Microbiology Chapter 14
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
pathology
study of disease
2
New cards
etiology
cause of disease
3
New cards
pathogenesis
development of disease
4
New cards
infection
invasion of the body by pathogens
5
New cards
disease
abnormal state in which the body is not performing normal functions
6
New cards
normal microbiota
permanent colonize host, do not cause disease (under normal conditions)
7
New cards
transit microbiota
present for days, weeks or months
8
New cards
microbial antagonism (competitive exclusions)
competition between microbes
9
New cards
normal microbiota protect the host by
1. competing for nutrients
2. producing substances harmful for invading microbes
3. affecting pH and available oxygen
10
New cards
symbiosis
relationship between normal microbiota and host
11
New cards
commensalism
one organism benefits, and the other is unaffected
12
New cards
mutalism
both organisms benefit
13
New cards
paratism
one organism benefits at the expense of others
14
New cards
incidence
\# of people who develop a disease during a time period
15
New cards
prevalence
\# of people who develop or have a disease at a specified time, regardless of when it first occurred
takes into account both old and new cases)
takes into account both old and new cases)
16
New cards
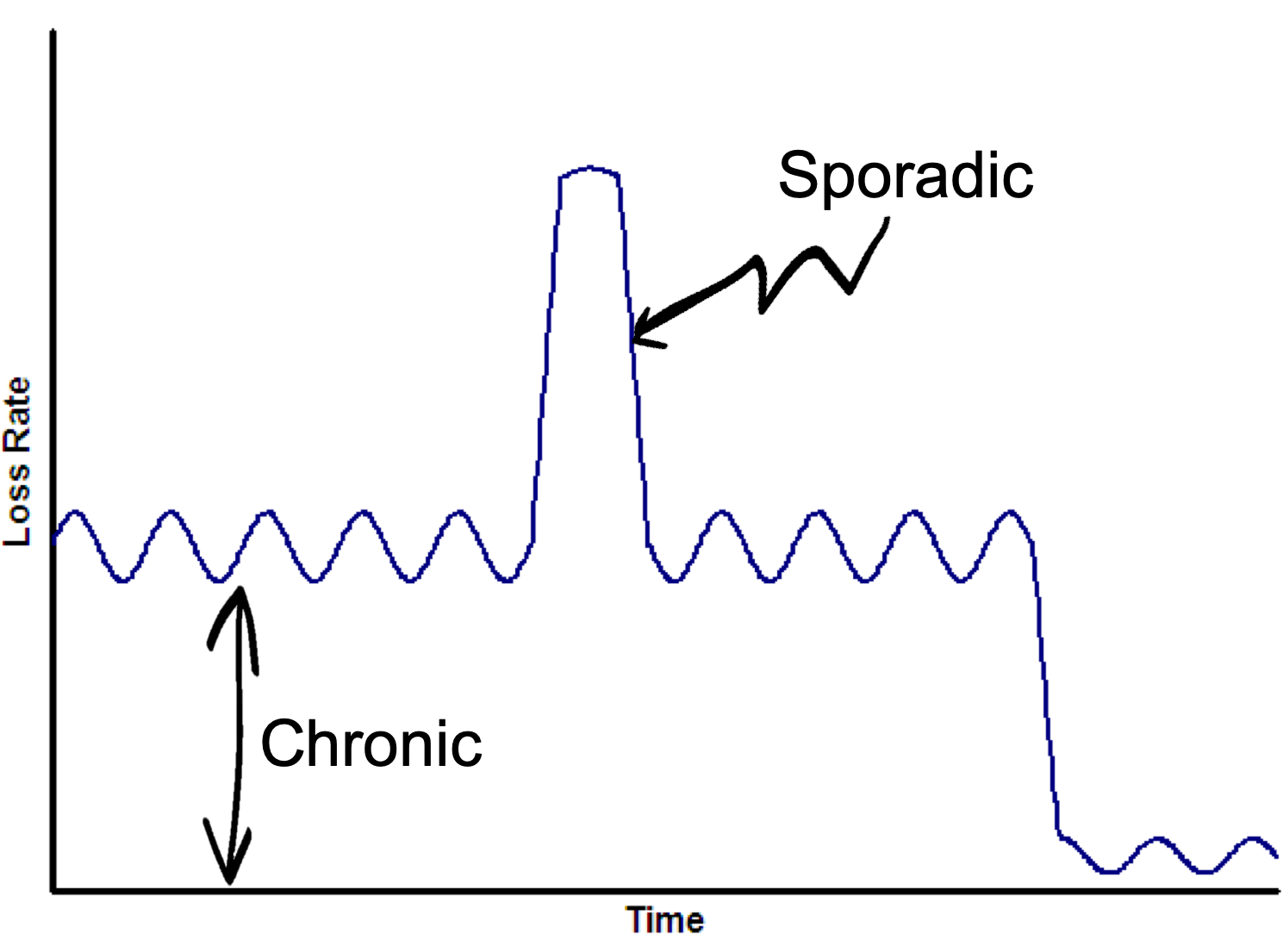
sporadic disease
occurs only occasionally
17
New cards

endemic disease
constantly present in population
18
New cards

epidemic disease
acquired by many people in a given area in a short time
19
New cards
pandemic
worldwide epidemic
20
New cards
acute disease
symptoms develop rapidly but lasts a short time
21
New cards
chronic disease
symptoms develop slowly
22
New cards
subacute disease
intermediate between acute and chronic disease
23
New cards
latent disease
causative agent is inactive for a time but then activates and produces symptoms
24
New cards
herd immunity
immunity in most of a population
25
New cards
what is a R° value
how many people the average person infects
26
New cards
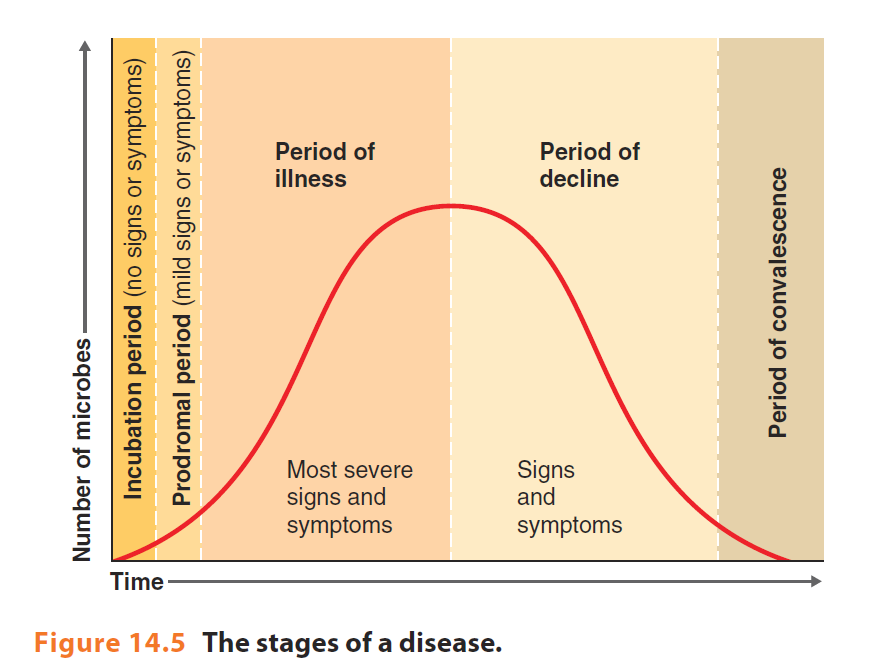
5 stages of development of disease
incubation disease
prodromal disease
period of illness
period of decline
period of convalescence
prodromal disease
period of illness
period of decline
period of convalescence
27
New cards
incubation period
initial infection
first signs and symptoms
first signs and symptoms
28
New cards
prodromal period
pre-symptomatic
infectious
infectious
29
New cards
period of illness
when the disease is more severe
30
New cards
period of decline
signs and symptoms will decline
31
New cards
