Circuit Analysis
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Superposition
Identify all power sources
Consider all the effects of each one and deactivate the others
For the selected source, find the unknown voltage/current
Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all sources
Find the algebraic sum of the results I = I(a) + I(b)
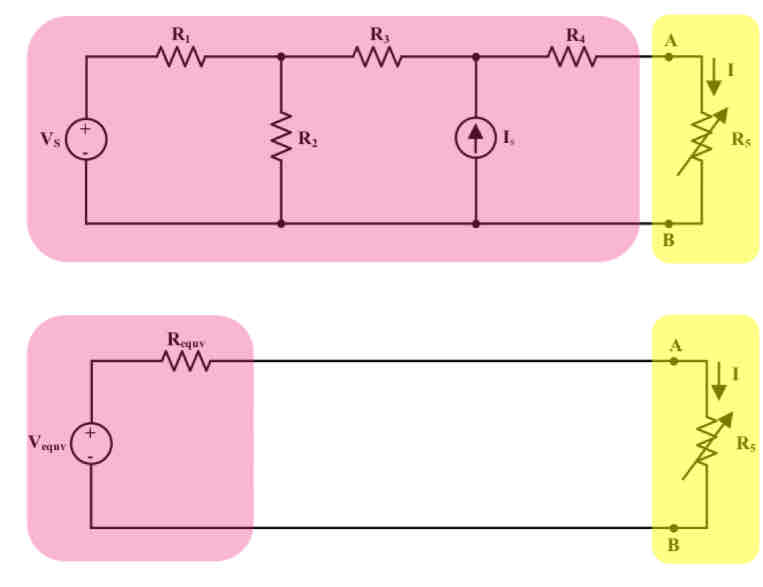
Thevenin’s Equivalent Circuit ( Thereom)
Any collection of power sources and resistances connected between two terminals = voltage source and a single resistance connected in series between the same two terminals
Thevenin’s Equivalent Voltage (VTH)
The open circuit voltage between two terminals
Thevenin’s Equivalent Resistance (RTH)
Total circuit resistance with all power sources off
Thevenin’s Equivalent Circuit ( process)
Create an open circuit
Calculate the open circuit voltage between terminals = VTH
Calculate the equivalent resistance between terminals while all power sources deactivated = RTH
Draw Thevenin’s Equivalent Circuit
Nodal Analysis
Identify all nodes
Select one node as the reference node to have 0V
Apply KCL to each of the non-reference nodes, using Ohm’s Law to express the current in terms of NODE voltages
Solve the simultaneous equations
Use the derived values of the node voltages to determine the current in each branch of the circuit
What does Thevenin’s Equivalent Circuit look like?