POLYMER FINAL
1/855
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
856 Terms
polysaccharides are more familiarly known as __________
carbohydrates
what makes up ¾ of the dry weight of the plant world?
polysaccharides
what can produce polysaccharides?
plants
animals
yeast
where does a lot of photosynthesis take place?
ocean
polysaccharides are polymers of…
monosaccharides
D-glucose structure
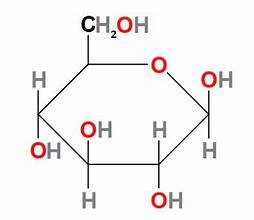
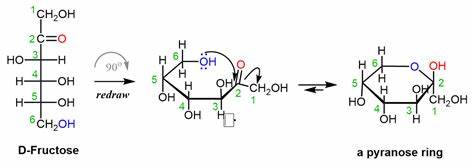
D-fructose structure
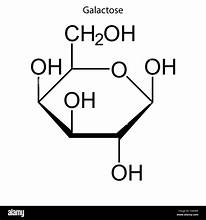
D-Galactose structure
each monomer can exist in the __________ or __________
alpha anomer / beta anomer
difference b/w alpha and beta anomer
alpha = OH on C1 is pointed up
beta = OH on C1 is pointed down
molecular weights of naturally occurring polysaccharides tend to be _______
large
alpha linkage
OH are on interior & exterior of polymer chain, allowing H-bonding within the chain → better wettability & potentially a helical structure
bonds point down
can be digested by humans
starch
can alpha linkages be digested by humans?
yes
beta linkages result in a _______ structure that cannot be _________
linear / digested (think fiber)
beta linkage
linear structure that can’t be digested (fiber)
OH are on exterior and allow for H-bonding b/w different chains, making it rigid & insoluble
good for cell walls in plants
2 most abundant polysaccharides
cellulose
starch
what is cellulose made of?
beta linkages of D-glucose
cellulose is more than ____ of the dry weight of plants
1/3
what is the world’s largest renewable resource by weight?
cellulose
polysaccharide chains in plants are present in thread-like strands or bundles called _________
fibrils
polysaccharide chains in plants are ________ and __________
rigid / insoluble
what are polysaccharide chains in plants good for for humans?
constructin and fuel (wood)
paper (wood)
clothes (cotton)
what is the major source of commercial cellulose?
plant pulp
pulping
extraction of cellulose
cellulose extraction from wood is a major source of ___________ fibers for paper
non-textile
cellulose extraction from ________ is a major source of textile fibers for clothes
cotton
common modification to cellulose done in industrial properties
methycellulose
how is methylcellulose formed?
cellulose-OH + NaOH + CH3Cl → cellulose-O-CH3 + NaCl + H2O
methylcellulose is commonly used as an ________
adhesive
uses of methycellulose
adhesive
ceramics (provides water retention & lubricity)
cosmetics (to control rheological properties & stabilization of foams)
food (as binder, emulsifier, stabilizer, thickner, and suspending agent)
paints, paper products, and plywood as rhelogy control for adhesive)
inks and textiles as a binder
advantages of methycellulose
biologically sourced
renewable
inexpensive
nontoxic
circular
what is starch made of?
alpha linkages of D-glucose
what is starch used for in plants?
energy storage (food for us)
ratio of amylose and amylopectin in most starches
10-20% amylose, 80-90% amylopectin
amylose is a _______ polymer
linear
common structural formation of amylose
helical formation with 6 glucose per turn/spiral
amylopectin is a _______ polymer
branched
typically, amylopectin has one branch per ______ units
6
on the 6th carbon
is amylose or amylopectin longer?
amylopectin
what leads to the fan-like structure of amylopectin?
branches off branches
is amylopectin easy or hard to break down? why?
easy - many chain ends for reactivity
polyisoprenes
occur in nature as hard plastics called gutta, percha, and balata
occur in nature as an elastomer/soft ruber called hevea brasiliensis
produced from trees
polyisoprenes are obtained from the _______ tree in central america
archras sapota
molecular formula of isoprene
C5H8
gutta, percha, and balata are polymerized as the __________ isomers
trans
natural rubber is polymerized with _____ isomers
cis
describe polyisoporene chains in the trans version
stack well
crystalliz
hard solid
linear
describe polymer chains in the cis version
take up more space
don’t stack well
make an amorpous solid with a low Tg
what happens when a cis polyisoprene chain is stretched at a temp higher than Tg?
