Ch 10 - Photosynthesis
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/116
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
How do photosynthetic cells use light to change carbon dioxide and water into organic molecules and oxygen?
Carbon dioxide and water are used in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis will also use light energy in order to generate organic molecules and dioxide from the CO2 and H2O that we started with.
\
These organic molecules are then used in cellular respiration which generate ATP and our starting molecules. Now the cycle can take place again.
\
These organic molecules are then used in cellular respiration which generate ATP and our starting molecules. Now the cycle can take place again.
2
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process that converts light energy into chemical energy stored in sugars and other organic molecules
3
New cards
Photosynthesis takes place in which organisms?
Plants, algae, and some photosynthetic prokaryotes
4
New cards
Directly or indirectly, _____ will nourish the entire living world.
Photosynthesis
5
New cards
What are the two types of organisms with regard to how they gain their energy?
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
6
New cards
Autroph
An organism that sustains itself without eating anything derived from other organisms. It makes its own food inside its body.
7
New cards
Almost all plants are __*_____*__
Autotrophs and producers (they provide nutrients and oxygen for other organisms)
8
New cards
Photoautotroph
Organisms that use light as a source of energy to synthesize organic substances (ex: plants)
9
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or substances derived from them
10
New cards
Consumers
Living organisms that have to hunt, gather and eat their food. They are heterotrophs.
11
New cards
Decomposers
Organisms that break down dead and decaying organic matter. They are also considered heterotrophs/consumers because they consume organisms for their energy instead of producing their own food.
12
New cards
Chloroplasts
An organelle found in plants and photosynthetic protists that absorb sunlight and use it to synthesize organic compounds from CO2 and H2O
\
They are the site of photosynthesis.
\
They are the site of photosynthesis.
13
New cards
_____ are the major sites of photosynthesis in most plants.
(Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis but this question is asking about which part of the plant does the photosynthesis)
(Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis but this question is asking about which part of the plant does the photosynthesis)
Leaves
14
New cards
Mesophyll
The tissue of the interior of the leaf. The cells of this tissue are specialized for photosynthesis.
15
New cards
Chloroplasts are found mainly in the cells of the ____
Mesophyll
16
New cards
In C3 and CAM plants, mesophyll cells are located where?
Between the upper and lower epidermis
17
New cards
In C4 plants, mesophyll cells are located where?
Between the bundle-sheath and the epidermis
18
New cards
Stoma (plural, stomata)
A microscopic pore surrounded by guard cells in the epidermis of leaves and stems that allow gas exchange between the environment and the interior of the plant
19
New cards
CO2 enters the leaf and O2 exits, by way of microscopic pores called ____
Stomata
20
New cards
A typical mesophyll cell has about how many chloroplasts?
About 30 to 40
21
New cards
A chloroplast has how many membranes?
Two
22
New cards
Stroma
The dense fluid within the chloroplast that is involved in the synthesis of organic molecules from CO2 and H2O
23
New cards
Stroma surrounds the _____
thylakoid membrane
24
New cards
Stroma contain ____
Ribosomes and DNA
25
New cards
Thylakoid
A flattened, membranous sac inside a chloroplast. Thylakoid membranes convert light energy to chemical energy of ATP and NADPH
26
New cards
Thylakoids often exist in interconnected stacks called _____
Grana
27
New cards
Chlorophyll
A green pigment that gives leaves their color. Located in thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts.
28
New cards
Light absorbed by _____ drives the synthesis of organic molecules in the chloroplasts
Chlorophyll
29
New cards
6CO2 + 12 H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
\
This is the equation of _____
\
This is the equation of _____
**Photosynthesis**
\
Carbon dioxide + water + light energy become Glucose, Dioxide, and Water
\
Carbon dioxide + water + light energy become Glucose, Dioxide, and Water
30
New cards
Photosynthesis and _____ undo each other
Cellular respiration
31
New cards
Chloroplasts split water into _____, incorporating the electrons of hydrogen into sugar molecules
Hydrogen and Oxygen
32
New cards
What type of process is photosynthesis?
Redox Process
33
New cards
How is photosynthesis a redox process?
It oxidizes water and reduces carbon dioxide
34
New cards
Photosynthesis consists of two processes. These two stages are ______.
