P2B - Inheritance 1
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
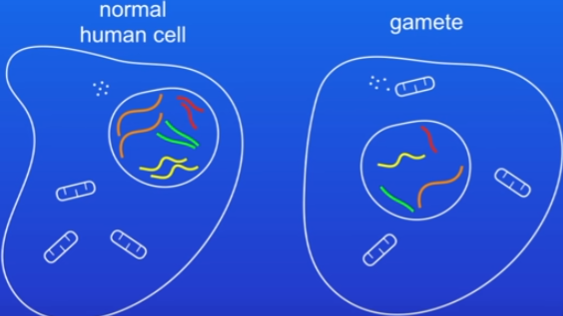
Gametes in animals
ova and sperm (much smaller)
not paired = contain 23 single chromosomes
made by type of cell division called meiosis
Gametes in certain plants
made by meiosis = produces non-identical cells
happens in flowering plants - gametes are pollen and egg cells
Sexual reproduction in animals and flowering plants
fusion of male and female gametes = fertilisation
mixing of genetic info = offspring has DNA from both parents
since every gamete is different, theres variation in offspring
Asexual reproduction
only one parent = no mixing of DNA
doesn't involve gametes = only involves mitosis, not meiosis
offspring are all genetically identical = Clones
seen in aphids and certain plants that grow buds which fall off
v1 - sexual and asexual reproduction
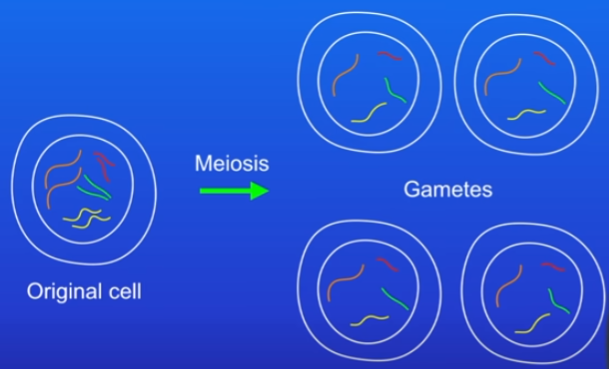
Meiosis
only happens in reproductive organs, humans = testes and ovaries
produces 4 gametes from 1 cell - each gamete is genetically diff from another (has diff alleles)
All chromosomes are copied
Cell divides into 2
Both divide again forming gametes with single chromosomes (half the number of chromosomes)
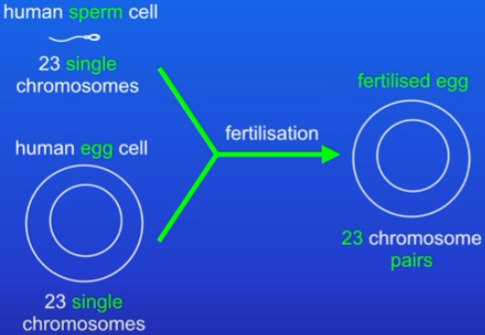
Fertilisation
in sexual reproduction male and female gametes fuse
after this fertilisation, the cell now has the normal number of chromosomes
After fertilisation
cell divides by mitosis producing a clump of identical cells = Embryo
As embryo develops, cells differentiate forming different cell types
in animals; nerve and muscle cells
v2 - meiosis and fertilisation
Adv of sexual reproduction
Variation in offspring
Species can adapt to new environments due to variation = some offspring survive = species survival advantage by natural selection
Humans take advantage of this variation when doing selective breeding for crops (wheat - high yield, good quality)
A disease is less likely to affect all the individuals in a population
Adv of asexual reproduction
one parent needed
No need to find a mate = more efficient in time and energy
Faster than sexual
Fast = very useful when conditions are favourable. Organism produces many genetically identical offspring rapidly
Dis of asexual reproduction
Since genetically identical, theres a risk of all offspring dying if conditions become unfavourable
species may be only suited to one habitat
no variation in a population
Dis of sexual reproduction
time and energy needed to find a mate
not possible for isolated individual
Malaria parasite - its type of reproduction
In human - asexually
In mosquito - sexually
