Chapter 25&26 BIOL3340
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Viruses
Small obligate intracellular parasites.
Virion
A virus particle that delivers its RNA or DNA genome into a host cell.
Nucleocapsid
A structure formed by a nucleoprotein and the genome.
Enveloped viruses
Viruses that have a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the nucleocapsid.
Baltimore System of Classification
A system used to classify viruses based on their genome type and replication method.
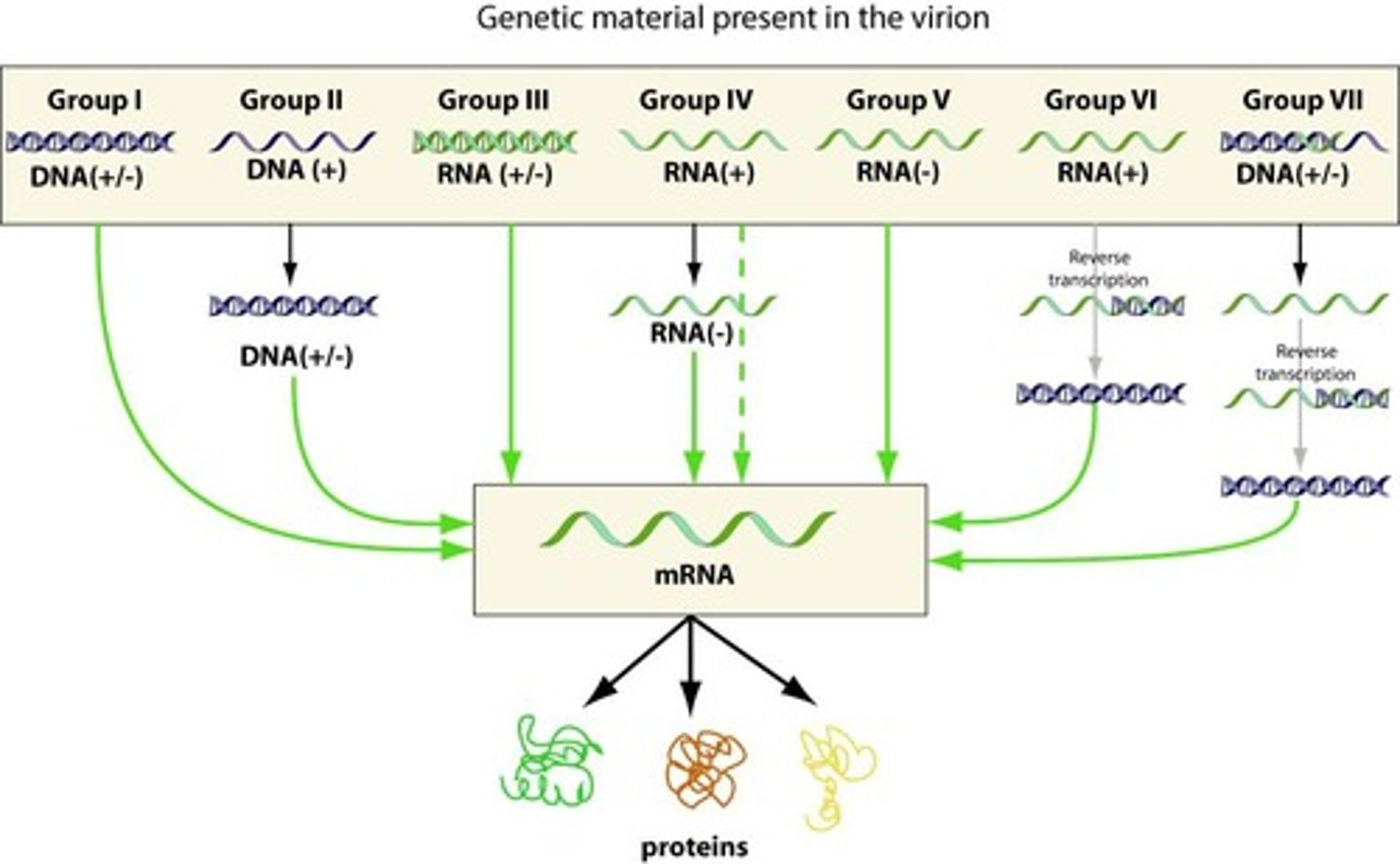
Morphology
Based upon size and shape, chemical composition, and structure of genome (RNA/DNA, SS, DS) & mode of replication.
