Unit 7 AP Final Review, AP World History Unit 7: Global Conflict
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
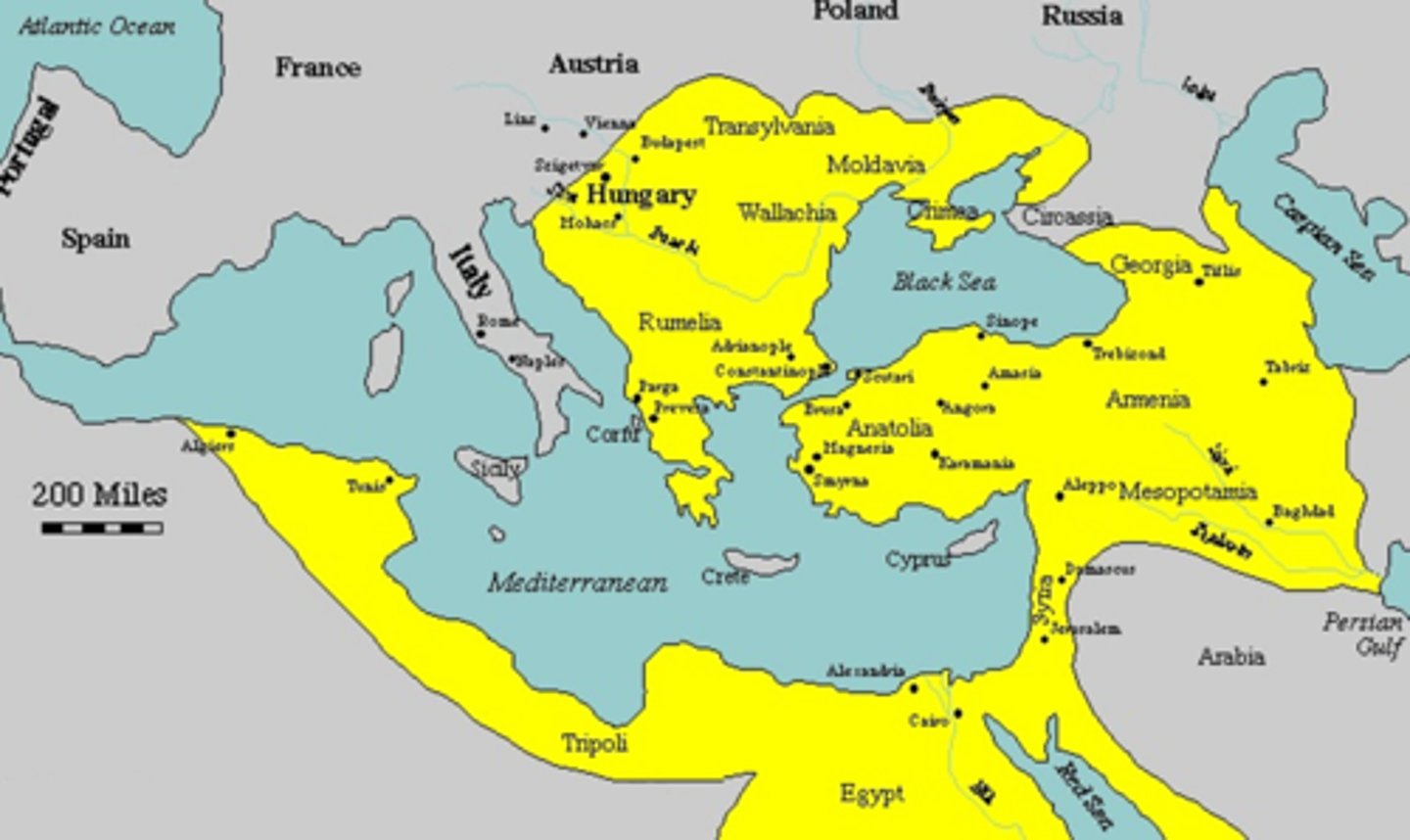
Describe the factors that led to the collapse of the Ottoman Empire.
The Ottoman economy was disrupted by inflations, caused by the influx of precious metals into Europe from the Americas and by an increasing of trade between East West. Ottoman industry fell into rapid decline. (Cady)
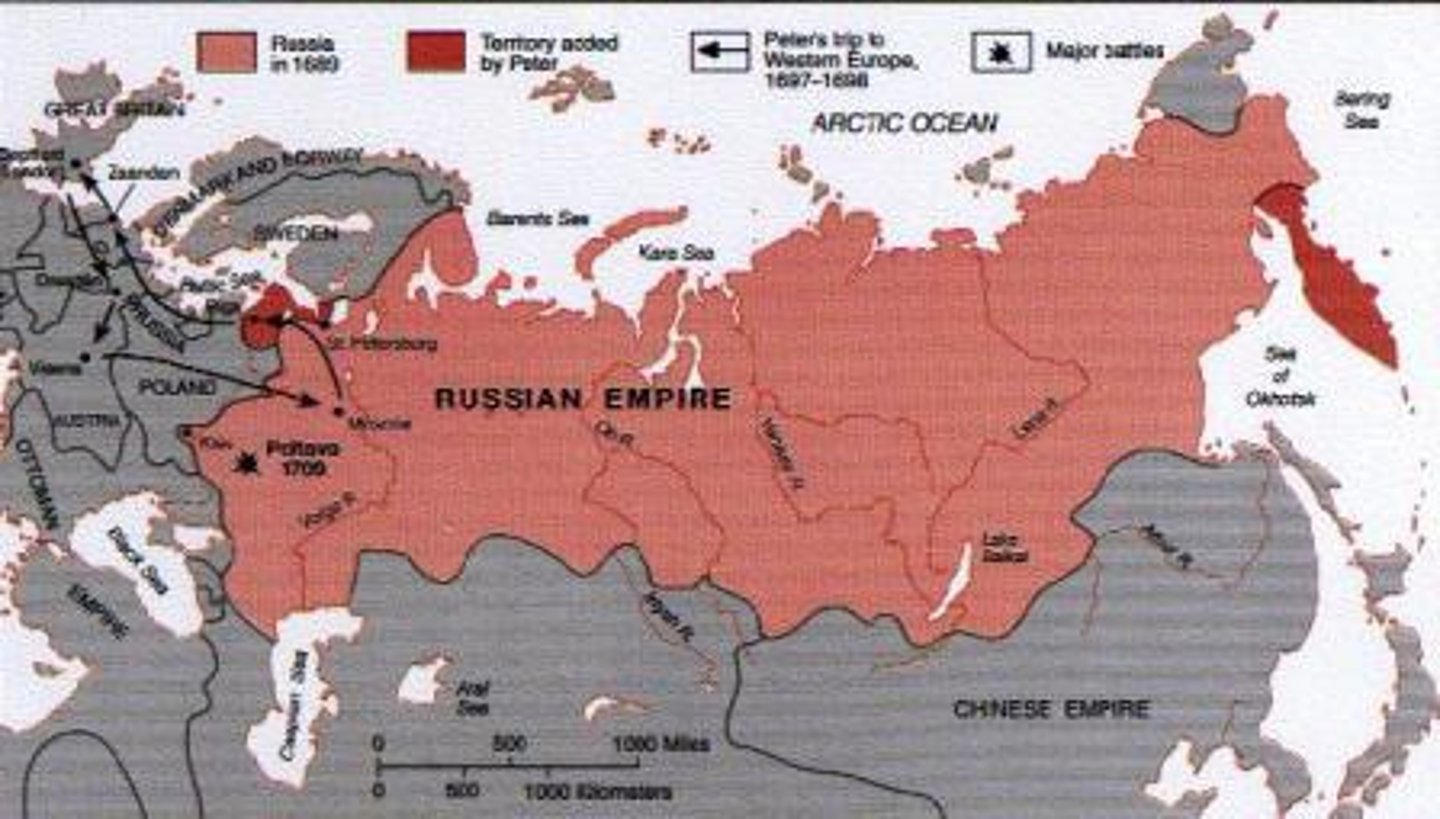
Describe the factors that led to the collapse of the Russian Empire.
As Russia became engulfed in World War I, over 15 million men joined the army, which left a shortage of workers for the factories and farms. This led to widespread shortages of food and material. Prices went through the roof and soon famine consumed Russian cities. (Cady)
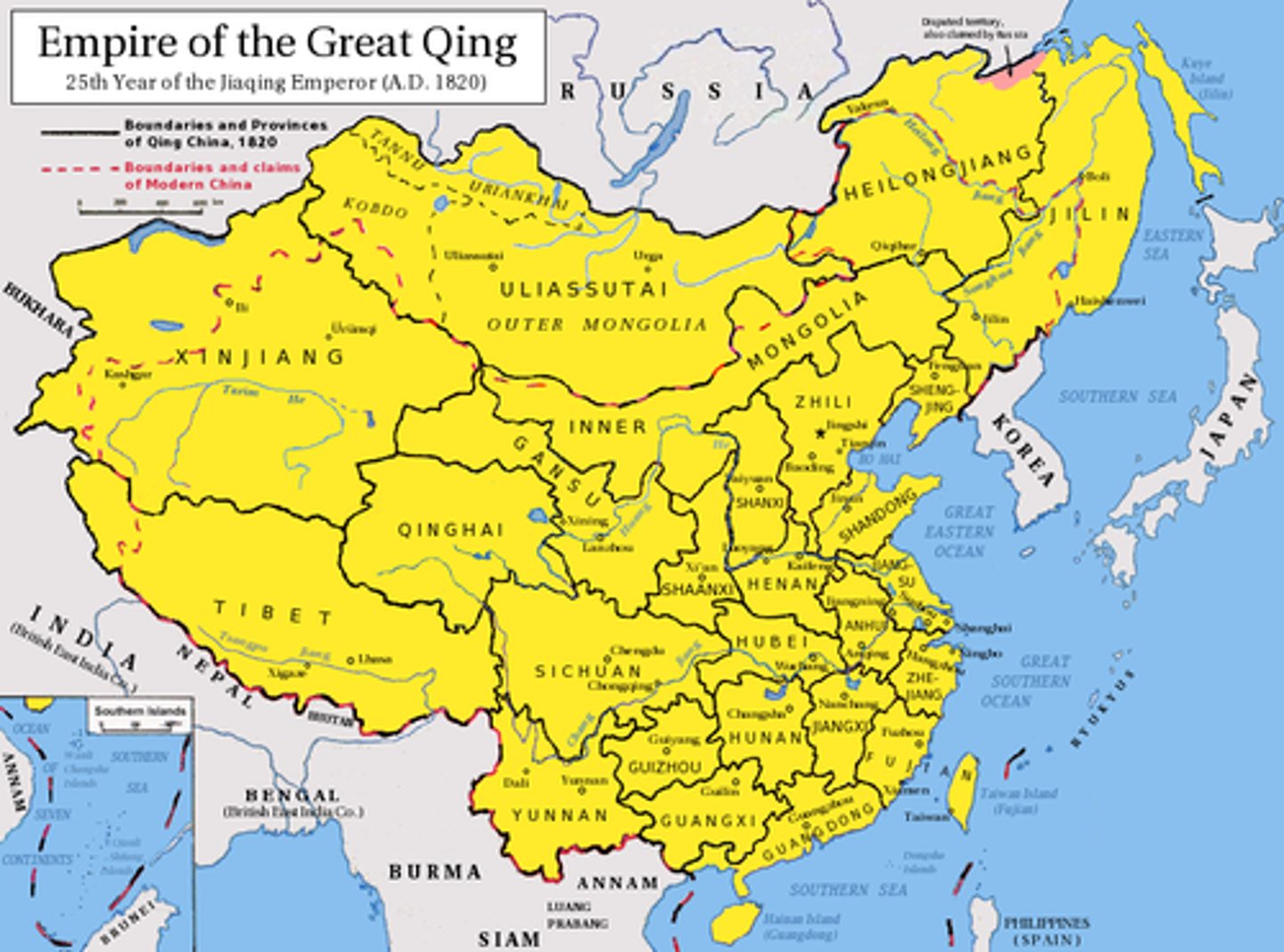
Describe the factors that led to the collapse of the Qing Dynasty in China.
Political corruption, peasant unrest, and governmental incompetence. (Cady)
What factors led to the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia in 1917?
The widespread inflation and food shortages in Russia contributed to the revolution. Military, inadequate supplies, logistics, and weaponry led to heavy loss that the Russians suffered during World War I. This further weakened Russia's view of Nicholas II, they viewed him as weak and unfit to rule. (Cady)

