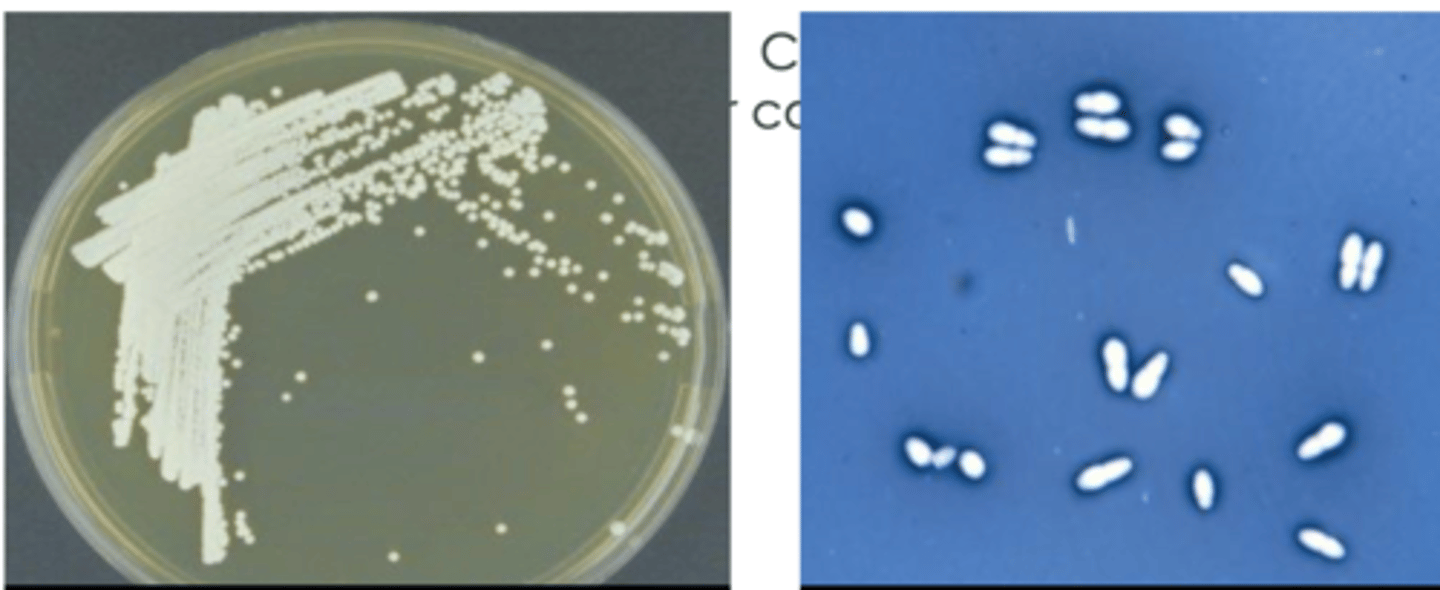
microbio- yeasts
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
true
true or false: yeasts are eukaryotic and unicellular
eukaryotic
are yeasts prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
blastoconidia
what type of conidia is produced asexually by yeasts?
false- yeasts do not have hyphae at all
true or false: yeasts have aseptate hyphae
Candida, Cryptococcus, Malassezia
what are the 3 important genuses of yeasts?
Candida albicans
what is the important species in the genus Candida?
Cryptococcus neoformans
what is the important species in the genus Cryptococcus?
Malassezia pachydermatis
what is the important species in the genus Malassezia?
chlamydo-, cornmeal
the genus Candida grows ______spores on _______agar
chlamydospores
what type of spores are produced by the genus Candida when isolated on cornmeal agar?
Candida
which yeast genus is related to immunosuppression in both humans and animals?
no
do we commonly find Candida in the environment?
Cryptococcus
which genus produces a large mucopolysaccharide capsule?
localized granulomas or disseminated disease (DIC)
Cryptococcus causes what issues in cats, dogs, horses, and cattle?
