Fate of Pyruvate & TCA cycle
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what’s the different fate for pyruvate?
Anaerobic glycolysis - no mitochondria / O2
need to regenerate NAD+ by using NADH to make lactate to keep glycolysis going, uses up H+
lactate can accumulate → acidosis
Aerobic metabolism - mitochondria & O2 available
pyruvate enters mitochondria & oxidized in TCA cycle
producing CO2 & H2O while consuming H+
generate energy in ETC
What is the structure for mitochondria membrane?
Double-membraned
outer membrane - freely permeable
inner membrane - impermeable, has specificity using transporters
inter-membrane space - where all enzymes are
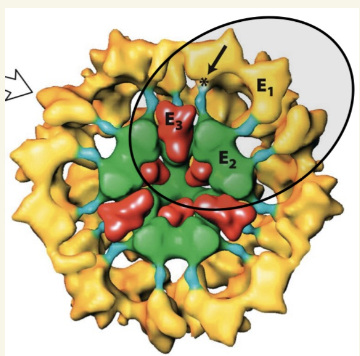
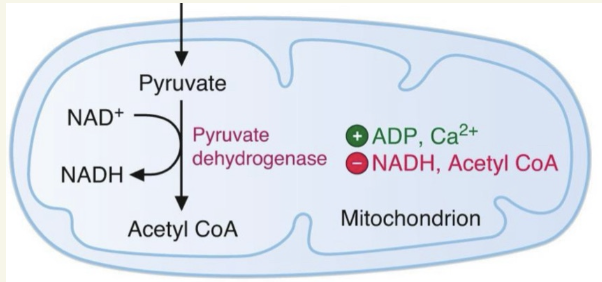
what’s the structure of PDC?
my multiple copies of 3 enzymatic subunits: E1, E2, E3
requires 5 cofactors for catalysis, found in mitochondria matrix
TPP, Lipoamide, FAD, CoA, NAD+
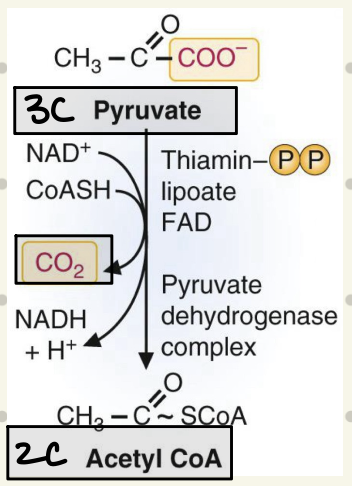
What’s the role of CO2 in PDC reaction?
resulted from redox decarboxylation
drives reaction forward because it doesn’t dissolve → immediately leaves
How is PDC reaction regulated?
Feedback Inhibition:
Acetyl-CoA inhibits E2
NADH inhibits E3
turns off process, causing pyruvate build up & glycolysis off
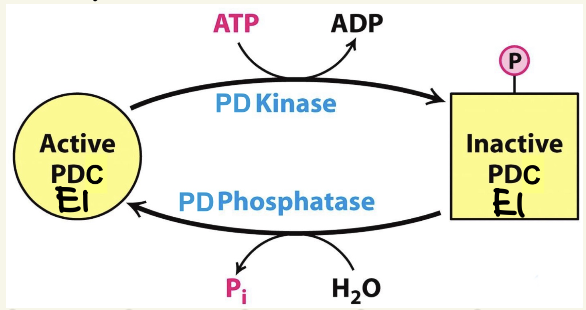
PTM:
phosphorylation onto E1
PD Kinase - turn PDC OFF
add P, using ATP
when ⬆energy (ATP, NADH, Acetyl-CoA)
PD Phosphatase - turn PDC ON
remove P by hydrolysis
when ⬇energy (ADP, NAD+, Ca2+)
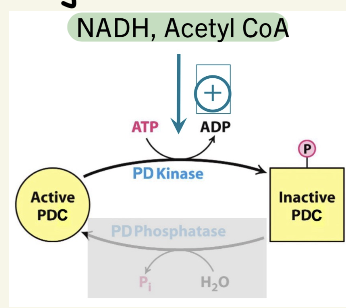
How is PDC reaction regulated @ muscle at rest?
