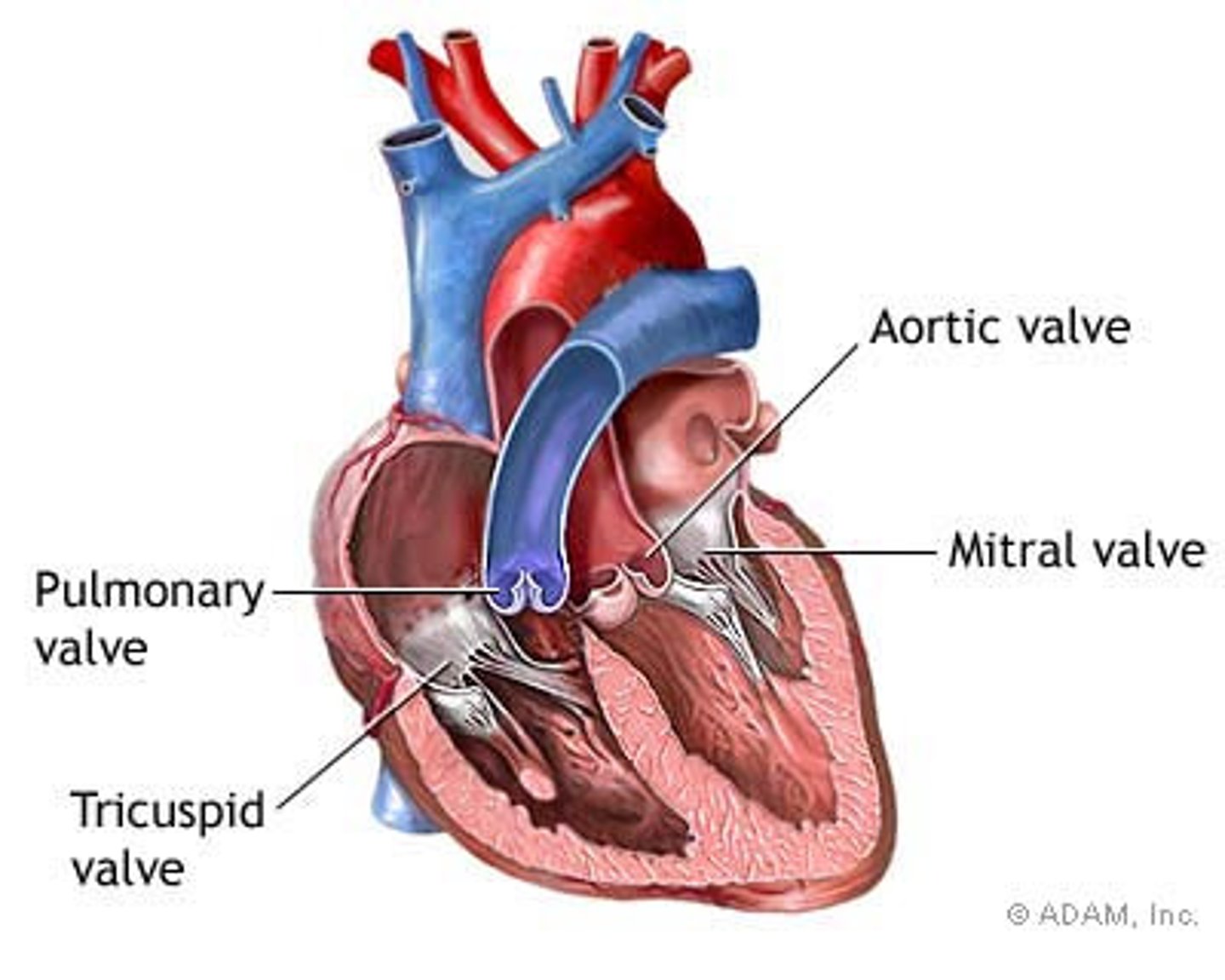
Atrial
pertaining to atrium
Ventricular
pertaining to ventricular
Atrioventricular
valves between the atria and ventricles
endo-
inside
pulmon/o
lung
aort/o
aorta
Aorta
the artery by which blood leaves the heart to be routed through out the body
Remember blood flow through valves
Tri before you Bi
Pericardium
sac made up of a double membrane, encloses the heart
Endocardium
forms the lining inside the heart
Myocardium
heart muscle, thickest tissue of the heart; middle layer of heart tissue
Visceral pericardium or epicardium
innermost layer of the pericardium
Coronary Arteries
blood vessels that supply oxygen to the heart are coronary arteries
Coronary
means encircling, in the manner of a crown, and refers to the way in which coronary arteries encircle the heart in a crown-like fashion
