CH 3: Activity 2: Acids, Bases, pH
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen (H+) ion concentration of a solution.
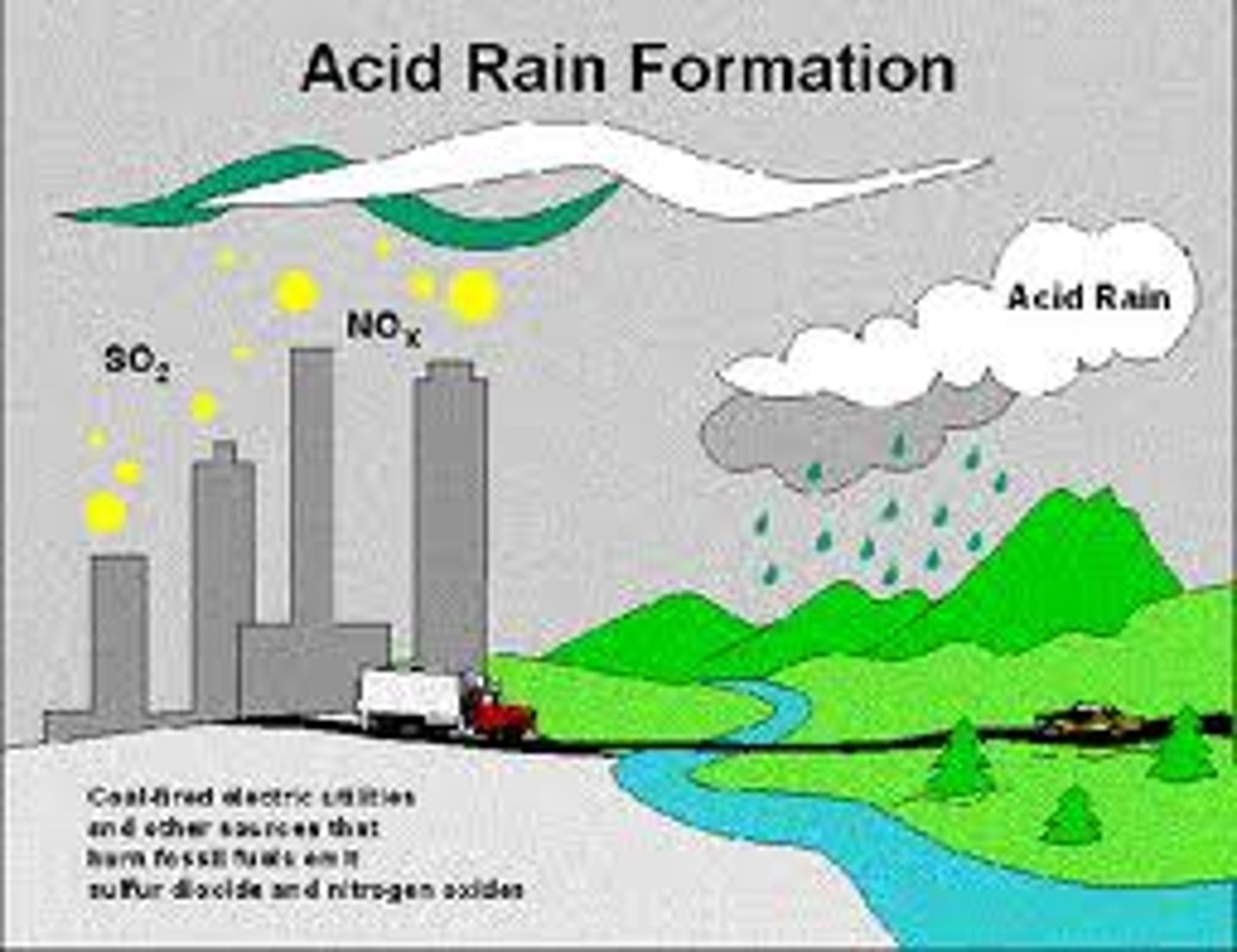
Acid Rain
Rain containing acids that form in the atmosphere when industrial emissions (especially sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) combine with water.
Base
A substance that increases the hydroxide (OH-) ions concentration of a solution.
Binary Acid
An acid that contains only two different elements, hydrogen (H+) and one of the more electronegative elements (Cl-).