What were some of the outcomes of the Bolshevik Revolution? What changes did they bring?
They seized power over Russia and set up a COMMUNIST government. Soviet Union abolished private trade, distributed peasant's crops to feed urban workers. Took over the ownership of the country's factories and heavy industries. (Sydnee)

How did the Mexican Revolution (1910 and beyond) challenge the existing political and social order in Mexico?
Mexico adopted a new constitution in 1917, including the goals of land redistribution, universal suffrage, and public education- continued to guide Mexico's government. PRI- dominated Mexican politics. (Sydnee)

Generally, what are some external factors that led to change in states after 1900?
Collapse of empires was caused by a struggle to keep up with neighboring westernization causing them to be behind. (Addie)
Generally, what are some internal factors that led to change in states after 1900? .
Nationalism led to the creation of new states by allowing different cultures to come together, for example, Germany. (Addie)
What role did militarism play in causing WWI?
Countries began growing their militaries as they became threatened by other growing militaries and by the thought of war approaching. (Rachel)

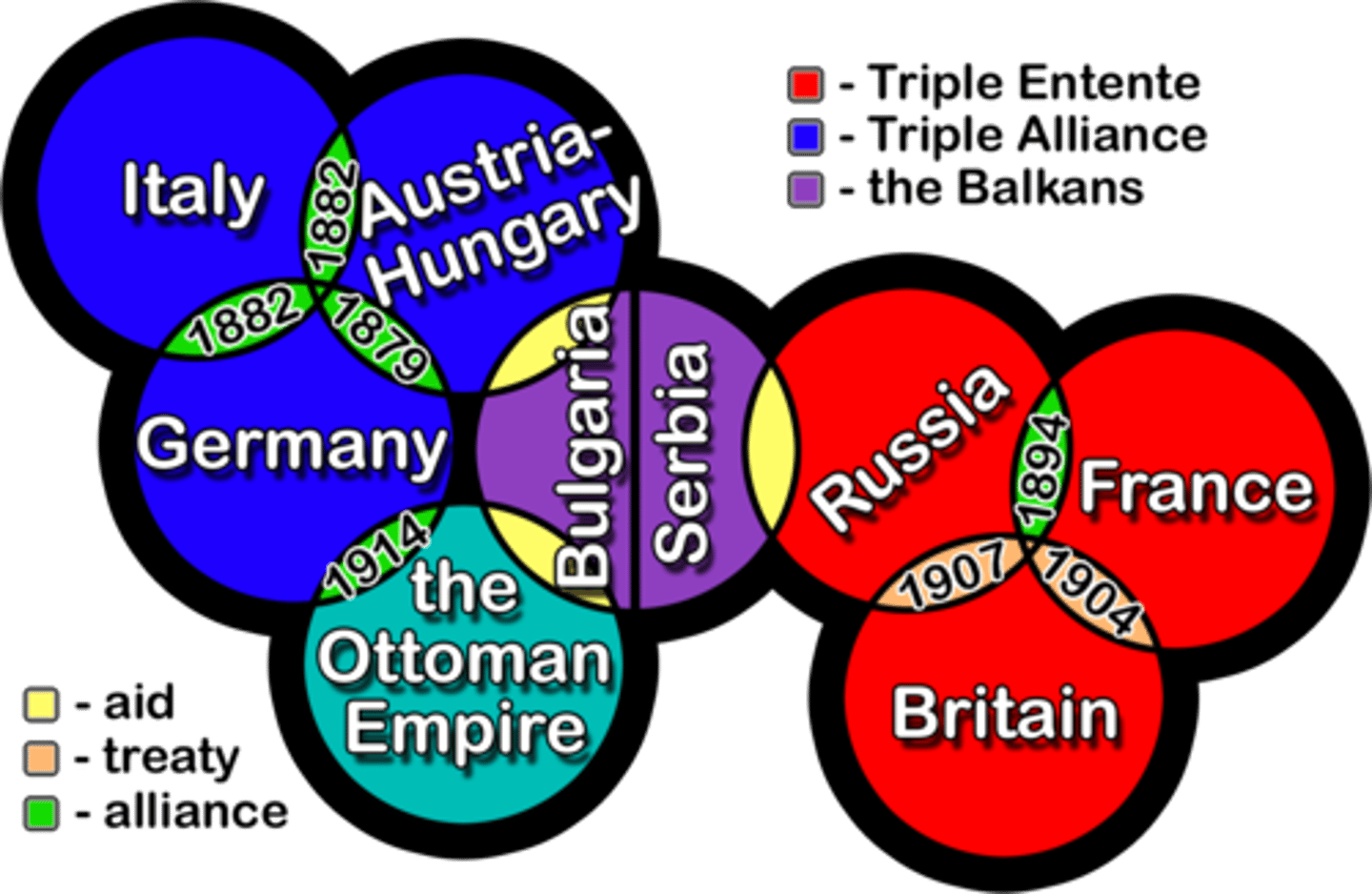
What role did alliances play in causing WWI?
Nations were obliged to join their allies if they were to ever have war to be declared on them. It goes like this. Serbia is declared war on by Austria-Hungary. Russia has to back Serbia up. Germany backs Austria-Hungary up. Germany invades France through Belgium which prompts Great Britain to join. Countries join their allies until a global war unravels without them realizing it. (AP)
What role did nationalism play in causing WWI?
Nationalism was the cause of the assassination of the Archduke Franz Ferdinand because Slavic's wanted independence from Austria-Hungary. (Rachel)

