Act, basic grammar, via Princeton review
1/60
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
The four Cs
Complete (sentences), consistent (tense, content), clear (message is clear) consise(uses little words to express idea)
Five steps
Identified topic. 2. Context clue and answer. 3. POE, use rules of grammar to eliminate. 4. Ear. 5. Don fix what’s broken
Singular Subjects:
I(am), you(are), she(is), he(is)
Plural Subjects
They(are), we (are), you guys (are)
Collective Nouns:
The team is practicing hard.
The committee meets every Monday.
My family enjoys hiking together.
Despite the subject reflecting something plural, it needs to go with a singular pronoun thus it is singular.
Present Perfect
Something that started in the past and continues into the present
Form: has/have + past participle]
She has been in college for a year now.
Past Perfect
Two events that happened in the past but started in different times
Form: had + past participle
He had studied before the test.
Future Perfect
An event that will happen in a definite time
Form: will have + past participle
By next year, I will have graduated.
Present Perfect Continuous
Form: has/have been + present participle verb + -ing
She has been working all day.
What is past prefect?
to show an action completed before another action in the past.
Present Perfect
to indicate an action that started in the past and continues today.
Future Perfect
an action that will be completed at some point in the future
Irregular Verb: Go
Present: Go
Past: Went
Past Participle: Gone
How to distinguish the participle form of an irregular verb?
The participle form sometimes ends on “en” or “n” they DON’T typically end in “ed”
After years of practice, he has finally driven across the country
Adverbs
Adverbs modify everything; verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs by providing information about how, when, where, or to what extent
She sings beautifully.
He ran quickly to catch the bus.
Adjectives:
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns by describing, quantity and points out something.
It was a big house.
This book is interesting
There are many friends
Stop punctuation
ONLY used between two complete clauses.
Comes with FANBOYS
Go punctuation
links anything expect two complete ideas
Four reasons the ACT uses commas
Stop: Comma can’t be bettwen two complete sentences, has to go with FANBOYS.
Go: complete an idea or link complete idea with incomplete in either order.
List: Commas used to separate items in a list. Act always had a comma before the “and” in a list with more then three items
Unnecessary info: The is still complete without it. Commas are added around unnecessary info.
Half stop.
Colons are used to link complete and incomplete clauses.
Semi-colon are used to link ONLY complete clauses.
Dashes used with unnecessary info
Relative Pronouns
Who
Use: Refers to people.
Example: "The man who is standing there is my uncle."
Whom
Use: Refers to people (object form).
Example: "To whom did you give the book?"
Which
Use: Refers to things or animals.
Example: "The car which is parked outside is mine."
That
Use: Refers to people, things, or animals.
Example: "The book that I borrowed from you is excellent."
Whose
Use: Indicates possession.
Example: "The man whose car broke down called for help."
Conjunctions defined and examples
Coordinating Conjunctions: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet
-Joins words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance.
"He likes tea and he likes coffee."
Subordinating Conjunctions: although, because, if, when, while, since, before, after, until, unless, etc.
-Joins a subordinate (dependent) clause to a main (independent) clause.
“She will go outside if it stops raining."
Purpose of conjunctions.
Used to link ideas by making one or both clauses incomplete.
"She wants to go for a walk but it's raining outside."
Relative pronouns.
links a incomplete clause with a complete clause by adding more information to the noun.
Example: "The book that I borrowed from the library is very interesting."
“The girl whose bag was stolen reported it to the police."
“The man who lives next door”
First person, subject, pronouns.
I, We
First person object pronouns
Me, Us
First person possessive pronouns
My, Mines, our, ours
Second person subject pronouns
You
Second person object pronouns
You
Second person possessive pronouns.
Your, yours
Third person subject pronouns
They, he, she, it
Third person Object pronoun.
Her, him, it, them
Third person Possessive pronoun.
Hers, his, its, her, their, theirs
Example Sentence with Subject Pronouns
I and she are planning to visit the museum tomorrow.
the verbs are changing in the answer choices. What is the ACT testing?
