Psych brain and behavior final
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Which regions of the cortex project to the basal ganglia?
all areas of the cortex project to the basal ganglia
3 multiple choice options
neurons that fire when we execute a movement and when we observe another person making the same movement are referred to as:
mirror neurons
3 multiple choice options
the gate theory of pain can help explain:
why rubbing an injury can reduce pain.
3 multiple choice options
The cerebellum's role in motor behavior is primarily involved with:
timing of movements and maintaining movement accuracy
3 multiple choice options
to which of the following systems is the somatosensory system most closely linked?
motor
3 multiple choice options
the sensory and motor cortices are:
continuously modified with learning and experience
3 multiple choice options
Emotion can be considered _____, whereas motivation can be considered _____.
cognitive interpretations of subjective feelings; behavior that is purposeful and goal directed
_____ skin is much more richly endowed with receptors and is exquisitely more sensitive to a wider range of stimuli than ____ skin.
Glabrous (hairless); hairy
Nociception
perception of pain
Signals from motor cortex to the spinal cord are transmitted via cortical layer(s):
cortical layers 5 to 6
action potentials in the semicircular canals are stimulated by:
bending hair cells
3 multiple choice options
which part of the brain is responsible for planning movements?
frontal lobe
3 multiple choice options
vivid dreaming usually takes place in:
REM sleep
3 multiple choice options
If you are cold, you begin to shiver. If you are hot, you begin to sweat. These are examples of:
physiological responses
3 multiple choice options
sleep is important for
memory consolidation
3 multiple choice options
During LTP_____ (as well as Na+) enters postsynaptic NMDA receptors to begin a chain of events that lead to an increase in the number of postsynaptic AMPA receptors.
Ca2+
3 multiple choice options
Language, memory, and emotion are:
constructs and inferred from behavior
The medial forebrain bundle helps transmit ____ to the ____.
dopamine; basal ganglia
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following structures is not part of the classic Limbic circuit once thought to mediate emotion?
the anterior putamen
3 multiple choice options
Olfactory receptors neurons code different scents because:
each neuron responds to a specific scent.
2 multiple choice options
Another word for explicit memory is:
episodic memory
according to Robinson and Burridge, wanting is controlled by ___, whereas liking is controlled by ____.
dopamine; opioids
the _____ receives projections from the olfactory system and plays an important role in computing the valuation underlying a variety of emotional and social behavior.
Orbitofrontal cortex
Which of the following lobes is most analogous to an orchestra conductor?
frontal lobes
3 multiple choice options
reinforcement is thought to be regulated largely by
dopamine
Young human infants can mimic facial expressions. This is:
an example of innate releasing mechanism
Pheromones are detected by:
vomeronasal organ
the frontal lobe is most involved in:
goal-directed planning
Broca's aphasia is associated with:
deficits in initiating the motor programs for speech.
Wernicke's area is located in the:
posterior temporal lobe
You are in a crowded supermarket with your 4-year-old nephew. When you are in the candy aisle, he asks you for a chocolate bar. You initially refuse, saying that it is not good for him to eat candy. He begins to cry and whine loudly. Embarrassed by all the attention you are attracting, you buy him the chocolate bar to stop him from crying. Now every time you go to the store, your nephew whines until you buy him something. This is an example of:
Operant conditioning
a ____ is a neural-spatial representation of areas of the sensory world perceived by a sensory organ.
