10.1 - angular position, angular displacement, in range of motion
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
angular kinematics
rotation; degrees, radians, resolutions, etc.
angle, angular displacement (ROM), angular velocity, angular acceleration
human movement involves rotation of body segments
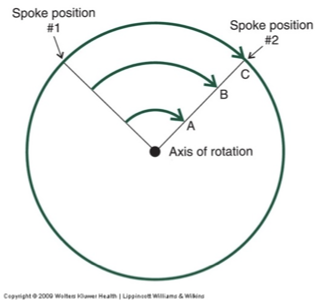
angular motion
all points move through the same angular isplacement
points farther from center move through larger “linear” displacement
axis and spoke
axis = joint
spokes = body segments
1 degree
1/360th rotation
1 radian
½pi of a complete rotation (1 rad = 57.3 degrees)
1 revolution
1 complete rotation
don’t really talk about that, as most joints shouldn’t move 360+ degrees
vertex
instantaneous center of rotation
for a human joint is not fixed (not still), but we assume it is for measuring
the knee doesn’t just flex, the tibia glides forward to close the gap
angular position
angle that a segment (limb) is relative to an arbitrary reference
examples:
arm is roughly 0 degrees relative to the trunk in sagittal plane in anatomical position
arm is roughly 90 degrees relative to line parallel to the ground in the sagittal plane in anatomical position
arbitrary reference
sometimes a body segment, sometimes more about absolute (parallel to the ground)
absolute angle
angle of a segment compared to an externally defined line (typically parallel to the ground)
named after the segment whose movement we are measuring
@ elbow = arm angle
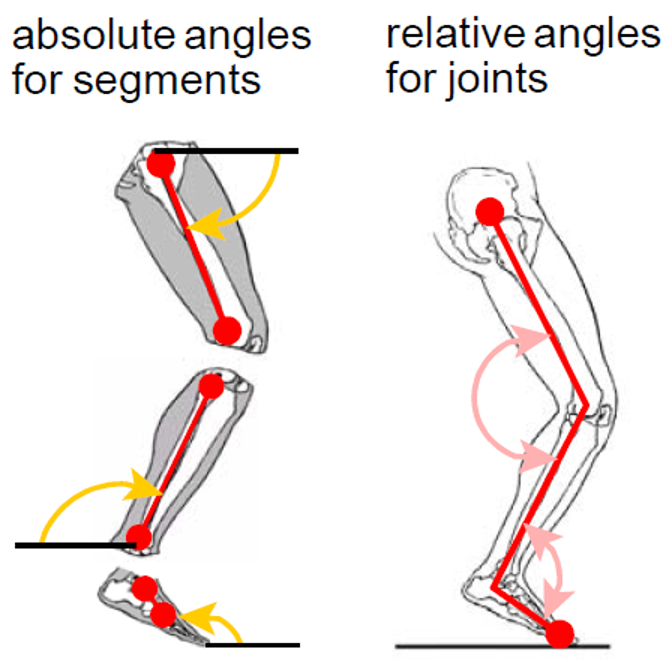
relative (“joint”) angle
included between two body segments
named for the joint that is at the vertex of the angle
in frontal plane, most joint angles have a value of __
180 degrees
exceptions: foot, shoulder
2 ways to measure joint agles
assuming anatomical position = 0 degrees; deviating from that position (elbow is 12 degrees of flexion)
goniometry - segments lined up with the goniometer, measuring like a protractor
in anatomical position, elbow angle is 180 degrees
forearm absolute angle
2 possible vertex: arm or wrist
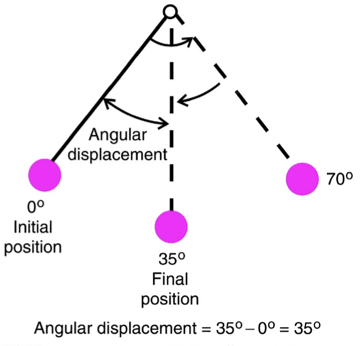
angular displacement
the change in absolute angular position experienced by a rotating line
the angle between a line segment in its initial position and in its final position with the direction of rotation noted
units are degrees (or rad, or rev)
angular displacement: 70 degrees
active range of motion
ROM moved through by the patient/client’s own muscle power
passive ROM
ROM moved through with assistance from a therapist or equipment
active assisted ROM
ROM moved through by the patient/client with assistance via a strap, wall, etc.
angular displacement vs position
position of a joint says some important information, but displacement is more informative
angular displacement of a joint angle is more commonly known as ROM