AMINO ACIDS
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
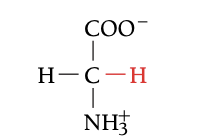
GLY
GLYCINE, G
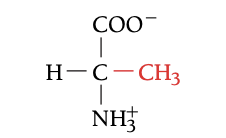
ALA
ALANINE, A
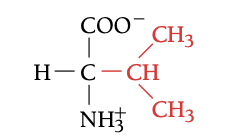
VAL
VALINE, V
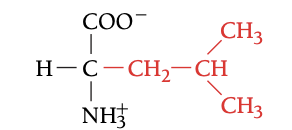
LEU
LEUCINE, L
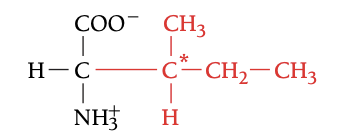
ILE
ISOLEUCINE, I
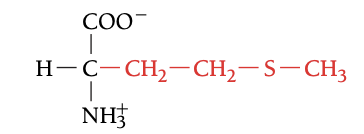
MET
METHIONINE, M
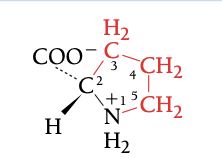
PRO
PROLINE, P
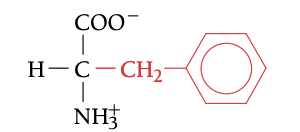
PHE
PHENYLALANINE, F
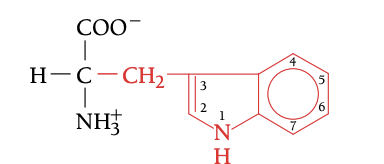
TRP
TRYPTOPHAN, W
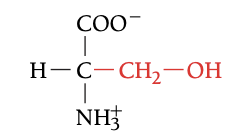
SER
SERINE,S
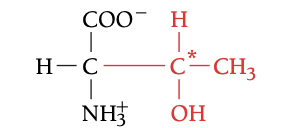
THR
THERONINE, T
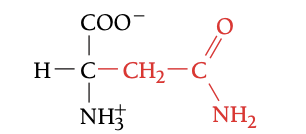
ASN
ASPARAGINE, N
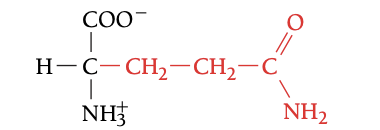
GLN
GLUTAMINE, Q
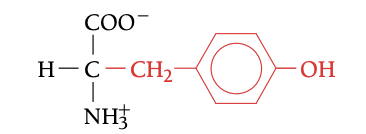
TYR
TYROSINE, Y
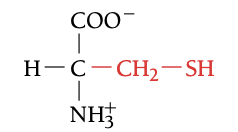
CYS
CYSTEININE, C
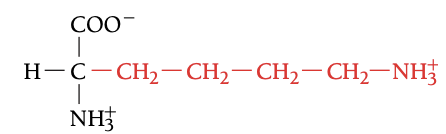
LYS
LYSINE, K
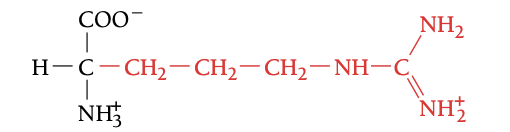
ARG
ARGININE, R
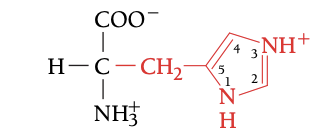
HIS
HISTIDINE, H
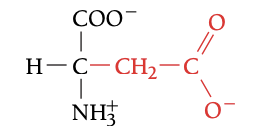
ASP
ASPARTIC ACID, D
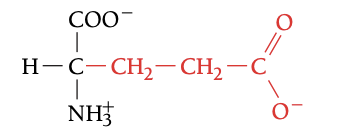
GLU
GLUTAMIC ACID, E
PKA FOR TYR
10.46 (phenol)
PKA FOR CYS
8.37 (sulfhydryl)
PKA FOR LYS
10.54 (ε-NH+ 3 )
PKA FOR ARG
12.48 (guanidino)
PKA FOR HIS
6.04 (imidazole)
PKA FOR ASP
3.90 (β-COOH)
PKA FOR GLU
4.07 Glu (γ-COOH)
pH decreases
When pH decreases (becomes more acidic):
There are more H⁺ ions in solution.
Amino acids become more protonated (they gain H⁺).
Common changes:
Amino group (–NH₂) → –NH₃⁺
Carboxyl group (–COO⁻) → –COOH
Side chains with acidic/basic groups also pick up protons.
Overall effect:
Amino acids carry more positive charge in low pH.
pH increases
When pH increases (becomes more basic):
There are fewer H⁺ ions in solution.
Amino acids become deprotonated (they lose H⁺).
Common changes:
–NH₃⁺ → –NH₂
–COOH → –COO⁻
Basic and acidic side chains lose protons depending on their pKa.
Overall effect:
Amino acids carry more negative charge in high pH.