Valves of the Heart
angi/o, vas/o, vascul/o
vessel
arter/o, arteri/o
artery
arteriol/o
arteriole
ather/o
yellow fatty plaque
phleb/o, ven/o
vein
venul/o
venule
Cardiomyopathy
general diagnostic term that designates primary disease of the heart muscle itself
Myocarditis
inflammation of the heart muscle, example of cardiomyopathy
echo-
sound
Echocardiogram
Cardiac catheterization
the passage of a long, flexible tube into the heart chambers through a vein or an arm or leg or the neck
scop/o
to view
Positron emission tomography
especially helpful in examining blood flow in the heart and blood flow in the heart and blood vessels
Angina Pectoris
severe chest pain and constriction about the heart caused by an insufficient supply of blood to the heart itself
pectora
chest
Arrhythmia
irregularity or loss of rhythm of the heartbeat
Cardiomegaly
enlarged size of the heart
Congenital Heart Defects
abnormalities present in the heart at birth
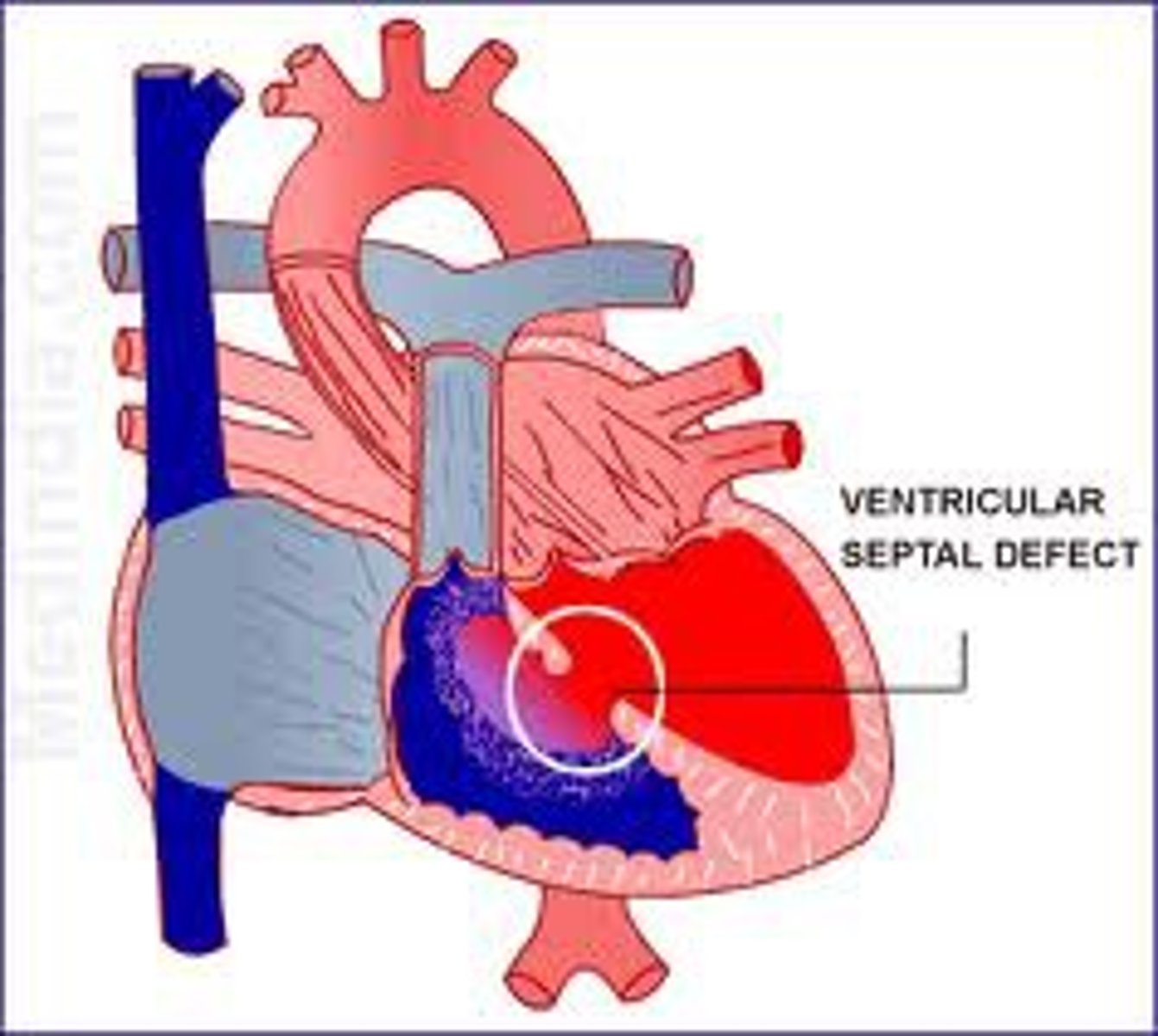
Ventricular Septal Defect
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
the work demanded of the heart is greater than its ability to perform
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
abnormal condition that affects the heart's arteries and produces various pathological effects
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
heart damage resulting from insufficient oxygen caused by pathological changes in the coronary arteries
Fibrillation
severe cardiac arrhythmia in which contractions are too rapid and uncoordinated for effective blood circulation