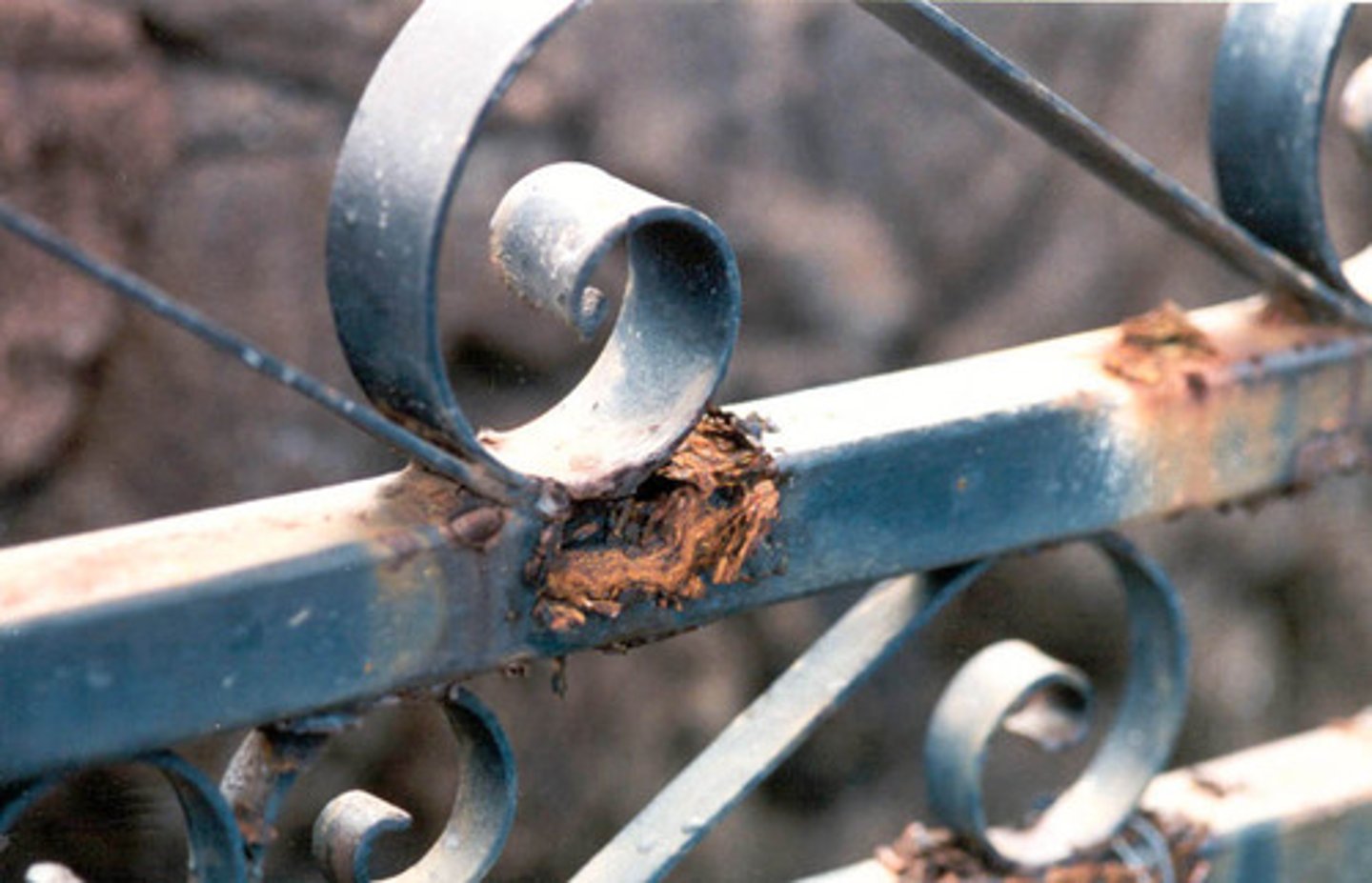
Corrosive
The way in which acids react with some metals so as to eat away the metal.

Hydrogen Ion
A positively charged ion formed when a hydrogen atoms loses its electron (H+).
