301 Final MC Q's
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:00 PM on 5/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following statements is not correct?
\-Patients with hearing loss have problems in formulating thoughts.
\-Representation of thought in language seems to be important in the mental activities of language users.
\-Language is used to express thoughts.
\-Thoughts are an internal representation of experiences.
\-Patients with hearing loss have problems in formulating thoughts.
\-Representation of thought in language seems to be important in the mental activities of language users.
\-Language is used to express thoughts.
\-Thoughts are an internal representation of experiences.
Patients with hearing loss have problems in formulating thoughts.
2
New cards
Which of the following rules is not governing language?
\-Syntax
\-Etymology
\-Semantics
\-Phonology
\-Syntax
\-Etymology
\-Semantics
\-Phonology
\-Etymology
3
New cards
The domains of the neural processes can not be observed with?
\-Electronic Resonance Imaging
\-Magnetic Resonance Imaging
\-Magnetoencephalography
\-Electroencephalography
\-Electronic Resonance Imaging
\-Magnetic Resonance Imaging
\-Magnetoencephalography
\-Electroencephalography
\-Electronic Resonance Imaging
4
New cards
Which of the following sequences of levels represent the speech chain?
-Acoustic › Linguistic › Physiological › Linguistic › Physiological.
\-Linguistic › Physiological › Linguistic › Acoustic › Physiological.
\-Linguistic › Physiological › Acoustic › Physiological › Linguistic.
\-Physiological › Linguistic › Acoustic › Linguistic › Physiological.
-Acoustic › Linguistic › Physiological › Linguistic › Physiological.
\-Linguistic › Physiological › Linguistic › Acoustic › Physiological.
\-Linguistic › Physiological › Acoustic › Physiological › Linguistic.
\-Physiological › Linguistic › Acoustic › Linguistic › Physiological.
\-Linguistic › Physiological › Acoustic › Physiological › Linguistic.
5
New cards
As the tine of a vibrating tuning fork moves away from its rest position, which force increases?
\-Both of them
\-None of them
\-Elasticity
\-Inertia
\-Both of them
\-None of them
\-Elasticity
\-Inertia
\-Elasticity
6
New cards
In a compression area, the air molecules are close together?
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-True
7
New cards
Which is the number of frequency components in a simple wave (pure tone)?
\-0
\-Infinite
\-1
\-10
\-0
\-Infinite
\-1
\-10
\-1
8
New cards
The Period is the distance between corresponding points in successive cycles of waves.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
9
New cards
The amount of force applied to a vibrating body determines the frequency of vibration.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
10
New cards
A 100 Hz pure tone has shorter wavelengths and periods compared to a 1000 Hz pure tone.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
11
New cards
Which of the following statements is not correct?
\-Wavelength is indirectly proportional to frequency.
\-Period is directly proportional to wavelength.
\-Period is indirectly proportional to frequency.
\-Period is directly proportional to frequency.
\-Wavelength is indirectly proportional to frequency.
\-Period is directly proportional to wavelength.
\-Period is indirectly proportional to frequency.
\-Period is directly proportional to frequency.
\-Period is directly proportional to frequency.
12
New cards
If the following components were combined: 540 Hz, 630 Hz, and 720 Hz, what would be the fundamental frequency?
\-80
\-70
\-60
\-90
\-80
\-70
\-60
\-90
\-90
13
New cards
What is the wavelength of a sound that has a frequency of 453 Hz? \n Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-75 m
\-0.75 cm
\-0.075 m
\-75 cm
\-75 m
\-0.75 cm
\-0.075 m
\-75 cm
\-75 cm
14
New cards
What is the lowest frequency of resonance of a tube open at one end and closed at the other and which is 8 cm long? Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-2125 Hz
\-10.62 Hz
**-**1062 Hz
\-21.25 Hz
\-2125 Hz
\-10.62 Hz
**-**1062 Hz
\-21.25 Hz
**-**1062 Hz
15
New cards
What is the lowest frequency of resonance of a tube which is 0.5 m long, open at both \n ends? Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s.
\-3400 Hz
**-**340 Hz
\-3.4 Hz
\-170 Hz
\-3400 Hz
**-**340 Hz
\-3.4 Hz
\-170 Hz
**-**340 Hz
16
New cards
A destructive interference consists of adding two waves in phase.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
17
New cards
If the following components were combined: 120 Hz, 180 Hz, and 210 Hz, what would be the fundamental frequency?