Defibrillator
electronic apparatus that delivers a shock to the heart
Defibrillation
used to slow the heart or restore its normal rhythym
Heart Murmur
soft blowing or rasping sound that may be heard when listening to the heart with a stethoscope
Hyperlipidemia
excessive lipids in the blood
Hypertension
elevated blood pressure above the normal values of 120/80 mm Hg in an adult (over the age of 18)
Hypotension
low blood pressure 95/60
Infarction
necrosis of a localized area of tissue caused by lack of blood supply to that area
Occlusion
obstruction
Stenosis
narrowing
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
death of an area of heart muscle that occurs as a result of oxygen deprivation
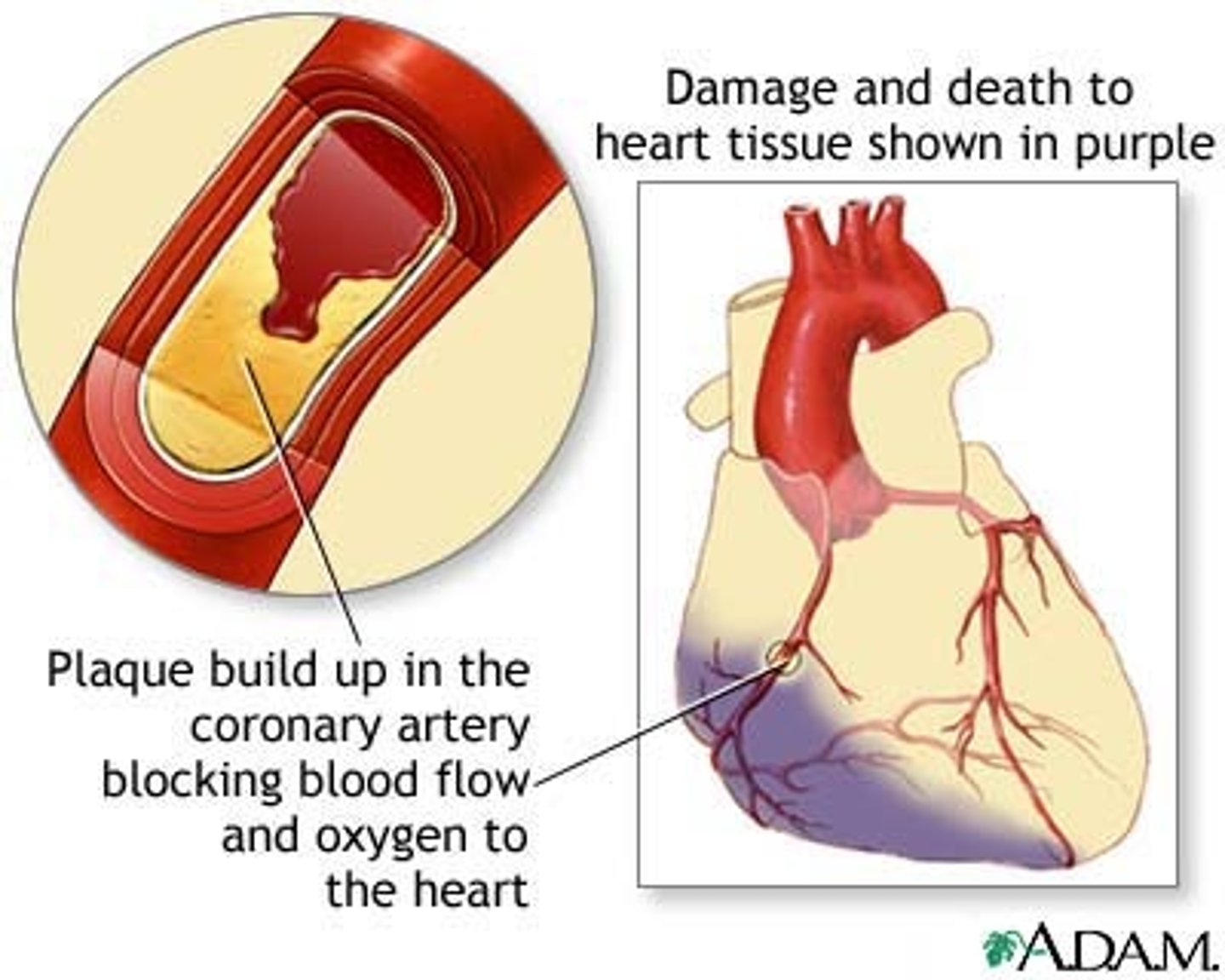