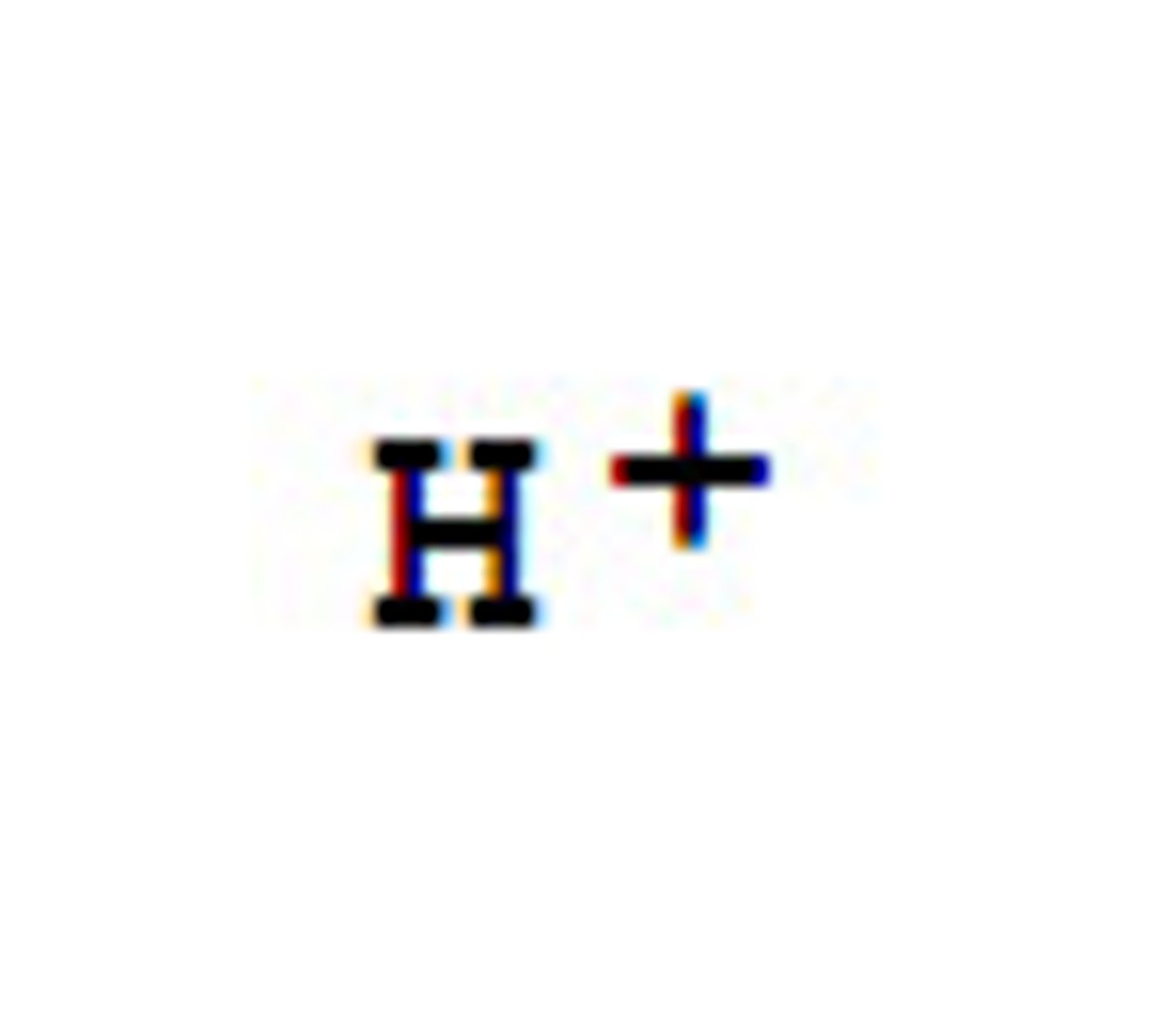
Hydroxide Ion
A negatively charged ion (OH-).

Litmus paper
An indicator paper that turns reed in an acid and blue in a base.

Neutralize
The reaction of an acid and a base to form a neutral solution of water and a salt (pH 7).