What role did Balkan nationalism specifically play in causing WWI?
A Serbian, Princip eliminated the Archduke Franz Ferdinand. This led to Austria-Hungary to declare war on Serbia. This was the beginning. (AP)
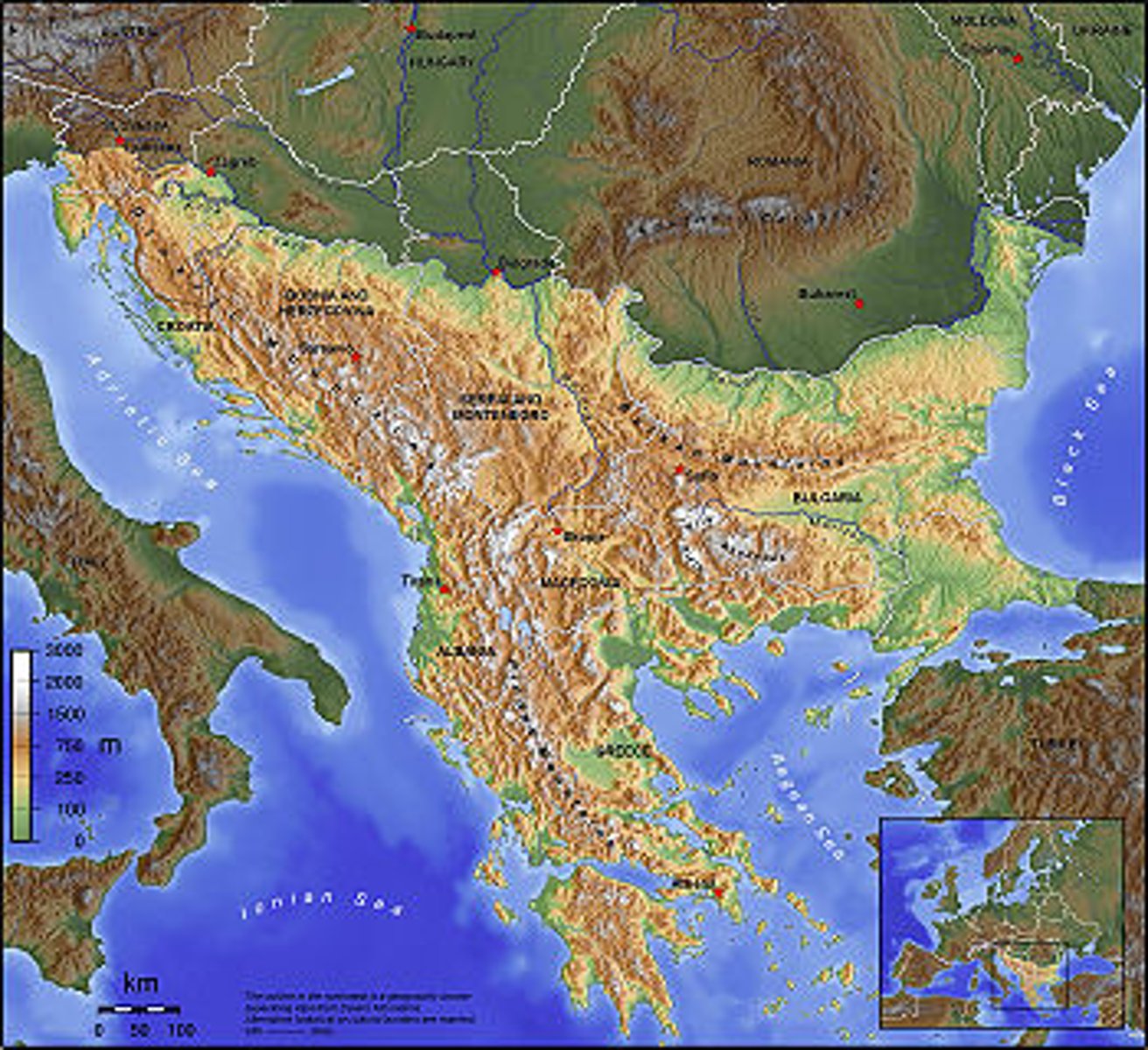
What role did imperialism play in causing WWI? (How could you tie this back to the Berlin Conference?)
Countries that were under an imperial rule wanted to be freed from that and able to govern themselves. Some of these countries including Africa, India, China, Australia, New Zealand, and Canada. Imperialism created rivalries between nations. (Rachel)

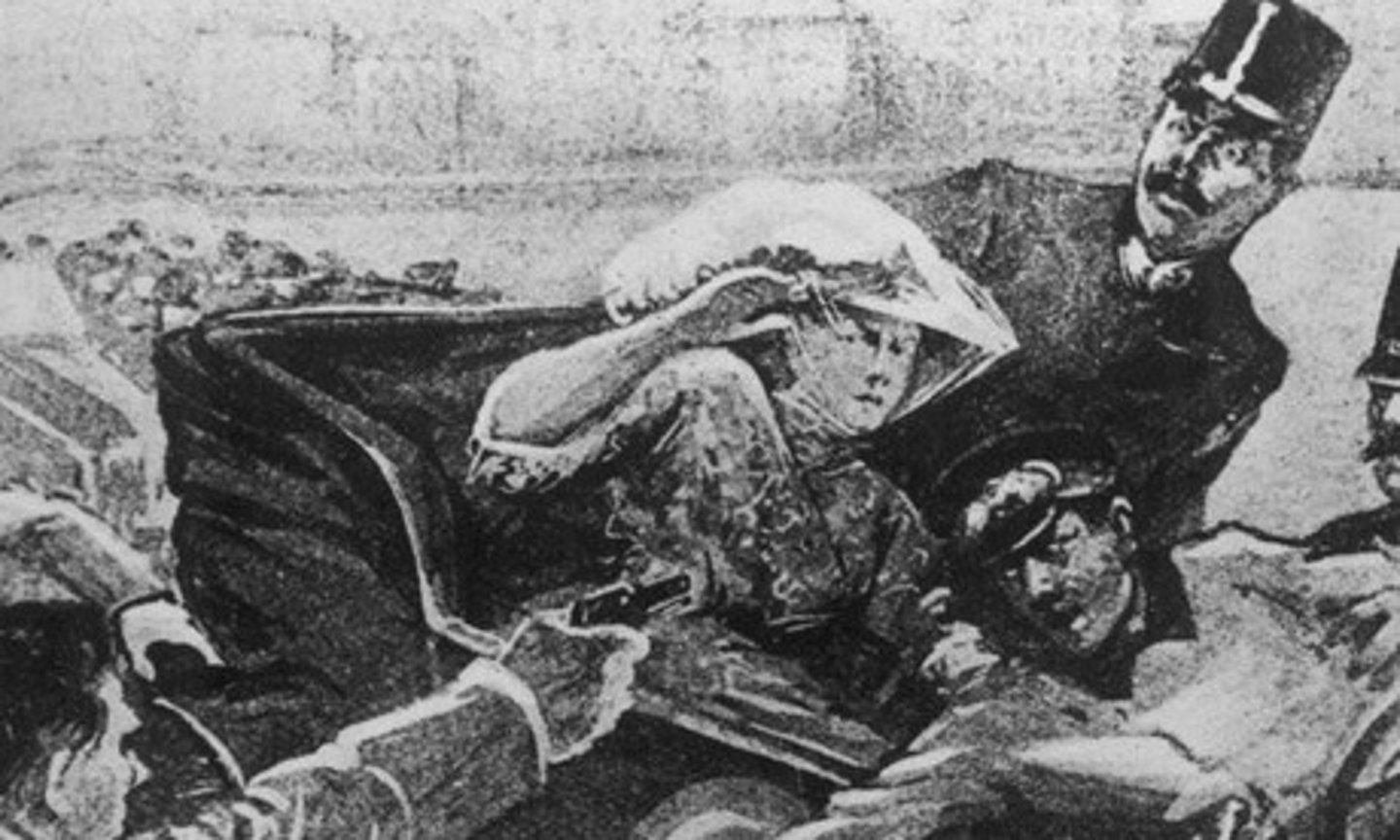
What role did the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary play in causing WWI?
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand was the very beginning of the war. After his assassination, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia. When this happens, Russia, an ally of Serbia, mobilizes and prepares for war. Germany, an ally of Austria-Hungary, declares war on Russia, Serbia, and France. When Germany invades Belgium to get to France, Great Britain declares war against Germany and Austria-Hungary. (Rachel)
What is a total war?
People are devoted to the war effort. All the nation's resources are dedicated to the war in hopes of winning. (AP)

Why is WWI considered to be a total war?
All countries involved devoted as much people, money, and resources as they possibly could in attempt to win the war, and there was also millions of casualties. (Rachel)
How did governments use propaganda to mobilize populations for the purpose of waging war?
The spread barbaric and cruel ideas of the rivals to created a hatred between them and the rival on a civilian level. (Rachel)

How did governments use nationalism to mobilize populations for the purpose of waging war?
They used their feeling of pride for their country and national identity to recruit armies for war. They wanted to contend with other countries. (Sydnee)

What new military technology used in WWI (1914-1918) led to increased levels of wartime casualties?
There was an introduction to atomic warfare, poison gas, machine guns, air force, tanks. (Sydnee) Faster, more efficient warfare.
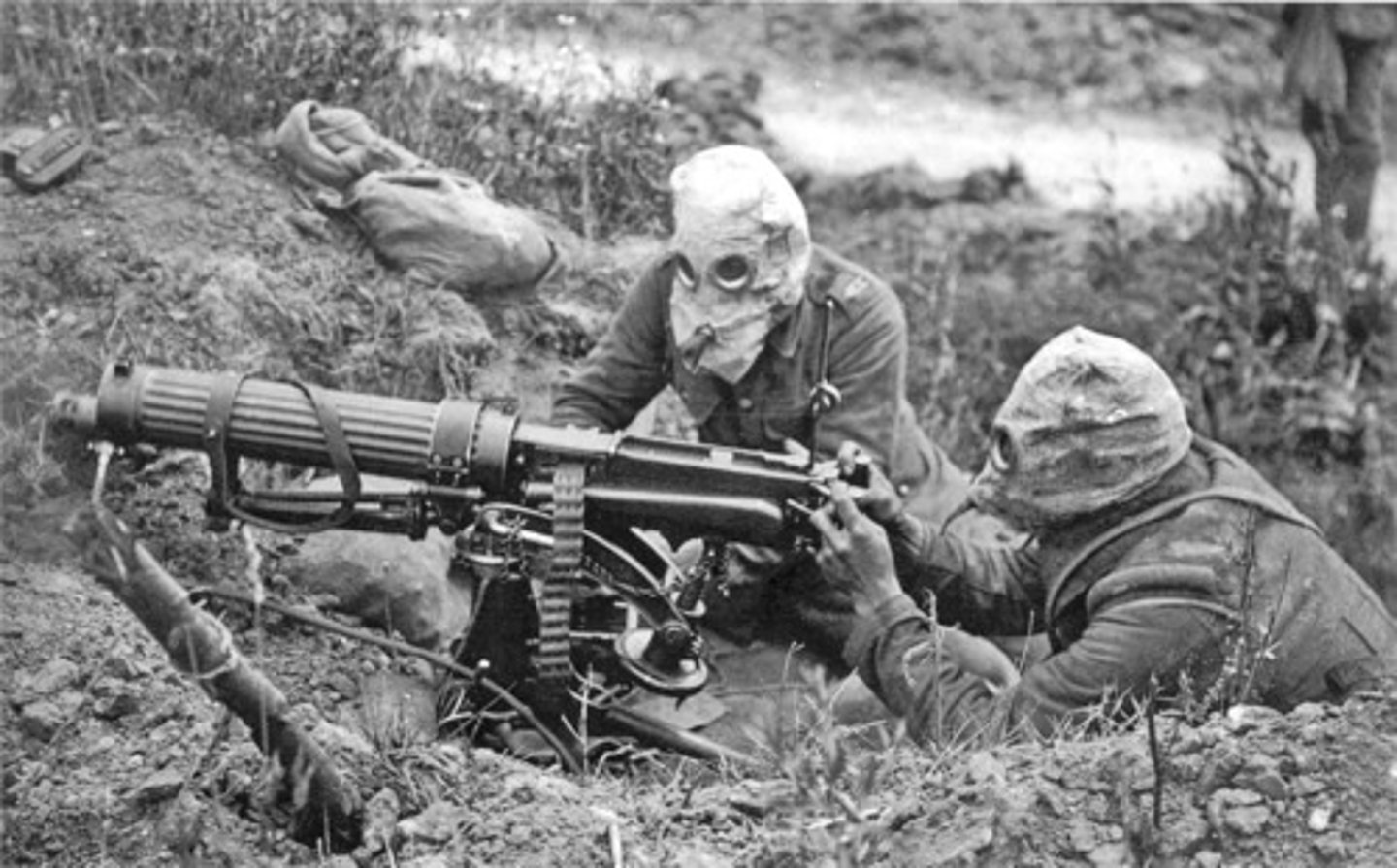

