B10 Brain, Eye & Eye Problems
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
B10.4, 10.5 & 10.6 (not all off B10!)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
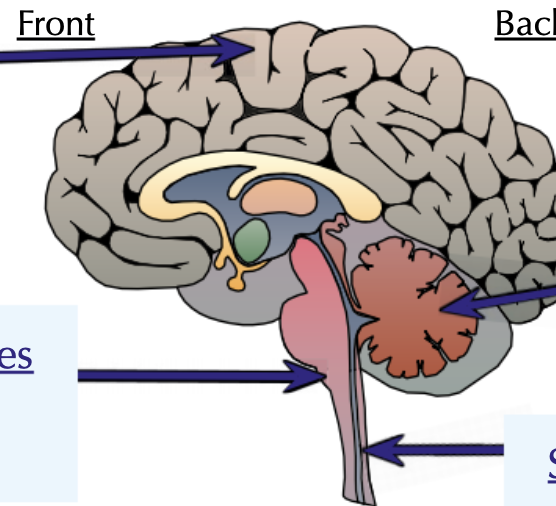
The Brain
Label the parts of the brain, 4 labels
dont look at definitions
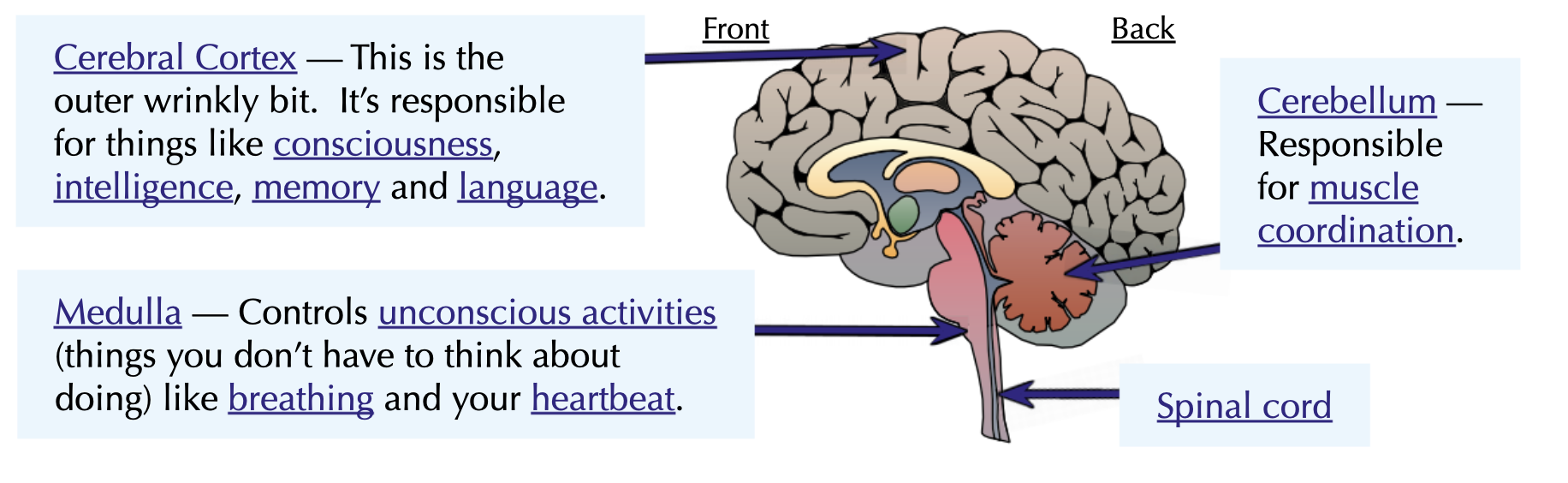
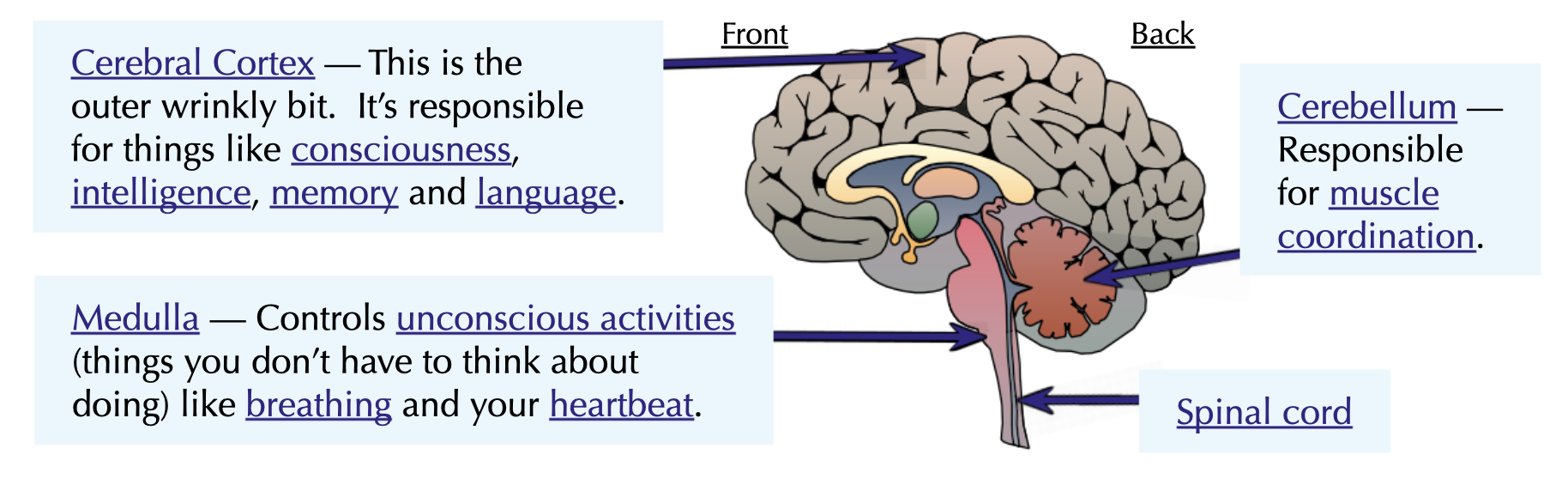
What do the parts do?
2 methods of studying the brain and how they work
Magnetic resonance imaging - mri scans use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body
