farming
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
give 4 farming practices which increase GPP/NPP:
pesticides - insecticides and herbicides
biological agents - parasites and pathogenic bacteria/viruses
integrated systems (pesticides and biological agents)
keeping animals in pens
explain how using pesticides increases GPP/NPP:
killing of pests simplifies food web
insecticides - kill insect pests os less biomass lost from crops ∴ NPP greater
herbicides - kill weeds, removing direct competition for solar energy and removes insect pests’ habitat/food source
explain how biological agents increase GPP/NPP:
reduces no. of pests so simplifies food web
crops lose less energy and biomass, increasing efficiency of energy transfer to humans
parasites - live in/lay eggs on pest insect, killing it/reducing its ability to function
pathogenic bacteria/viruses also kill pests e.g. by secreting toxins
explain how integrated systems increase GPP/NPP:
combination of pesticides and biological agents
has greater effect on reducing pest numbers, further increasing NPP
explain how keeping animals in pens increases GPP/NPP:
restricts movement and increases warmth (indoors) - decreases rate of respiration ∴ less energy wasted via movement/thermoregulation
increases biomass production and chemical energy storage, further increasing NPP and efficiency of energy transfer to humans
BUT ethical concerns - may cause distress to animals as they cannot exhibit natural behaviour
describe and explain the process of eutrophication:
soluble nutrients e.g. nitrates/phosphates washed out of soil, into water
increased nitrates/phosphates increase plant growth, causing algal bloom
plants cover surface and lock out light, meaning that aquatic plants cannot photosynthesise, causing them to die
death of aquatic plants initiates increase in saprobionts which decompose plants and respire aerobically, using up oxygen
less oxygen is available to aquatic animals, so they are unable to respire and die
what is leaching?
the process in which water soluble compounds e.g. fertilisers are lost from soil and washed off into bodies of water
give 2 factors which make leaching more likely:
fertiliser applied just before heavy rainfall
inorganic ions in artificial fertilisers - soluble so more likely to leach if not immediately used
give 2 factors which make leaching less likely:
N/P in organic fertilisers less likely to leach as contained in organic compounds, making their release into soil more controlled
phosphates less soluble than nitrates so leaching less likely
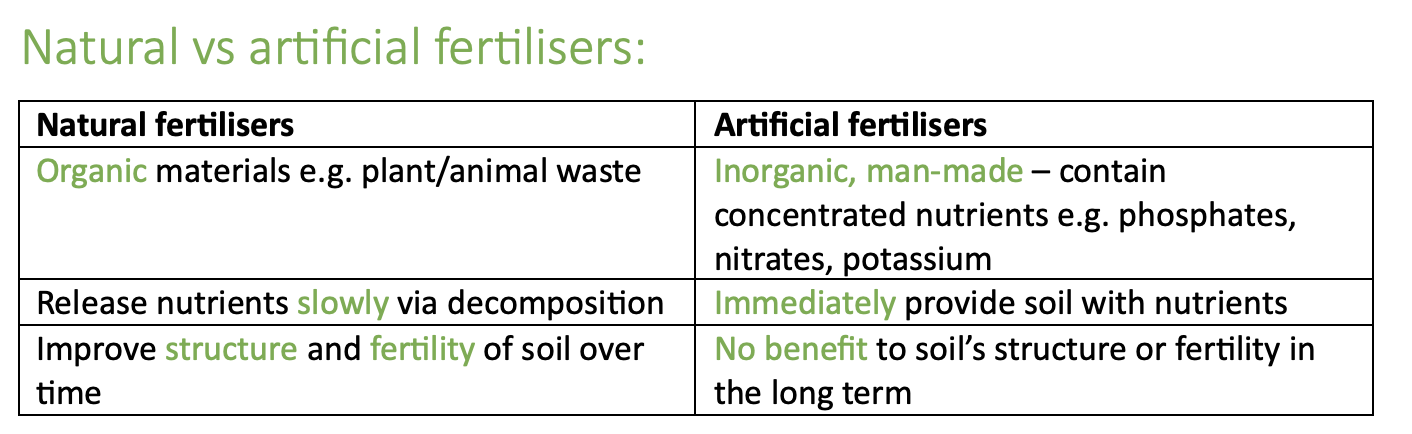
compare natural and artificial fertilisers:
how does productivity differ between natural and artificial ecosystems?