What caused the Great Depression?
The Allied nations had spent tremendous amounts of money during the first world war and after Germany was forced to pay for reparations to the wars victors, they could not make these payments. This caused Germany to print more money, therefore causing inflation. So, since Germany couldn't repay France or Britain, France and Britain could repay wartime loans to the U.S. Additionally, the Soviet government refused to pay their prerevolutionary debts. This basically means that everyone was in debt, poor, and living with a crashed economy. (Bailey)

What were the effects of the Great Depression on the USA?
The crash of the stock market, 25% of adults were unemployed, a third of all banks failed, and fall of industrial production. (Bailey)
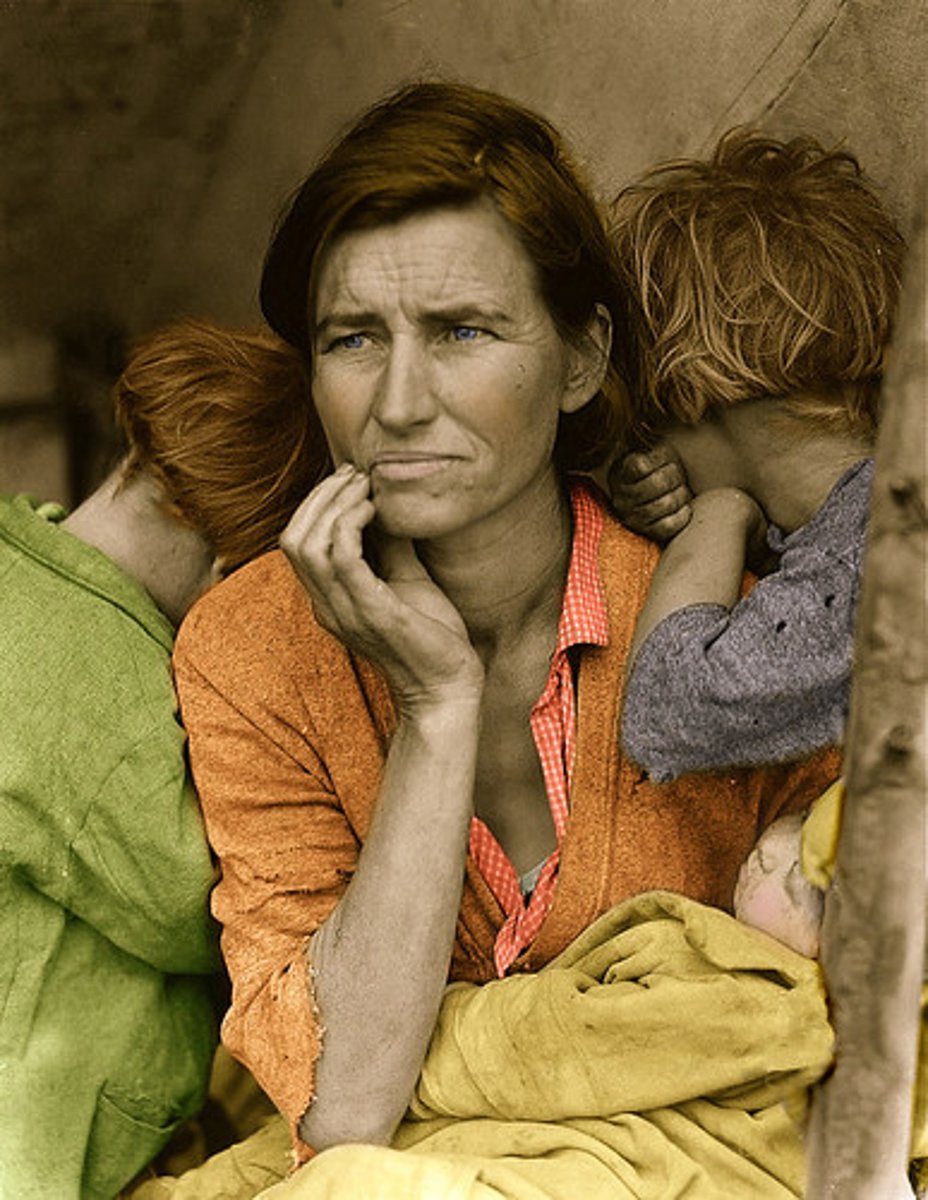

What were the effects of the Great Depression outside of the US?
Germany suffered after Americans withdrew their money held in German banks during the crash of the stock market; Asian, African, and Latin American nations suffered because they had been depending on the imperial nations; Japan's exports were cut in half. (Bailey)

How did FDR's New Deal attempt to intervene in the US economy?
Roosevelt and his backers created a group of policies and programs with a goal to bring the U.S relief for its citizens who were suffering (poor, unemployed, farmers, minorities, women, etc.), recovery to bring the U.S out of the Great Depression (partially through government spending), and reform to change government policies to avoid future disasters such as this one. (Bailey)

How did the US emerge from the Great Depression?
Once the U.S entered WW2, the Great Depression soon ended as the need for military equipment and weapons made way for new factory jobs to produce those goods. (Bailey)
How did the economic crises of the Great Depression contribute to the rise of totalitarian governments?
As countries began to economically decline, they needed some sort of hope, or a leader to step up that they could rely on to fix their economy, bring order, and make their nation great again. (Bailey)

Describe the goals of Stalin's Five Year Plans.
Stalin desired to remove and replace any policies created under the New Economic Policy. The plan overall was to transition the Soviet Union from a weak, poorly controlled, agriculture state, into an industrial powerhouse. (Cady)

What were the outcomes of Stalin's Five Year Plans. Were they successful? Why or why not.
The collectivization of agriculture was a huge failure. Millions of peasants starved to death, especially in the Ukraine. However, heavy industry grew tremendously in the 1930s. Although consumer goods were in short supply, there were plenty of factory jobs available, and the cost of living was low. (Sydnee)
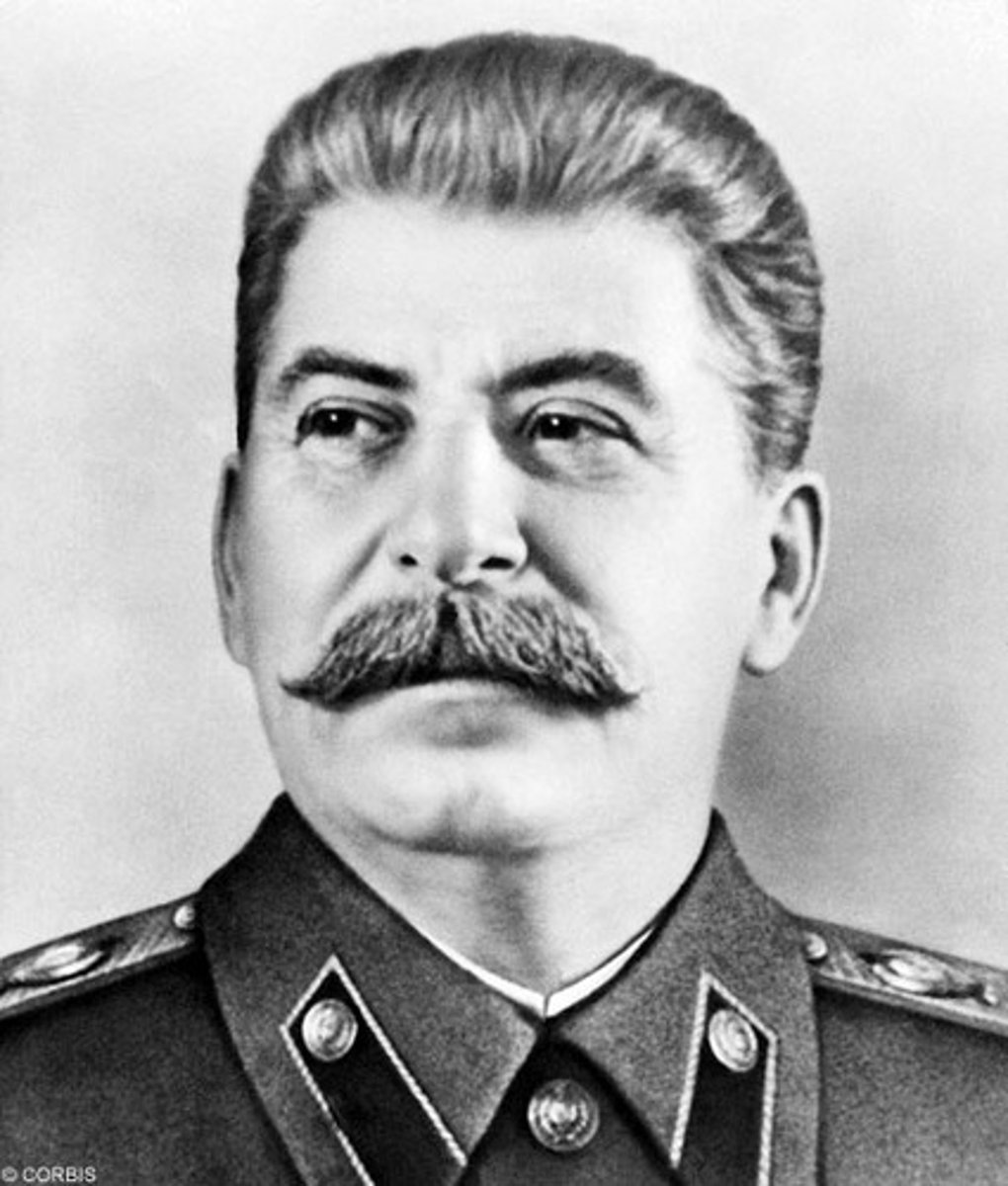

