Audiology EXAM 1
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
sound is a type of energy that occurs because of distrubed ___ and results from the ___ of a molecule in the medium it travels by.
pressure waves
compression
requirements for sound (2)
source of vibratory energy (vocal cords)
medium that has mass and is elastic
properties of sound (4)
intensity
amplitude/frequency
phase
spectrum
the the magnitude of a compression wave equals the ___intensity of the signal
higher
higher
intensity is measured in
decibels
decibles is measure in a ___ scale
lograithmic
spl stands for
sound pressure level
at what dB for slight discomfort
90 dB
at what dB for pain
140dB
frequency is measured in
hertz
frequency is the ___ of vibration: cycles per ___
speed of vibrations: cycles per second
human hearing range in Hz
20Hz - 20,000Hz
the higher the speed of vibration of compression wave is the ___ the frequency of the signal
higher
for pure tones, the periodic wave is called a
sinusoidal wave. it repeats itself at regualr intervals
normal speech sounds and nature sounds exhibit a ___ wave.
complex wave. For complex sounds ( like nature and speech) the interaction between intensity and frequency is called the sound spectrum.
where does physical processing occur:
outer, middle, and inner ear
where does neural processing occur
inner ear then 8th nerve then central auditiory nervous system
where does psychological processing occur
begins in brain stem then pons t
afferent
sensory
carries signal TO cns
responsible for sensing stimulus
efferent
motor
carries signals AWAY from cns
initiates action
describe sturctures in outer ear. functions of outer ear
auricle/pinna
ear canal/ or EAM
outer layer of tympanic membrane (TM)
Functions: collects, localizes, resonates sound
protects middle ear
auricle serves as a resonator. resonators are set into vibration by another vibtration. this enhances sound energy.
structures of tympanic membrane
made of several layers of skin
at the very end of EAM
includes: pars tensa- larger, stiff, inferior
pars flaccia- more flexible and smaller
{manubrium, umbo and light reflex} mentioned later
middle ear structure
air filled cavity
within the temporal bone
functions as an impedance matching device
bridge between airbone vibtration from TM and the fluid traveling waves in cochlea
ossicular chain
responsible for boost in sound
made up of 3 small bones suspended in air:
1. malleus (hammer)
2. incus (anvil)
3. stapes (footplate)
malleus rest on TM and stapes is on the oval window of the cochlea (specifically the scala vestibula in the cochlea)
what about the middle air cavity
filled with air.
air is kept pressurized by eustachian tube. e tube leads to the back of the throat.
swallowing helps open the tube if pressure isn`t equalized .
the e tube is a passageway from nasopharynx to anterior wall of middle ear
inner ear structures
contains auditory and vestibular labryinths’
vibrations in ossicles vibrates cochlea labyrinth and set of neural impulses generated by 8th cranial nerve that travel to auditory nerve
name the 3 ossciles bones (in order); along with where the manubrium is
The malleus consists of a long process called the manubrium that is attached to the tympanic membrane and a head that is attached to the body of the incus.
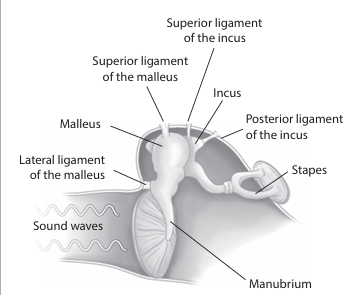
the malleus moves ___ than the stapes. This shows an example of impedance matching.
