async lecture: standardized assessments
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
purposes of standardized tests
screening (e.g., comparing a child, child’s scores, child’s performance to a criterion checklist; if criterion isn’t met, further testing can assume)
TO ASSIST IN THE determination of a medical or educational diagnosis
document a child’s development, functional, and participation status
aid in planning an intervention program
measure an objective baseline, so we know how to move forward
measure outcomes of programs
types of standardized tests
interview-based
interview the parent, caregiver, or teacher (someone familiar with the child’s participation/performance)
ask about routines that happen in the natural setting
observation-based
done when the child is engaging in a naturally occurring activity (e.g., engaging in play, engaging with objects, engaging with other children)
performance-based
ask the child to perform a certain task
will have specific protocols and guidelines, guidelines for cueing/instructing the child, and instructions for scoring the test; always standardized!!
will be compared to the norm (the average of many children of the same age)
self or parent-report questionnaire
ask either the adolescent or the caregiving adult how often they experience the symptoms on a questionnaire (e.g., sensory behaviors)
becoming a competent test user
choosing the appropriate test
understanding the clinical usefulness of the test (usually the test being used will be a major clue in on why the child may need services)
e.g., a sensory-based assessment may be used to test a child with sensory problems
learning the test
knowing how to set it up, administer it, instruct and cue the child throughout, how to score it, etc. (so you don’t break administration protocol)
selecting and preparing the optimal testing environment
children behave differently in different environments (e.g., structured vs unstructured open-spaced environment)
ideally: 1-on-1 quiet environment w/ no environmental distractions
administering test items
preparation and skill development for administering standardized assessments
strategic interview
ask key questions to the child, parent, caregiver, or teacher to get information regarding the occupational profile; can also look at records (e.g., school records, educational records, prior evaluations, etc.)
e.g., “how often does your child experience this?”
e.g., “what are your concerns”
e.g., “how has the behavior exacerbated”
skilled observation
looking at other things the test isn’t specifically looking at
e.g., a child stacks 3 blocks (may get a perfect score, in terms of quantity of blocks stacked or completion of the task)
but also, look at their grasp patterns, posture, attention, etc.; don’t just rely on test scores!
consideration of context and environment
scores may not be reflective of the true performance of the child
e.g., the parent says the child is particularly upset today because they aren’t feeling well; may affect the scores for that day
types of standardized tests:
ipsative
standardized procedures to measure outcomes against previous evaluation outcomes
e.g., repeating the test 6 months later (post-receiving intervention)
without norms or criteria for comparing results
comparing only to themselves- their own results
interview and/or observation-based
types of standardized tests:
norm-referenced
large diverse population
norm or average is derived from scores
performance is compared with a normal sample
typically looks at one or more areas of behavior
e.g., fine motor, gross motor, social, emotional, participation, etc.
materials and activities are familiar and typical for children of the age group
must use materials that come with the kit, as the conditions must exactly replicate the norm of the sample
strict standardized protocols for administration and scoring
types of assessments:
criterion-referenced
performance is compared with a particular criterion or level of performance of a certain skill
e.g., in writing letters, is the child aligning to conventional letter structures and sequences
the purpose is to determine what skills a child can or cannot accomplish, not to compare the child with his/her peers
moreso, can the child perform this activity or not
administration and scoring may or may not be standardized
certain scales are both norm and criterion-referenced
also important to perform in the natural environment
e.g., test eating skills in a cafeteria
hawaii early learning profile: help-strands 0-3 plus
curriculum-based assessment utilized to plan family-centered interventions
population-children birth to 3 years old who are delayed, considered “at risk” or have medical conditions/developmental disability
58 concept-based strands (adds up to 685 skills): looks at the 5 areas of development
cognitive
language
motor (gross motor and fine motor)
social-emotional
self-help
assist professionals in identifying strengths and needs, identify approximate developmental levels, conduct family-directed assessment, recognize environmental factors and caregiver interactions, and develop child and family outcome standards
help scoring
skill is…
+ present as defined in Inside HELP by observation or caregiver reports as part of the child’s typical functioning
+ / - emerging, not considered as full part of repertoire; may have learned during assessment period in imitation, need reminders, or partially displays skill (i.e., child shows readiness for the skill but it is not mastered yet)
child needs more time or reminders
- not observed or reported in any situation
N/A not appropriate to assess due to age, disability, cultural or functional relevance, or family preference; do not include when determining approximate age levels
A atypical, dysfunctional, or quality concerns that interfere with development and everyday functioning (i.e., child may be doing the skill but in an atypical way)
e.g., child is not playing with their toy cars by driving them, but rather just lining them up in a line
O circle any credit if family requests support, or environmental/interactional needs

characteristics of standardized tests
test manual
gives purpose, population (that is was normed on), technical information, administration information, scoring information, and interpretation information
fixed number of items
administer all!