Give two examples of how different governments responded to economic crises after 1900.
Mexico used a PRI rule to vastly improve the economy. Nationalizing the oil industry. Soviet Union collectivizing agriculture. (sydnee)
What were the terms of the Versailles Peace Treaty?
Germany had to pay billions of dollars in reparations. They lost all their colonies to the allies, and they had to severely limit their military. Their empire was also reduced, along with the break up of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. (AP)

How did these terms create political and economic tensions in the 1920s and 1930s?
Germany became angry at how they were being punished in the treaty, and also did not believe that they were being led well. This allowed for stern leaders like Hitler to come into power easily. (Addie)
What are the League of Nations mandates?
The League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed- upon terms administering the territory on behalf of the League of Nations. (Cady)
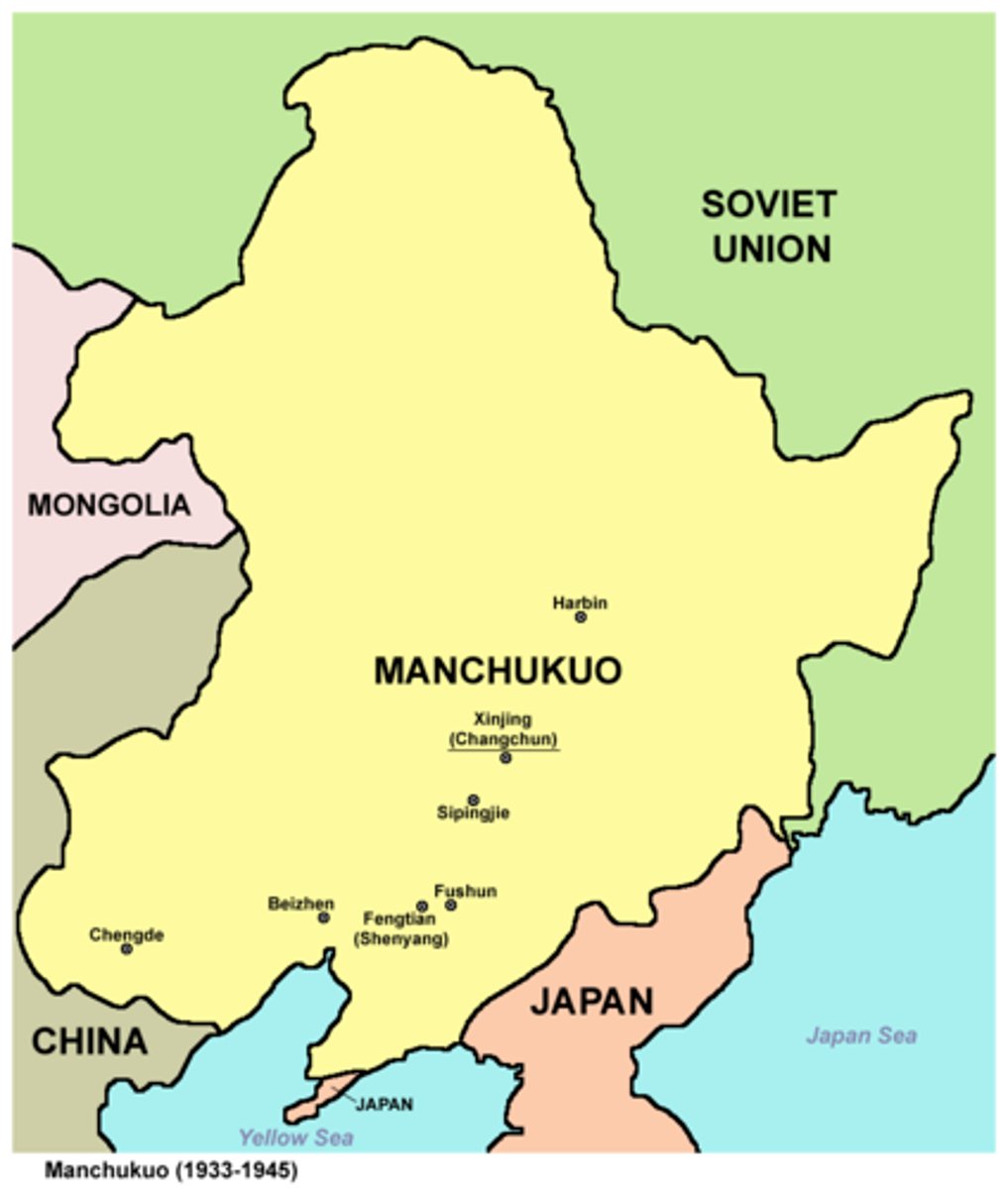
What was Manchukuo?
The Japanese invaded Manchuria and established the Puppet state of Manchukuo. (AP)
What was Japan's vision for a Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere and how would this lead to tension causing WWII?
Japan wanted to take control of much of Asia because they believed that they could unify Asia and make it prosperous. This led to the U.S. needing to get involved to put an end to Japan's imperialism. (Addie)
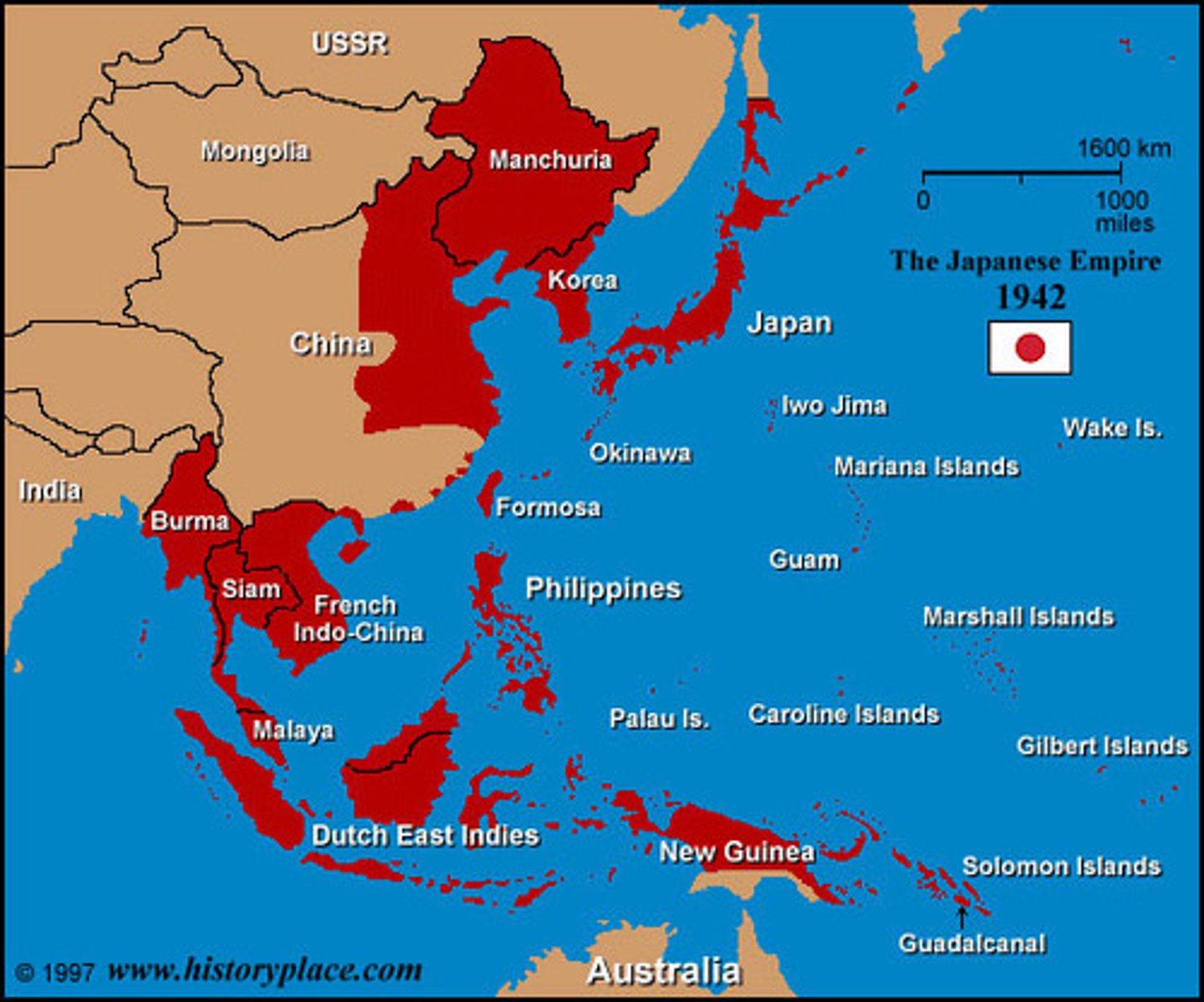
Give examples of changes in territorial holdings from 1900 to the present.
Describe the causes of WWII.
The immediate cause was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand- part of Austro-Hungary. (Also militarism. imperialism, alliances, and nationalism. (sydnee)