**Light reactions** (the photo part of photosynthesis) **and the** **Calvin Cycle** (the synthesis part of photosynthesis)
35
New cards
Light reactions
The first stage in photosynthesis. These reactions convert solar energy to ATP and NADPH, split water and release oxygen
36
New cards
Light reactions take place where?
On the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts or on the membranes of certain prokaryotes
37
New cards
Calvin Cycle
The second stage of photosynthesis. This stage involves fixation of atmospheric CO2 and reduction of the fixed carbon into carbohydrate. Produces sugar.
38
New cards
NADP+
An acceptor. This is the oxidized form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate, an electron carrier that can accept electrons, becoming NADPH.
39
New cards
Light reactions use solar energy to reduce NADP+ to _____ by adding a pair of electrons along with an H+
NADPH
40
New cards
NADPH
The reduced form of NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
\
It temporarily stores energized electrons produced during the light reactions. It also reduces electron acceptors.
\
It temporarily stores energized electrons produced during the light reactions. It also reduces electron acceptors.
41
New cards
Function of NADPH
Temporarily stores energized electrons produced during the light reactions and reduces electron acceptors
42
New cards
Photophosphorylation
The process of generating ATP from ADP and phosphate by means of chemiosmosis. This process is done during light reactions.
43
New cards
What is the energy currency of cells?
ATP
44
New cards
Calvin cycle is named after ____
Melvin Calvin
45
New cards
The first step of the Calvin cycle is carbon fixation, which is?
The initial incorporation of carbon from CO2 into an organic compound by an autotrophic organism
46
New cards
Light
A form of energy known as electromagnetic energy, also called electromagnetic radiation
47
New cards
Like other electromagnetic energy, light travels in _____
Rhythmic waves
48
New cards
Wavelength
Distance between crests of waves
49
New cards
Wavelength determines ____
The type of electromagnetic energy
50
New cards
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The entire spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, ranging in wavelength from less than a nanometer to more than a kilometer
51
New cards
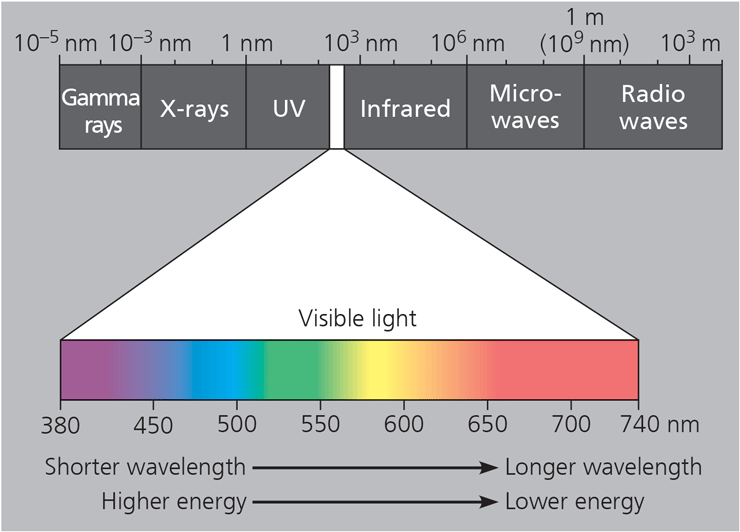
Visible Light
The segment of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be detected as various colors by the human eye, ranging in wavelength from about 380nm to about 740nm
52
New cards
Photons
A quantum, or discrete quantity, of light energy that behaves as if it were a particle
53
New cards
Light behaves as though it consists of discrete particles called _____
Photons
54
New cards
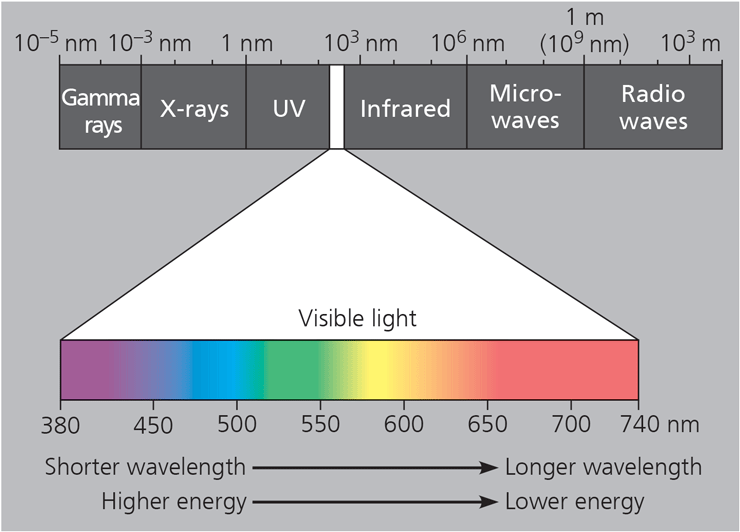
The amount of energy is inversely related to the wavelength of the light. The shorter the wavelength, the ____ the energy of each photon of that light and vice versa.
