10.4 dynamic equilibrium and le chatelier's principle (+ Kc)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
dynamic equilibrium
the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
the concentrations of reactants and products do not change
the system must be closed
a closed system
is isolated from its surroundings, so the temperature, pressure and concentrations of reactants and products are unaffected by outside influences
position of equilibrium
indicates the extent of the reaction. In a reversible reaction, if the temperature, pressure (for reactions involving gases) or the concentration ff the reactants or products is changed, then the positions of equilibrium may change
le chatelier’s principle
when a system in equilibrium is subjected to an external change the system readjusts itself to minimise the effect of that change
investigating changes to the position of equilibrium with concentration (chromate and dichromate ions)
add a solution of yellow potassium chromate to a beaker
add dilute sulphuric acid until there is no further colour change. The solution will turn an orange colour
add aqueous sodium hydroxide until there is no further colour change. The solution will go back to a yellow colour
As you add sulphuric acid, the concentration of H+ ions increases. This causes the position of equilibrium to shift to minimise the change in H+ concentration. As you add the sodium hydroxide, the added OH- ions react with the H+ ions, decreasing the concentration of H+ ions.
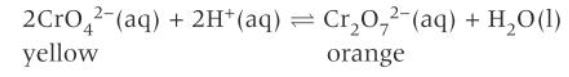
investigating changes to the position of equilibrium with temperature
an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium position in the exothermic direction
a decrease in temperature shifts the equilibrium position in the exothermic direction
eg. dissolving copper chloride in water in a boiling tube. Place in ice water and the solution is a pink colour. Place in a water bath of boiling water and the solution turns a blue colour.
effect of pressure changes on equilibrium
increasing the pressure of the system will shift the position of equalibirum to the side with fewer moles, reducing the pressure of the system
effect of a catalyst on equilibrium
A catalyst does not change the position of equilibrium; it merely speeds up the rate of the forwards and reverse reactions equally. A catalyst will, however, increase the rate at which an equilibrium is established.
the Haber process
a low temperature will push the equilibrium to the right
a high pressure will push the equilibrium to the right
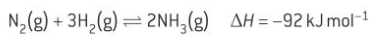
reasons for the conditions used in the Haber process
a low temperature would produce a high yield of product but would do so very slowly
a high pressure not only increases the yield but also increases the rate of reaction as it forces molecules closer together. A very high pressure requires a lot of energy and a strong container. Safety is also a concern as a high pressure to lead to leaks of toxic gases such as ammonia
the compromised conditions are 350-500 degrees and 100-200 atm and an iron catalyst
equation for Kc
square brackets are shorthand for concentration of

what does the value of Kc mean
A Kc value of 1 indicates a position of equilibrium that is halfway between reactants and products
a Kc value over one indicates a position of equilibrium that is towards the products
a Kc value under 1 indicates a position of equilibrium that is towards the reactants