bonds flex and chains uncoil until they’re stretched out enough to crystallize, like the chains in gutta percha
at the point of crystallization in polyisoprene chains, there is an ________ and the rubber band warms
exotherm
crystallization prevents further ________
stretching
if held in the stretch shape long enough, chain ___________ and ____________ occurs
slippage / deformation (creep)
to prevent chain slippage, natural rubber is often ___________ which cross-links the material
vulcanized
what does vulcanization mean?
natural rubber is reacted with elemental sulfur, S8, which cross-links the material preventing chain slippage
who discovered vulcanization?
Charles Goodyear
today, most rubber is _________
synthetic
what is the one natural rubber product still used today? why?
rubber bands — has better elasticity than synthetic rubber
there are ___ levels of protein structure
4
primary structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
shape of amino acid sequence
helix, sheet
determined by H-bonding & size of pendant groups
what is secondary structure determined by?
H-bonding
size of pendant groups
internal H-bonding b/w amino acids in the polymer chains and pendant groups favor _________
helices
H-bonding b/w neighboring polymer chains & smaller pendant groups favor ___________
sheets
tertiary structure
protein folding
can be locked in by hydrogen bonding, salt bridges, and disulfide cross-linking
quaternary structure
when 2+ proteins associate to make a larger structure
ex. 4 myoglobin units come together to make 1 hemoglobin
3 types of protein in the body
fibrous
globular
membrane
fibrous protein
for structure/support, such as tendons, muscles, and bones
globular proteins
enzymes
membrane proteins
attached to/associated with cell membranes
what are critical for determining the type of protein?
H-bonding
types of pendant groups
hair is made of which polypeptide?
alpha keratin
amino acids in alpha keratin
glycine
leucine
what contributes to the helix structure of alpha keratin?
relatively large pendant groups (Leu)
lots of internal H-bonding
what makes hair flexible?
less intermolecular interactions
what helps give hair its shape?
disulfide cross-links
what causes alpha keratin to become tough & rigid?
lots of disulfide cross-links
what are fingernails made of?
heavly cross-linked alpha-keratin without pigment
what is silk made of?
beta-keratin
amino acids making up beta-keratin
glycine
alanine
smaller pendant groups in beta-keratin lead to ______________ H-bonding
moderate intermolecular
describe protein chains in beta keratin
almost fully extended → good tensile strength
describe tensile strength of silk
good tensile strength due to protein chains being almost fully extended
what makes silk feel soft?
moderate H-bonding (as opposed to heavy)
most abndant single protein in vertebrates (1/3 of total protein mass)
collagen
collagen
forms matrix of bones, major part of tendons, major part of skin
holds our body together
what is collagen called when used in food?
gelatin
amino acids of collagen
glycine (every 3rd residue)
proline
lysine
in collagen, glycine must be every ____ residue
3rd
the large pendant groups of amino acids in collagen lead to a _________ formation
helix
in collagen, proline is converted to ________
hydroxyproline
hydroxyproline leads to ___________ via __________
cross-linking / H-bonding
collagen is a ___________ of 3 polypeptide chains called the __________ unit
triple helix / tropocollagen
each collagen chain is about DP _________ (or Mn a~ 100,000) with a full turn every _____ amino acids
1000 / 3.3
is collagen loosely or tightly wrapped?
tightly
what is required for the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline?
vitamin C
the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline leads to additional ______________ bonding within the tropocollagen unit, making it ________
intermolecular H-bonding / strong
chemical modification of collagen
cross-linking of lysine side chaisn within tropocollagen units, making collagen even more strong
describe chemical modification & cross-linking of lysine sidechains within tropocollagen units
lysine side chains are oxidized to aldehydes & then either react with another lysine residue or another oxidized lysine via an aldo condensation and dehydration
which is stronger, chemical cross-links or H-bonding?
chemical cross-links
overall, collagen in tendons has a strength similar to __________
copper wire