topographic map
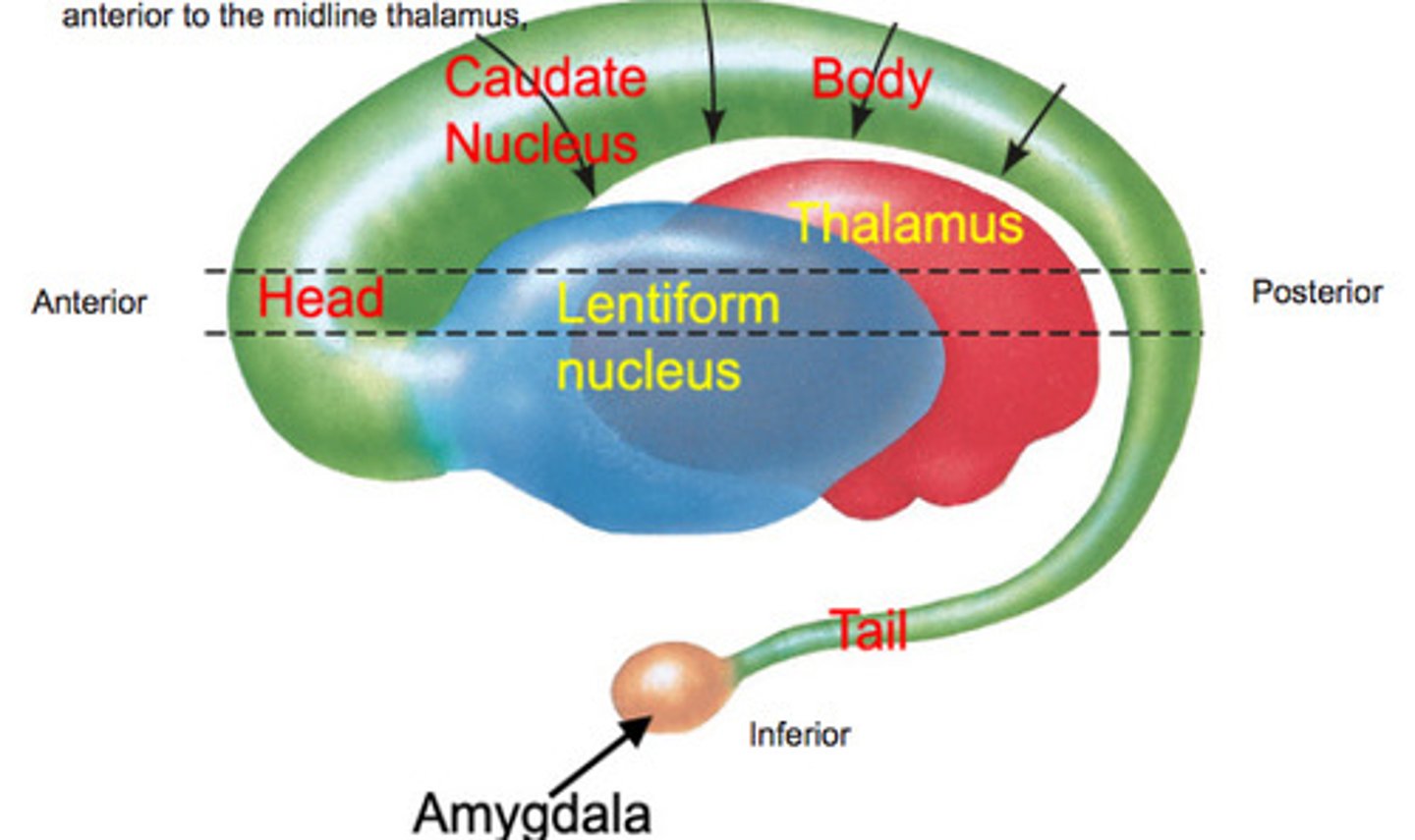
locate the following areas of the brain
tail of the caudate nucleus
amygdala
substantia nigra
striatum
parvocellular cells
primarily receive their input from cones.
the primary visual cortex is also known as
V1
the inner ear ossicles are involved in what aspect of sound processing
Amplification
the frontal lobes are fully developed
at around 25 y.o.
which of the following is the correct sequence of brain development?
cell birth, cell migration, cell differentiation, cell maturation
the part of the sensory world that stimulates a neuron is called the neurons
receptive field
you can create a simplistic model of Parkinsons disease in a rat by:
lesioning the substantia nigra
cells that respond to a moving bar of light in a specific orientation are called:
simple cortical cells
the ventral stream projects to the:
temporal lobe
Orientation detection is first coded by:
retinal ganglion cells
____ uses light to control targeted cells in living tissue in order to activate proteins.
optogenetics
rods are used primarily in ____, whereas cones are found primarily in ____.