\-0
\-15
\-120
\-30
\-0
\-15
\-120
\-30
\-30
18
New cards
How many nodes and antinodes does a standing wave with 3 ½ cycles have?
\-2 nodes and 3 antinodes
\-3 nodes and 2 antinodes
\-3 nodes and 4 antinodes
\-4 nodes and 3 antinodes
\-2 nodes and 3 antinodes
\-3 nodes and 2 antinodes
\-3 nodes and 4 antinodes
\-4 nodes and 3 antinodes
\-4 nodes and 3 antinodes
19
New cards
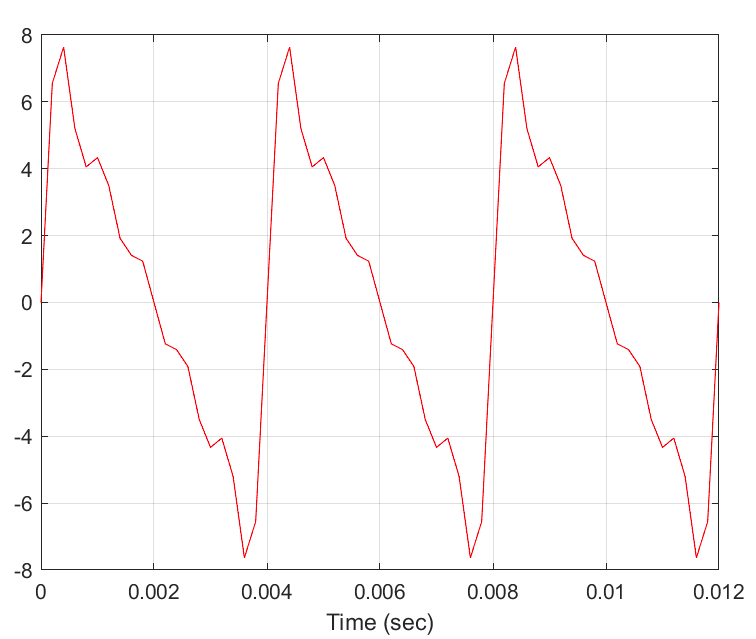
What is the fundamental period (To) of the waveform in seconds?
\-4
\-0.02
\-20
\-0.004
\-4
\-0.02
\-20
\-0.004
\-0.004
20
New cards
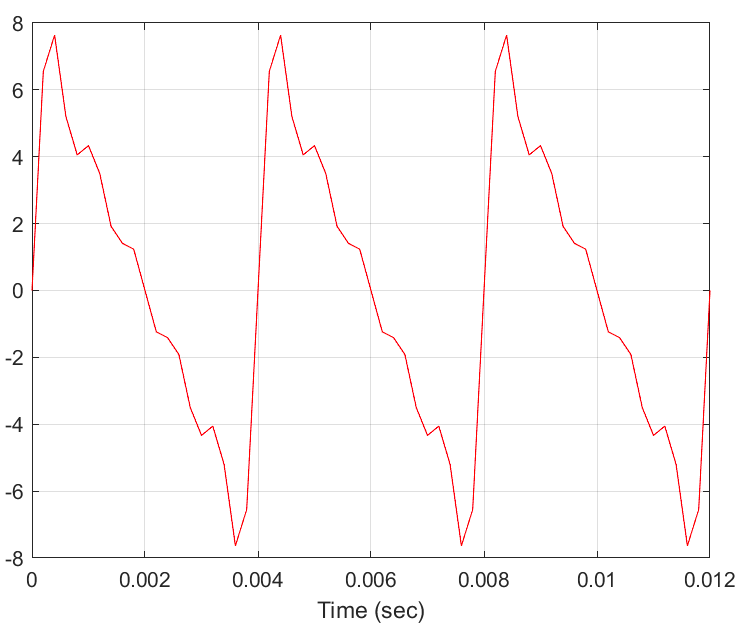
What is the fundamental frequency (fo) of the waveform in Hz?
\-125Hz
\-250Hz
\-100Hz
\-200Hz
\-125Hz
\-250Hz
\-100Hz
\-200Hz
\-250Hz
21
New cards
Which of the following statement is correct?
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has longer wavelengths but shorter period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has longer wavelengths and period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has shorter wavelengths but longer period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has shorter wavelengths and period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has longer wavelengths but shorter period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has longer wavelengths and period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has shorter wavelengths but longer period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has shorter wavelengths and period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
\-A 300 Hz pure tone has longer wavelengths and period compare to a 500 Hz pure tone
22
New cards
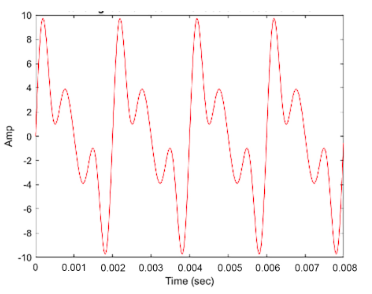
What is the fundamental period (To) of the waveform?
\-0.008 s
\-0.002 ms
\-0.002 s
\-0.004 ms
\-0.008 s
\-0.002 ms
\-0.002 s
\-0.004 ms
\-0.002 s
23
New cards
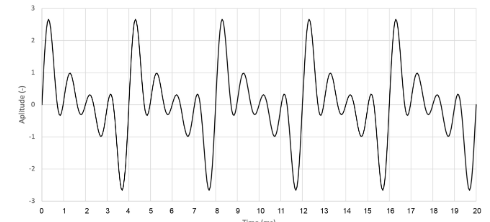
What is the fundamental frequency (fo) of the waveform in Hz?
\-0.25 Hz
\-250 Hz
\-2.5 Hz
\-25 Hz
\-0.25 Hz
\-250 Hz
\-2.5 Hz
\-25 Hz
\-250 Hz
24
New cards
If the following components were combined: 140 Hz, 280 Hz, and 560 Hz, what would be the fundamental frequency?
\-70 Hz
\-35 Hz
\-28 Hz
\-140 Hz
\-70 Hz
\-35 Hz
\-28 Hz
\-140 Hz
\-140 Hz
25
New cards
If the following components were combined: 320 Hz, 560 Hz, and 720 Hz, what would be the fundamental frequency?
\-320 Hz
\-80 Hz
\-65 Hz
\-150 Hz
\-320 Hz
\-80 Hz
\-65 Hz
\-150 Hz
\-80 Hz
26
New cards
What is the wavelength of a sound that has a frequency of 1292 Hz? \n Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-260 cm
\-0.026 m
\-0.26 m
\-0.26 cm
\-260 cm
\-0.026 m
\-0.26 m
\-0.26 cm
\-0.26 m
27
New cards
What is the frequency of a sound that has a wavelength of 340 cm? \n Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-10 Hz
\-100 Hz
\-1 Hz
\-1000 Hz
\-10 Hz
\-100 Hz
\-1 Hz
\-1000 Hz
\-100 Hz
28
New cards
What is the lowest frequency of resonance of a tube closed at both ends which is 0.14 m long? Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-12.14 Hz
\-121.4 Hz
\-1214 Hz
\-2428 Hz
\-12.14 Hz
\-121.4 Hz
\-1214 Hz
\-2428 Hz
\-1214 Hz
29
New cards
What is the lowest frequency of resonance of a tube which is 8 cm long, open at both ends? Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-21.25 Hz
\-4250 Hz
\-2125 Hz
\-212.5 Hz
\-21.25 Hz
\-4250 Hz
\-2125 Hz
\-212.5 Hz
\-2125 Hz
30
New cards
What is the lowest frequency of resonance of a tube open at one end and closed at the other and which is 2 cm long? Assume the speed of sound is 340 m/s. Hint: 100 cm = 1 m
\-425 Hz
\-4250 Hz
\-8500 Hz
\-42.5 Hz
\-425 Hz
\-4250 Hz
\-8500 Hz
\-42.5 Hz
\-4250 Hz
31
New cards
Consider the normal inhalation process:
\-air entering the lungs causes the lungs to expand
\-none of the above
\-depending on the initial air pressure within the lungs, the air entering the lungs causes the lungs to expand or the expansion of the lungs causes air to enter the lungs
**-**expansion of the lungs causes air to enter the lungs
\-air entering the lungs causes the lungs to expand
\-none of the above
\-depending on the initial air pressure within the lungs, the air entering the lungs causes the lungs to expand or the expansion of the lungs causes air to enter the lungs
**-**expansion of the lungs causes air to enter the lungs
**-**expansion of the lungs causes air to enter the lungs
32
New cards
During the active expiration
**-**Above resting volume, the inspiratory muscles maintain lungs in an expanded state
\-Below resting volume, the muscles counteract passive collapse of the respiratory system
\-Above resting volume, the muscles force the respiratory system into a compressed state
\-Below resting volume, the inspiratory muscles maintain lungs in an expanded state
**-**Above resting volume, the inspiratory muscles maintain lungs in an expanded state
\-Below resting volume, the muscles counteract passive collapse of the respiratory system