Fungi - its type of reproduction
Asexually by producing spores
Sexually to generate variation in offspring
Flowering plants - its type of reproduction
Sexually to produce seeds
Strawberry plants can also reproduce asexually by sending out runners
Or asexually with daffodils when their bulbs divide
v3 - adv and dis of sexual / asexual reproduction
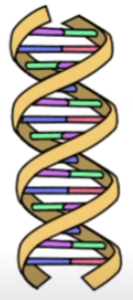
DNA
Molecule that makes up chromosomes
It’s genetic material because it determines our inherited features
consists of 2 strands, each are polymers that wrap around each other to form a double helix
Genes
A gene is a small section of DNA on a chromosome
Each gene encodes for a specific sequence of amino acids to make a specific protein
Humans have thousands, e.g chromosome 9 has over 700 diff genes
Chromosome pairs both have the same genes
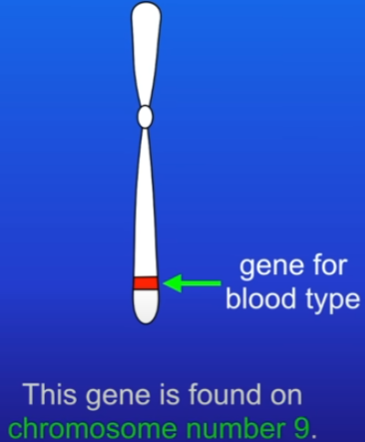
Genome
is the entire genetic material of an organism
Benefits of understanding the human genome
search for genes that are linked to a disease (genes increasing cancer or alzheimer’s disease risk)
understand and treat inherited disorders (cystic fibrosis)
trace human migration patterns from the past = discover peoples ancestry
v4 - DNA and the genome
DNA in detail
DNA is a double stranded polymer of molecules called nucleotides:
Phosphate group attached to sugar molecule (pentagon) which is attached to a molecule called a base
Phosphate and sugar group never change but bases do
Theres are 4 bases - ATCG = DNA has 4 different nucleotides
Same bases always pair on the opposite strands = A&T, C&G = DNA strands are complementary
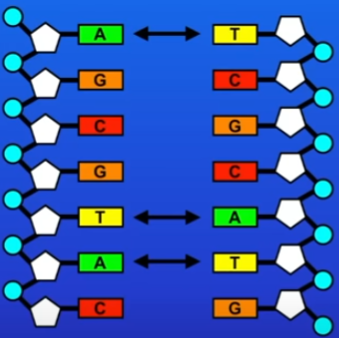
v5 - DNA structure
how DNA determines the structure of proteins
sequence of triplet bases in the gene for that protein determines order of amino acids
specific order of amino acids determines the proteins shape
proteins shape determines function
proteins form enzymes, structural proteins (collagen) or hormones
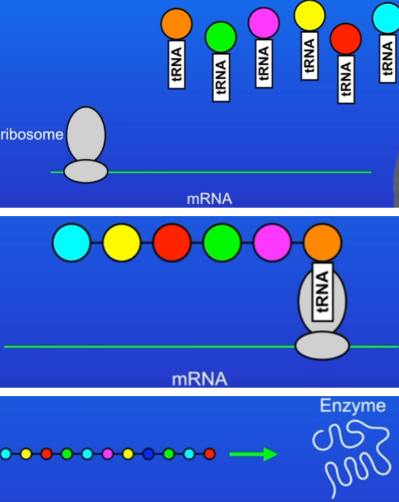
Diagram: a cell making an enzyme (protein), shows a small part of one strand of DNA
the cell reads the DNA sequence as triplets of bases
each triplet encodes for a specific amino acid
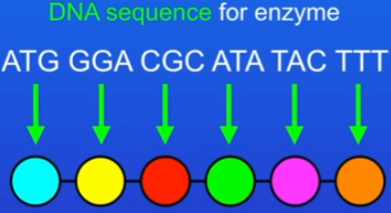
Protein synthesis stage 1
Transcription - the base sequence (ATCG) of a gene is copied into a complementary template molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA).
mRNA is single-stranded molecule.
mRNA now passes out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
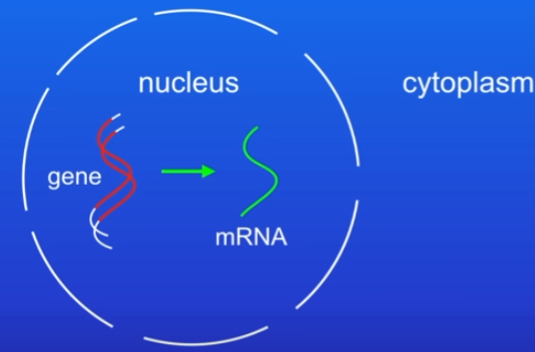
Protein synthesis stage 2
Translation
mRNA attaches to a ribosome.