Consistency of verbs
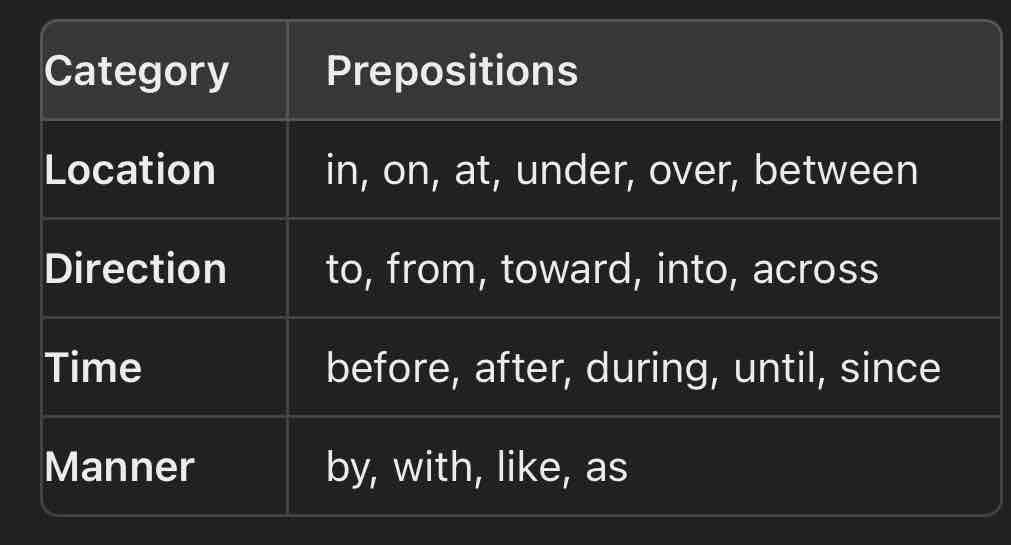
What are prepositions?
Little words that show relationships between nouns and modifys what describes the noun. They often indicate direction, time, location, or manner.
Compound Prepositions
A preposition plus its object (noun or pronoun) creates a phrase, e.g., "on the table," "at the park."
Ending Sentences with Prepositions
It's acceptable in modern English (e.g., "Where are you at?").
Usage Tips. Prepositions.
Always check if the preposition fits the context of the sentence.
Remember that some verbs require specific prepositions (e.g., "interested in," "depend on").
always look to the left of the preposition to find the subject. They are used to distract you on the ACT.
Quick Quiz: Fill in the blanks with the correct preposition:
The book is ______ the shelf. (in/on/at)
He went ______ the store. (to/from/beside)
They arrived ______ 5 PM. (before/after/at)
on
to
before
3 steps for using the correct verb on the ACt
Identify the subject. Verb agrees with subject. (Pural/ singular)
Identify the tense or participle. Use context to determine weather verb should be past, present or future.
Pick the concise answer. Shortest and free or errors.
What’s the difference between conjunction and preposition?
Conjunctions Connects clauses/phrases, while prepositions Show relationships between nouns (or pronouns) and other words in a sentence.
Position |
Conjunctions: Often between clauses |
preposition: Before a noun/pronoun |
How to spot a verb?
A verb is an action, state of being and feeling.
Do particles must always go
With the helping verb?
Yes, the simple past works on its own but prefect tense words needs help “to have” to function.
I went somewhere.
I’ve gone somewhere.
Passive vs active voice
Active voice preserve the performer of action. Passive voice promotes the reciver of action.
Brice made rice.
The rice was made by Brice.
Act prefers Active voice or passive voice?
Active voice.
How to spot a passive voice
Look out for the verb “to be” And prepositions “by”
Modifier
Definition
a word, phrase, or clause that provides additional information about another word, typically an adjective, adverb, or noun.
Types of Modifiers
Adjective Modifiers:
Example: The red car is fast.
Adverb Modifiers:
Example: She runs quickly.
Phrases as Modifiers:
Example: The book on the table is mine.
Clauses as Modifiers:
Example: The man who is wearing a hat is my uncLe.
Caution For modifiers
Misplaced Modifiers: Can cause confusion.
Example:
Walking to the store, the rain soaked my clothes. (Confusing)
Correct Placement:
Walking to the store, I got soaked by the rain.
What pronouns are misleadingly singular ?
Everyone, anybody, nobody, somebody, someone, no one and each.
What is the pronoun “whose” used for?
It is the possessive form of the relative pronoun who, whom, whose and it.
interrogative pronouns
Pronouns used when asking questions.
Who are you?
Whom I stabbed
Whose watch is this?
Relative pronouns
Pronouns used to introduce clauses.
My uncle, who lives next door.
what is the basic approach with pronouns?
1) has to be consistent with the noun, gender, number. 2) has to be the correct pronoun
What’s one way test writers confuse you with pronouns?
By using the same contractor of the same pronoun. Possessive form it’s contractor form.
What does contraction mean in grammar?
When a pronoun is apostrophized to abverate the helping verb.
They’re.
You’re.
I’ll
It’s.
Never use possessive pronouns with apostrophes.
Apostrophizing nouns
Singular nouns need “‘s” to show possession. Pural nouns ending in “s” just add an apostrophe after it.