- how is PD Kinase regulated?
rest = ⬆energy state (lots Acetyl-CoA, NADH, ATP)
turns PDC off by feedback inhibition & phosphorylation by PD Kinase
PD Kinase activated by ⬆NADH & Acetyl-CoA
How is PDC reaction regulated @ muscle at exercise?
- how is PD Phosphatase regulated?
when exercising, ⬆intracellular Ca2+ & ⬇energy state
causes ⬆ADP, pyruvate (∵active glycolysis) → need more energy
⬆ADP, pyruvate inhibits PD Kinase
turns PDC ON → PD Phosphatase
PD Phosphatase is:
activated by Ca2+
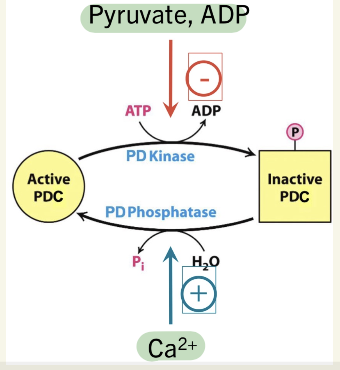
Summarize the allosteric control of PDC
Acetyl-CoA, NADH, pyruvate, ADP, Ca2+
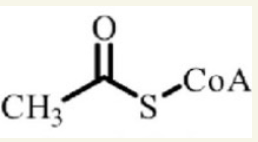
why is Acetyl-CoA important? What is its structure?
it’s central to generating energy from any dietary source
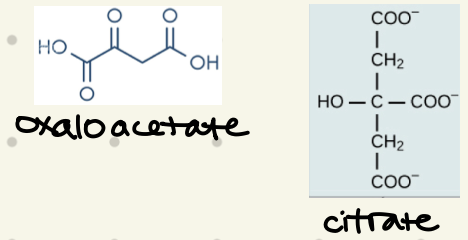
