Salivary Gland Disorders
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
mucocele
due to trauma
especially in children
lower lip most common
bluish, translucent hue
which salivary gland issues did we discuss which are NON NEOPLASTIC?
mucocele/ranula
salivary duct cyst
cheilitis glandularis
necrotizing sialometaplasia
nicotine stomatitis
sialolithiasis
LESA
mumps
etc…
what 3 salivary gland issues did we discuss which are BENIGN and NEOPLASTIC
pleomorphic adenoma
warthin’s tumor
canalicular adenoma
what are the MALIGNANT NEOPLASTIC salivary gland disorders?
mucoepidermoid carcinoma
polymorphous adenocarcinoma
adenoid cystic carcinoma
carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma
what is a mucocele caused by?
trauma, severance of the duct and spills mucin
a mucocele on the FOM is called
ranula
a mucocele on the ventral tongue is called
blandin-nuhn
mucocele treatment
excision of lesion and minor salivary glands
characteristics of a ranula
floor of mouth, sublingual gland
lateral to midline
increases in size before and during meals
what is a plunging ranula?
mucin dissects through mylohyoid muscle and process a neck swelling (bull frog)
salivary duct cyst
“mucus retention cyst”
true cyst
upper lip
difference between mucocele, ranula, and salivary duct cyst?
mucocele : lower lip, kids, no epi lining
ranula : floor of mouth, sublingual
salivary duct cyst : upper lip, adults, epithelial lining
cheilitis glandularis
rare inflammatory condition of minor salivary glands
lower lip
openings of ducts are dilated and inflamed
necrotizing sialometaplasia
uncommon lesion locally destructive inflammatory condition of salivary gland
ischemia leading to infarction of glands
hard palate
mimics malignancy
what is the clinical appearance of necrotizing sialometaplasia?
begins as painful, non-ulcerated swelling and develops over 2-3 weeks with necrotic tissue sloughing and a non-painful ulcer
nicotine stomatitis
pipe and cigar contact
NOT precancer
inflamed salivary glands = volcano like papules with red central dots
sialolithiasis
calcified structures that develop in the ductal system
commonly submandibular gland
swelling or episodic pain during chewing
radiopaque, seen with occlusal x ray
sialadenosis
enlargement of salivary gland due to a non-infectious cause
usually bilateral parotid
caused by stone, systemics, or recent surgery (surgical mumps)
what are the systemic conditions that can cause sialadenosis?
diabetes, malnutrition, alcoholism, bulimia, sjogren’s
also can be caused by recent surgery because pt kept without food or drink for awhile
sialadenitis
acute or chronic inflammation of salivary glands
mainly submandibular
caused by infection such as bacterial or mumps
lymphoepithelial sialadenitis (LESA)
autoimmune condition
parotid and lacrimal glands
sjogren’s association
females
main concern of lymphoepithelial sialadenitis (LESA)?
progression to lymphoma
sialorrhea
excess saliva
due to local irritants, meds, or poor muscular control
what is pilocarpine?
sialogogue which stimulates saliva in xerostomia
xerostomia
extreme dry mouth
gland hypofunction, meds, radiation, Sjogren’s can all cause
clinically fissured tongue, ropey, foamy saliva
what are some meds that can cause xerostomia?
antihistamines
anticholinergics
antidepressants
sedatives & anxiolytic
antihypertensives
what are some side effects of xerostomia?
frothy saliva
infections (candida)
ulcers
rampant caries
halitosis
how do you treat xerostomia?
good hydration
sialogogues, sugar free lemon drops
salagen (pilocarpine) and evoxac (cevimeline)
sjogren’s syndrome
autoimmune condition with decreased saliva and tears from unknown cause
primary affects salivary and lacrimal glands without any other autoimmune diseases
secondary accompanies another autoimmune disease
exophthalmia and keratoconjunctivitis
dry eyes and damage to eyes
sjogren’s syndromes buzz words
females
bilateral parotid swelling
dry mouth, dry eyes
what is a concern for sjogren’s?