Helical
A morphology seen in nucleocapsids where capsid proteins can be wrapped around nucleic acid.
Icosahedral
Nucleocapsids of spherical viruses.
Polyhedral
A type of viral morphology.
Complex
A morphology characterized by a head and tail structure.
Genomic RNA strand
In single stranded (SS) RNA viruses, it is called a sense.
+sense viral RNA
Identical to viral mRNA and is immediately translated into protein by the host cell.
-sense RNA
Complementary to mRNA and must be converted to (+)sense RNA by RNA polymerase before translation.
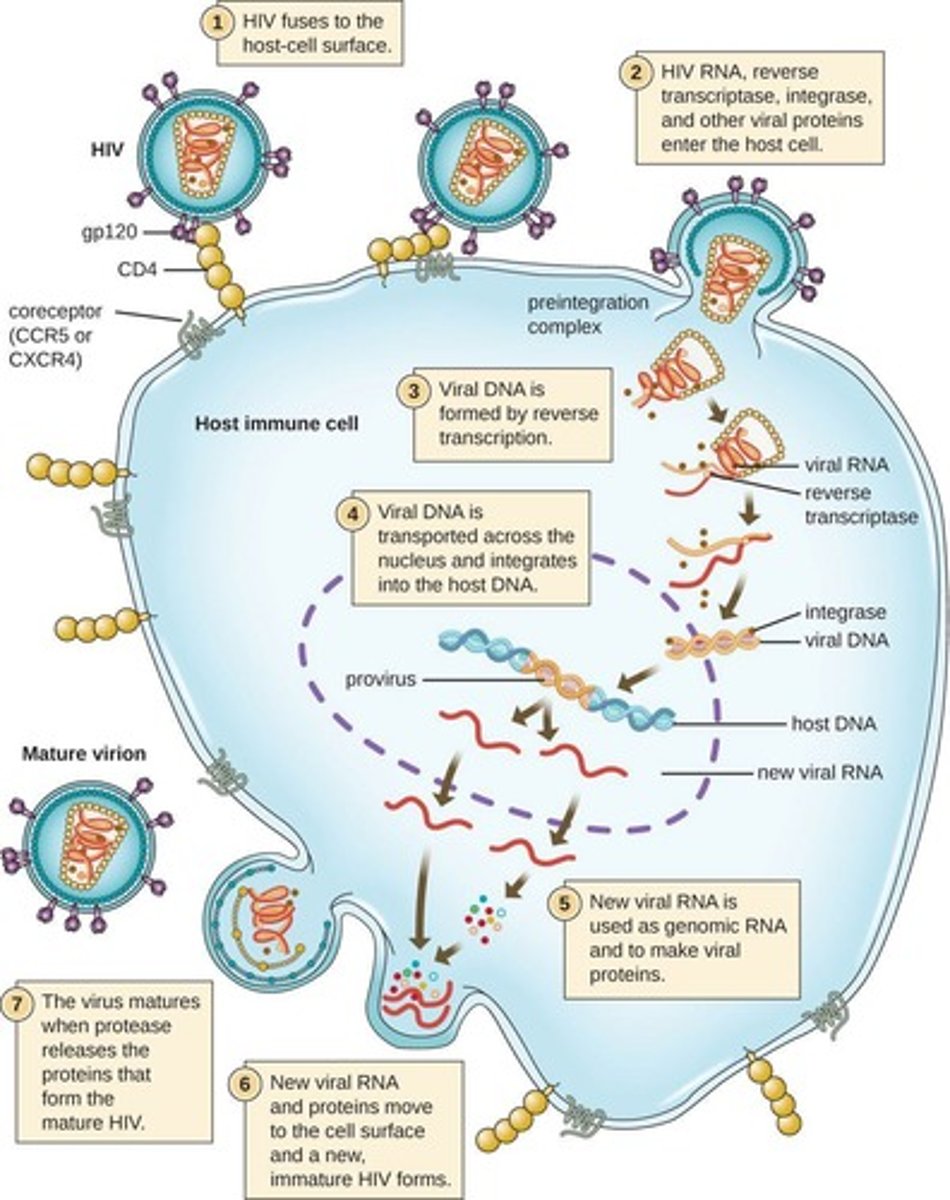
Viral Multiplication/Replication
The mechanism used depends on viral structure and genome.