Amino acids are brought to the ribosome on carrier molecules called transfer RNA (tRNA)
ribosome reads the triplet bases on mRNA
uses this to join together the correct amino acids in the correct order
once protein chain is complete, it folds into its unique shape which lets the protein do its job
v6 - protein synthesis
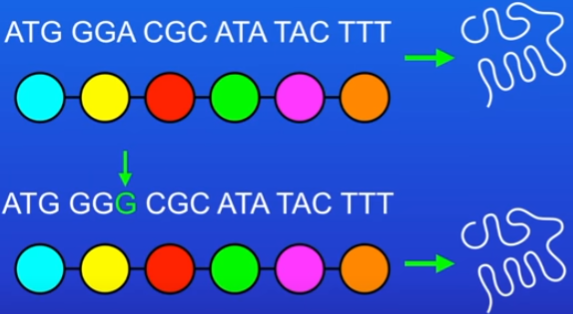
Regular mutation in DNA which codes for proteins
mutation = a change to a base
happen very often
different base triplets can sometimes encode for the same amino acid = most mutations have no effect on the proteins shape/function
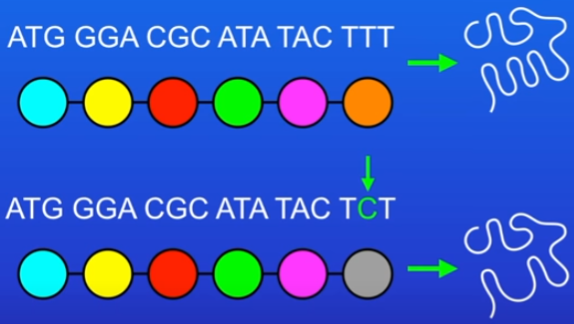
Bad mutation in DNA which codes for proteins
sometimes a mutation can lead to the protein having a different amino acid = shape change has a dramatic effect on a proteins function
e.g active site of an enzyme may change shape, so it can no longer attach to the substrate
if structural protein (collagen) changes shape then it may lose its strength
Mutation in a part of DNA that doesn’t code for proteins
non-coding parts of DNA switch regions of genes on and off
they tell genes when to produce proteins
mutations in these affect how genes are switched on or off
e.g a gene turned on when it should be off
meaning a cell produces a protein that it’s not meant to have at that time
can be a very significant effect e.g uncontrolled mitosis leading to cancer
v7 - Mutations
Who do chromosomes come from
1 in the pair is from your father, and 1 your mother
Genes controlling characteristics, amount of copies of a gene
most characteristics are controlled by many genes acting together (height)
since chromosomes come in pairs, we have 2 copies of every gene
Alleles
versions of a gene
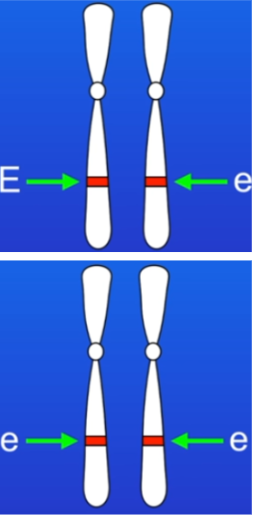
Gene for ear wax example
has 2 alleles - wet (E), dry (e)
ear wax is controlled by a single gene (2 copies of this)
wet ear wax is dominant to the allele for dry ear wax
dry ear wax allele is recessive
1st photo = phenotype is wet
2nd photo = phenotype is dry
Genotype
tells us the alleles present
homozygous
2 copies of the same allele
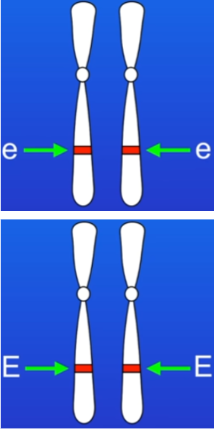
phenotype
tells us characteristics caused by the person’s alleles
heterozygous