CONCERN for MALT lymphoma, non hodgkins B cell lymphoma
frey syndrome “auriculotemporal syndrome”
facial flushing and sweating along the distribution of the auriculotemporal nerve during mastication due to nerve damage
what is mumps caused by ?
viral, paramyxovirus
mumps is also called …
epidemic parotitis
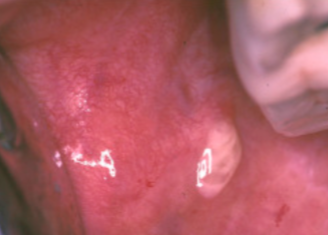
mucocele image
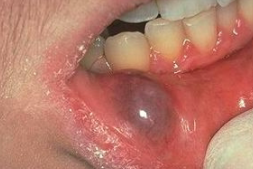
ranula image
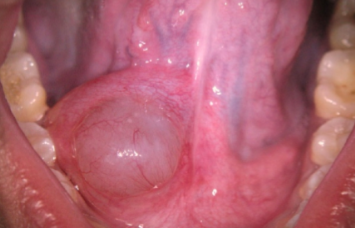
salivary duct cyst / mucus retention cyst image
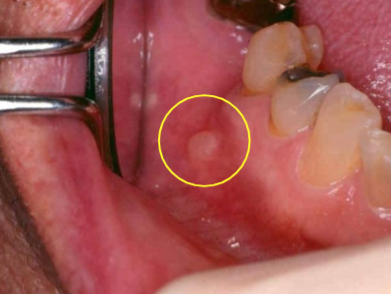
cheilitis glandularis image
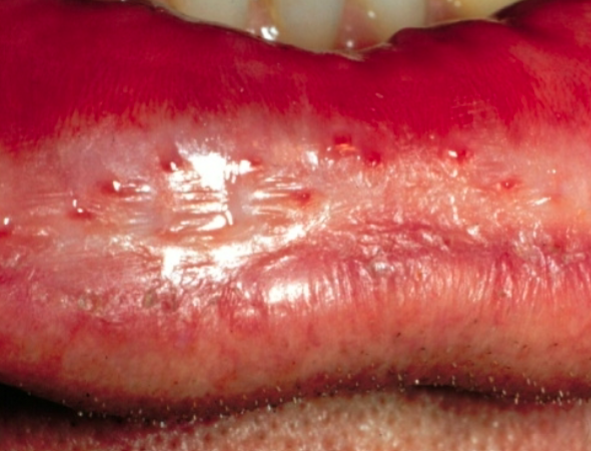
necrotizing sialometaplasia image
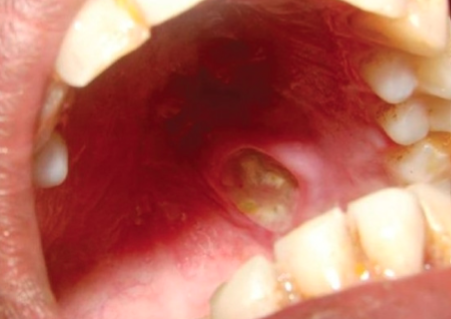
nicotine stomatitis image
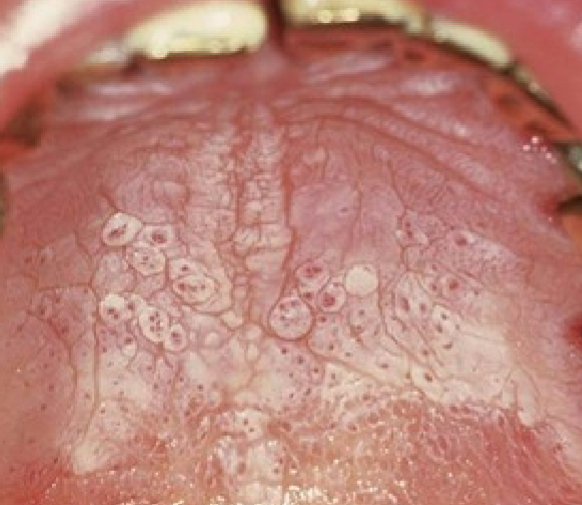
sialolithiasis image
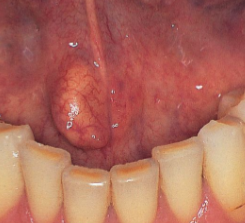
sialadenosis image
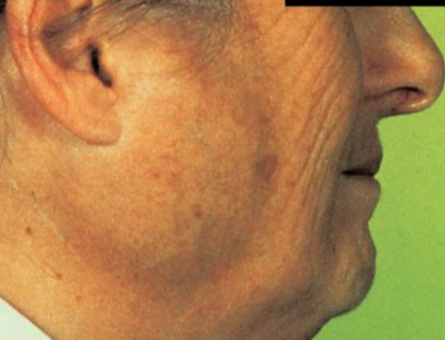
sialadenitis image