what is exception when period of illness does not lead to period of decline
death
32
New cards
period of convalescence
body returns to its predeceased state
33
New cards
human reservoirs
**carriers:** inapparent infections/ latent diseases
34
New cards
animal reservoirs
**zoonoses:** diseases transmitted from animals to humans
35
New cards
give two examples of non-living reservoirs
soil and water
36
New cards
contact transmission is…
human to human
37
New cards
direct contact transmission
close association of infected → susceptible host
38
New cards
congenital transmission
mother → fetus or newborn at birth
39
New cards
indirect contact transmission
spreads to a host by a nonliving object called a **fomite**
40
New cards
droplet transmission
transmission via airborne droplets
less than 2 meters
less than 2 meters
41
New cards
vehicle transmission is…
environment to human
42
New cards
what are three examples of vehicle transmission
airborne
waterborne
foodborne
waterborne
foodborne
43
New cards
ID 50
infectious dose for 50% of a sample population, measures virulence of a microbe
44
New cards
vectors
examples, anthropods, fleas, ticks, mosquitoes
transmit disease by two methods… mechanical and biological
transmit disease by two methods… mechanical and biological
45
New cards
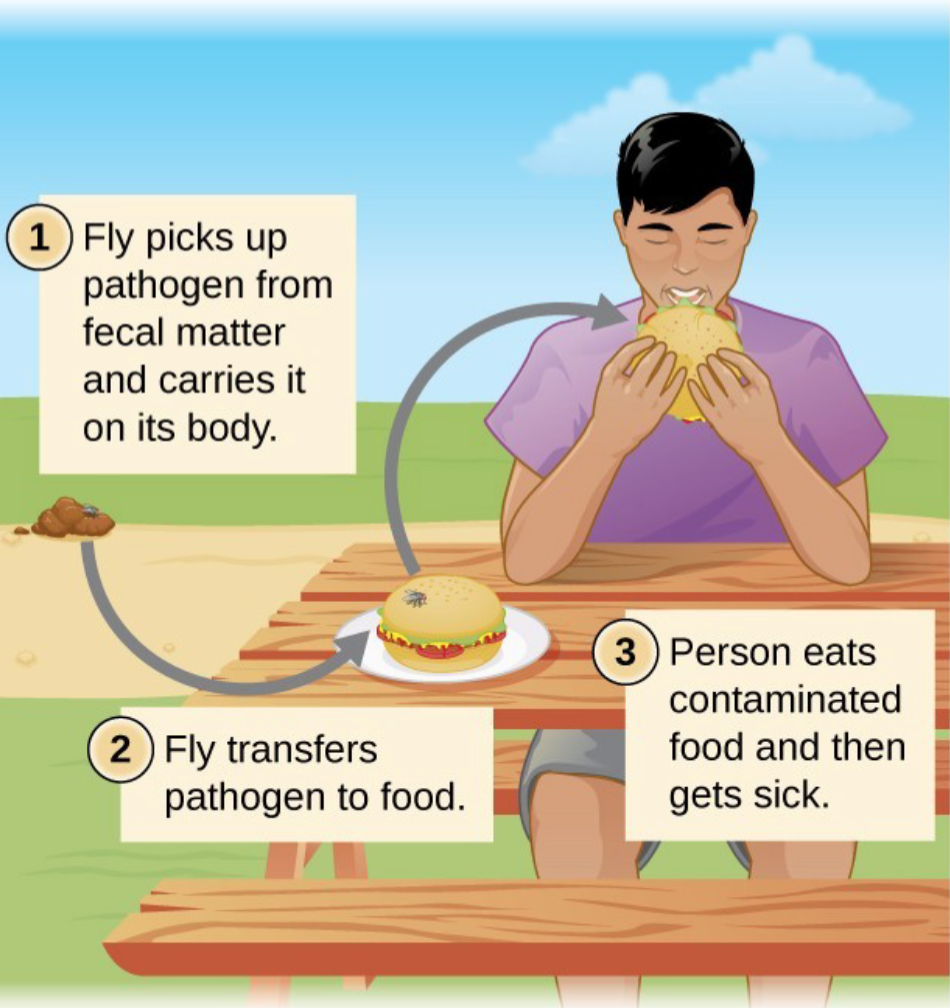