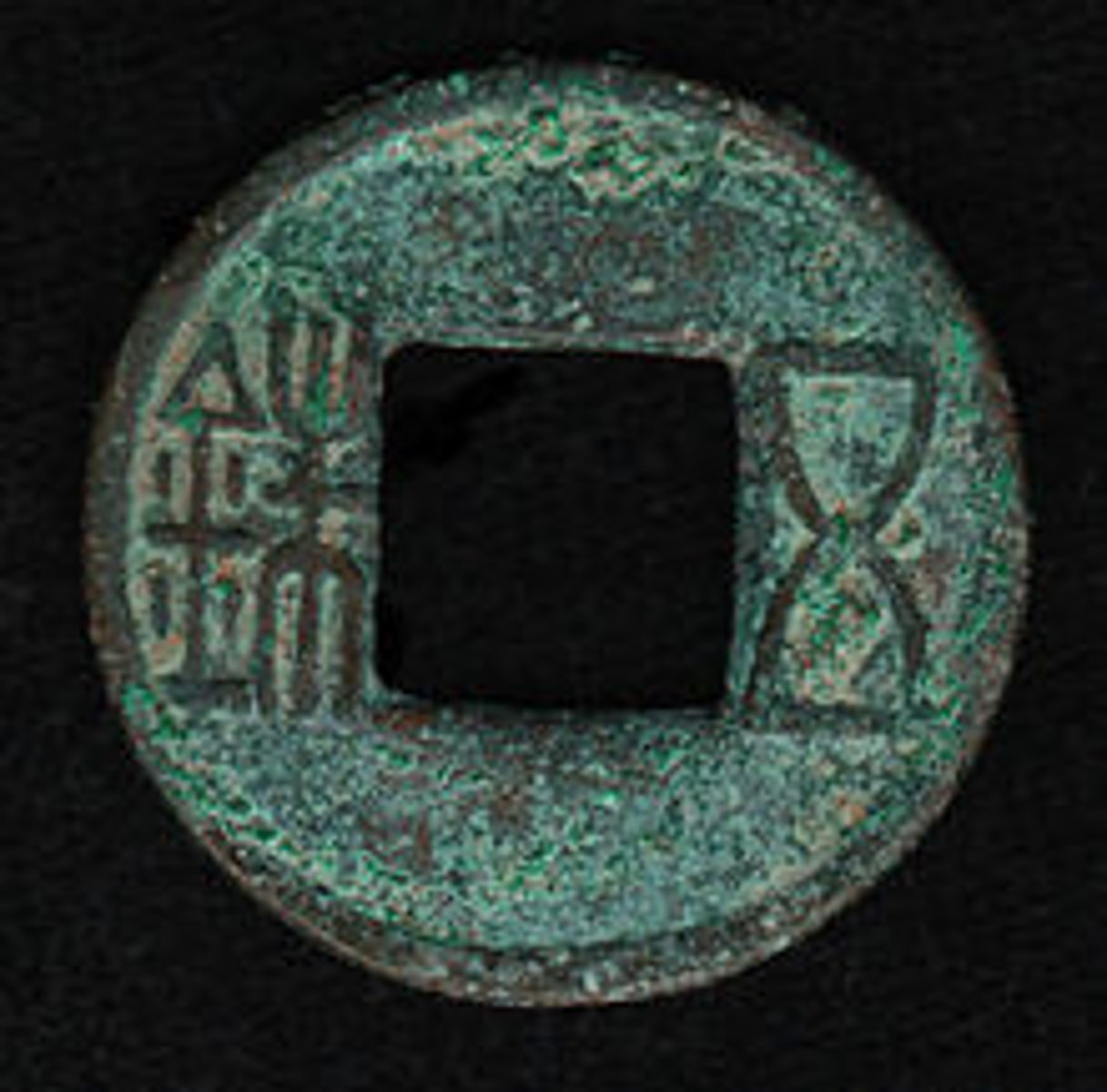
Patina
A thin green coating that also coats and protects (copper oxide).

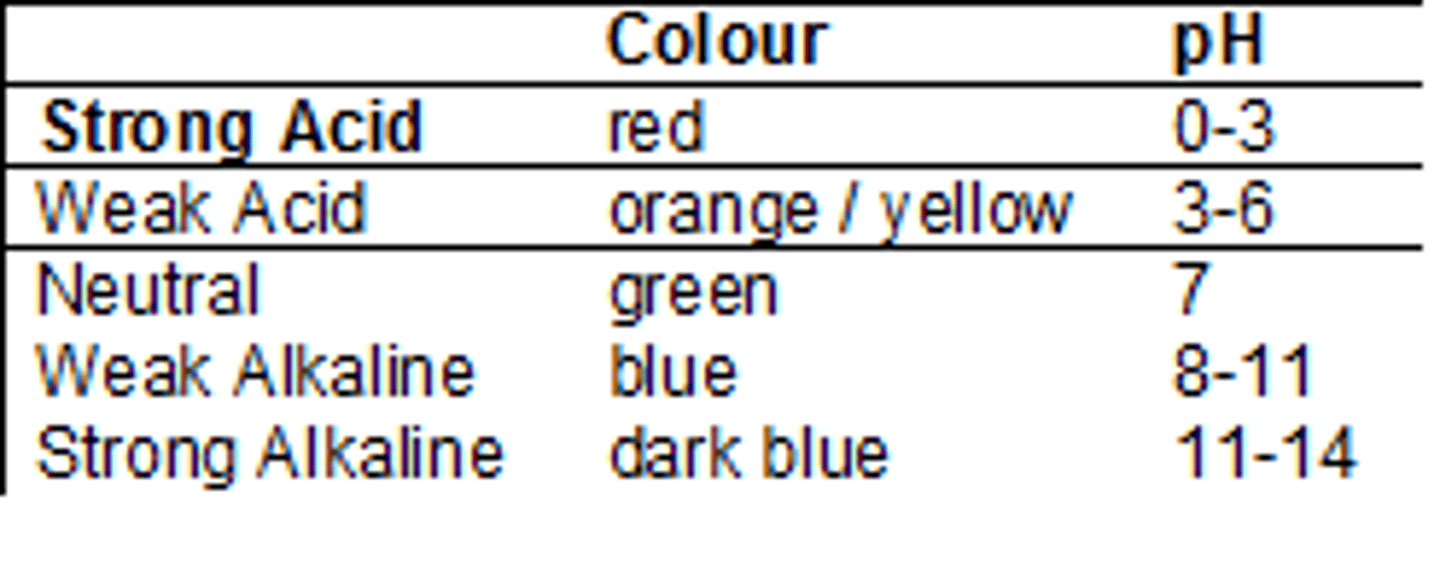
pH
Ia a measure of how much H+ is in a solution sample.