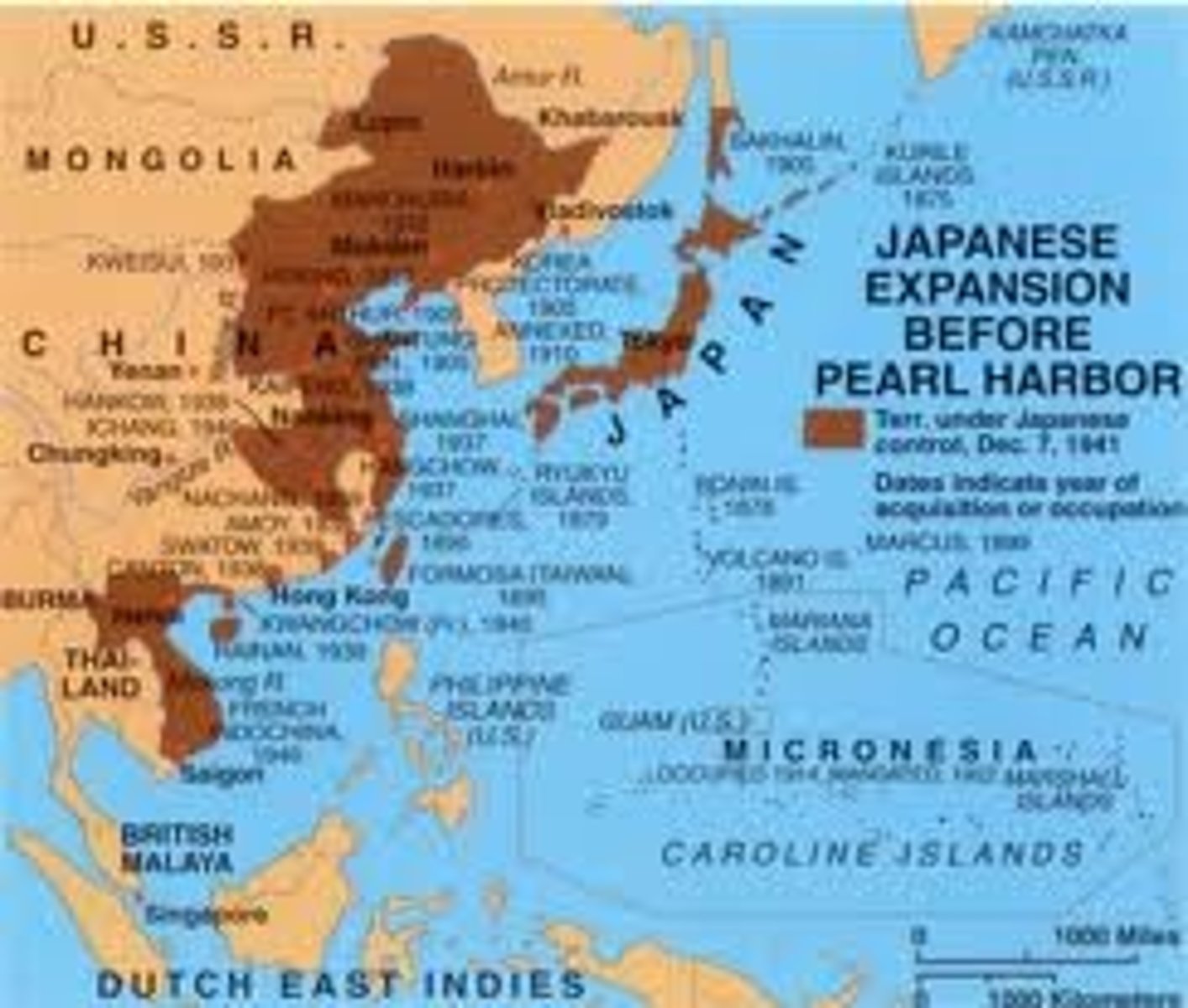
How did imperialist aspirations of Japan lead to WWII?
Japan wanted to take control of German colonies in the Pacific. They joined the Allied side. (Sydnee)
How did imperialist aspirations of fascist Nazi Germany lead to WWII?
Nazi Germany wanted to control all of Europe in the form of a dictatorship which led to a need for interference from countries like France and Europe to not allow this to happen.
Describe the aggressive militarism of Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler.
Describe Hitler's plan for Germany. What role did anti-semitism and extreme nationalism play in this vision?
Hitler was going to expand Germany's boundaries to recreate the German Empire. Hitler was an articulate speaker and with his speeches, he could rally crowds to support him because they were desperate for a good leader. He claimed that the Jews were the reason they lost the war effort and this made people form prejudices against the Jewish. (AP)

What were some of the consequences of WWII? How would it set the stage for the Cold War?

In what ways was WWII a total war?
People were working in either factories to produce things like tanks or entering the military. Civilians were fair game to other nations fighting and they were the most targeted. (AP)

Give examples of how facsist Germany under Hitler waged war during WWII. How did Germany mobilize their resources and populations?

Give examples of how the USSR under Stalin waged war during WWII. How did the USSR mobilize their resources and populations?
How did Great Britain mobilize for war under Winston Churchill?
Winston Churchill held many test naval mobilizations that prepared Great Britain for war when it occurred. (Max)

How did the US mobilize for war under FDR?
FDR gave the whole population contracts to produce products for war such as weapons, ammunition, vehicles, etc. He also created a draft that selected soldiers for war. (Max)

What new military technology/tactics were used during WWII that led to increased levels of wartime casualties?
The new idea of "lighting war" involved planes bombing certain areas and then was closely followed my tanks and artillery fire which greatly increased casualties. (Max)

How were government methods to wage war during WWII similar?
How did democratic governments’ methods of waging war differ from methods utilized by totalitarian states?
What is genocide?
The deliberate killing of a large number of people from a particular nation or ethnic group with the aim of destroying that nation or group. (Max)
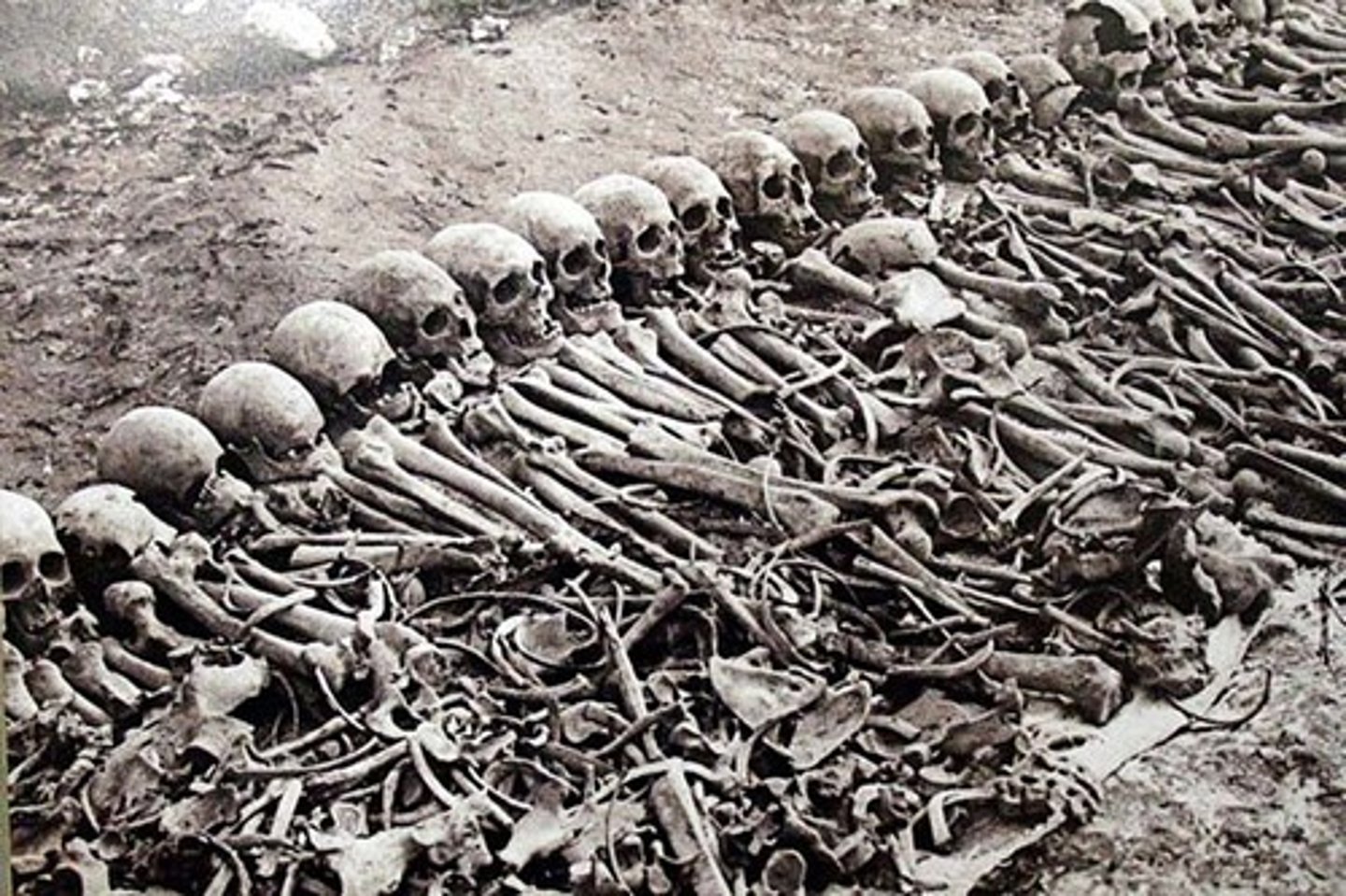