7 Steps of Viral Replication
Attachment/Adsorption to host cell, Entry into cell, Uncoating of genome, Replication/Synthesis, Assembly, Maturation, Release.
Infection
A microbe growing and multiplying on or within a host.
Pathogenicity
The ability of a pathogen to cause disease.
Virulence
The degree of harm (pathogenicity) inflicted on the host.
Intracellular pathogens
Pathogens that grow and multiply within host cells.
Extracellular pathogens
Pathogens that grow outside host cells in tissues and fluids.
Facultative intracellular pathogens
Pathogens that reside within the cells of the host or in the environment but can also be grown in pure culture without host cell support.
Obligate intracellular pathogens
Pathogens that only grow when inside host cells.
Incubation period
Period after pathogen entry, before signs and symptoms appear.
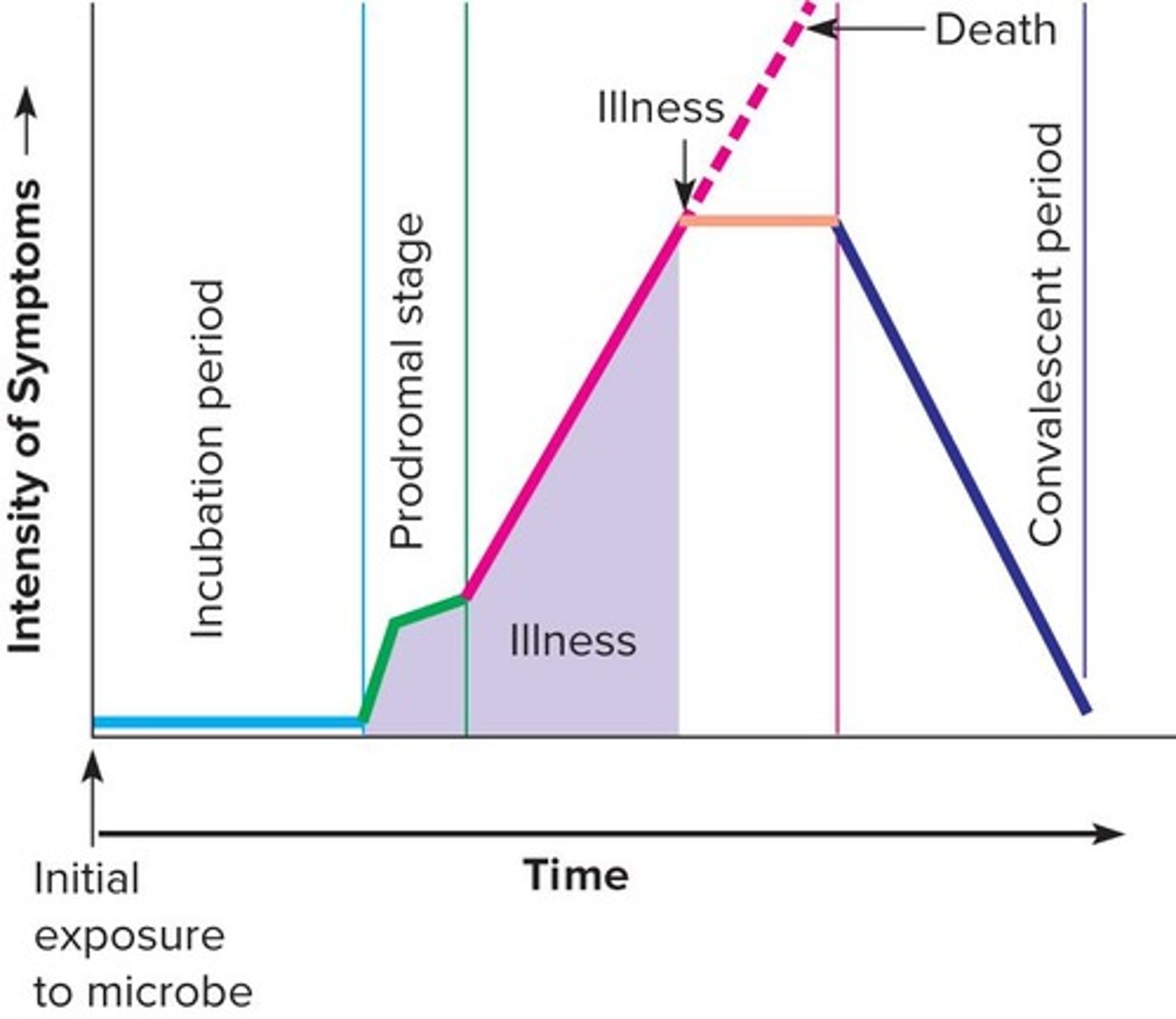
Prodromal stage