peripheral vision; the fovea
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) uses
radioactive isotopes
Neurons migrate to their appropriate location by following a road laid down by:
radial glial cells
according to recent research, which of the following scenarios is most likely to lead to an infant death from SIDS?
faster reuptake of serotonin in the synapse
on-center cells
-Excited when light falls on the center portion of the receptive field
fMRI has high _____ but low _____
spatial resolution; temporal resolution
the superior colliculus plays an important role in:
orienting responses
a computed tomography (CT) scan is a:
series of x-rays
the central nervous system originates from:
neural tube
EEG can be used to:
monitor sleep, estimate depth of anesthesia, and detect epilepsy
Neurons migrate to the correct locations by following:
radial glial cells and chemical signaling
studies have shown that children are able to solve the _____ prior to the _____.
nonmatching to sample task prior to concurrent discrimination task.
Magnocellular cells
have low visual acuity, are insensitive to color, and primarily receive inputs from rods
The main advantage of MEG over EEG is:
MEG is better at localizing the source of electrical signals in the brain
Human lesion patients are good for studying:
long duration, spatially non-specific neural influences over behavior
sound transduction occurs on the:
basilar membrane
anencephaly is a result of
failure of the front end of the neural tube to close
EEG measures what aspect of neuronal activity?
The electrical summation of graded potentials on dendrites.
Neuroblasts and glioblasts are formed directly from:
progenitor cells
Thalamic ____ geniculate nucleus is involved in vision, whereas ____ geniculate nucleus is involved in sound.
lateral; medial
which of the following is the correct order of neuron layers in the retina from outermost (rostral) to innermost (caudal)
photoreceptor layer, bipolar cell layer, ganglion cell layer
Prosody means the same as:
tone of voice
cerebral palsy is most often caused by:
oxygen deprivation
A ____ is a neural-spatial representation of areas of the sensory world perceived by a sensory organ.
topographic map
____ is the process that works to suppress gene expression.
methylation
The blood brain barrier does not allow ____ to pass.
neurochemicals
ionotropic receptors consist of
both a binding site and a pore
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are used to treat
depression
Benzodiazepines and barbiturates are often prescribed as
antianxiety drugs
Relatives to the synapse, axon terminals are found on the ____ whereas dendritic spines are found on the ____.
presynaptic membrane; postsynaptic membrane
_____ is the deactivation of a neurotransmitter by transporter proteins that bring the transmitter back into presynaptic side for reuse.
reuptake
the movement of ions from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is called:
diffusion
neurotransmitters are produced in the: cell body and presynaptic terminals
Na and K channels on axons are mainly:
voltage dependent
a drug that prevents the breakdown of ACh at synapses is an example of an:
agonist
a second messenger system can:
Alter ion flow through the membrane channels, cause a series of reactions that result in the formation of new membrane ion channels, and initiate the production of new proteins
a synapse is the space between
an axon terminal and a dendrite
a drug that blocks the release of ACh is called
antagonist
the speed at which nerve impulses travel down an axon are greatly increased by
myelin
metabotropic channels are defined by the existence of a:
G protein coupled receptors
Nicotine, a chemical found in tobacco smoke, has its effect by:
promoting the release of ACh
the action potential normally consists of the summed current changes caused by the ____ and the ____.
inflow of sodium; outflow of potassium
when the neuron is at rest, _____ channels are normally closed, whereas _____ is free to enter and leave the cell.
Na; K
Another term for incentive-sensitization theory of addiction is:
wanting and liking theory
In the mammalian brain ______ is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, and ______ is the main excitatory neurotransmitter.
GABA; glutamate
Another term for volts is:
electrical potential between two poles.
_____ can also act as neurotransmitters.
hormones
_____ is a neurotransmitter that slows down heart rate, whereas _____ speeds it up.
Acetylcholine; norepinephrine
A change in the resting potential from -70 mV to -73 mV is called
hyperpolarization
Agonist is to antagonist as:
accelerate is to brake.
acetylcholine is most often deactivated through
enzymatic degradation
action potential originate in the:
axon hillock
GABA
decreases the firing of cells
which of the following is least efficient method of drug administration
Oral consumption
3 multiple choice options
saltatory conduction refers to:
action potential jumping from one node to the next