Cryptococcus
which genus is found in the environment and uses creatine from bird droppings?
canine seborrhoeic dermatitis and otitis externia
the genus Malassezia is associated with what diseases?
the skin
Malassezia affects what part of the animal?
Malassezia
which genus affects the skin of mammals and birds?
Malassezia
which genus is associated with canine seborrhoeic dermatitis and otitis externa?
37, SDA
Candida albicans grows aerobically at ______ degrees on _______
Candida albicans
which species are polymorphic- appear as pseudohyphae or hyphae in animal tissues?
mucous membranes of the oral cavity, GI tract, and urogenital tract
what part of the animal does Candida albicans commonly affect?
-immunodeficiency
-corticosteroid therapy
-prolonged administration of antibody
what factors predispose an animal to a Candida albicans infection?
hematogenous spread- hyphae/pseudohyphae invade the blood vessels and can cause systemic lesions
how does Candida albicans spread throughout the body?
adhesion to host cell proteins
what do the surface proteins of Candida albicans allow for?
Candida albicans
which species has surface structures than can bind proteins and complement components for protection?
tissue invasion
Candida albicans produce phospholipases (enzymes) to aid __________
phenotypic switching- it avoids the immune response
what is the advantage of Candida albicans' ability to transform into hyphae or psedohyphae?
Candida albicans
which species infects the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, GI tract, and urogenital tract?
Candida albicans
which species exhibits polymorphism, and changes to hyphae/pseudohyphae inside of animal tissues?
Candida albicans
this mycosis is caused by what species?
cotton swab
what is the appropriate sample for this?
it can be isolated, but not differentiated from other species/ to be able to differentiate yeast colonies, we need to use a selective indicator media
what is the problem with isolating yeasts on SDA?
blue/green
on a selective indicator media, Candida albicans appear what color?
Candida albicans
which species can produce these 3 forms?
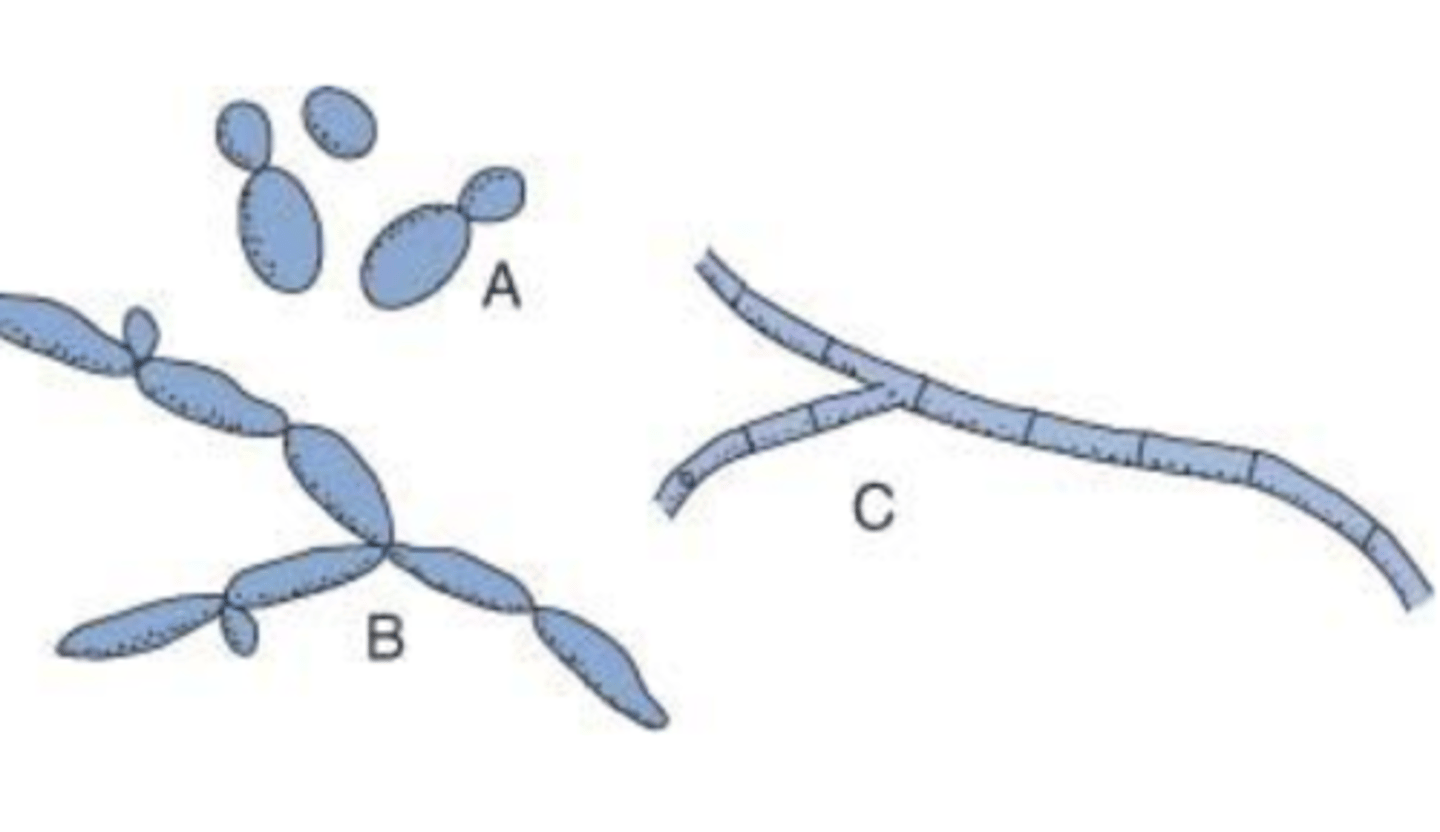
pseudohyphae with chlamydospores and blastoconidia
when isolated on cornmeal agar, Candida albicans produces what?
germ tubes
what is produced by Candida albicans when isolated in serum?
Candida albicans
which species produces germ tubes when isolated in serum?
Candida albicans
what species?
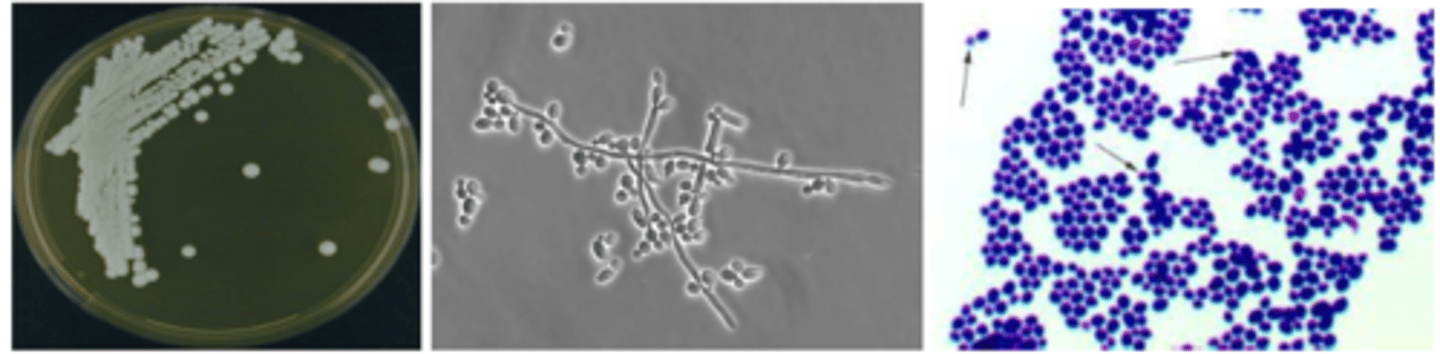
cornmeal agar (because there is pseudohyphae with chlamydospores and blastoconidia)
what medium was this Candida albicans isolated on?