Greater
55
New cards
Plants like which light colors?
Blue (450-500nm) and Red (650-750nm)
56
New cards
Gamma Rays can result in what illness?
Cancer
57
New cards
X-Rays can result in what illness?
Sterility
58
New cards
UV Rays if long term can give you what illness?
Skin Cancer
59
New cards
UV Rays can be seen by which animals?
Birds and insects
60
New cards
Infrared light can be seen by which animals?
Reptiles, bats, and insects
61
New cards
Pigments
Substances that absorb visible light. Different pigments absorb different wavelengths.
62
New cards
Wavelengths that are not absorbed are _____
Reflected or transmitted. For example, chlorophyll looks green because it does not absorb green wavelengths.
63
New cards
Absorption Spectrum
A graph plotting a pigment’s light absorption versus wavelength
64
New cards
Spectrophotometer
An instrument that measures the proportions of light of different wavelengths absorbed and transmitted by a pigment solution
65
New cards
*Chlorophyll a*
The main photosynthetic pigment. It participates directly in light reactions.
66
New cards
*Chlorophyll b*
An accessory photosynthetic pigment that transfers energy to *chlorophyll a.*
67
New cards
Action Spectrum
A graph that profiles the relative effectiveness of different wavelengths of radiation in driving a particular process
68
New cards
The absorption spectrum of *chlorophyll a* suggests that these two colors work best for photosynthesis: ______
Violet-blue and Red
69
New cards
Other accessory pigments include Carotenoids, which are?
An accessory pigment, either yellow or orange, in the chloroplasts of plants and in some prokaryotes. By absorbing wavelengths of light that chlorophyll cannot, carotenoids broaden the spectrum of colors that can drive photosynthesis.
70
New cards
Accessory pigments, such as *chlorophyll b*, function to _____. These pigments are also called carotenoids.
Broaden the spectrum used for photosynthesis
71
New cards
When a pigment absorbs light, its state changes from *_____* to __*____*__
Ground state to excited state which is unstable
72
New cards
When excited electrons fall back to the ground state, photons are given off, an afterglow called _____
Fluorescence
73
New cards
Photosystem
**A light-capturing unit is located in the chloroplast's thylakoid membrane or in some prokaryotes' membranes.**
\
Below is extra info I will put on a separate question:
\
There are two types of photosystems: Photosystems 1 and 2
\
A photosystem consists of a reaction-center complex surrounded by numerous light-harvesting complexes
\
Below is extra info I will put on a separate question:
\
There are two types of photosystems: Photosystems 1 and 2
\
A photosystem consists of a reaction-center complex surrounded by numerous light-harvesting complexes
74
New cards
There are two types of photosystems; What are they?
Photosystem I and Photosystem II (they are numbered by the order of their discovery)
75
New cards
A photosystem is composed of _____
A reaction-center complex surrounded by several light-harvesting complexes. These light-harvesting complexes funnel the energy of photons to the reaction center.
76
New cards
Reaction-Center Complex
An organized association of proteins holding a special pair of *chlorophyll a* molecules and a primary electron acceptor.
77
New cards
Where is the reaction-center complex located?
Center of a photosystem
78
New cards
What triggers the light reactions of photosynthesis?