relatively low in natural ecosystems
increases in agricultural ecosystems due to additional energy input and exclusion of other species via pesticides/herbicides, reducing competition for abiotic factors
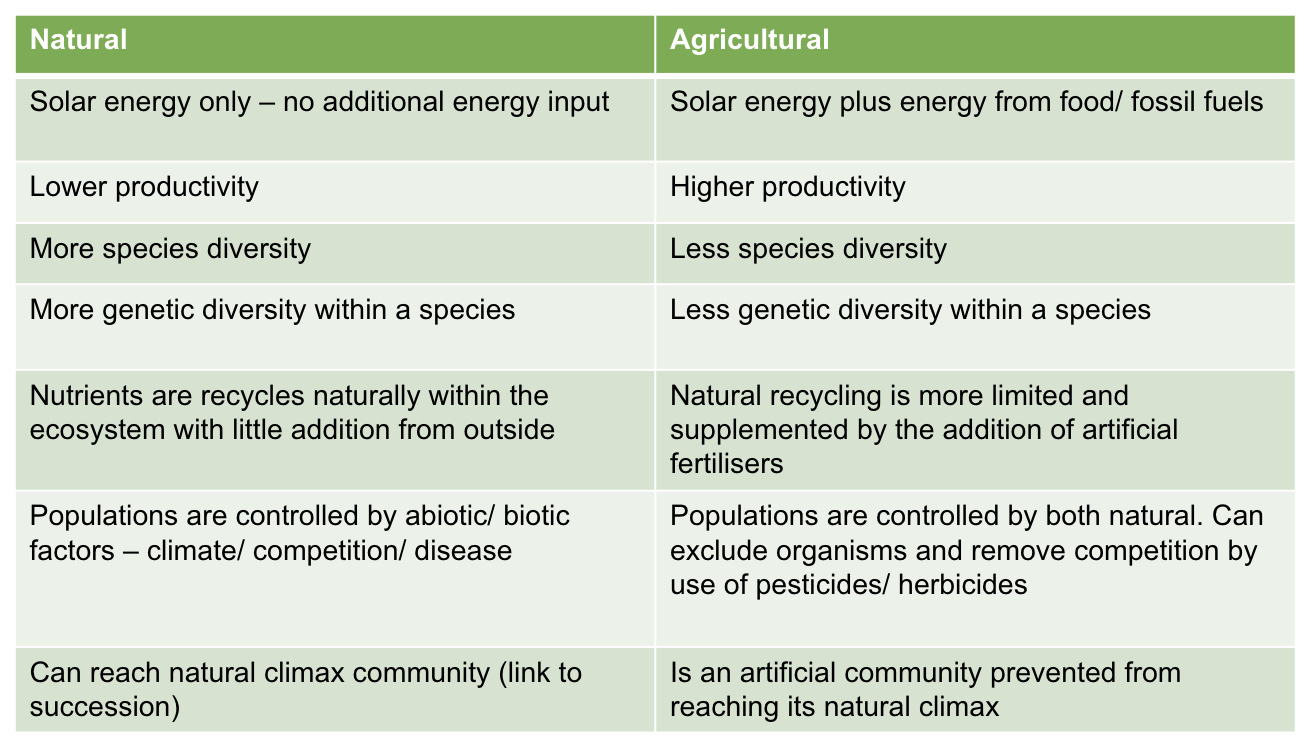
compare and contrast natural and agricultural ecosystems: