Dog Cat exam 2
1/557
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
558 Terms
common abdominal hernias:
umbilical
inguinal
diaphragmatic
peritoneal-pericardial
scrotal
perineal
hiatal
strangulation
entrapment of viscera and obstruction of blood supply
incarceration
contents are irreducible and contraction of scar tissue at hernia ring may result in delayed signs ± strangulation
simple hernia treatment:
may spontaneously close
surgery
complicated hernia
hernia with GI signs
complicated hernia treatment:
full exlap
check intestinal viability
inguinal hernia treatment:
surgery with ventral midline incision
diaphragmatic hernia is usually caused by _____
trauma
radial tear
tear of caval foramen of diaphragm
circumferential tear
tear of pars sternalis of diaphragm
peritoneo-pericardial diaphragmatic hernia
communication between abdomen and pericardium
cells of stratum corneum are suspended in lipids comprised of…
nonpolar lipids, ceramides, free fatty acids, and cholesterol
lamellar bodies are synthesized in…
stratum spinosum
lamellar bodies secrete and store…
lipids
desmosomes
major cell adhesion molecule
3 desmosome families:
cadherins
plakins
armadillo proteins
hemidesmosomes
attach epidermis to dermis
dogs and cats have a _________ hair follicle arrangement
compound
hair cluster consists of…
2-5 guard hairs surrounded by smaller secondary hairs
anagen phase
hair growth
catagen phase
transitional period
telogen phase
resting period
what sweat glands are not found on footpads or nasal planum?
sebaceous gland
epitrichial sweat glands
what sweat glands are found on the footpads?
atrichial
SCRATCH acronym for pruritic animal:
S- severity
C- contagion
R- response to previous therapy
A- affected areas
T- timeline
C- conditions
H- hereditary
what are the common distributions of lesions and pruritus associated with atopic dermatitis and food allergy?
paws
inguinal region
axillary region
ears
muzzle
what are the common distributions of lesions and pruritus associated with sarcoptic mange?
ears
hocks
elbows
abdominal region
what are the common distributions of lesions and pruritus associated with demodectic mange?
paws
multifocal areas around body
what are the common distributions of lesions and pruritus associated with flea bite hypersensitivity?
neck
dorsum
inguinal region
what are the common distributions of lesions and pruritus associated with malassezia dermatitis?
paws
mouth
axillary region
perineum
eyes
pruritus onset at < 6 months old likely etiology is:
parasitic
food
pruritus onset at 6 months-3 years old likely etiology is:
parasitic
food
environment
pruritus onset at >5 years old likely etiology is:
parasitic
food
infectious
causes of non or variable pruritus onset in young dog:
infections
parasites
fungal
juvenile cellulitis in dogs
hereditary scaling disease
hereditary follicular disease
hereditary subepidermal blistering diseases
causes of non pruritic onset in middle aged dog:
endocrine diseases
immune mediated diseases
causes of non pruritic onset older dog:
immune mediated diseases
metabolic disease
endocrine diseases
neoplasia
macule
well circumscribed non-palpable area od color change less than 1 cm diameter
patch
well circumscribed nonpalpable area of color change more than 1 cm
plaque
solid elevation more than 1 cm in diameter
diascopy
press clear slide against erythematous area of skin to see if it blanches with pressure
papule
solid elevation less than 1 cm in diameter
pustule
small, well circumscribed area within the epidermis that can be filled with neutrophils or eosinophils
vesicle
small area within or below epidermis less than 1 cm diameter and filled with clear fluid
bulla
blister > 1 cm diameter
nodule
solid elevation more than 1 cm in diameter that extends into deeper tissue layers
tumor
large mass in skin or SQ
alopecia
partial to complete hair loss
scale
accumulation of loose fragments consisting of horny layer of skin
follicular cast
accumulation of keratin on hair shaft
fronds
multiple hairs together surrounded by casts in paintbrush appearance
crust
adherence of dried exudate containing serum, blood, pus, or scales
comedone
dilated hair follicle filled with corneocytes and sebaceous material
epidermal collarette
shallow scaly ring
erosion
shallow epidermal defect
excoriation
erosion secondary to self trauma
ulcer
full thickness loss of epidermis revealing underlying dermis
lichenification
thickening of skin resulting in exaggerated skin surface appearance
callus
thickened skin associated with pressure points
fissure
linear cleavage of epidermis
severe cases of otitis should be pretreated with…
corticosteroids
causes of otitis externa:
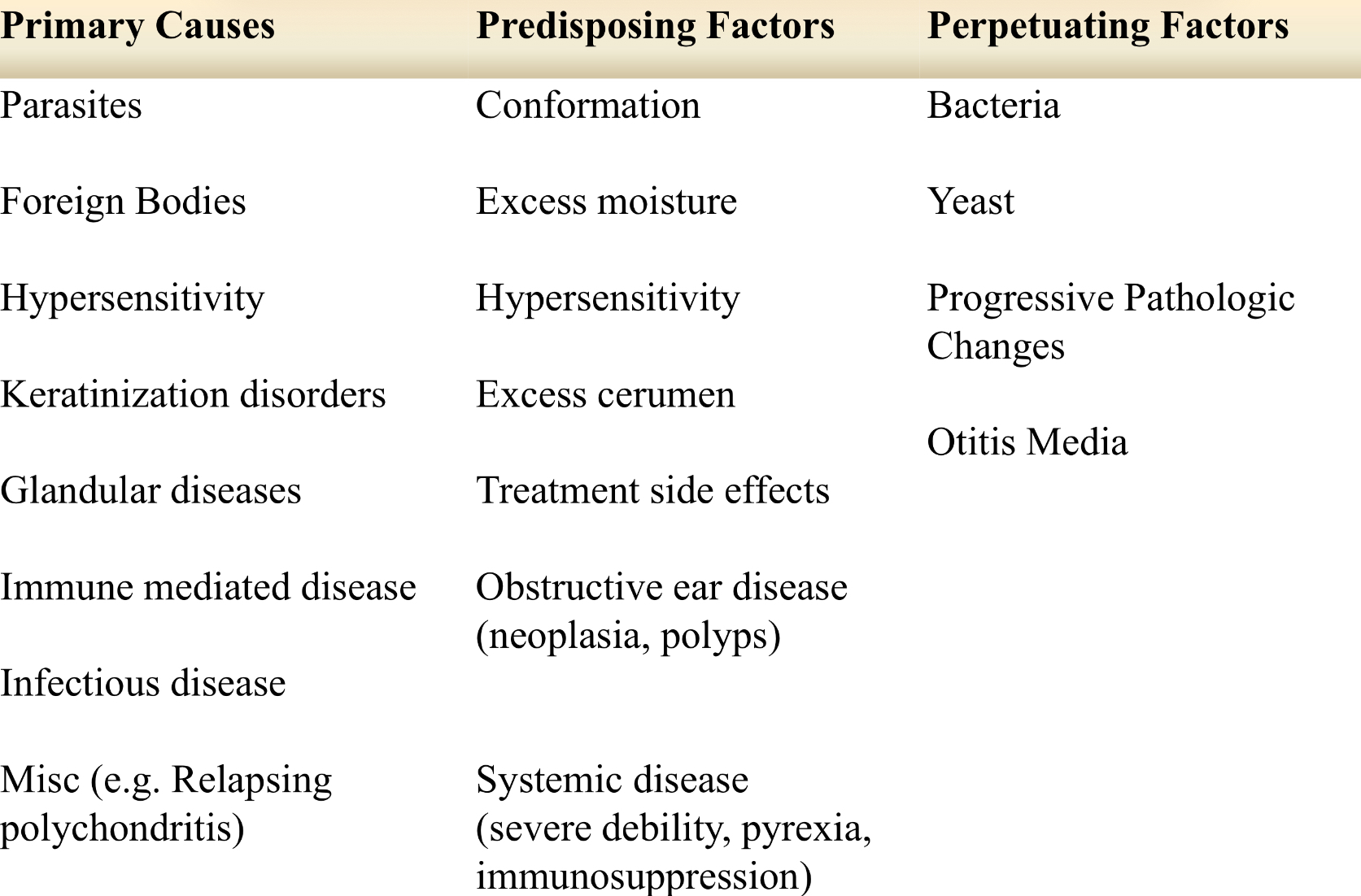
moist brown ear discharge =
yeast or staph
coffee ground ear discharge =
mites
creamy yellow ear discharge =
gram - organisms
waxy, greasy ear discharge =
hypersensitivity
glandular disease
disorders of keratinization
____% of ear tumors in cats are malignant
87.5
what is the most common ear tumor in cat?
ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma
____% of ear tumors in dogs are malignant
60%
sarcoptes signs:
highly contagious
pruritus (not always seen)
cheyletiella spp diagnosis:
skin scrape or tape prep
lice signs:
mild to moderate pruritus
alopecia
scales
crust
demodex canis signs:
papulopustular dermatitis
alopecic macules to patches
erythematous dermatitis
hyperpigmented patches/comedones
scaling dermatosis
pododemodicosis
demodex injai signs:
seborrheic dermatitis
common on dorsal lumbar region
short bodied demodex of dog
morphological variant of d canis that causes it to be 50% the length of d canis
demodex cati signs:
variably pruritic ptachy, lopecia, and crusting
periocular, head, neck, ears
demodex gatoi signs:
erythema, excoriations, scaling, and crusting
head, neck, elbows, flanks, ventrum, rear legs
demodex gatoi diagnosis:
superficial skin scrape
acetate tape
SAF fecal fixation and centrifugation
demodex gatoi and cati treatment:
lime sulfur
ELDU: fluralaner, selamectin
localized demodicosis treatment:
reduce stress
benzoyl peroxide shampoo
generalized demodicosis
more than 5 affected regions or more than 50% involvement in single region or pododemodicosis
generalized demodicosis is treated for __ months after negative scrape
2
what is treatment of choice for generalized demodicosis
isoxazolines (fluralaner/sarolaner/lotilaner/alfoxolaner)
surface pyoderma signs:
erythema
superficial exudation and erosions in absence of pustules and collarettes
bacterial overgrowth syndrome (BOG) signs:
erythema
lichenification
hyperpigmentation
malodorous greasy seborrhea
excoriation
alopecia
2/3 of BOG is caused by ________
allergy
what is the most common form of skin infection in dog?
superficial bacterial folliculitis
superficial bacterial folliculitis signs:
erythematous papules
pustules
epidermal collarettes
crusts
alopecia
67% of patients with recurrent pyoderma had _______________ as underlying etiology
allergic dermatitis
when is bacterial culture needed for pyoderma?
when long term treatment will be needed
rods on cytology
<50% reduction in extent of lesions after 2 weeks of systemic therapy\
new lesions are occurring
poorly responsive cases
history of drug resistance
history of recurrent infections
the most common methicillin resistant staphylococcus species are…
staphylococcus pseudintermedius
staphylococcus schleiferi
methicillin resistant staphylococcus have what gene?
mecA
how can mecA be detected?
mecA PCR
penicillin binding protein 2a
what coagulase negative staphylococcus is clinically important?
staphylococcus schleiferi
staphylococcus coagulans is coagulase +/-
-
what fungal diseases affect skin, hair, claws?
dermatophytosis
malassezia dermatitis
candidiasis
what fungal diseases affect skin and subcutis?
sporotrichosis
dermatophytic pseudomycetoma
eumycotic mycetoma
phaeohyphomycosis
pythiosis
lagenidiosis
zygomycosis
what fungal diseases affect internal organs with hematogenous spread to skin?
cryptococcosis
blastomycosis
coccidiomycosis
histoplasmosis
common causes of dermatophytosis:
microsporum canis
microsporum gypseum
trichophyton mentagrophytes complex
dermatophytosis pathogenesis:
arthrospores infective and adhere strongly to keratin
trauma/mechanical disruption of skin facilitates penetration
fungal hyphae invade hair follicle of anagen hairs and migrate downwards
fungal metabolic by-products incite an inflammatory reaction, including folliculitis which may lead to furunculosis (rupture of hair follicle)
type IV hypersensitivity
dermatophytosis signs in dogs:
classic annular lesion
patchy alopecia, erythema, scale, crust
folliculitis and furunculosis
kerion