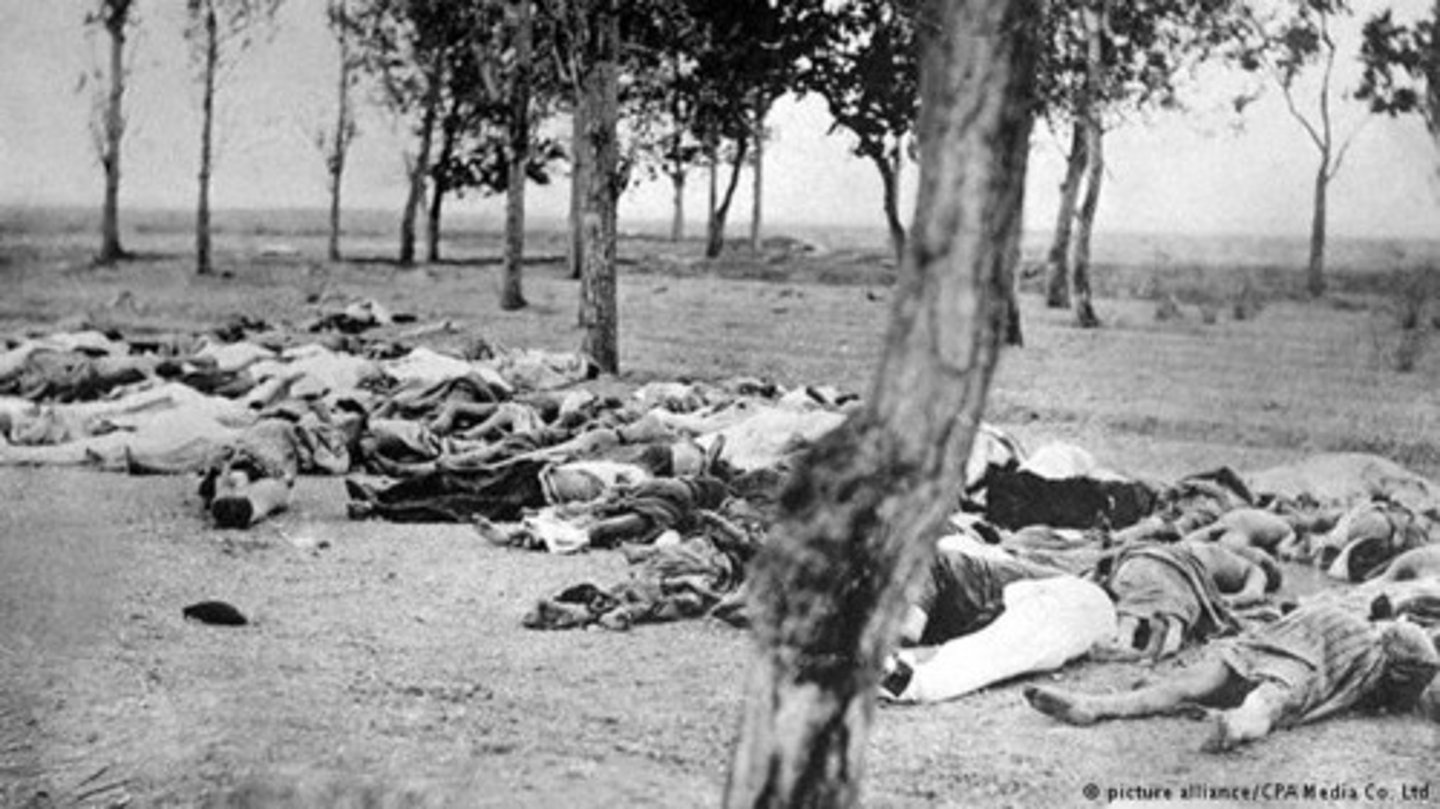
Describe the causes of the Armenian Genocide during WWI.
Introduction of Armenian Revolutionary groups to protect themselves in the Ottoman Empire sparked fear among the Muslims of the Ottoman Empire. Anti-Armenian feelings emerged and it did not take much to lead to mass killings. (Addie)
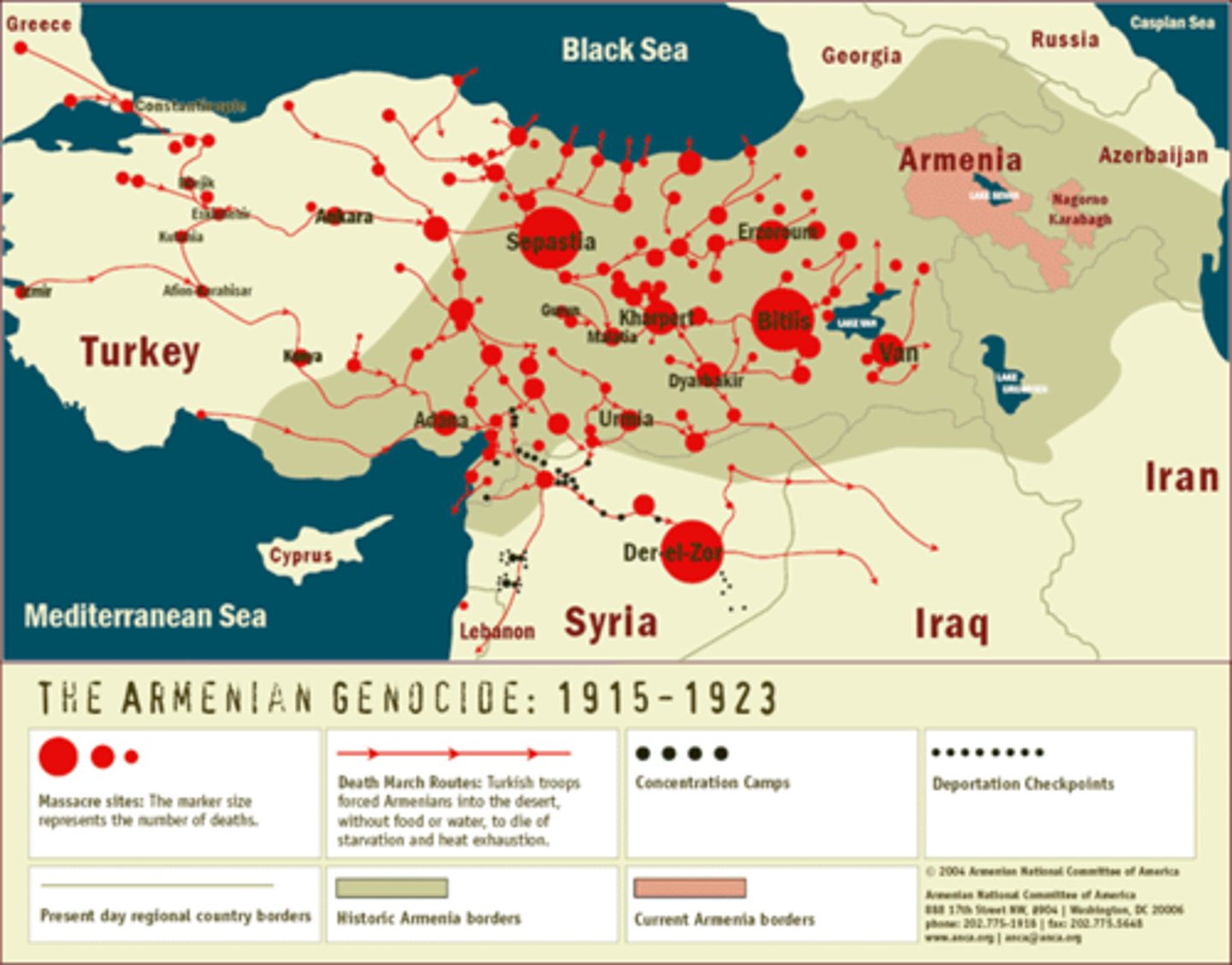
Describe the consequences of the Armenian Genocide.
Led to the eradication of Armenians from their native land. (Addie)