fixed protocol for administration
administer per instructions! (to make comparisons to the norm)
fixed guideline for scoring
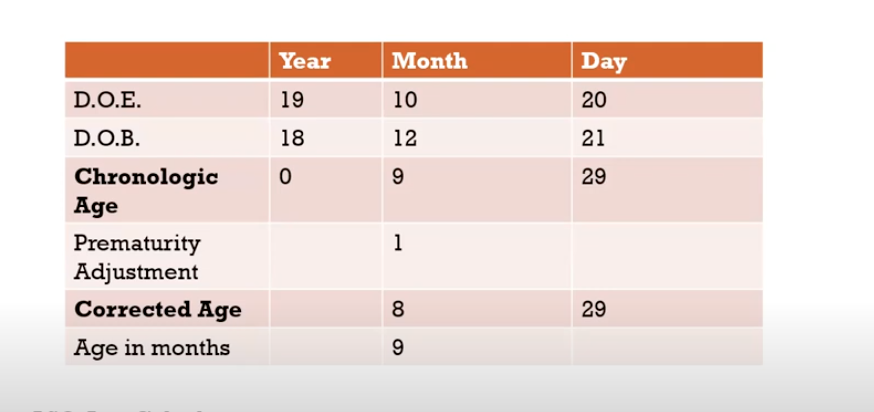
calculating age
corrected age=
chronological age - months and days preterm
technical aspects
occupational therapists must understand technical aspects of standardized assessments to:
analyze and select appropriate assessments, according to the purpose of testing and the child’s age and functional level
e.g,. Peabody is appropriate for children from birth-5 years and 11 months
interpret and report scores accurately
explain scores and data in terms that are understandable to the caregivers and team working with the child
types of scores
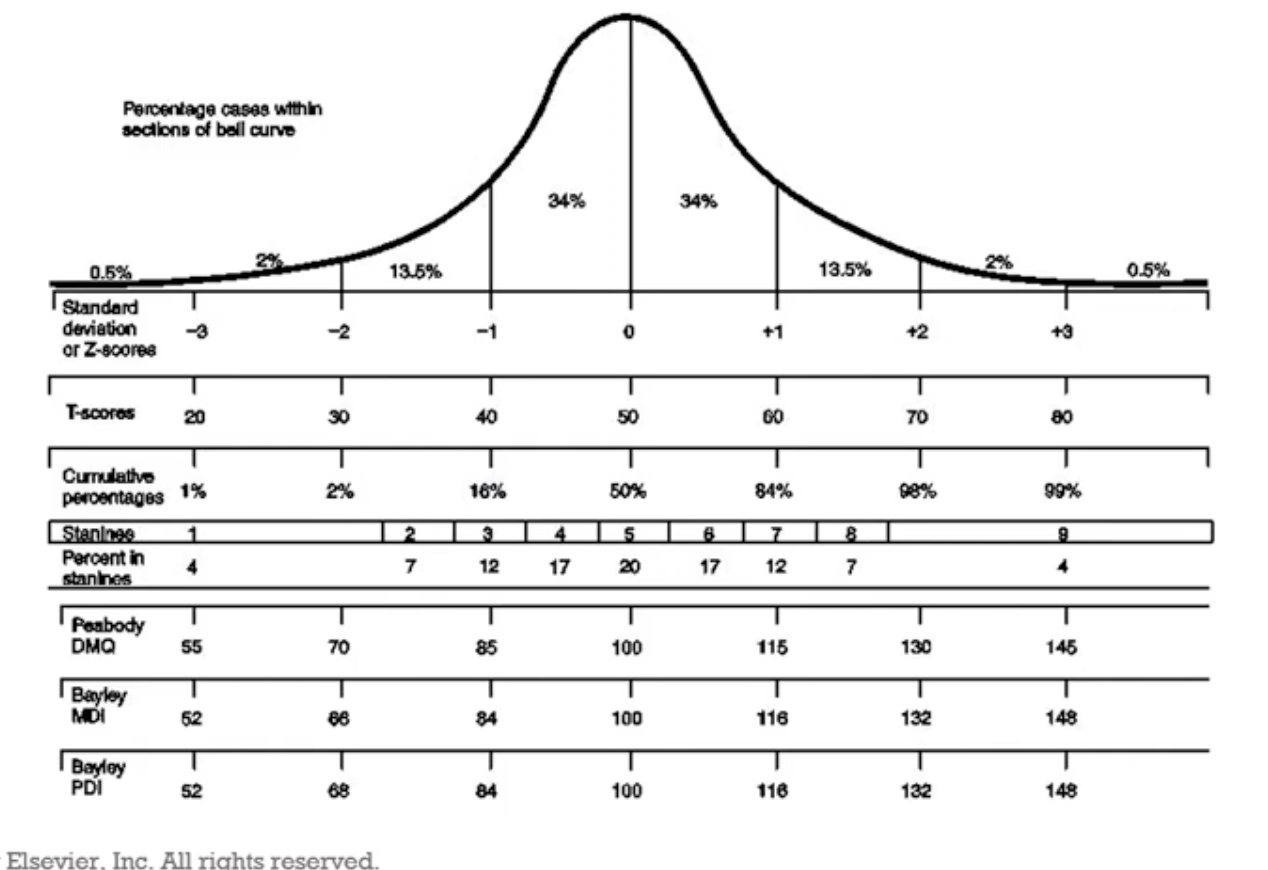
standard scores
*Z score
*T scores
deviation IQ scores (OTs don’t really test for this)
developmental index scores
*percentile
age equivalent (typically not used bc it’s hard for parents to wrap their head around)
*more reliable/accurate
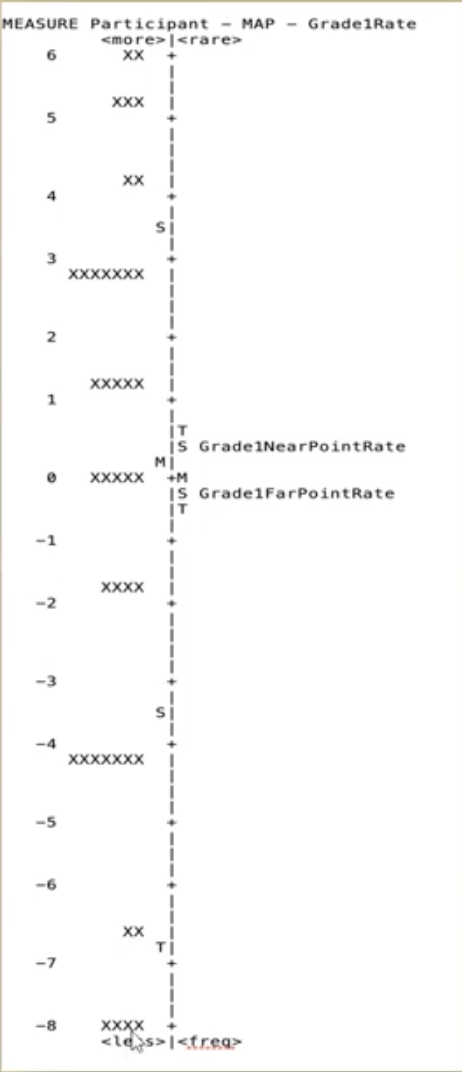
rasch scores; Vertical Rulers Rate
hierarchic ranking of items
expected pattern
(divides into) range of performance
can break performance up w/ Vertical Rulers Rate, making it more sensitive; pro! (not just looking at the average of everyone clustered together)
e.g., also looks at below average, above average
(divides into) scale of performance or difficulty
can break performance up w/ Vertical Rulers Rate, making it more sensitive; pro! (not just looking at the average of everyone clustered together)
e.g., also looks at below average, above average
SFA, PEDI-CAT and the School AMPS assessments utilize Rasch methodology
percentile scores and age equivalents
percentage of people in a standardization sample whose score is at or below a raw score
the age at which the raw score is at the 50th percentile
age equivalents are typically not used
normal bell-shaped curve
compare to the 50th percentile
children are qualified for services when 2 SD below (can sometimes get away with 1 SD below, if there’s additional reasons justifying services)
test psychometrics
reliability
test-retest reliability
administer the test; re-administer the test later; look for similar results (i.e., the test is consistently showing me similar results)
inter-rater reliability
2 raters rating the same child should get similar scores, if reliable
standard error of measurement
our scores are not a true score; every test has an error range
confidence interval
^ e.g, a score of 10 could also be in the range of a 7 or 13, given the confidence interval is a 3
technical aspects
validity
construct-related validity
does test discriminate groups?
e.g., average performance, low performance, high performance
use of factor analysis to identify test constructs
does the test capture progress in child’s performance?
content-related validity
are skills for the test’s domains adequately represented?