2 different alleles
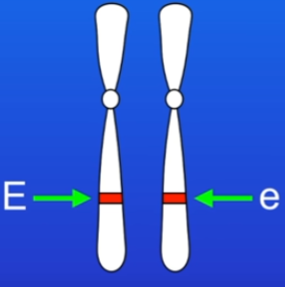
Dominant vs recessive
a dominant allele will show in the phenotype even with 1 copy present
a recessive allele will show in the phenotype only if 2 copies are present
v8 - alleles
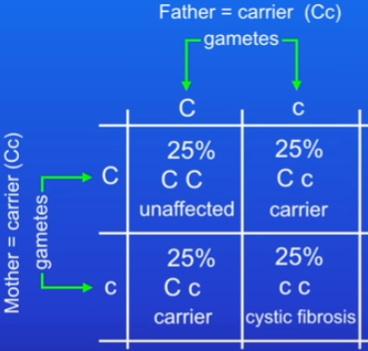
Cystic fibrosis and punnet square
inherited disorder of cell membranes
controlled by a single gene
2 alleles: C = normal cell membrane function (dominant), c = defective cell membrane (recessive)
Carrier = Cc OR cC, carrying a single allele but not having the disorder
Punnet square ratio of carrier to not affected is 1:1
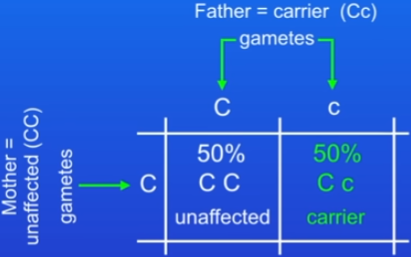
Allele ratio issues
e.g on average 50% will be carriers and 50% won’t
just probabilities means it’s possible that all offspring could be carriers OR all could be unaffected
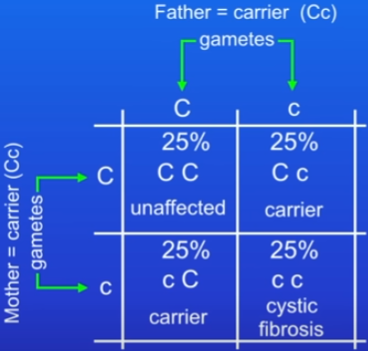
v9 - cystic fibrosis
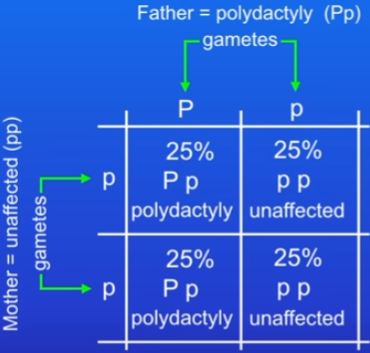
Polydactyly
inherited disorder where people have extra fingers or toes
caused by dominant allele = you can’t be a carrier of it - this is true to any dominant allele because if you have a dominant, you will have the characteristic
in the e.g the ratio is 1:1
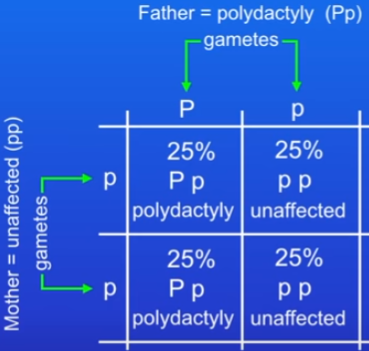
Solution to inherited disorders
Embryo screening:
embryos are tested to see if they have the alleles for inherited disorders
embryos that don’t have the defective alleles are implanted into the woman = develop into healthy offspring
Issues of embryo screening
expensive - some think money should be spent elsewhere in the Health Service
often a large number of embryos are created but small number are implanted = healthy embryos are destroyed and some think this is unethical
in the future we may be able to screen embryos to produce offspring with desirable features e.g taller or more intelligent offspring which people think is unethical
Gene therapy
in the future scientists may be able to correct faulty alleles and use this to treated inherited disorders - still experimental
v10 - polydactyly
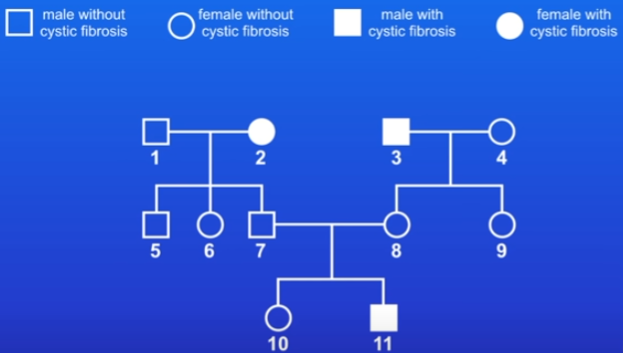
Family tree - only shows phenotypes, not genotypes
practice question: work out genotype of person 2
CF allele is recessive = person 2 must have the genotype cc.