mechanical transmission
arthropod carries pathogen on its feet
46
New cards
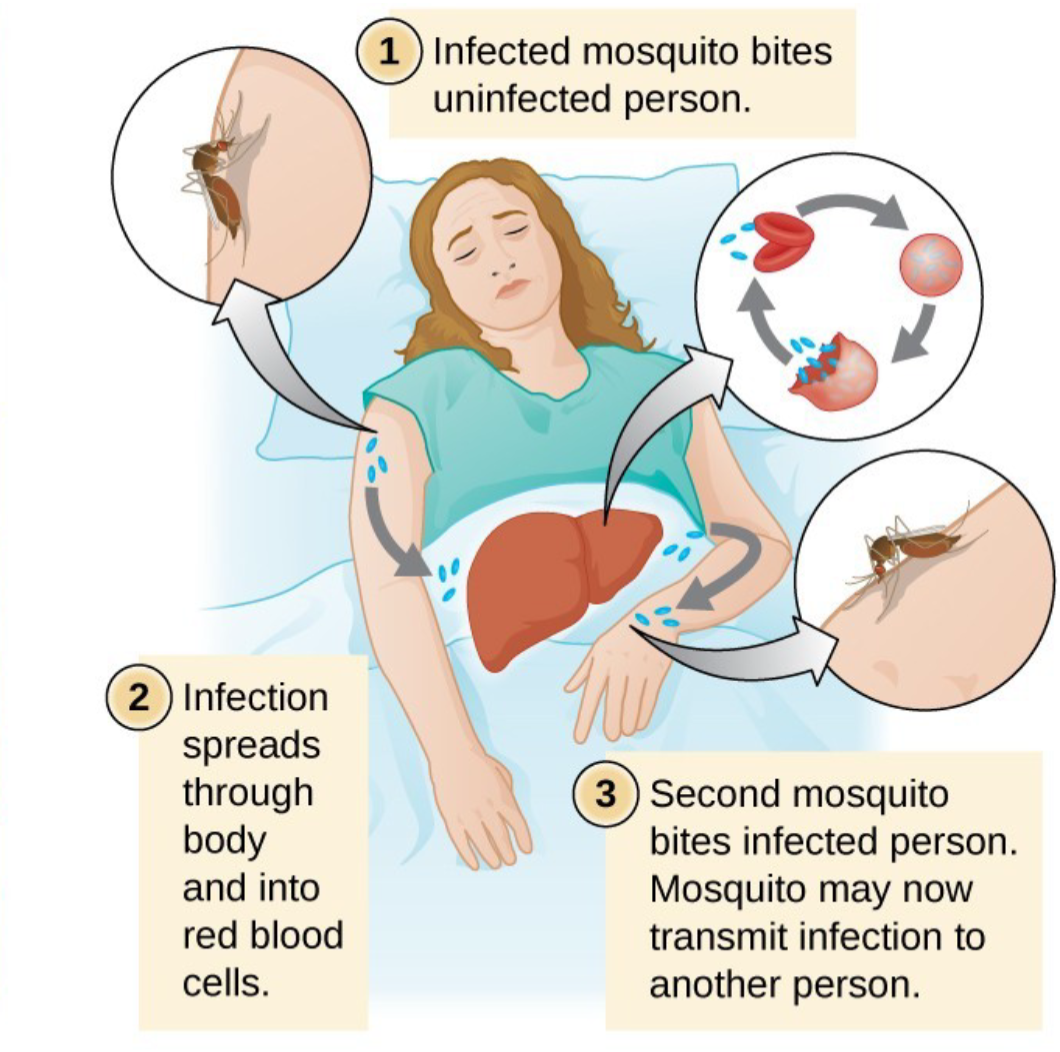
biological transmission
pathogen reproduces in the vector, transmitted via bites or feces
47
New cards
healthcare associated infections are…
and also known as…
and also known as…
acquired while receiving treatment in a health care in facility
nosocomial infections
nosocomial infections
48
New cards
what are two types of universal precautions
standard precautions
transmission-based precautions
transmission-based precautions
49
New cards
what are three types of transmission based precautions (give examples)
contact precautions (e.g. gloves and frequent sanitation)
droplet precautions (e.g. masks)
airborne precautions (e.g. ventilation)
droplet precautions (e.g. masks)
airborne precautions (e.g. ventilation)
50
New cards
epidemiology
study of where and when diseases occur and how they are transmitted in populations
51
New cards
notable infectious disease
physicians are required to report occurrence
52
New cards
morbidity rate (incidence)
\# people affected in relation to total population in given time
53
New cards
mortality rate
\# of deaths in relation to population in a given time
54
New cards
incidence= (math)
\# affected / total population
55
New cards
mortality= (math)
\# deaths / # affected