what’s the structure of oxaloacetate & citrate?
what’s the enzyme linking TCA & ETC?
location?
how does it work?
succinate dehydrogenase
embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane
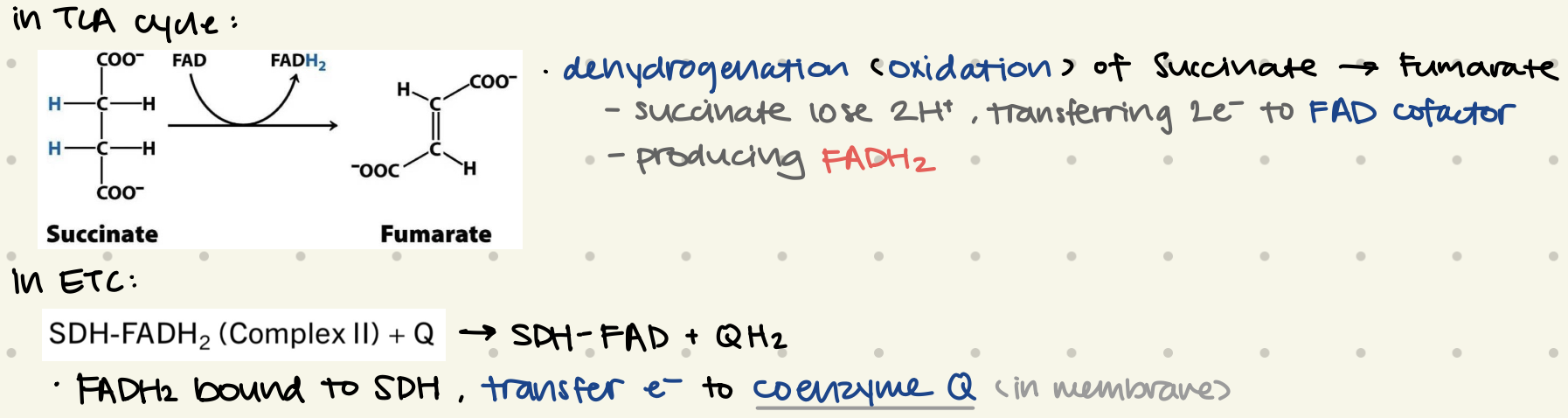
in TCA:
dehydrogenation of succinate → fumarate
succinate lose 2H+, transferring 2e- to FAD
producing FADH2
in ETC:
FADH2 bound to SDH, transfer e- to coenzyme Q
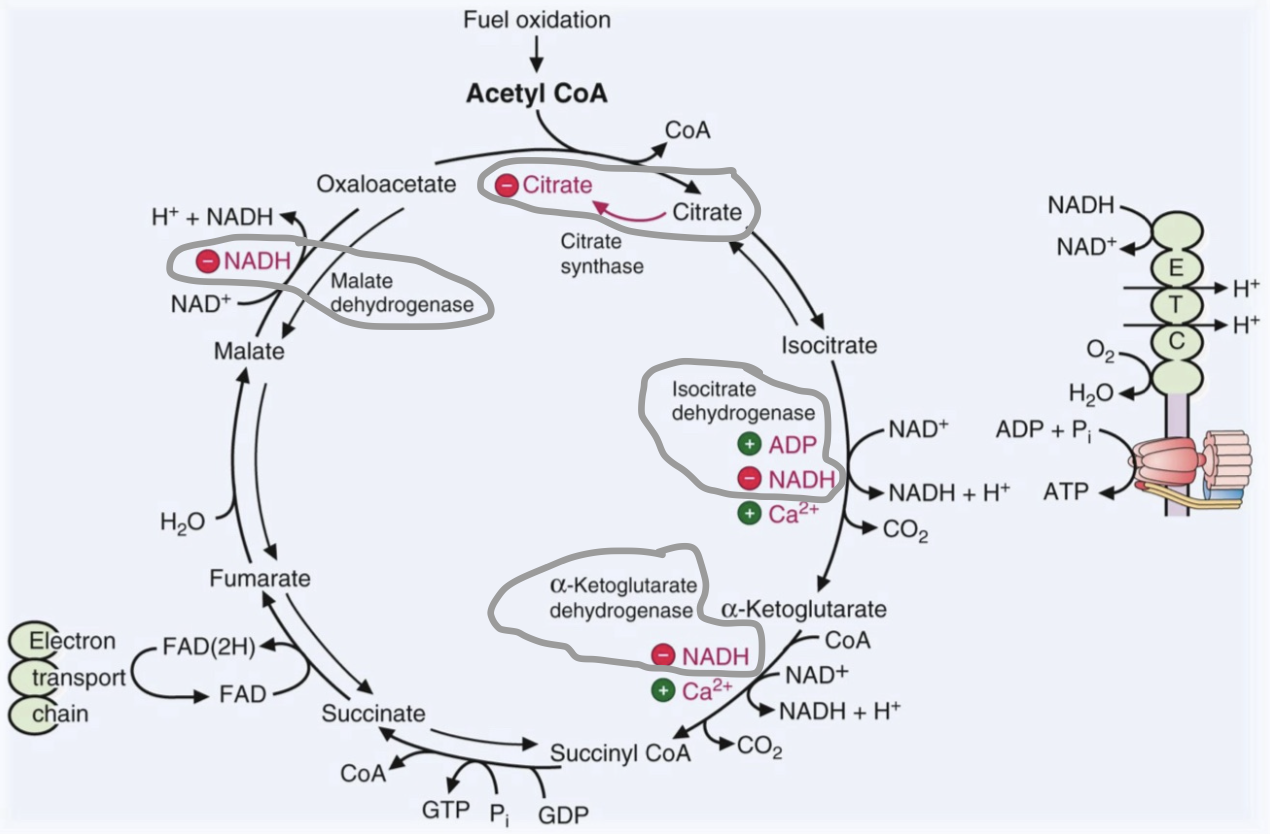
How is TCA cycle regulated by?
Stimulated by:
ADP, Ca2+ (⬇energy & muscle use)
Ca2+ activates dehydrogenase, generating NADH/FADH
Inhibited by:
citrate (product inhibition), NADH, ATP
*NADH is the main energy sensor of mitochondria
⬆NADH = stop TCA / ⬇NADH = start TCA
what’s the source of Acetyl-CoA for TCA cycle?
sugars, fatty acids, amino acids