Myocardial Ischemia
deficiency of blood supply to the myocardium
Septal defect
defect in the wall separating the left and right sides of the heart
ASD
atrial septal defect
VSD
ventricular septal defect
Shock
serious condition in which blood flow to the heart is reduced to such an extent that body tissues do not receive enough blood
Vasodilation
increase in the diameter of a blood vessel
Vasoconstriction
decrease in the diameter of a blood vessel
Cholesterol and Triglycerides
lipids
Arteriogram
Angiomas
tumors consisting of blood vessels, usually benign
Aortography
radiography of the aorta
Aortagram
record produced from a aortography
Ateriography
radiography of arteries after injection of radiopaque material into the bloodstream
Angiocardiography
radiography of the heart and great vessels after intravenous injection of a radiopaque solution
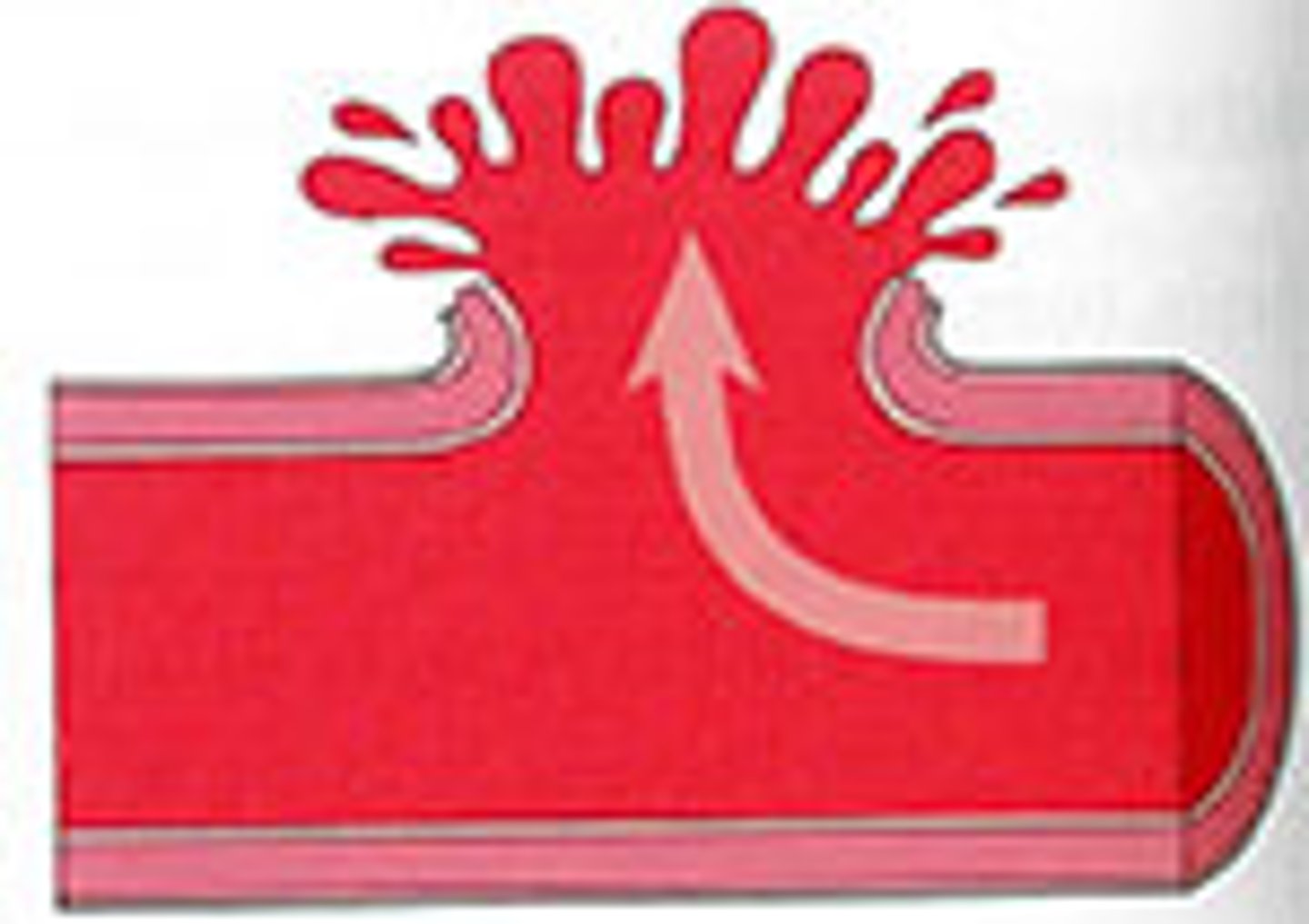
Aneurysm
ballooning out of the wall of a vessel, caused by a congenital defect or weakness of the wall of the vessel
Hemorrhage
loss of a large amount of blood in a short time
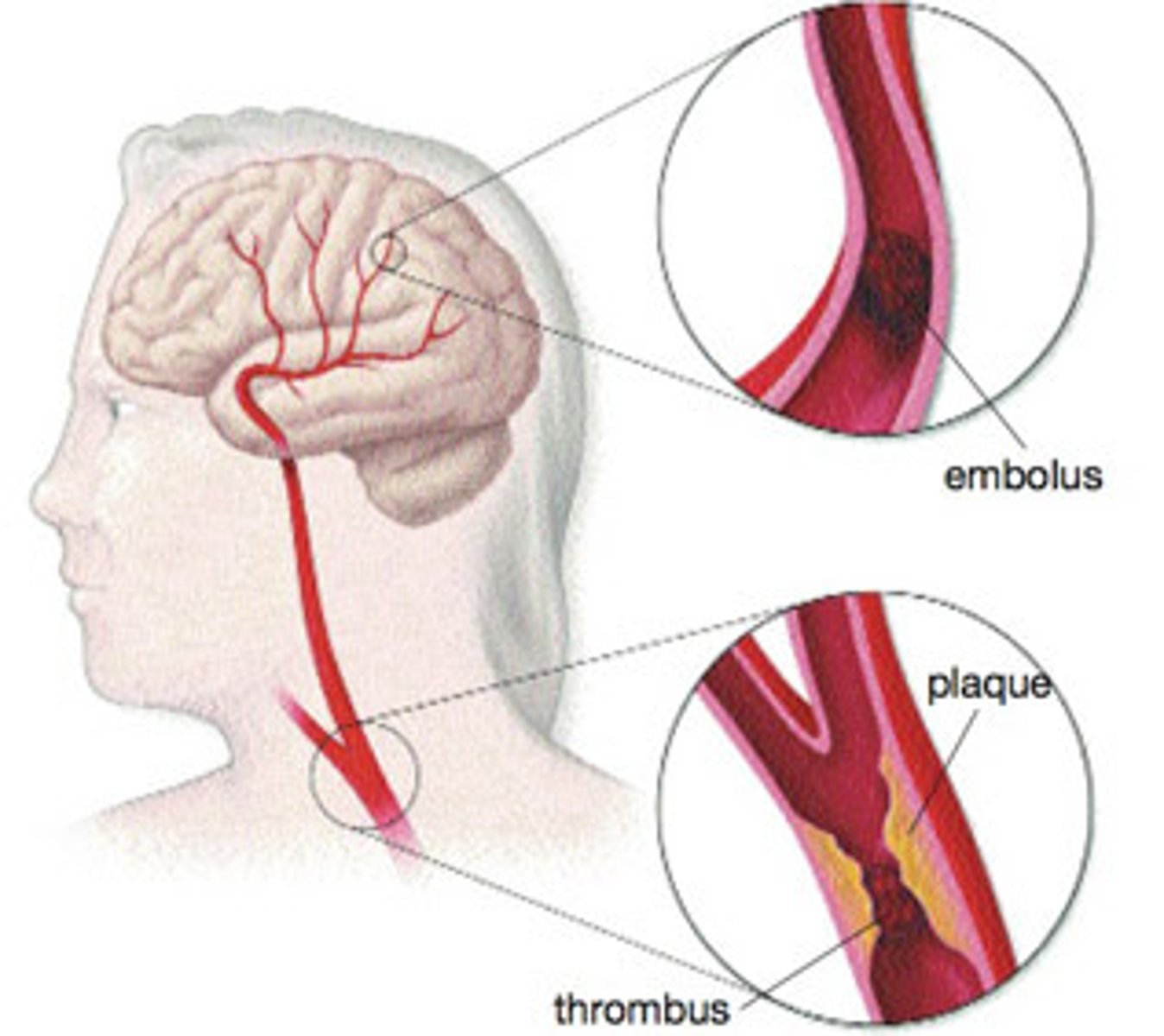
Thrombus
internal blood clot
Embolism
sudden blocking of an artery or lymph vessel by foreign materiel that has been brought to the site of blockage by the circulating blood
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
a.k.a. "Stroke". Lack of blood supply to the brain causing brain damage
Hemorrhagic Stroke
blood vessel bursts and allows blood to seep into brain tissue

Thrombotic Stroke
plaque can cause a clot to form that blocks blood flow