ask experts for their opinions! (e.g. are the test items appropriate? are the test items measuring handwriting accurately?)
criterion-related validity
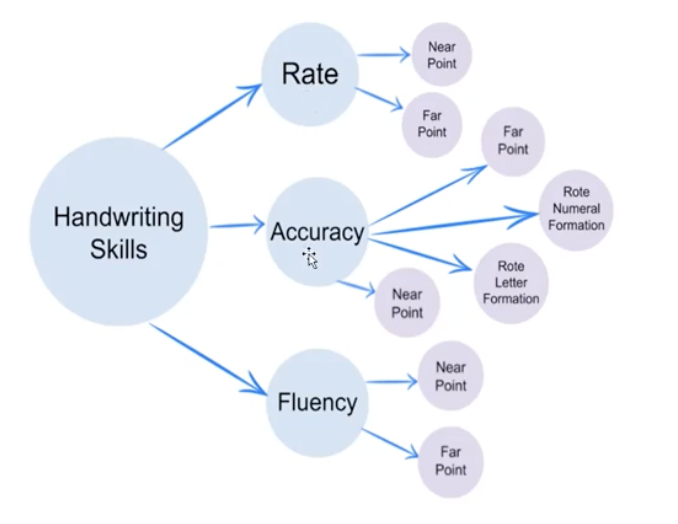
picture example:
testing handwriting; handwriting constructs are split into
rate; rate constructs are split into
near point
far point
accuracy; accuracy constructs are split into
near point
far point
rote of numeral formation
rote letter formation
fluency; fluency constructs are split into
near point
far point
interpreting test scores
interpreting the test
did the child’s performance represent typical performance?
confirm findings w/ someone the child knows well
do the results concur with parent/teacher report?
confirm findings w/ someone the child knows well
are the results complete?
evaluating the clinical usefulness of the test
minimal clinical important difference
minimal detectable change
e.g.,
“are the tests easy to administer?”
“does the test take a long time to administer?”
“is this practical? how likely is a practitioner to use this?”
==> send assessment drafts out to real practitioners to get their input!
ethical considerations in testing
examiner competency
practice the test; be familiar; have supervisors observe you
client privacy
communication of test results
report findings from a strength-based approach
cultural bias
advantages of standardized testing
well-known and commercially available
e.g., everyone knows how to administer the Peabody
common interdisciplinary language
e.g., OTs, PTs, teachers all understand
monitor developmental progress
from baseline to intervention
disadvantages of standardized testing
cannot be stand-alone measure
may need to test multiple times, or with different types of tests
provides only a brief “snapshot” of functioning
test situations are artificial and not a totally accurate interpretation of daily functioning (i.e., environmental problems)
that’s why you need to confirm findings w/ a known adult
summary
standardized tests…
screen children for a variety of performance or conditions;
assist in the determination of a medical or educational diagnosis;
document a child’s developmental, functional, and participation status;
aid the planning of an intervention program;
and measure outcomes of programs
OT develops competency in using tests by understanding concepts, familiarizing with test procedures, materials and setting requirements, observing others, and preparing
types of test include ipsative, norm-references, and criterion referenced
standardized tests have procedures for administration, scoring, and interpreting performance
reliability refers to the consistency of scores between multiple raters
validity is the extent to which a test measures what it claims
primary standard scores used are Z and T scores
ethical testing procedures include…
considering the purpose of the assessment;
adapting procedures to match child and family culture, characteristics, and values;
adjusting for testing context;
understanding test administration, scoring and mechanics and synthesizing information from standardized tests, observations, and interview
chronological (age) age
start w/ today’s date
Yr
Month
Day
add the child’s DOB
Yr
Month
Day
subtract
e.g.,
Today: (2013) 13 years, (May) 5 months, (7th) 7 days
-
DOB: (2007) 07 years, (January) 1 month, (11th) 11 days
i.e.,
13, 5, 7
-
07, 1, 11
== 6, 3, 26
==> 6 years, 3 months, 26 days
e.g.,
Today: (2013) 13 years, (May) 5 months, (7th) 7 days
-
DOB: (2010) 10 years, (September) 9 month, (1st ) 1 day
i.e.,
13, 5, 7
-
10, 9, 1
== 2, 8, 6
==> 2 years, 8 months, 6 days (***but since he is under the age of 3, we must convert it to months; the child is 32 months old)
e.g.,
Today: (2013) 13 years, (May) 5 months, (7th) 7 days
-
DOB: (2012) 12 years, (December) 12 month, (27th ) 27 days
i.e.,
13, 5, 7
-
12, 12, 27
== 0, 4, 10
==> 0 years, 4 months, 10 days
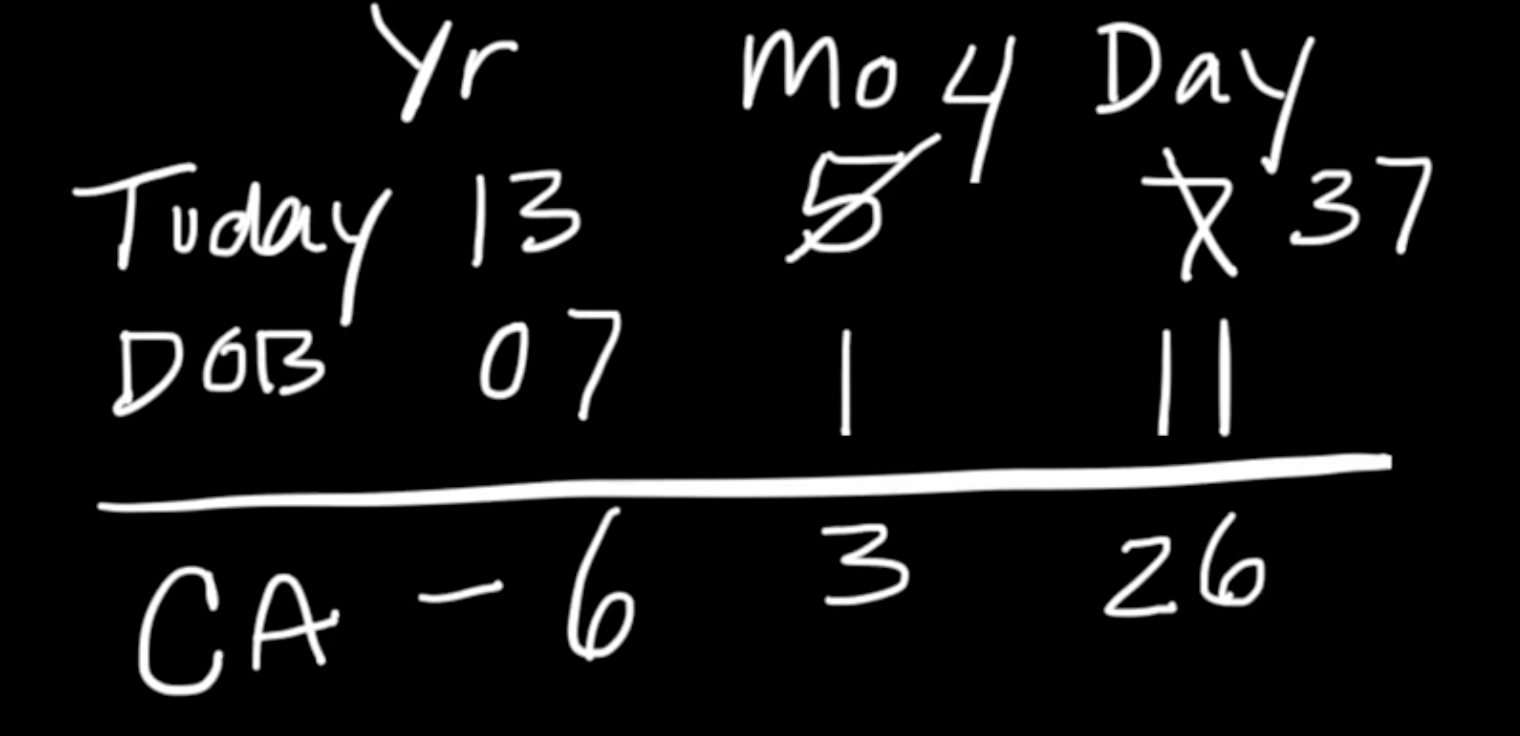
adjusted (corrected) age
==> calculate chronological age
today: 10th of July
DOB: 10th of April
—> chronological age= 3 months (or 91 days)
==> calculate the number of days your baby was born too early
= expected delivery date - actual birth date
expected delivery date: 10th of June
actual birth date: 10th of April
—> your baby was born 2 months (or 61 days) too soon
==> calculate for corrected (adjusted) age
= actual age - number of days by which the child was born too early
91 days (of chronological age)
-61 days (of “prematurity”)
= 31 days
==> even though the baby’s chronological age (or actual age) is around 3 months, your baby’s corrected age (or adjusted age) is around 1 month
adjust developmental expectations of the baby; preterm babies need extra time!