The auditory labyrinth is called the ____ and is the ____ of hearing.
cochlea
sensory end organ
the cochlea structure
within the temporal bone
2.5 turns
encircles a bony central core called the modiolus
the TOP of cochlea
apex; aka helicotrema
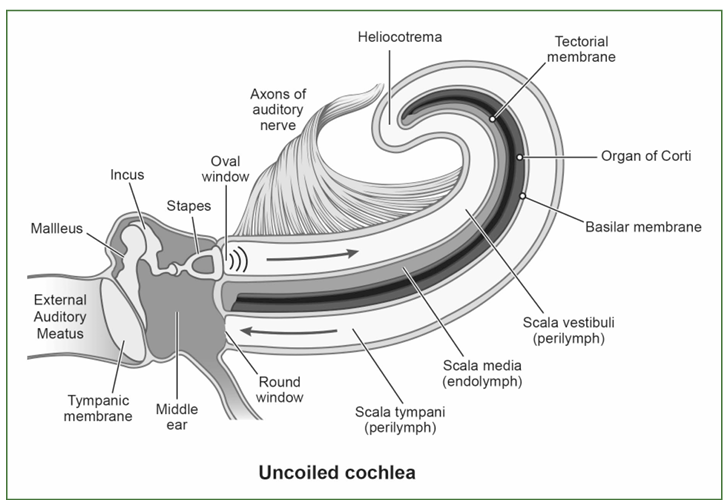
uncoiled cochlea: understand where scala tympani vs scala media vs scala vestibuli ( with their respective fluids).
where is organ or corti
tympani/vesitubli - both contrain perilymph fluid
the scala media/cochlear duct - filled with endolymph fluid
organ of corti is in cochlear duct. top of Organ of Corti is temporal membrance (STIFF, oscillating) bottom of Organ of corti is basilar membrane (gelatinous, osicllating, has hair cells.
result of oscillating/bending hair cells
depolarization/hyperpolization
after organ of corti recieves vibration it ___ back to ___
circles back to round window
soft noises trigger specific spots in ____membrane and is reflected as background noise/ soft noise
basilar
describe impedance matching with oval window to cochlea
louder vibration is recieved from stapes at oval window to account for the fluid in cochlea. vs vibration in TM
what are the two types of sensory cells called in cochlea
stereo cillia
outer hair cells and inner hair cells
both are elongated in shape with small cilia attached on top
cilia is impeded in tectorial membrane
these hair cells are mostly outer efferent hair cells
inner hair cells are NOT in direct contact with tectorial membrane. these inner are mostly afferent
the traveing wave goes down the __ membrane
basilar
higher frequencies occurs closer to the __ ___ near the ___end of the cochlea
oval window
basal or bottom
lower frequencies are ____ from the oval window.
At the ___ of the cochlea.
farther from the oval window.
at the TOP or apical end of the cochlea.
tonotopic arrangement (in the basilar membrane) simply means
each frequency stimulates a different stop/place along the basilar membrane
outer and inner hair cells work __ to translate wave of motion
together
outer hair cells are embedded in ___ ___
which produces contracting/expanding forces that influence…
which allows the ___ ___ __ to be stimulated
tectorial membrane
the position of the tectorial membrane
inner hair cells
autiorty nervous system
primarily afferent but includes a efferent component that regulates outer hair cells and general inhibitory actions. (gen inhib actions lowers background noises when listening)
is functionally crossed.
list the steps of traveling sound once the nerve vibers form inner hair cells exit the organ of corti
the cochlear branch of the 8th cranial nerve exits the modiolus (thru tonotopic arrangement)
then joins the vesitbular branch of the 8th cranial nerve
leaves the cochlea thru internal auditiory canal of the temporal bone
intensity is coded as the ___ of nueral firing
frequency is coded as the ___ of neural firing
rate
place
nuclei involved in primary auditory pathway of the central auditory nervous system (CANS)
cochlear nucleus
superiod olivary complex (S.O.C)
lateral lemniscus
inferior colliculus
medial geniculate
auditory radiations
auditory cortex
interepting audiograms are in the scope of SLPs (T/F)
T
absolute senstivity
capacity of aud. system to detect faint/ soft sound
differential sensitivity
capacity of aud. system to detect changes in sound
hearing senstivity refers to absolute or differential sensitivity
absolute
hearing acuity refers to absolute or differential sensitivity
differenital
absolute threshold is the threshold of
audiobility
absoulute sensitivity of hearing is usually a sound that can be heard what precent of the times presented
50%
2 out of 4 times
our auditory system is most sensitve to pressure changes aorund what frequencies
speech frequences
0 dB is the threshold for ___hearing
normal hearing.