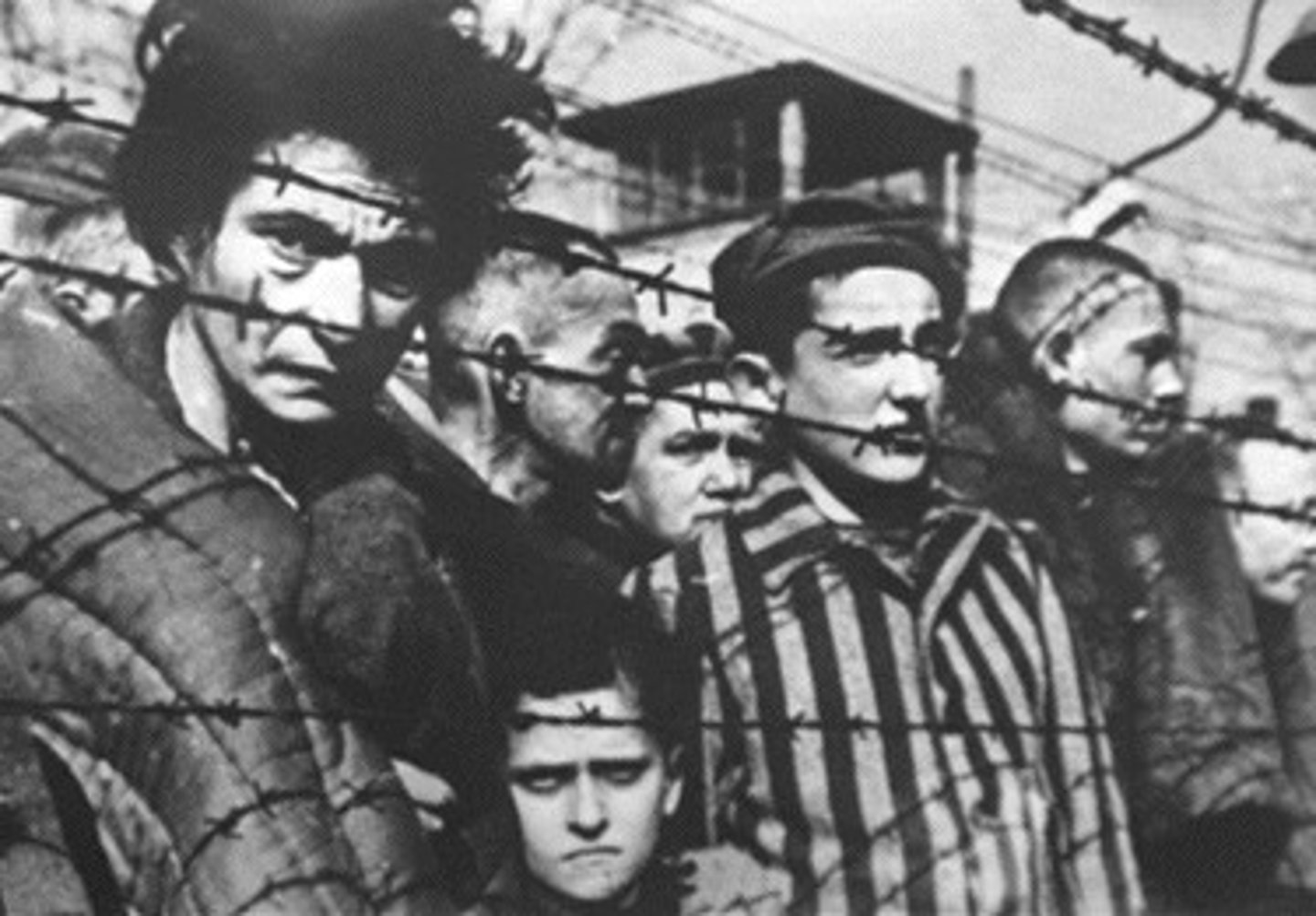
Describe the causes of the Holocaust during WWII.
Nationalism, the aftermath of world war 1, the rise of the Nazis, and the role of Adolf Hitler. (Max)
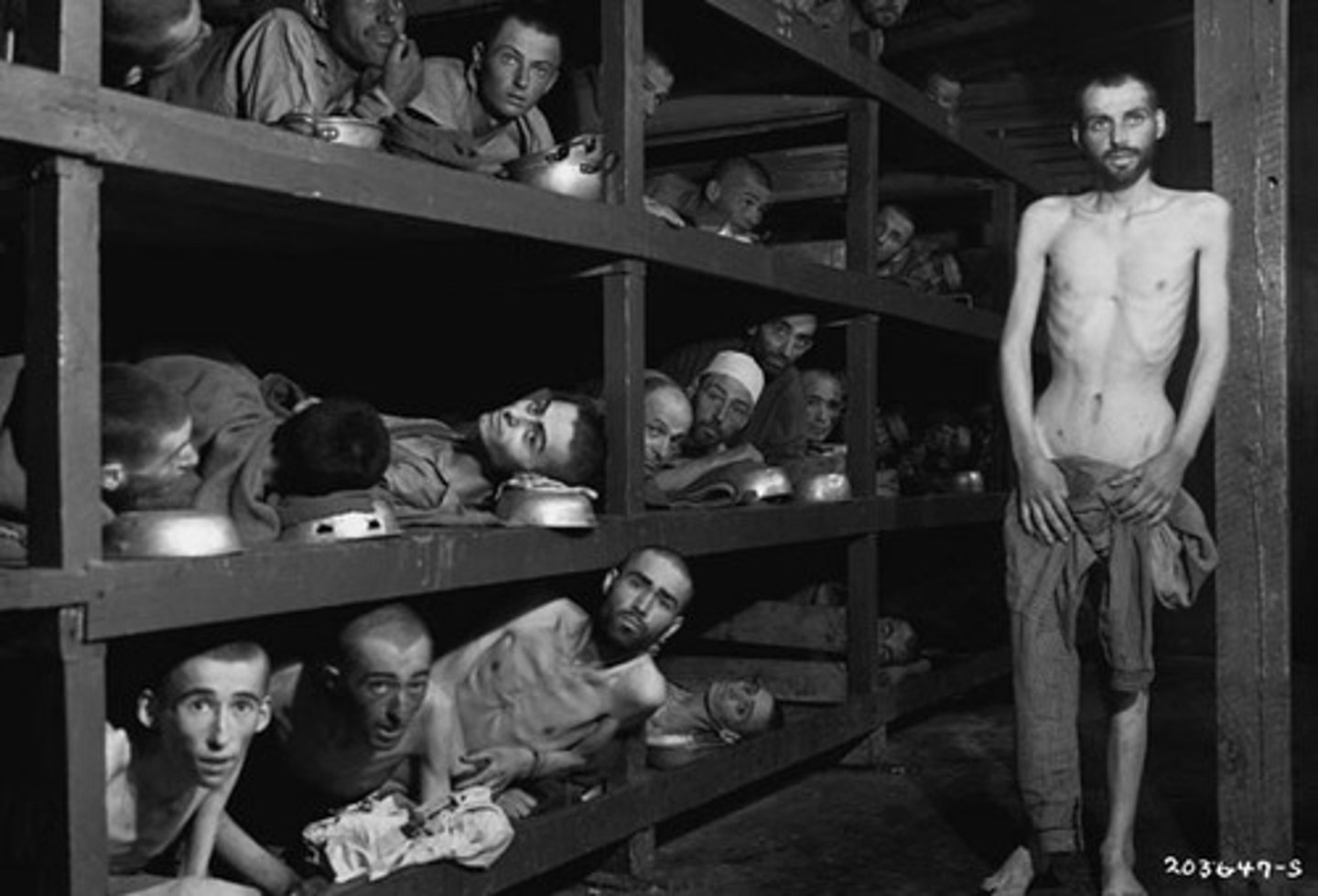

Describe the consequences of the Holocaust during WWII.
Approximately 6 million Jews lost their lives, survivors feared returning to their former homes, and finding refuge in other countries was often times problematic and dangerous for Jews. (Max)

Russian Revolution of 1917
two revolutions, the first of which, in February (March, New Style), overthrew the imperial government and the second of which, in October (November), placed the Bolsheviks in power.
Mexican Revolution
(1910-1920 CE) Fought over a period of almost 10 years form 1910; resulted in ouster of Porfirio Diaz from power; opposition forces led by Pancho Villa and Emiliano Zapata.
Triple Alliance
An alliance between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy in the years before WWI.
Triple Entente
Britain, France, Russia
Central Powers
Austria-Hungary, Germany, Ottoman Empire
Allied Powers (WWI)
Britain, France, Russia, Italy and the United States
Total War
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort
Propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.
Great Depression
starting with collapse of the US stock market in 1929, period of worldwide economic stagnation and depression. Heavy borrowing by European nations from USA during WW1 contributed to instability in European economies. Sharp declines in income and production as buying and selling slowed down. Widespread unemployment, countries raised tariffs to protect their industries. America stopped investing in Europe. Lead to loss of confidence that economies were self adjusting
Five Year Plan
Stalin's economic policy to rebuild the Soviet economy after WWI. tried to improve heavy industry and improve farm output, but resulted in famine
The New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression.
Fascist Corporatist economy
Involved management of sectors of the economy by government or privately controlled organizations
League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations
League of Nations Mandates
A system established after WWI whereby a nation officially administered a territory) mandate_ on behalf of the League of Nations. Thus, France administered Lebanon and Syria as mandates, and Britain administered Iraq and Palestine.
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere
Japan offered to liberate Southeast-Asian countries from western colonial rule but instead used them as conquered land for natural resources
Indian National Congress
A movement and political party founded in 1885 to demand greater Indian participation in government. Its membership was middle class, and its demands were modest until World War I. Led after 1920 by Mohandas K. Gandhi, appealing to the poor.
Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I which demanded exorbitant reparations from the Germans
Fourteen Points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.
Fascism
A political system headed by a dictator that calls for extreme nationalism and racism and no tolerance of opposition
Totaltarian
referring to a form of government in which one person or party holds absolute control
Adolf Hitler
Austrian born Dictator of Germany, implement Fascism and caused WWII and Holocoust.
Joseph Stalin
Bolshevik revolutionary, head of the Soviet Communists after 1924, and dictator of the Soviet Union from 1928 to 1953. He led the Soviet Union with an iron fist, using Five-Year Plans to increase industrial production and terror to crush opposition
Benito Mussolini
Fascist Dictator of Italy that at first used bullying to gain power, then never had full power.
Atomic Bomb
bomb dropped by an American bomber on Hiroshima and Nagasaki destroying both cities
Fire bombing
Bombs dropped on Germany and Japan with intentions to spread fires and take down cities
Winston Churchill
A noted British statesman who led Britain throughout most of World War II and along with Roosevelt planned many allied campaigns. He predicted an iron curtain that would separate Communist Europe from the rest of the West.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
President of the US during Great Depression and World War II
Genocide
Deliberate extermination of a racial or cultural group
Holocaust
A methodical plan orchestrated by Hitler to ensure German supremacy. It called for the elimination of Jews, non-conformists, homosexuals, non-Aryans, and mentally and physically disabled.
Armenian Genocide
Assault carried out by mainly Turkish military forces against Armenian population in Anatolia in 1915; over a million Armenians perished and thousands fled to Russia and the Middle East.
Cambodian Genocide
Pol Pot eliminated educated, artists, religious, and minorities
Rwandan Genocide
The killing of more than 500,000 ethnic Tutsis by rival Hutu militias in Rwanda in 1994. The conflict between the dominant Tutsis and the majority Hutus had gone on for centuries, but the suddenness and savagery of the massacres caught the United Nations off-guard. U.N. peacekeepers did not enter the country until after much of the damage had been done.
Ukranian Famine
Joseph stalin took away food from the people of Ukraine, which resulted in the death of millions of people
Bolsheviks
A group of revolutionary Russian Marxists who took control of Russia's government in November 1917
Institutional Revolutionary Party
(PRI) the political party introduced in 1929 in Mexico that helped to introduce democracy and maintain political stability for much of the 20th century
Franz Ferdinand
Archduke of Austria-Hungary assassinated by a Serbian nationalist. A major catalyst for WWI.
Militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government
Paris Peace Conference
The peace conference that decided the terms of WWI peace and Treaty of Versailles.
Woodrow Wilson
President of the United States (1913-1921) and the leading figure at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. He was unable to persuade the U.S. Congress to ratify the Treaty of Versailles or join the League of Nations.
Georges Clemenceau
French statesman who played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Versailles (1841-1929)
David Lloyd George
Britain's prime minister at the end of World War I whose goal was to make the Germans pay for the other countries' staggering war losses
Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.
New Economic Policy (NEP)
Lenin's 1921 policy to re-establish limited economic freedom in an attempt to rebuild agriculture and industry in the face of economic disintegration
John Maynard Keynes
British economist who argued that for a nation to recovery fully from a depression, the govt had to spend money to encourage investment and consumption
Totalitarianism
A form of government in which the ruler is an absolute dictator (not restricted by a constitution or laws or opposition etc.)