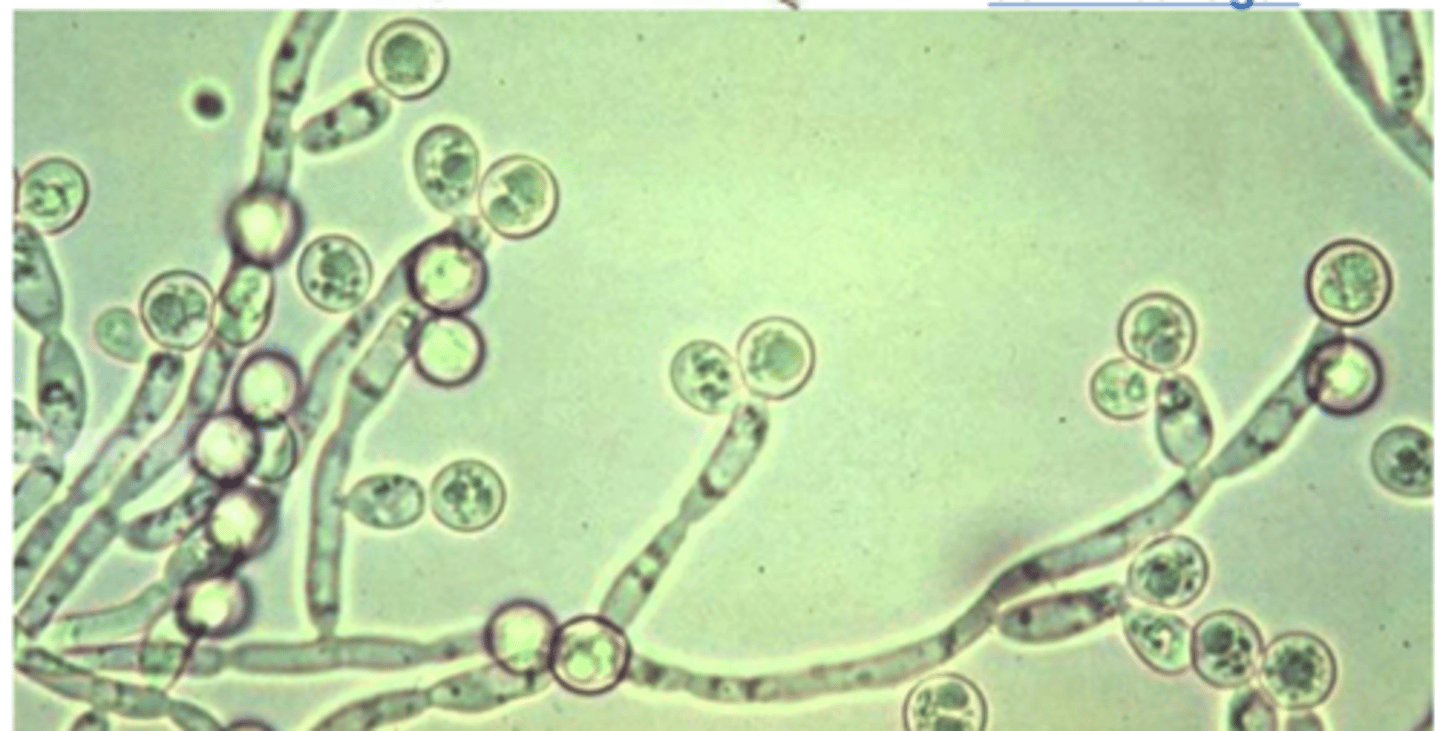
Candida albicans, serum at 37 degrees (produces germ tubes)
what species and what medium is used for isolation?