it does not mean the abscne of sound
right ear symbol on audiogram
red
round/circle
left ear symbol on audiogram
blue
x
air conduction measures two things
degree of hearing loss
configuration
bone conduction measures the
type of hearing loss
the diff between air and bone conduction is termed
the air-bone gap
loudness referes to
intensity
pitch refers to perception of
sound frequencies . these are directly proportionate
during hearing testing we always start:
with R ear at 1000Hz
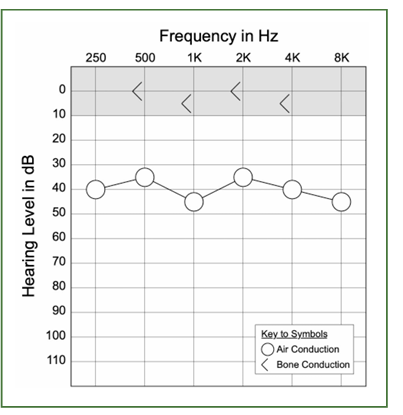
normal, conductive, senso?
conductive
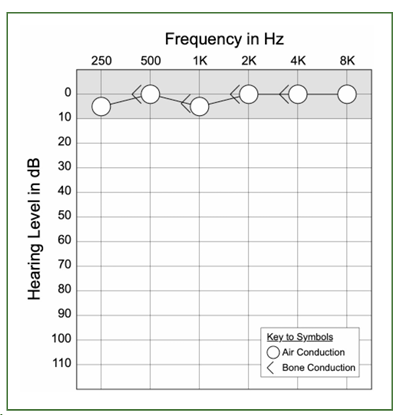
normal, conductive, senso?
normal
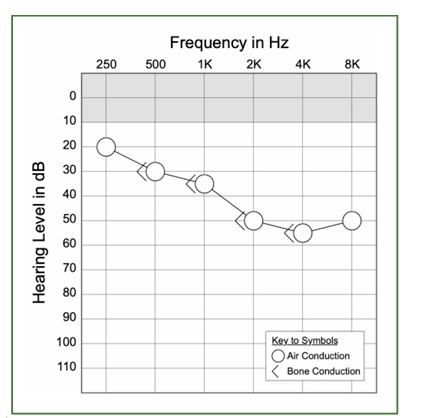
normal, conductive, senso?
senso
what is an audiologist
health care profession devoted to hearing
prevents/diagnosis hearing loss
treats communication disorders
evals need/ IMPACT hearing devices
requirements for audiology
masters degree, 4 year AuD (doctorate) the last yr of doctorate is the residency.
1870 clinical hours
pass PRAXIS
certifications: ASHA CCC-A, AAA Board
Licensure varies by state
Audiologist Roles
I.D (develops/oversees) of HL, Assessment, Diagnosis, Treatment (works w/ ENT doc), Education, Prevention, REsearch
Scope of Practice
HL prevention screening, newborn hearing screening (lots of progress here!), ear canal inspec.(AKA otoscopy), pedi/adult assessment, I.D hearing impairment (and if pt is eligible for disability), audiologic rehab (i.e school counseling), fitting of hearing devices, edu programming(IEP: individual education plan)
where to practice (as of 2016)
26% private practice
26% hospital/med centers
25% physicans practice
12% hearing/speech clinics
6% research
hearing instrumentation manufactures also need audiologist
what is a HIS
hearing instrument specialist.