\-Above resting volume, the muscles force the respiratory system into a compressed state
\-Below resting volume, the inspiratory muscles maintain lungs in an expanded state
**-**Above resting volume, the inspiratory muscles maintain lungs in an expanded state
33
New cards
The Tidal volume represents
**-1**0% of the Vital Capacity
\-5% of the Vital Capacity
\-20% of the Vital Capacity
\-15% of the Vital Capacity
**-1**0% of the Vital Capacity
\-5% of the Vital Capacity
\-20% of the Vital Capacity
\-15% of the Vital Capacity
**-1**0% of the Vital Capacity
34
New cards
Increasing subglottal pressure (Ps) yields an increase in
\-Duration of phonation
\-Intensity
\-Fundamental frequency
**-**All of the above
\-Duration of phonation
\-Intensity
\-Fundamental frequency
**-**All of the above
**-**All of the above
35
New cards
Of the following cartilages, which are paired?
\-cricoid
**-**arytenoid
\-all of the above
\-thyroid
\-cricoid
**-**arytenoid
\-all of the above
\-thyroid
**-**arytenoid
36
New cards
Extreme adduction of the vocal folds is typical of
\-a normal voice
\-a breathy voice
\-vocal fry
**-**a pressed voice
\-a normal voice
\-a breathy voice
\-vocal fry
**-**a pressed voice
**-**a pressed voice
37
New cards
Breathy voice is caused by:
\-extreme adduction
\-irregularities in laryngeal tissues
\-lesions produced by the impact of vocal folds during phonation
**-**incomplete vocal fold adduction
\-extreme adduction
\-irregularities in laryngeal tissues
\-lesions produced by the impact of vocal folds during phonation
**-**incomplete vocal fold adduction
**-**incomplete vocal fold adduction
38
New cards
Bernoulli’s principle states that a flow through a small passage (e.g., the glottis) yields
\-None of the above
**-**A decrease in pressure
\-An increase in pressure
\-A decrease in speed
\-None of the above
**-**A decrease in pressure
\-An increase in pressure
\-A decrease in speed
**-**A decrease in pressure
39
New cards
Which is the function of the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles?
\-To draw the arytenoids forward and down
\-All of the above
\-To draw the arytenoids together posteriorly and adduct vocal folds
**-**To rotate the arytenoids and separate the vocal folds
\-To draw the arytenoids forward and down
\-All of the above
\-To draw the arytenoids together posteriorly and adduct vocal folds
**-**To rotate the arytenoids and separate the vocal folds
**-**To rotate the arytenoids and separate the vocal folds
40
New cards
Boyle’s law states that the pressure is directly proportional to the volume
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
41
New cards
How does the vocal tract sustain the vocal fold oscillation?
\-Creating a positive pressure at the top of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
\-Creating a positive pressure at the bottom of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
**-**Creating a negative pressure at the bottom of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
\-Creating a negative pressure at the top of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
\-Creating a positive pressure at the top of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
\-Creating a positive pressure at the bottom of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
**-**Creating a negative pressure at the bottom of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
\-Creating a negative pressure at the top of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
**-**Creating a negative pressure at the bottom of the vocal fold that sucks them together.
42
New cards
The convergent shape of the vocal folds is characterized by:
\-Negative air pressure.
\-Bottom of vocal folds further apart than the top.
\-Top of vocal folds further apart than the bottom.
\-It is typical in the closing phase of the vocal fold.
\-Negative air pressure.
\-Bottom of vocal folds further apart than the top.
\-Top of vocal folds further apart than the bottom.
\-It is typical in the closing phase of the vocal fold.