Onset of signs and symptoms that are not clear enough for diagnosis.
Illness period
Period when the disease is most severe, displaying signs and symptoms.
Convalescence
Period when signs and symptoms begin to disappear, indicating recovery.
Signs
Objective changes in the body that can be directly observed, such as fever and rash.
Symptoms
Subjective changes experienced by the patient, such as pain and loss of appetite.
Disease syndrome
Set of characteristic signs and symptoms for a disease.
Zoonoses
Infections passed from animal to human.
Reservoir
Natural environmental location in which the pathogen normally resides and multiplies.
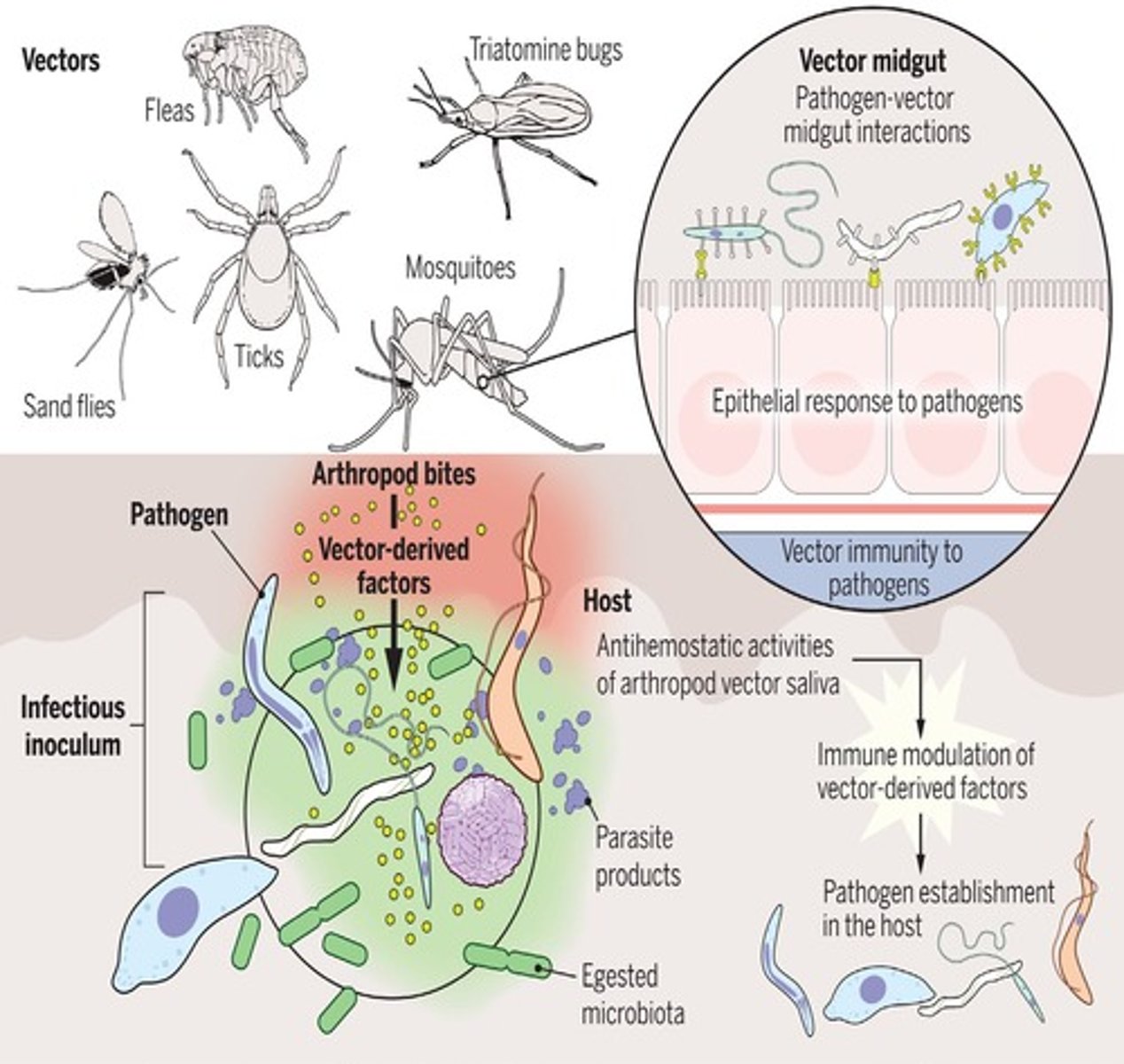
Vector
Organism that spreads disease from one host to another, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas.
Airborne Transmission
Transmission of pathogens via droplets or droplet nuclei.
Droplets
Direct transmission particles up to 2 mm in diameter produced when liquids are placed under force.
Droplet nuclei
Indirect transmission particles 1 to 5 μm in diameter that may remain airborne for hours or days.
Contact Transmission
Transmission involving the coming together or touching of source/reservoir and host.
Direct contact
Physical interaction between source/reservoir and host, such as kissing or touching.
Indirect contact
Involves an inanimate object (fomite), such as eating utensils or bedding.
Vehicle Transmission
Transmission involving inanimate materials that transmit pathogens, such as food or water.
Vector-Borne Transmission
Transmission by a direct living transmitter of a pathogen, often arthropods.
Vertical Transmission
Occurs when the unborn child acquires a pathogen from an infected mother.
Infectious dose 50 (ID50)
Number of pathogens that will infect 50% of inoculated hosts.