HS diploma and 6 months of training
B.C HIS are board certified
audiologist is a ___ profession
autonomous meaning not having to rely on other professions to complete your own work.
audiologist can have intraprofessional collaboration: ENT, PCP, nonaudiologist hearing aid dispensers, geriatric specialist, pediatrician, etc
SLP traits
eval/treatment of com. disord and swallong
collab, counsel, prevention/wellness,screening, asses, treat, etc
ASHA v CCC v State Licensure
asha- national body that grants CCCs
ccc-a/ccc-slp - you must pay annually, certificate of clinical compentency for audiology. requires your masters, fellowship/clinical, praxis
state licensure - can get this w/o ccc but you need to keep all your transcripts and observation hours. varies by state, bare minimum.
what questions would an audiologist ask
does hearing loss exist
to what extent
is the dysfunction of the audiological system a SYMPTOM
is the HL causing comm. impairment
can impairment be overcome with equip.
what are the specific tech needs of the pt.
The portion of the hearing mechanism from the auditory nerve to the auditory cortex is called the
central auditory nervous system
The ___ is a biological system that, in conjunction with vision and proprioception, functions to maintain balance and equilibrium.
vestibular system
what is an auditory brainstem response (ABR)
is an electrophysiologic response to sound that represent the neural function of auditory brainstem pathways.
The ___ cranial nerve refers to the auditory and vestibular nerves.
The VIII-th (8th)
Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs) are:
measurable sounds emitted by the normal cochlea, which are related to the function of the outer hair cells.
high frequencies are associated with __ sounds of speech
consonant.
poor artifulation would make sense in this scenario
individual factors that affect comm disorder
degree of sensitivty loss
audiometric config
type of hl
degree/nature of speech perception
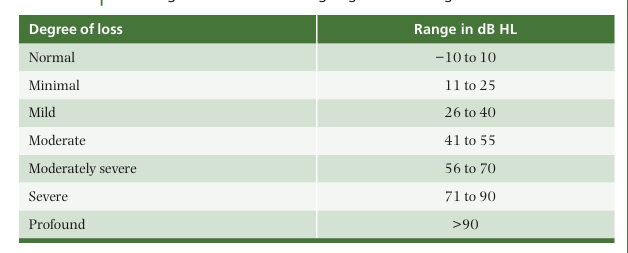
degree of loss chart
order?
normal, minimal, milk, moderate, moder. severe, severe, profound
0 db in an audiogram is ____.
NOT the absence of sound
in audiogram, if it falls on the line/border of two degrees of loss go with the:
lowest of the 2.
ex: between mild and moderate? go with mild.
what frequency is the most important for speech when looking at an audiogram
2000k
generally around1k-2k
what is air conduction primarily used for
degree of loss
configuration
what is bone conduction primarly used for
the type of HL
degree of hearing loss explained. When are these useful?
when needing to explain the effects/remaining hearing for a pt in THETA

why is the audiogram focused on 250-8000Hz?
it is focused on speech perception
what is the purpose of testing really high frequencies
to detect otoxicity.
on an audiogram what is 1500HZ an example of
a mid-octave
what is audiometric zero
the sound pressure level where audiobility occurs for the average listener
3 types of ways you can obtain information from an audiogram
pure tone audiometry
bone conduction testing’
soundfield testing
pure tone testing
earphones or headphones
aka air conduction testing
determines air conduction thresholds
BEHAVIORAL TEST: requires a response from the pt
sound travels thru the ear to cochlea
abbrev. for right ear and left ear
AD right ear
AS left ear
bone conduction testing
tight head band around head that vibrates and stimulates the cochlea directly.
tests the sensitivity of the cochlea
bone vibrator(oscillator) placed on the mastoid(bone right behind ear)
headband should never touch pinna
NOT ear specific, the better ear will always respond: masking helps ear specificity
right ear <
left year >
soundfield testing
test children and infants
large speakers emit sound. second screen shows image/video to reinforce sound.
records responses based off of head turns
visual reinforced audiology
tests hearing assisted devices too! this helps to compare w/ device and w/o
NOT EAR SPECIFIC!!!!!! profound hearing loss in ONE EAR will not show in soundfield testing. the better ear will always respond.