\-Bottom of vocal folds further apart than the top.
43
New cards
A resonator such as the vocal tract of length L resonates to frequencies that are:
**-**f=(2n-1)c/4L with n= integer.
\-f=(2n)c/4L with n= integer.
\-f=(2n-1)c/2L with n= integer.
\-f=(2n)c/2L with n= integer.
**-**f=(2n-1)c/4L with n= integer.
\-f=(2n)c/4L with n= integer.
\-f=(2n-1)c/2L with n= integer.
\-f=(2n)c/2L with n= integer.
**-**f=(2n-1)c/4L with n= integer.
44
New cards
The length of a female standard vocal tract (larynx to lips) is 14.2 cm. Which are the first to formants?
\-500 and 1500 Hz.
\-1200 and 2400 Hz.
\-1000 and 2000 Hz.
\-600 and 1800 Hz.
\-500 and 1500 Hz.
\-1200 and 2400 Hz.
\-1000 and 2000 Hz.
\-600 and 1800 Hz.
\-600 and 1800 Hz.
45
New cards
Which of the following statements is correct?
\-High F2 is associated with long oral cavity.
\-Low F2 is associated with short oral cavity.
\-Low F1 is associated with small pharynx and open mouth.
\-High F1 is associated with small pharynx and open mouth.
\-High F2 is associated with long oral cavity.
\-Low F2 is associated with short oral cavity.
\-Low F1 is associated with small pharynx and open mouth.
\-High F1 is associated with small pharynx and open mouth.
\-High F1 is associated with small pharynx and open mouth
46
New cards
If you hold the glottal source constant while changing the vocal tract, you will
\-Maintain the vowel and vary the fundamental frequency.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Vary the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and vary the vowel.
\-Maintain the vowel and vary the fundamental frequency.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Vary the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and vary the vowel.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and vary the vowel.
47
New cards
If you hold the vocal tract constant while changing the glottal source, you will
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and vary the vowel.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Vary the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Maintain the vowel and vary the fundamental frequency.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and vary the vowel.
\-Maintain the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Vary the fundamental frequency and the vowel.
\-Maintain the vowel and vary the fundamental frequency.
\-Maintain the vowel and vary the fundamental frequency.
48
New cards
\
In comparison to the formants of the neutral vowels, the \[i\] vowel has
\-Higher F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
In comparison to the formants of the neutral vowels, the \[i\] vowel has
\-Higher F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
49
New cards
In comparison to the formants of the neutral vowels, the \[u\] vowel has
\-Higher F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
\-Higher F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
50
New cards
In comparison to the formants of the neutral vowels, the \[a\] vowel has
\-Higher F1 and Higher F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
\-Higher F1 and Higher F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
\-Lower F1 and Higher F2.
\-Lower F1 and Lower F2.
\-Higher F1 and Lower F2.
51
New cards
The manner of articulation gives information on
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
\-Where the vocal tract is obstructe
**-**How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
\-All of the above.
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
\-Where the vocal tract is obstructe
**-**How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
\-All of the above.
**-**How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
52
New cards
The place of articulation gives information on
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
\-How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
**-**Where the vocal tract is obstructe
\-All of the above.
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
\-How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
**-**Where the vocal tract is obstructe
\-All of the above.
**-**Where the vocal tract is obstructe
53
New cards
The phonation classification gives information on
\-All of the above.
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
\-How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
\-Where the vocal tract is obstructe
\-All of the above.
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
\-How the noise is generated in the vocal tract.
\-Where the vocal tract is obstructe
\-The presence of the fundamental frequency in the sound generate
54
New cards
The liquid \[l\] is characterized by a flat F3.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-True
55
New cards
Nasal consonants are characterized by the resonance of the nasal cavity with a peak at
**-**200-300 Hz.
\-400-500 Hz.
\-100-150 Hz.
\-50-60 Hz.
**-**200-300 Hz.
\-400-500 Hz.
\-100-150 Hz.
\-50-60 Hz.
**-**200-300 Hz.
56
New cards
The \[s\] consonant is characterized by a frication noise with high frequency energetic content. Which is the starting frequency of the \[s\] consonant?
\-5000 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
\-4000 Hz.
\-2000 Hz.
\-5000 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
\-4000 Hz.
\-2000 Hz.
\-4000 Hz.