Electrically stimulating parts of the brain and seeing what it makes move
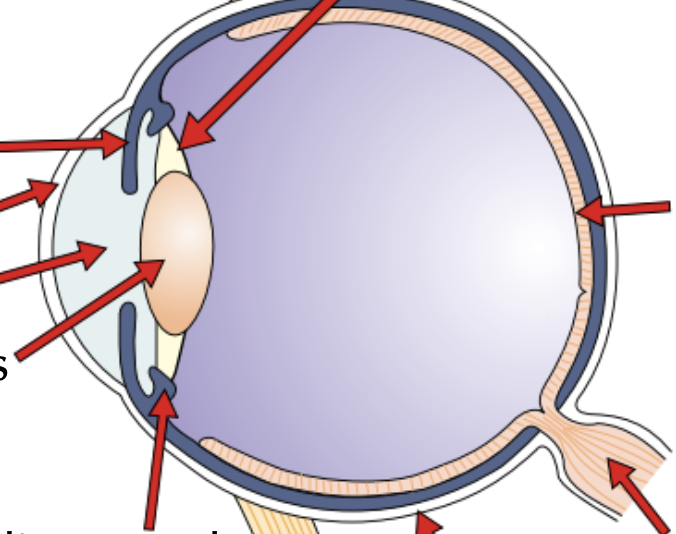
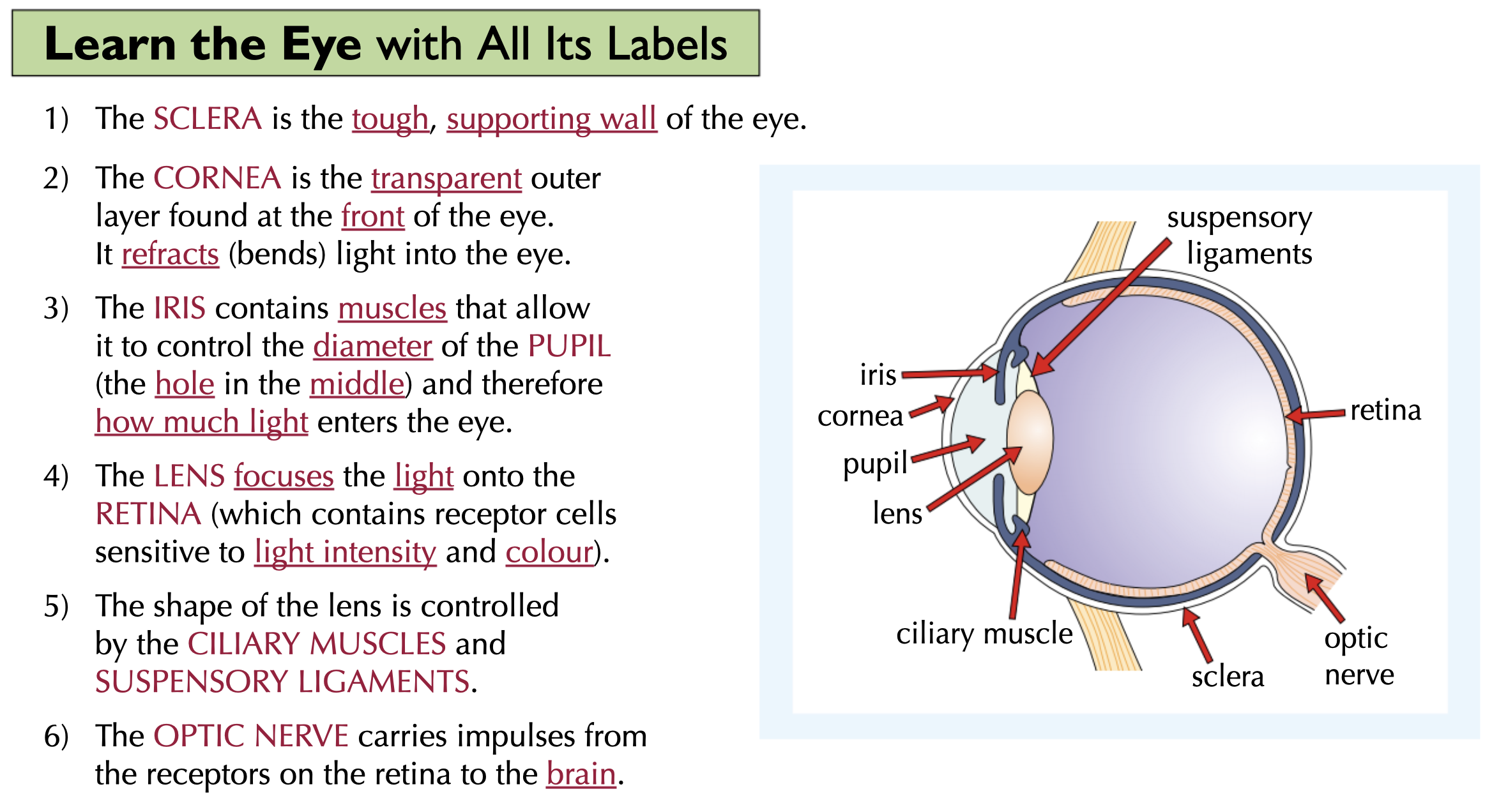
The eye
Label this eye
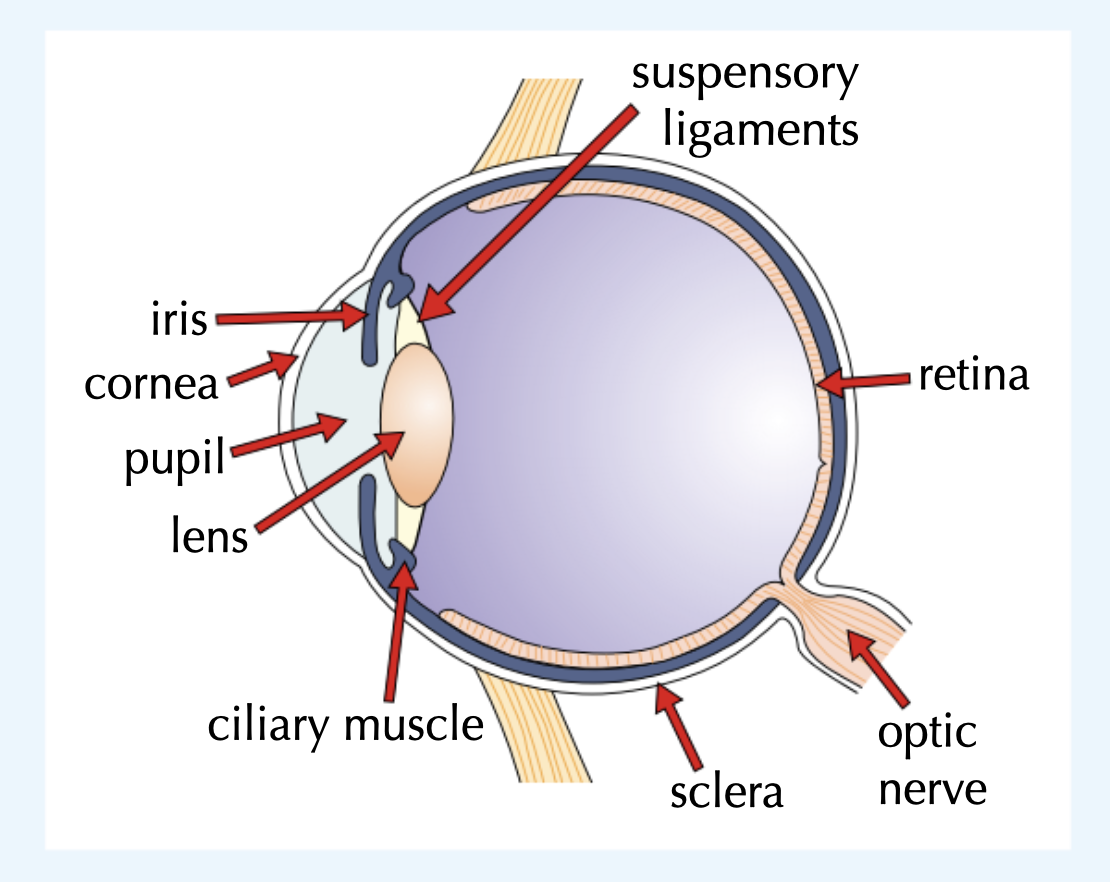
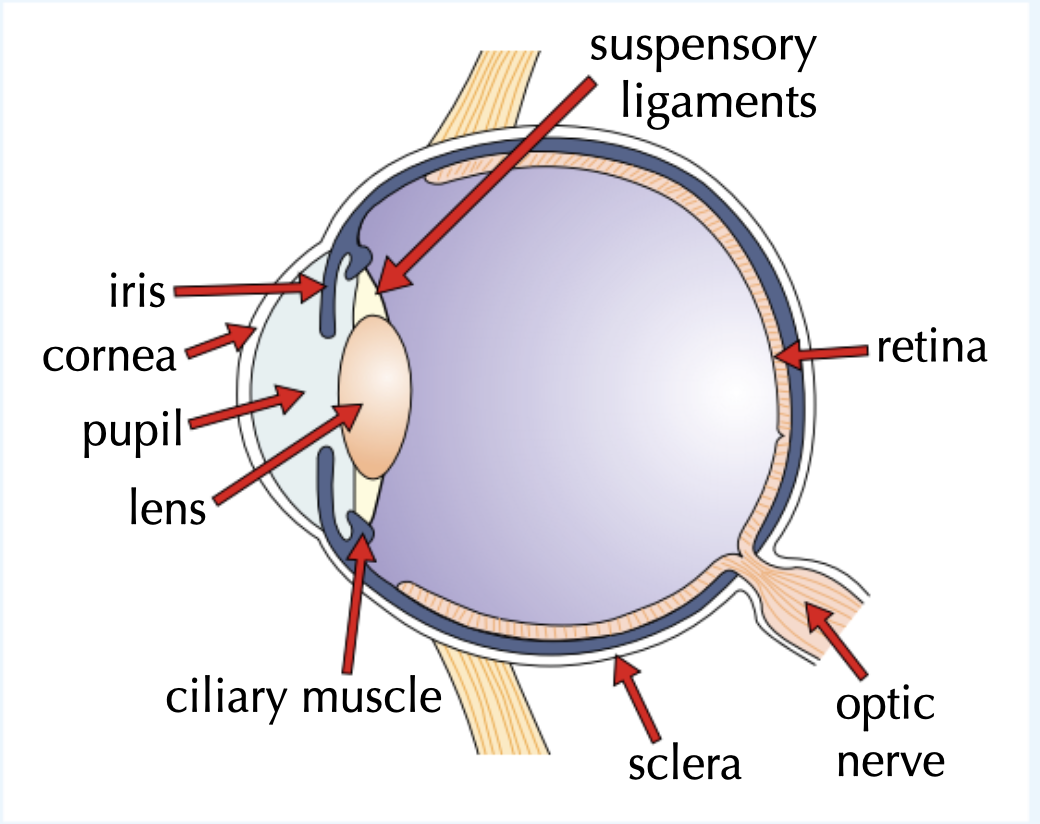
Functions of the parts
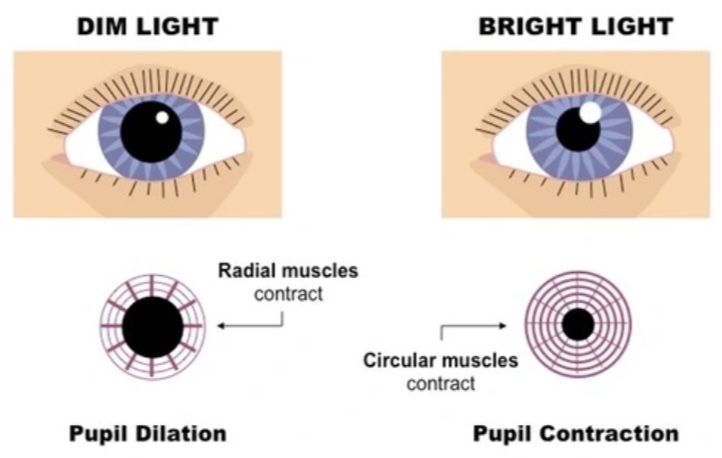
Adaption to light intensity / Iris reflex
In DIM light, the pupil is _____
In BRIGHT light, the pupil is ____
In DIM light, the pupil is dilated
In BRIGHT light, the pupil is contracted
pupil is…
dilated = big/small
contracted = big/small
dilated = big
contracted = small
To dilate, the ___ muscles contract
and the ___ muscles relax
To dilate the RADIAL muscles contract
and the CIRCULAR muscles relax
To contract the pupil, the ___ muscles contract
and the ___ muscles relax
To contract the CIRCULAR muscles contract
and the RADIAL muscles relax
not a question
Accommodation
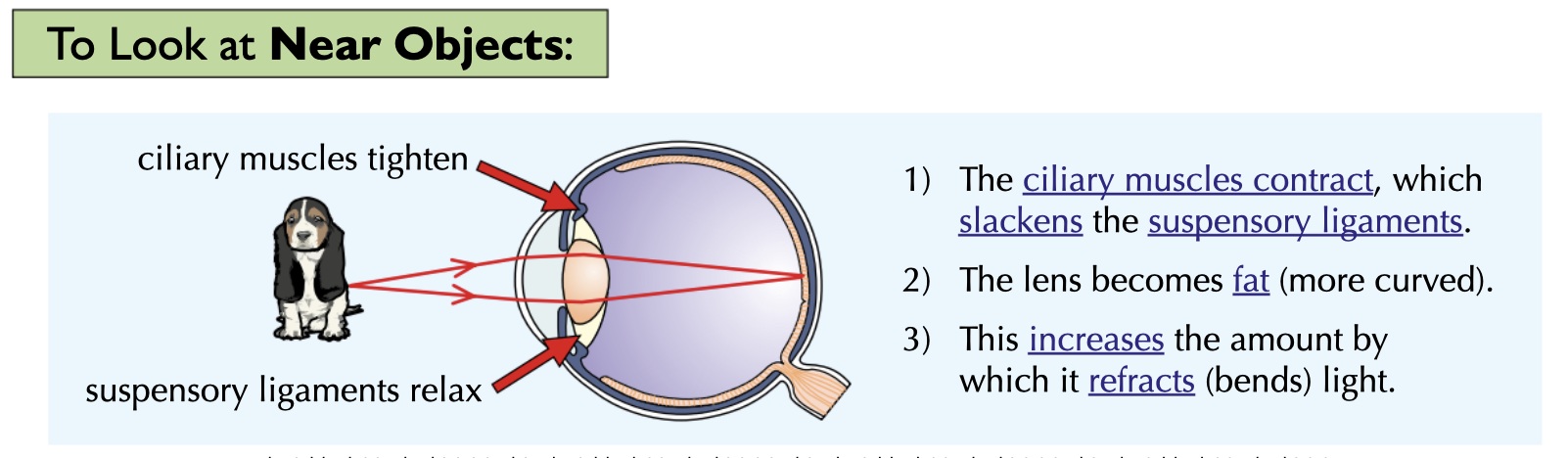
To focus on a NEAR object:
the ciliary muscles ___
the suspensory ligaments ___
the lens becomes ___
so it refracts light rays more ___
the ciliary muscles contract
the suspensory ligaments loosen
the lens becomes thicker
so it refracts light rays more strongly
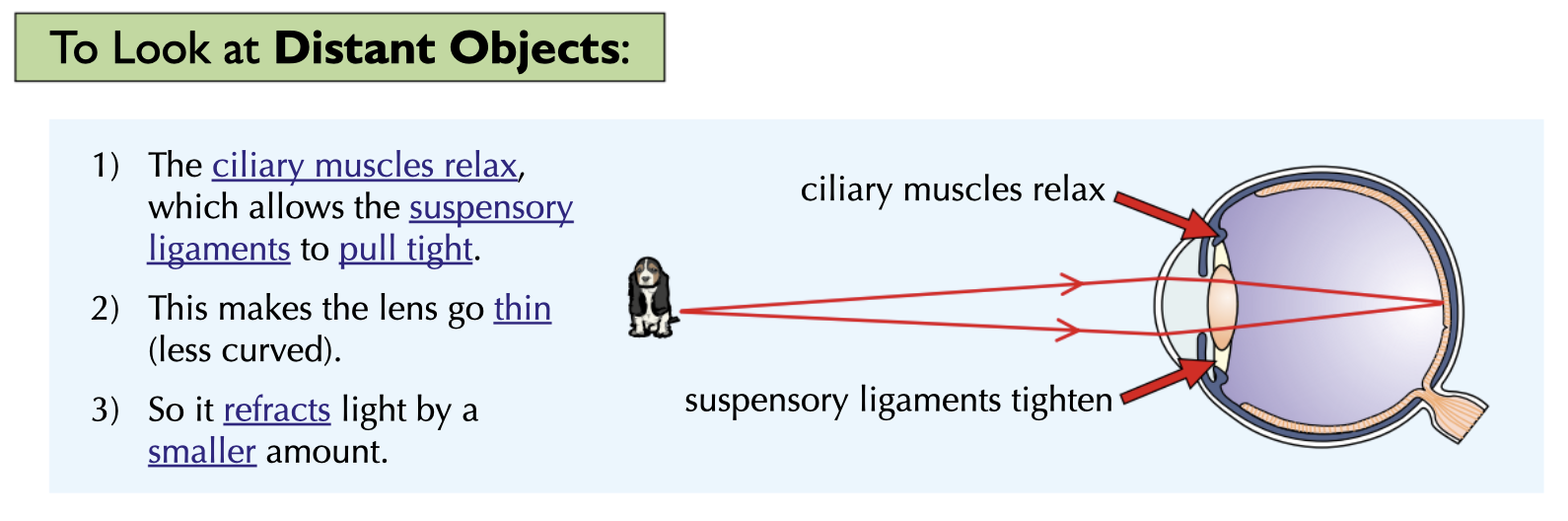
To focus on a DISTANT object:
the ciliary muscles ___
the suspensory ligaments ___
the lens becomes ___
so it ___ refracts light rays
the ciliary muscles relax
the suspensory ligaments tighten
the lens becomes thin
so it only slightly refracts light rays
light rays meet on the ___ at a point called the ___
light rays meet on the retina at a point called the fovea
Common problems of the eye
Short sightedness is called ___
Long sightedness is called ___
Short sightedness is called myopia
Long sightedness is called hyperopia
In myopia the eye can’t focus on ___ objects
In hyperopia the eye can’t focus on ___ objects
myopia = distant
hyperopia = nearby
In myopia the uncorrected image forms ___ the retina
in front of the retina
in hyperopia the uncorrected image forms ___ the retina
behind the retina
Why does myopia occur?
lens too strong
eyeball too long
Why does hyperopia occur?
Lens too weak
eyeball too short
What kind of lens is needed to correct myopia?
i.e. type of glasses or contact lenses
Concave

What kind of lens is needed to correct hyperopia?
Convex

Give 2 new technological treatments for hyper/myopia
Hard and soft contact lenses
Laser surgery to change shape of the cornea
Replacement lens in the eye (surgery)