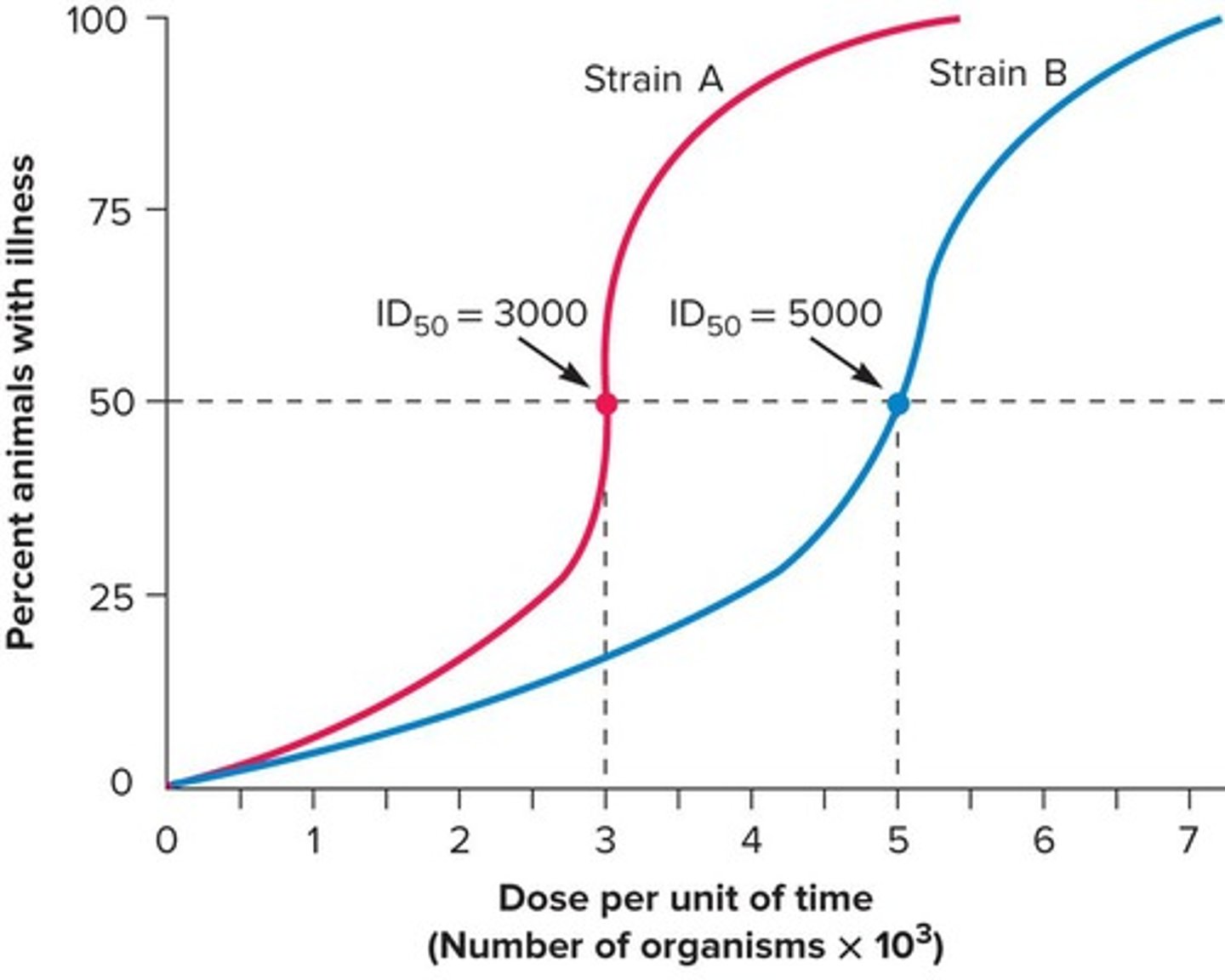
Lethal dose 50 (LD50)
Dose that kills 50% of experimental animals within a specified period.
Adherence
Mediated by special molecules called adhesins, crucial for establishing infection.
Colonization
Establishing a site of microbial replication on or within the host without necessarily causing tissue invasion.
Bacteremia
Presence of viable bacteria in the blood.
Septicemia
Bacterial or fungal toxins in the blood.
Exotoxins
Soluble, heat-labile proteins that are among the most lethal substances known.
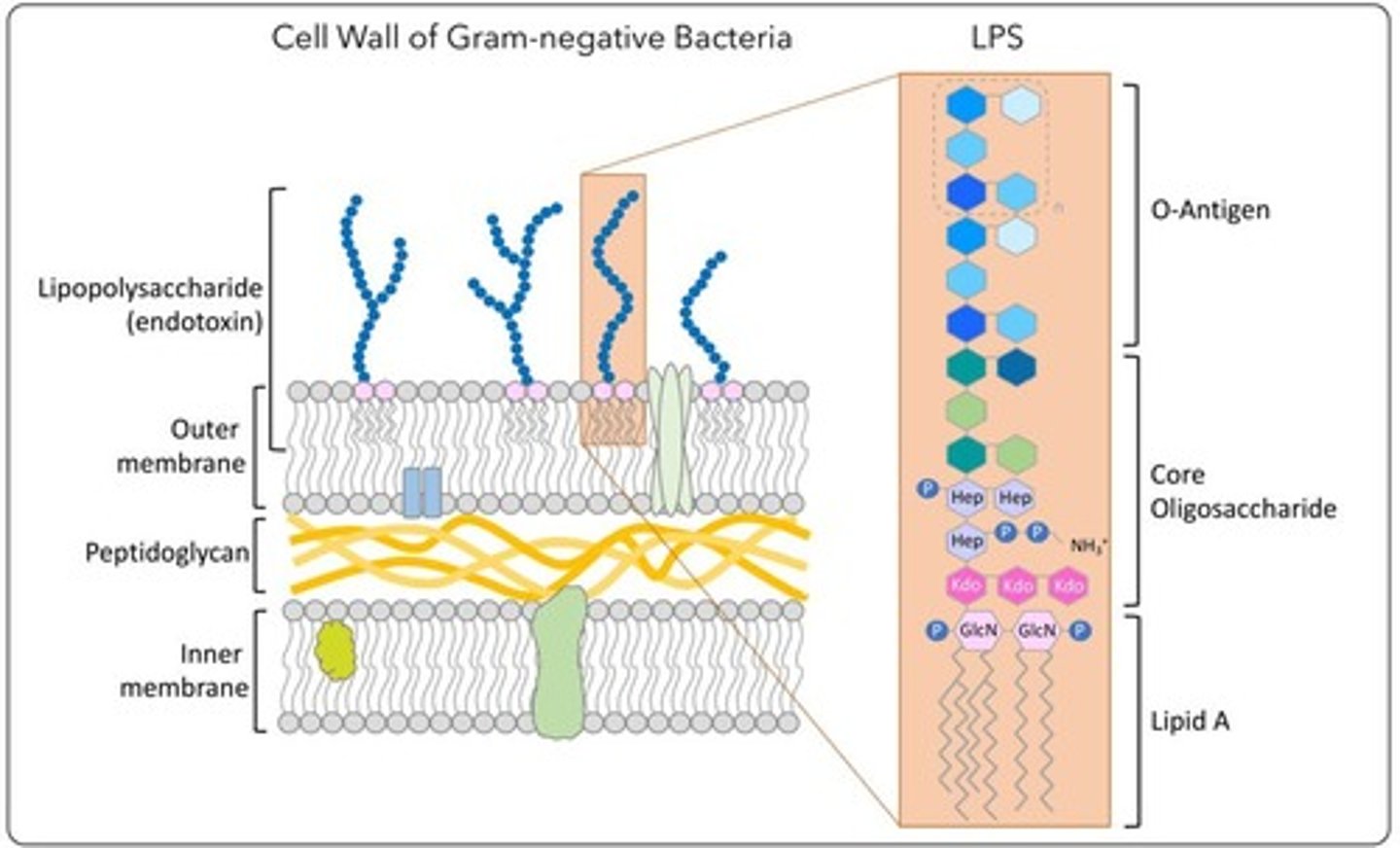
Endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharide in Gram-negative cell wall that can be toxic to specific hosts.
Mycotoxins
Toxins produced by fungi, commonly found as contaminants of food crops.
Aflatoxins
Toxins produced by parasitic fungi that cause chronic and acute liver disease and liver cancer.
Stachybotrys
A type of fungus that produces satratoxins, potent inhibitors of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis; induces inflammation, disrupts surfactant phospholipids in the lungs, and may lead to pathological changes in tissues.
Epidemiology
Science that evaluates occurrence, determinants, distribution, and control of health and disease in a defined human population.
Epidemiologist
One who practices epidemiology.
Sporadic disease
Occurs occasionally and at irregular intervals.
Endemic disease
Maintains a relatively steady low-level frequency at a moderately regular interval.
Hyperendemic diseases
Gradually increase in frequency above endemic level but not to epidemic level.
Outbreak
Sudden, unexpected occurrence of disease; usually focal or in a limited segment of population.
Epidemic
Outbreak affecting many people at once; sudden increase in occurrence above expected number.
Index case
First case in an epidemic.
Pandemic
Increase in disease occurrence within a large population over at least two countries around the world.
Prevalence
Total number of cases in population divided by total population.
Morbidity rate
Number of new cases during a specific period divided by number of individuals in population.
Mortality rate
Number of deaths due to given disease divided by total number of cases of the disease.
Infectious disease
Disease resulting from an infection by microbial agents.
Communicable disease
Can be transmitted from one host to another.
Common source epidemic
Epidemic caused by a single common contaminated source (food or water).
Propagated epidemic
Epidemic that starts with one infected individual into a susceptible group, with infection propagated to others.
Herd immunity
Resistance of a population to infection and pathogen spread because of immunity of a large percentage of the population.
Herd immunity level
Recommended that 80% to 95% of the population be immunized against common infectious diseases to provide necessary protection.
Systematic Epidemiology
Focuses on ecological and social factors that influence development and spread of emerging and reemerging diseases.
Emerging and Reemerging Infectious Diseases
Increases due to world population growth, urbanization, inadequate public infrastructures, increased international travel, mass migrations, climate change, habitat disruption, and microbial evolution.
Nosocomial Infections
Healthcare-acquired infections from pathogens within a hospital or clinical care facility, affecting 5 to 10% of all hospital patients.
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs)
Infections sourced from endogenous or exogenous pathogens, impacting patient health within healthcare settings.
Endogenous Pathogen
Pathogen brought into the hospital by a patient who is colonized after admission.
Exogenous Pathogen
Microbiota other than the patient's, potentially sourced from hospital staff, other patients, visitors, or environmental factors.
Control Measures for Nosocomial Infections
Includes reducing or eliminating sources of infection and increasing herd immunity through immunization.
Impact of Nosocomial Infections
Prolong hospital stays by 4 to 14 days, result in additional $28 to $33 billion per year in healthcare costs, and cause approximately 99,000 deaths annually.
Vaccine
Preparation of microbial antigens used to induce protective immunity, which may include killed, living, weakened microbes, or inactivated toxins.
Immunization
Result obtained when a vaccine stimulates immunity in the host.
Adjuvants
Nontoxic materials mixed with antigens in vaccines to enhance the immune response.
Acellular or Subunit Vaccines
Vaccines that use purified molecules from microbes to avoid risks associated with whole-cell vaccines.
Haemophilus influenza type b Vaccine
Polysaccharide-protein conjugate or bacterial polysaccharide used as a subunit vaccine.
Neisseria meningitides Vaccine
Polysaccharides of serotypes A/C/Y/W-135 used in subunit vaccines.
Streptococcus pneumoniae Vaccine
Contains 23 distinct capsular polysaccharides as a form of subunit vaccine.
Hepatitis B Virus Vaccine
Recombinant surface antigen (HbsAg) used as a vaccine.
Human Papillomavirus Vaccine
Recombinant protein subunits used in vaccination.
Toxoids
Inactivated exotoxins used in vaccines, such as those from Corynebacterium diptheriae and Clostridium tetani.
Recombinant-Vector Vaccines
Vaccines that use nonvirulent viruses or bacteria to express pathogen genes encoding major antigens.
DNA Vaccines
Vaccines that introduce DNA directly into host cells, leading to the expression of pathogen DNA fragments.