57
New cards
The \[sh\] consonant (as in ship) is characterized by a frication noise with a high-frequency energetic content. Which is the starting frequency of the \[sh\] consonant?
\-5000 Hz.
**-**2000 Hz.
\-4000 Hz.
-3000 Hz.
\-5000 Hz.
**-**2000 Hz.
\-4000 Hz.
-3000 Hz.
**-**2000 Hz.
58
New cards
The stop consonants are characterized by the presence of a (near) silent interval during stop closure, followed by a release-burst. In the bilabials, the frequency range of most intense portion of release-burst is at?
**-**600 Hz.
\-1000 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
\-300 Hz.
**-**600 Hz.
\-1000 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
\-300 Hz.
**-**600 Hz.
59
New cards
The stop consonants are characterized by the presence of a (near) silent interval during stop closure, followed by a release-burst. In the alveolar, the frequency range of most intense portion of release-burst is at?
\-600 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
\-300 Hz.
\-1000 Hz.
\-600 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
\-300 Hz.
\-1000 Hz.
\-3000 Hz.
60
New cards
Syllable-initial stops are mainly differentiated by voice onset time (VOT), which is defined as the time between stop release and phonation onset. Which type of VOT is associated with the consonant \[p\] in American English?
\-Long-lag VOT.
\-Voicing lead VOT.
\-Zero onset VOT.
\-Short-lag VOT
\-Long-lag VOT.
\-Voicing lead VOT.
\-Zero onset VOT.
\-Short-lag VOT
\-Long-lag VOT.
61
New cards
In English, the unit of stress is the word.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
62
New cards
Syllable affiliations of sounds are explained by analyzing the
\-Stress.
\-Juncture.
\-Duration.
\-Intonation.
\-Stress.
\-Juncture.
\-Duration.
\-Intonation.
\-Juncture.
63
New cards
Stressed syllables are characterized by
\-Longer duration.
\-All of the above.
\-Louder intensity.
\-Higher intonation.
\-Longer duration.
\-All of the above.
\-Louder intensity.
\-Higher intonation.
\-All of the above.
64
New cards
Information provided by intonation can override the information provided by the syntax of a phrase.
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
65
New cards
Which lobe contains Broca' s area?
**-**Frontal.
\-Parietal.
\-Cerebellum.
\-Temporal.
**-**Frontal.
\-Parietal.
\-Cerebellum.
\-Temporal.
**-**Frontal.
66
New cards
Which lobe contains Wernicke' s area?
\-Parietal.
**-**Temporal.
\-Frontal.
\-Cerebellum.
\-Parietal.
**-**Temporal.
\-Frontal.
\-Cerebellum.
**-**Temporal.
67
New cards
Neural impulses are conducted away from the cell body via the
\-Synapse
\-Axon
\-Dendrites
\-Brainstem
\-Synapse
\-Axon
\-Dendrites
\-Brainstem
\-Axon
68
New cards
Dysarthria is a deficit in the planning of speech.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
69
New cards
The juncture between neurons is called
\-Axon
\-Brainstem
\-Synapse
\-Dendrites
\-Axon
\-Brainstem
\-Synapse
\-Dendrites
\-Synapse
70
New cards
Which type of deficit in speech is associated with Apraxia?
\-Execution of speech
\-Planning of speech
\-Execution of speech
\-Planning of speech
\-Planning of speech
71
New cards
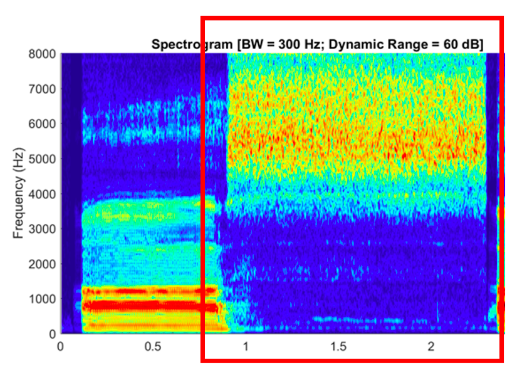
Which type of consonant is shown in the spectrogram?