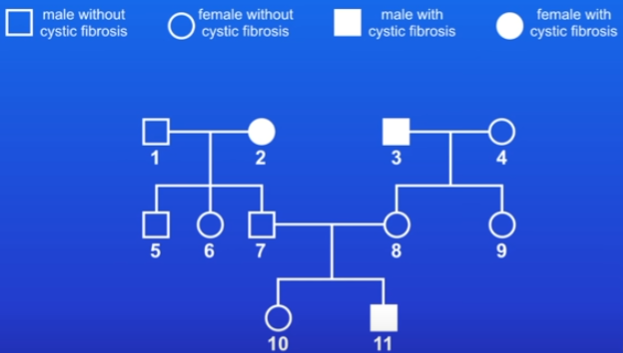
Family tree - only shows phenotypes, not genotypes
practice question: give one piece of evidence that CF is caused by a recessive allele
person 11 has CF but neither parent has it
7&8 are carriers and the CF allele must be recessive
if CF was dominant, then at least 1 of the parents would have to have CF in order to pass the allele on to person 11
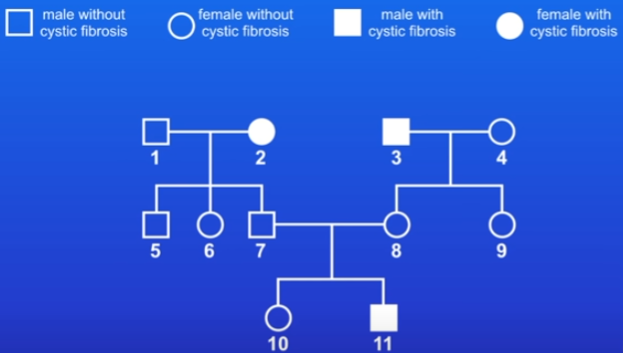
Family tree - only shows phenotypes, not genotypes
practice question: if person 7&8 had another child, what’s the chance that it would have CF?
7&8 are both carriers (heterozygous) = cC or Cc
1 in 4 chance
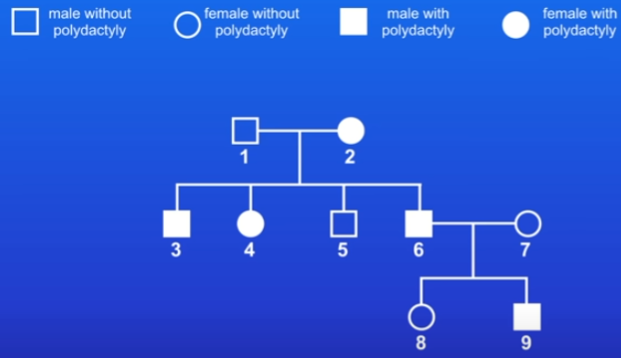
Family tree - only shows phenotypes, not genotypes
practice question: what’s the genotype of person 3?
alleles are inherited each from 1 parent
polydactyly is dominant
person 1 must be pp and person 2 can be PP or Pp/pP
person 3 has p from person 1 and has P from person 2 because they have polydactyly
person 3 = pP/Pp
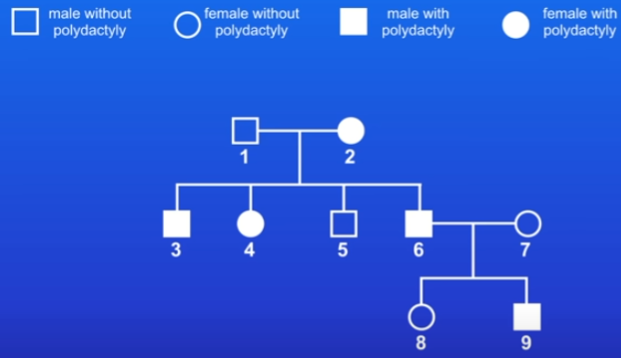
Family tree - only shows phenotypes, not genotypes
practice question: if person 6 and 7 have another child, whats the probability that they have poldactyly?
person 6 = pP/Pp
person 7 = pp
probability = 50%
v11 - family trees
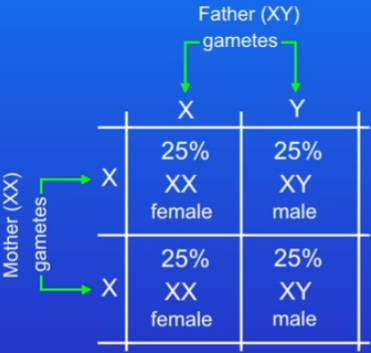
Inheritance of sex
22 chromosome pairs contain the genes that determine inherited characteristics only
1 of the pairs contains genes that determine sex
males = XY
females = XX
Inheritance of sex by punnet square
just probabilities - several offspring and ALL could be male or female
v12 - inheritance of sex