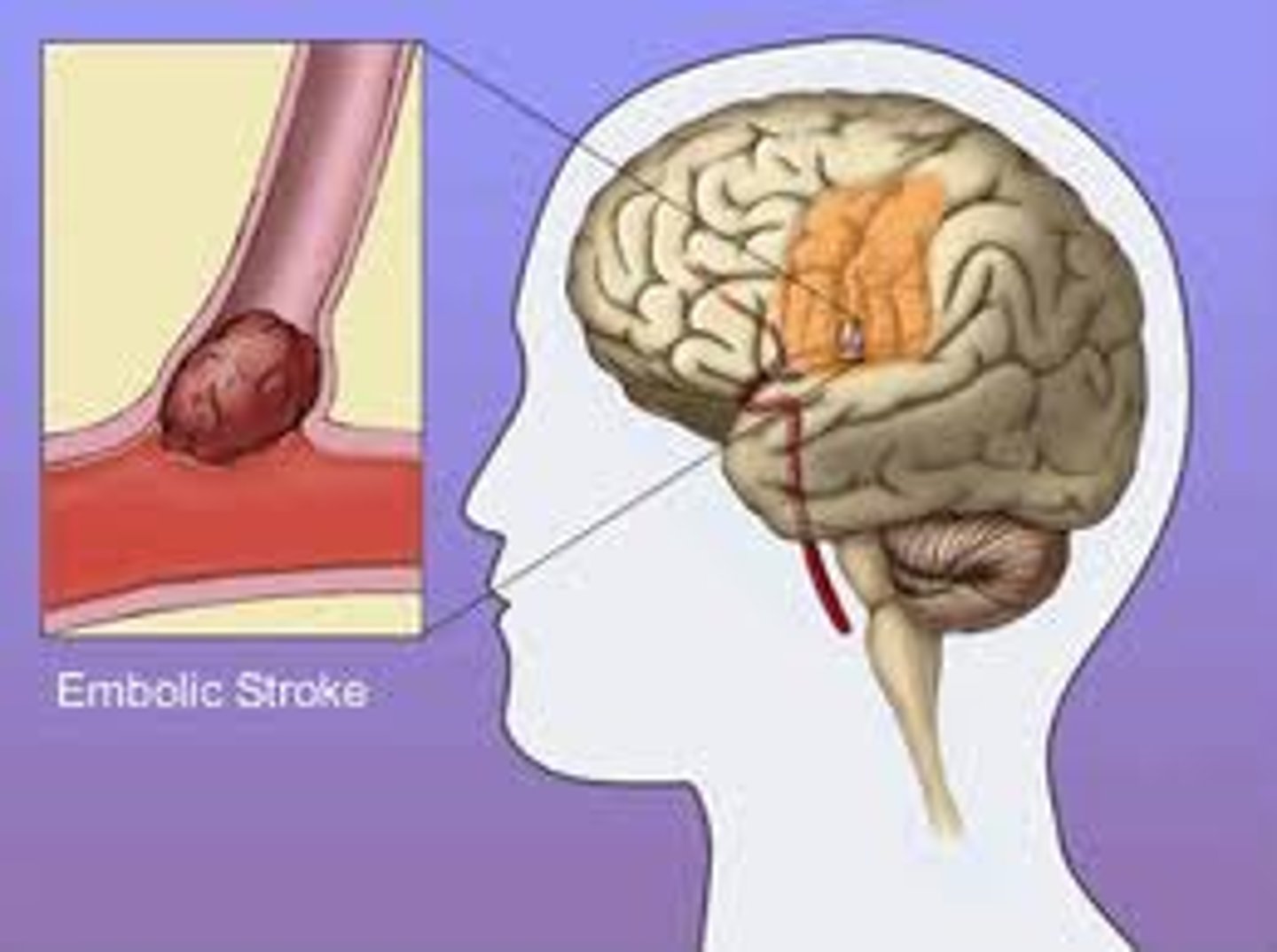
Embolic Stroke
blood clot or other embolus reaches an artery in the brain, lodges there, and blocks the flow of blood
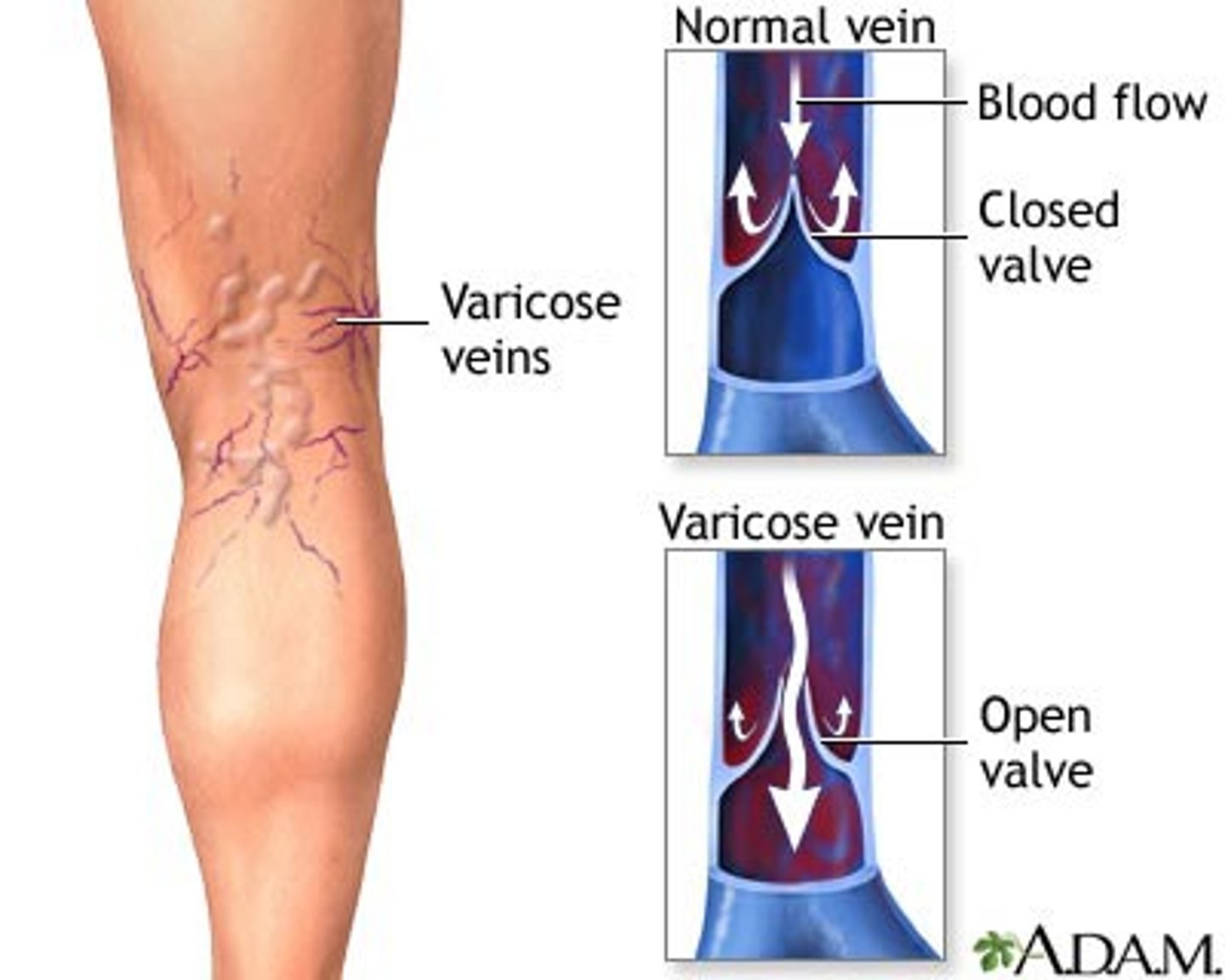
Varicose
swollen and knotted veins that occur most often in the legs
Varicose Veins
-ary
pertaining to
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
method used to divert blood away from the heart and lungs temporarily when surgery of the heart and major vessels is performed, a heart-lung machine collects the blood, replenishes it with oxygen, and returns it to the body
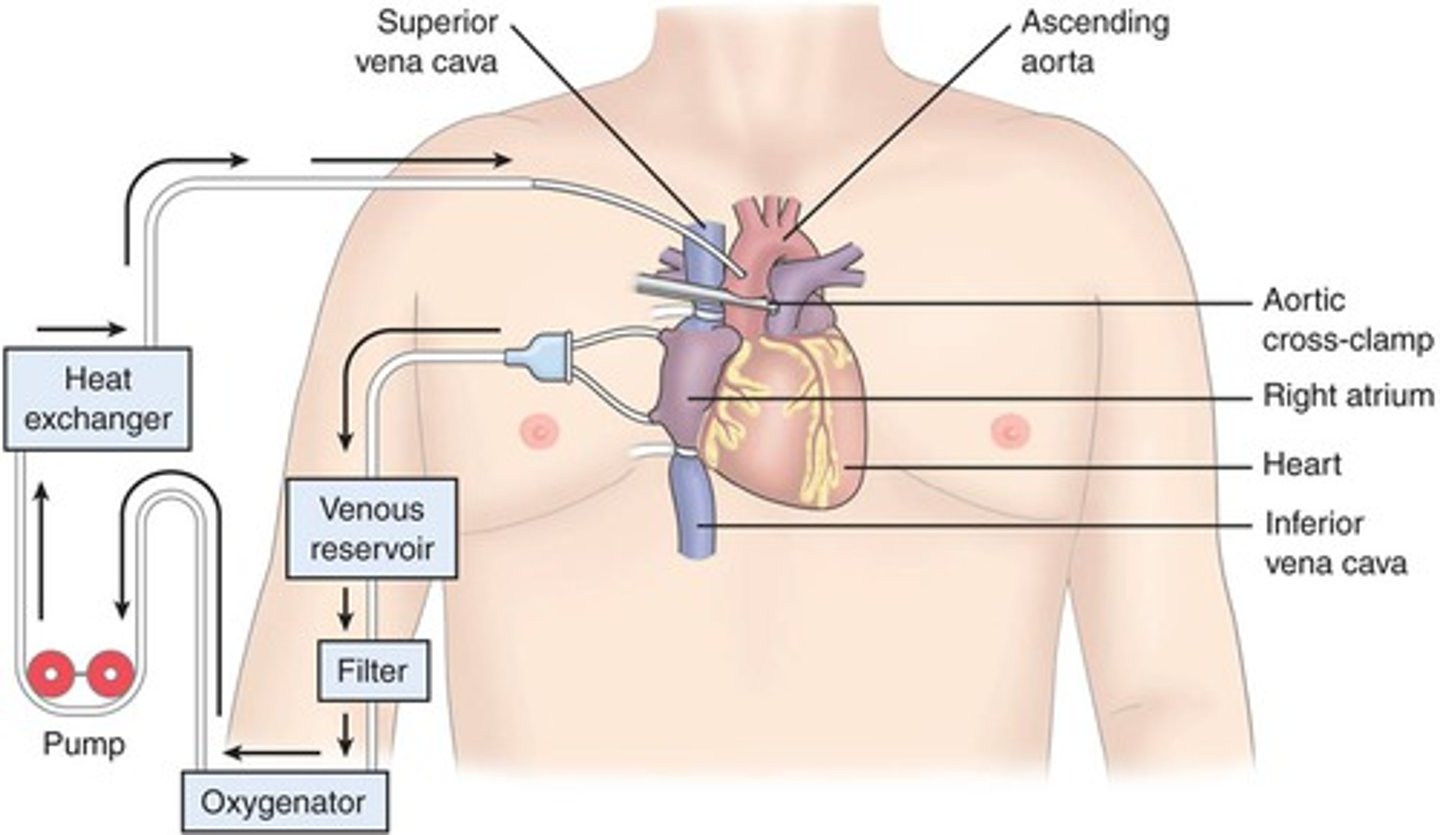
Cardiopulmonary
pertaining to the lungs
Artificial Cardiac Pacemaker
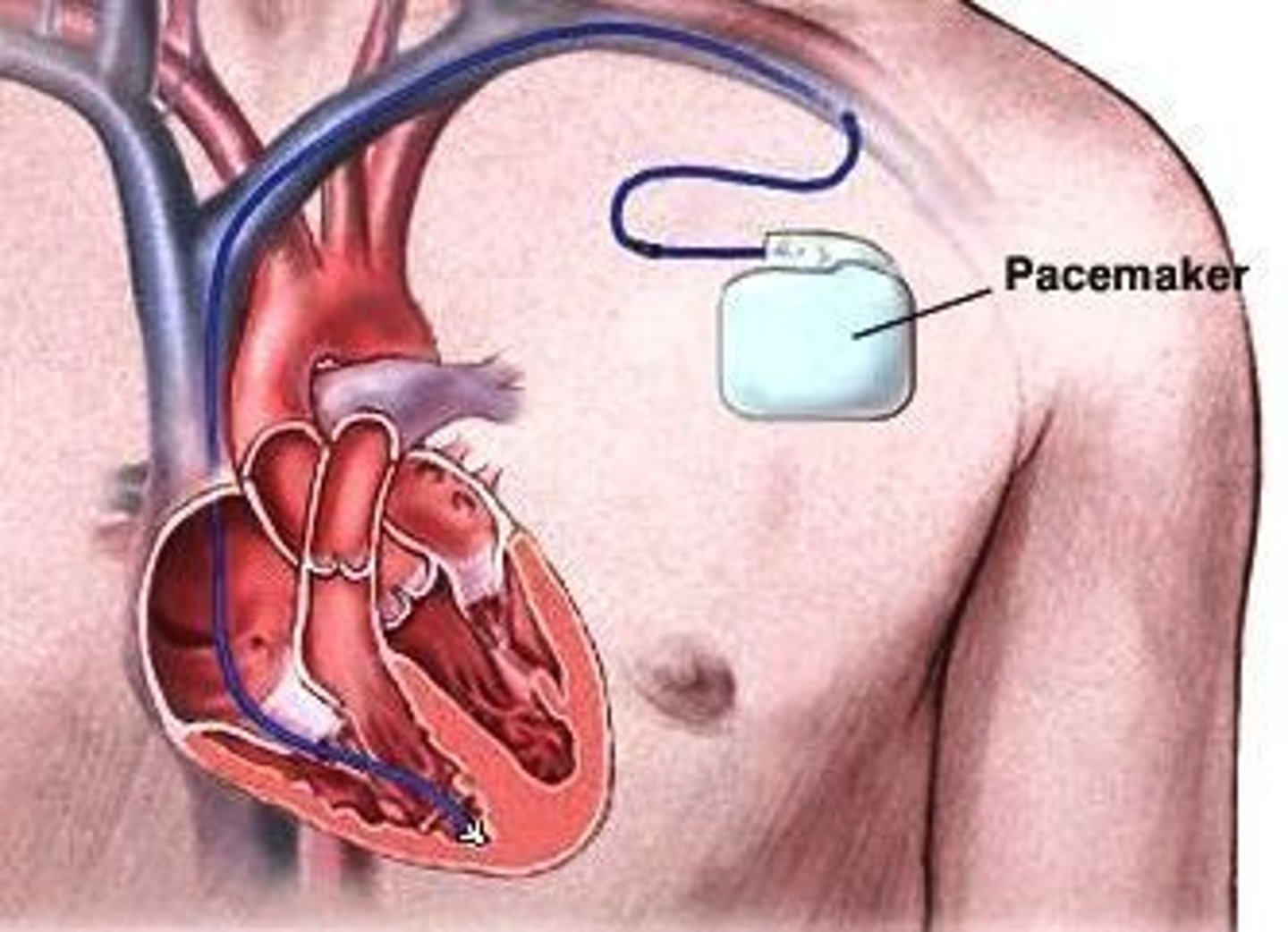
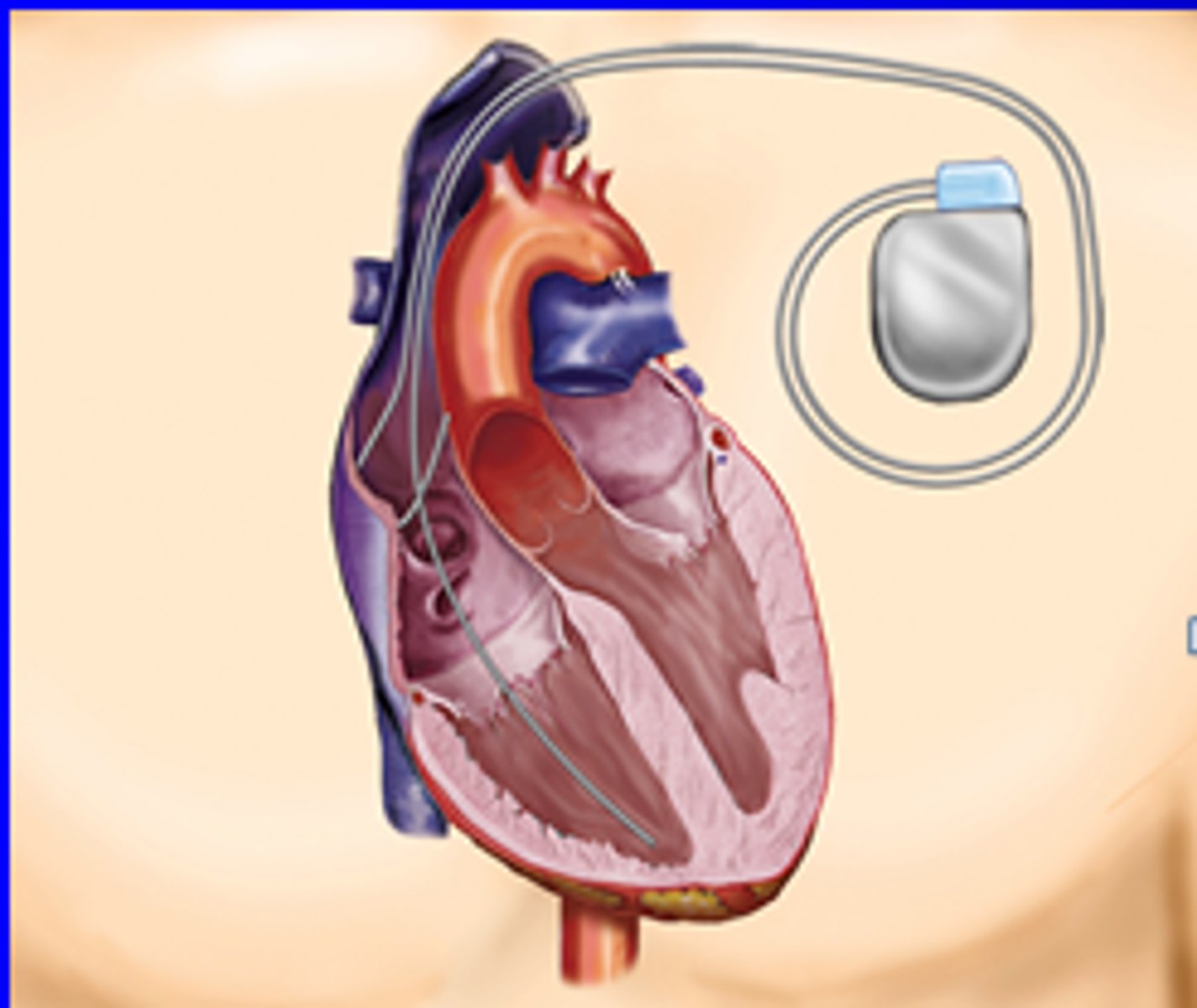
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator
automatically terminates arrhythmia's by delivering low-energy shocks to the heart
Sinoatrial node (SA)
hearts natural pacemaker
Pacemaker
a small-battery powered device generally used to increase the heart rate by electrically stimulating the heart muscle
Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
device that detects sustained ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation and delivers a low energy shock to the heart, restoring the normal rhythm
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
an emergency first-aid procedure to reestablish heart and lunch action if breathing or the heart has stopped
Anti-arrhythmic drugs
prevent, alleviate, or correct an abnormal heart rhythm