\-nasal
\-fricative
\-stop
\-glide
\-nasal
\-fricative
\-stop
\-glide
\-fricative
72
New cards
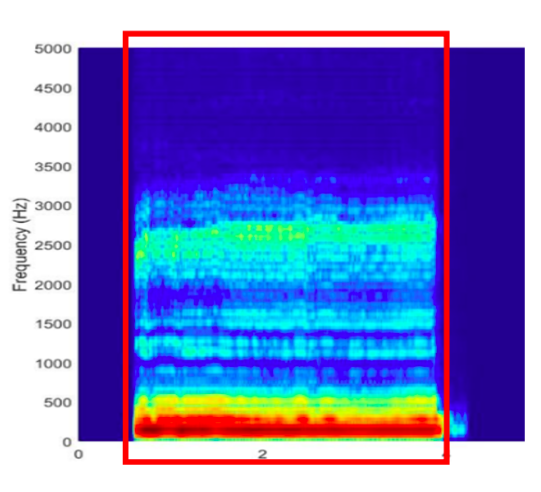
Which type of consonant is shown in the spectrogram?
\-nasal
\-fricative
\-stop
\-glide
\-nasal
\-fricative
\-stop
\-glide
\-nasal
73
New cards
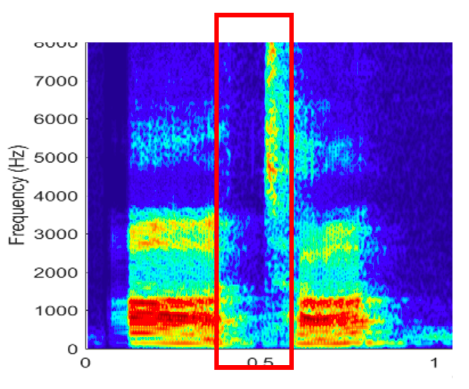
Which type of consonant is shown in the spectrogram?
\-nasal
\-fricative
\-stop
\-glide
\-nasal
\-fricative
\-stop
\-glide
\-stop
74
New cards
A rising intonation at the end of the sentence:
\-identifies a statement
\-change the meaning of the last word
-identifies a question
\-does not affect the meaning of the sentence
\-identifies a statement
\-change the meaning of the last word
-identifies a question
\-does not affect the meaning of the sentence
-identifies a question
75
New cards
Stressed syllables are characterized by
\-Lower Intensity
\-Higher pitch (f0)
\-Shorter duration
\-All of the above
\-Lower Intensity
\-Higher pitch (f0)
\-Shorter duration
\-All of the above
\-Higher pitch (f0)
76
New cards
Which of the following statements about Juncture is correct:
\-Juncture identify stressed and unstressed syllables
\-Juncture help differentiate questions from statements
\-Juncture describe the way sounds are joined or separated
\-Juncture identify stressed and unstressed syllables
\-Juncture help differentiate questions from statements
\-Juncture describe the way sounds are joined or separated
-Juncture describe the way sounds are joined or separated
77
New cards
* The patient produces distorting sounds. The articulators are not placed in the right place and the sound comes out wrong. Longer and complex words are particularly difficult to pronounce.
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have?
\-Broca’s aphasia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have?
\-Broca’s aphasia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
\-Apraxia
78
New cards
* The patient has damaged muscles and he has difficulty moving/controlling them in the mouth.
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have?
-Broca’s aphasia
-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have?
-Broca’s aphasia
-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
\-Dysarthria
79
New cards
* The patient struggle to find the words and his speech is not fluent. Additionally, he has difficulty with certain grammatical structures
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have? \n -Broca’s aphasia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have? \n -Broca’s aphasia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
\-Broca’s aphasia
80
New cards
* The patient does not understand the questions and his speech often does not make a lot of sense. He peppers his sentences with non-existent or irrelevant words. He may fail to realize that he is using the wrong words or using a non-existent word and often he is not fully aware that what he says doesn’t make sense.
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have?
\-Broca’s aphasia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
What kind of speech disorders is the patient most likely to have?
\-Broca’s aphasia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
\-Dysarthria
\-Apraxia
\-Wernicke’s aphasia
81
New cards
A servomechanism is part of a closed loop system.
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
82
New cards
The goal of the feedback is always to reach a point of equilibrium.
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
\-False
\-False
83
New cards
The external auditory feedback includes:
\-Proprioceptive feedback.
\-Tactile feedback.
\-Bone conduction.
\-Cerebellum feedback.