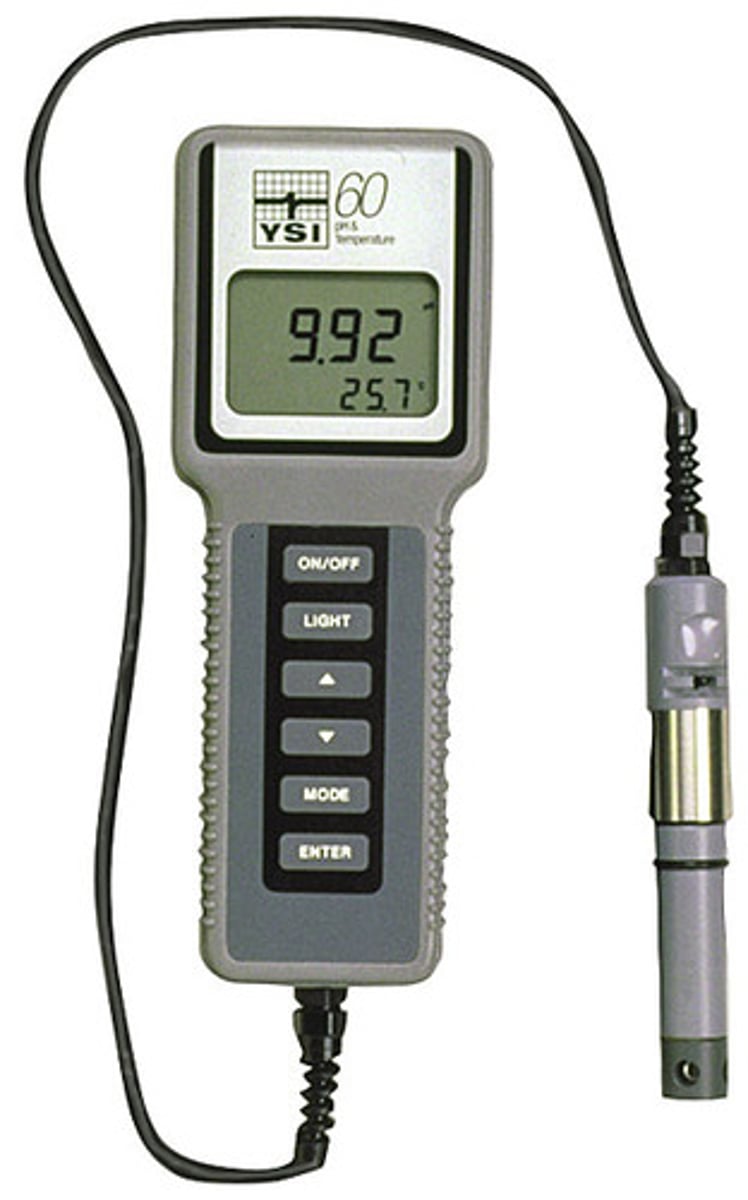
pH meter
A device used to determine the pH of a solution.

pH scale
Measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0-14

Ternary Acid
An acid composed of hydrogen (H+) and usually two other elements (NO3-); the second and third elements forming a polyatomic ion.
Universal Indicator
A solution which undergoes several color changes over a wide range of pH's (0-14)