Reaction-Center Complexes
79
New cards
Light-Harvesting Complex
**A complex of proteins associated with pigment molecules** **that captures light energy and transfers it to reaction center pigments in a photosystem**
\
Includes *chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b*, and carotenoids
\
Includes *chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b*, and carotenoids
80
New cards
The two photosystems work together to use light energy to generate ______
ATP and NADPH
81
New cards
Photosystem II functions first and is best at absorbing a wavelength of _____
680nm (red)
82
New cards
Photosystem I is best at absorbing a wavelength of _____
700 nm
83
New cards
Photosystem I is used to create _____
NADPH
84
New cards
Photosystem II is used to make _____
ATP
85
New cards
Primary Electron Acceptor
In the thylakoid membrane of a chloroplast or in the membrane of some prokaryotes, a specialized molecule that shares the reaction-center complex with a pair of *chlorophyll a* molecules and that accepts an electron from them
86
New cards
The first step of the light reactions is?
Solar-powered transfer of an electron from a *chlorophyll a* molecule to the primary electron acceptor
87
New cards
Photosystem II
One of two light-capturing units. It has two molecules of *P680 chlorophyll a* at its reaction center
\
Located in a chloroplast’s thylakoid membrane or in the membrane of some prokaryotes.
\
Located in a chloroplast’s thylakoid membrane or in the membrane of some prokaryotes.
88
New cards
Photosystem I (PS I)
One of two light capturing units. It has two molecules of P700 *chlorophyll a* at its reaction center
\
Located in a chloroplast’s thylakoid membrane or in the membrane of some prokaryotes
\
Located in a chloroplast’s thylakoid membrane or in the membrane of some prokaryotes
89
New cards
Linear/Noncyclic Electron Flow
The primary route of electron flow during the light reactions that involves both photosystems and produces ATP, NADPH, and O2. The net electron flow is from H2O to NADP+
90
New cards
Cyclic Electron Flow
A route of electron flow during the light reactions of photosynthesis that uses only photosystem I and produces surplus ATP, satisfying the higher demand in the Calvin Cycle
91
New cards
**Similarities and Differences Between Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts and Mitochondria**
\
1. Chloroplasts and mitochondria generate ATP by _____but have a different source of energy
2. Mitochondria transfer chemical energy from food to ATP; Chloroplasts transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP
3. The spatial organization of chemiosmosis different in chloroplasts and mitochondria
\
1. Chloroplasts and mitochondria generate ATP by _____but have a different source of energy
2. Mitochondria transfer chemical energy from food to ATP; Chloroplasts transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP
3. The spatial organization of chemiosmosis different in chloroplasts and mitochondria
Chemiosmosis
92
New cards
**Similarities and Differences Between Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts and Mitochondria**
\
1. Chloroplasts and mitochondria generate ____ by chemiosmosis but have a different source of energy
2. Mitochondria transfer chemical energy from food to ATP; Chloroplasts transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP
3. The spatial organization of chemiosmosis different in chloroplasts and mitochondria
\
1. Chloroplasts and mitochondria generate ____ by chemiosmosis but have a different source of energy
2. Mitochondria transfer chemical energy from food to ATP; Chloroplasts transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP
3. The spatial organization of chemiosmosis different in chloroplasts and mitochondria
ATP
93
New cards
**Similarities and Differences Between Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts and Mitochondria**
\
Both give energy to ATP, but how is it different for mitochondria and chloroplast?
\
Both give energy to ATP, but how is it different for mitochondria and chloroplast?
Mitochondria transfer chemical energy from food to ATP and chloroplasts transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP
94
New cards
The Calvin Cycle used ATP and the reducing power of NADPH to convert CO2 to ____
Sugar
95
New cards
Like the citric acid cycle, the calvin cycle will _____
regenerate its starting material after molecules enter and leave the cycle
96
New cards
___ enters the Calvin Cycle as CO2 and leaves as a sugar named glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
Carbon
97
New cards
Carbon enters the Calvin Cycle as CO2 and leaves as a sugar named _____
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
98
New cards
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
A three-carbon carbohydrate that is the direct product of the Calvin Cycle; it is also an intermediate in glycolysis
99
New cards
For the net synthesis of one G3P, the calvin cycle must take place how many times?
Three times, therefore also needed 3 molecules of CO2
100
New cards
The Calvin Cycle has 3 phases. What are they in order?
Carbon Fixation, Reduction, and Regeneration