\-Proprioceptive feedback.
\-Tactile feedback.
\-Bone conduction.
\-Cerebellum feedback.
\-Bone conduction.
84
New cards
Delayed auditory feedback and frequency-altered feedback are used as therapy for stuttering.
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
85
New cards
Filtering out high frequency in the external auditory feedback will generate:
**-**All of the above
\-Louder speech.
\-Higher fundamental frequency.
\-More brilliant (with a higher frequency energetic content) speech.
**-**All of the above
\-Louder speech.
\-Higher fundamental frequency.
\-More brilliant (with a higher frequency energetic content) speech.
**-**All of the above
86
New cards
Linguistic Oriented Models of speech production are based on
\-The order of the speech sounds.
\-Structure of the sound system of languages.
\-The feedback in the speech production.
\-A sequence of targets corresponding to speech sounds.
\-The order of the speech sounds.
\-Structure of the sound system of languages.
\-The feedback in the speech production.
\-A sequence of targets corresponding to speech sounds.
\-Structure of the sound system of languages.
87
New cards
The model of Chomsky and Halle redesigned a binary distinctive feature system in articulatory terms.
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
88
New cards
The model of Ladefoged proposed a system of features where a sound can have different features at the same time.
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
\-False
**-**True
89
New cards
In the model of Lashley, the pronunciation is ordering the motor activity for speech production.
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-False
90
New cards
Which model summarizes the coarticulation described from spectrograms, including static properties of phonemes and dynamic rules that blend the phonemes into running speech?
\-The model of Lashley
\-The model of Henke
\-The model of Ohman
\-The model of Martin
\-The model of Lashley
\-The model of Henke
\-The model of Ohman
\-The model of Martin
\-The model of Ohman
91
New cards
Which of the following is not a model of speech production?
\-Timing Models
\-Linguistic Orientated Models
\-Target Models
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
\-Timing Models
\-Linguistic Orientated Models
\-Target Models
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
92
New cards
Which type of loop would include the influence of auditory feedback?
**-**Closed loops
\-Open loops
**-**Closed loops
\-Open loops
**-**Closed loops
93
New cards
Which of the following types of feedback are not relevant to speech production?
\-Tactile
\-Auditory
\-Visual
\-Proprioceptive
\-Tactile
\-Auditory
\-Visual
\-Proprioceptive
\-Visual
94
New cards
Motor Equivalence is under which group of models of speech production?
\-Linguistic Orientated Models
\-Target Models
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
-Timing Models
\-Linguistic Orientated Models
\-Target Models
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
-Timing Models
\-Target Models
95
New cards
Which of the following is not true regarding the Lombard Effect?
\-It is an involuntary response
\-Vocal effort is increased
\-The goal is to increase audibility
\-Can occur in quiet environments
\-Effects acoustic features other than loudness
\-It is an involuntary response
\-Vocal effort is increased
\-The goal is to increase audibility
\-Can occur in quiet environments
\-Effects acoustic features other than loudness
\-Can occur in quiet environments
96
New cards
What feature is not affected by Lombard?
**-**Vocal tract length
\-Fundamental Frequency
\-Intensity
\-Duration
**-**Vocal tract length
\-Fundamental Frequency
\-Intensity
\-Duration
**-**Vocal tract length
97
New cards
The Lombard Effect results in an increase in the auditory signal to noise ratio of the speaker’s spoken words.
\-False
\-True
\-False
\-True
\-True
98
New cards
Which of the following is not a manipulation of auditory feedback?
\-Temporal shift
\-Pitch shift
\-Formant shift
\-All of these are manipulations of auditory feedback
\-Temporal shift
\-Pitch shift
\-Formant shift
\-All of these are manipulations of auditory feedback
\-All of these are manipulations of auditory feedback
99
New cards
Ventriloquism is best described by which speech production model?
\-Linguistic Orientated Models
\-Motor Equivalence Model
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
\-Timing Models
\-Linguistic Orientated Models
\-Motor Equivalence Model
\-Delayed Auditory Feedback Models
\-Timing Models
\-Motor Equivalence Model
100
New cards
Delayed auditory feedback can be used to treat which of the following?
**-**Stuttering
\-Aphasia
\-Dystonia
**-**Stuttering
\-Aphasia
\-Dystonia
**-**Stuttering