Plant Phys exam 3: 4 ATP synthesis
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Describe the structure of ATP synthase
alpha and beta- active site for ATP synthesis
beta- catalytic site
b- prevents alpha and beta from moving
Y- attached to c-ring, Y rotates as C ring rotates… between alpha and beta subunits
c- (c-ring) 8-14 subunits; H+ binding site, rotates 30-36 degrees when binging to C ring
a- H+ movement… H+ entrance from lumen/ H+ exit to stroma
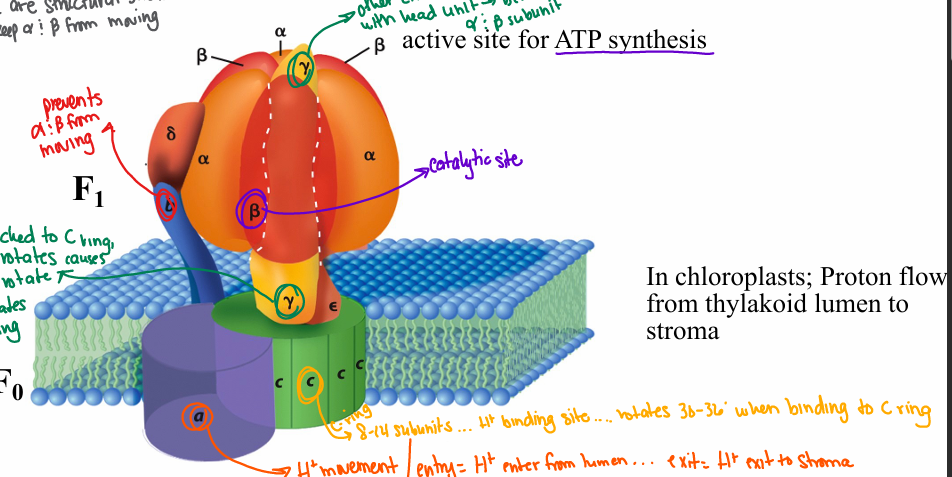
How do protons flow through ATP synthase?
H+ enter and exit ATP Synthase via the a subunit
H+ binding to C subunits causes rotation of ring (≅ 30-36 degrees)
C ring rotation causes rotation of 𝛄 subunit
𝛄 rotation changes conformational of catalytic site in B subunits and drives the synthesis of ATP
Head unit does not rotate – its static
(and held in place by b and 𝜹)
What influence does the H+ concentration have on ATP synthase?
higher concentration= more likely to bind
lower concentration= more likely to dissociate
Which subunit in ATP synthase is variable amongst organisms?
C ring subunit
What is rational catalysis?
For each beta subunit (β) the active site can exists as O (open) L (loose) T (tight) conformations
Proton flow and rotation of asymmetric gamma subunit changes the conformation
3 ATP/360 degree rotation of gamma subunit