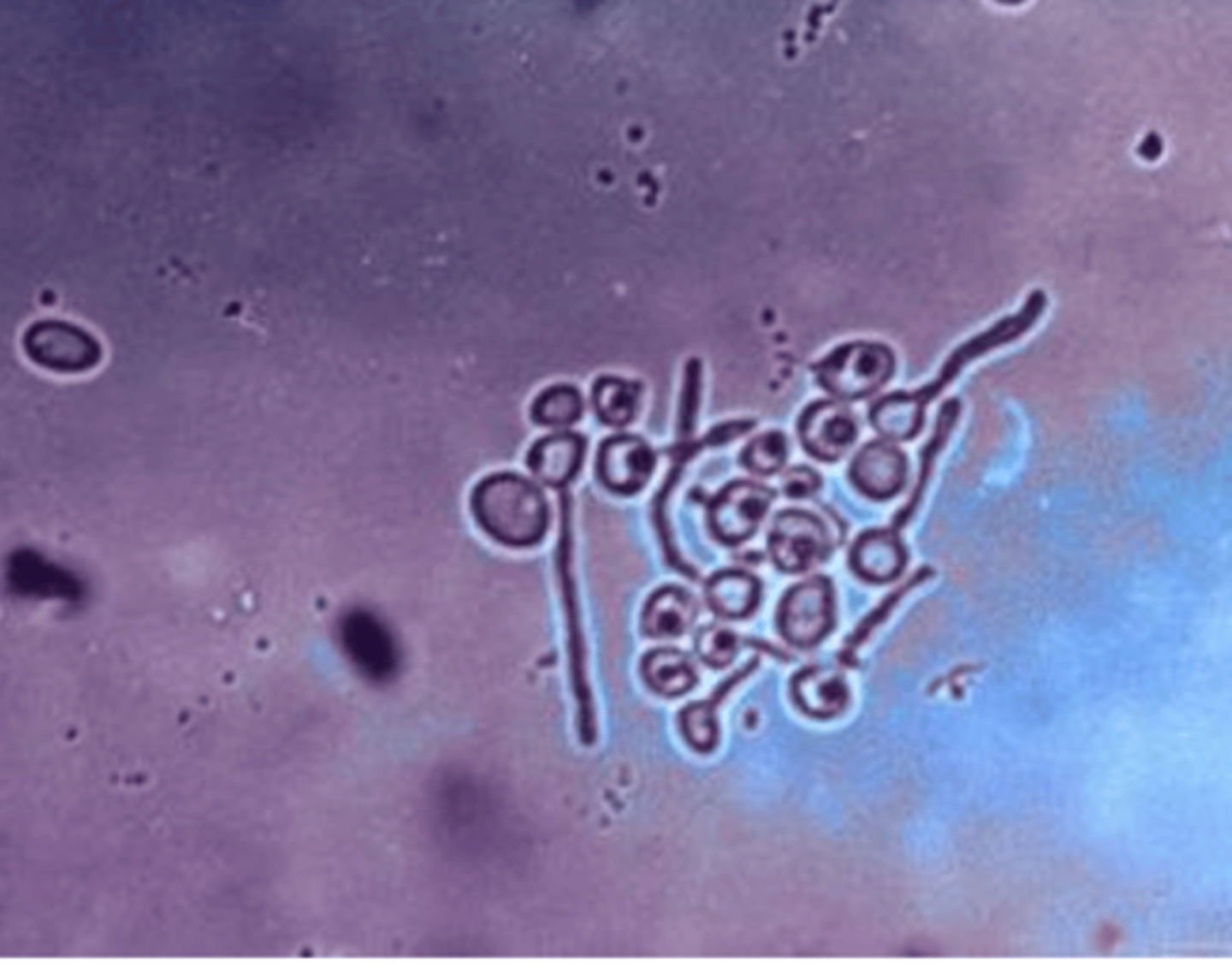
Cryptococcus neoformans
what species of Cryoptococcus do we study?
mucopolysaccharide capsule
Cryptococcus neoformans produces a thick ____________ around the yeast
Cryptococcus neoformans because there is a thick mucopolysaccharide capsule around the yeast
which species?
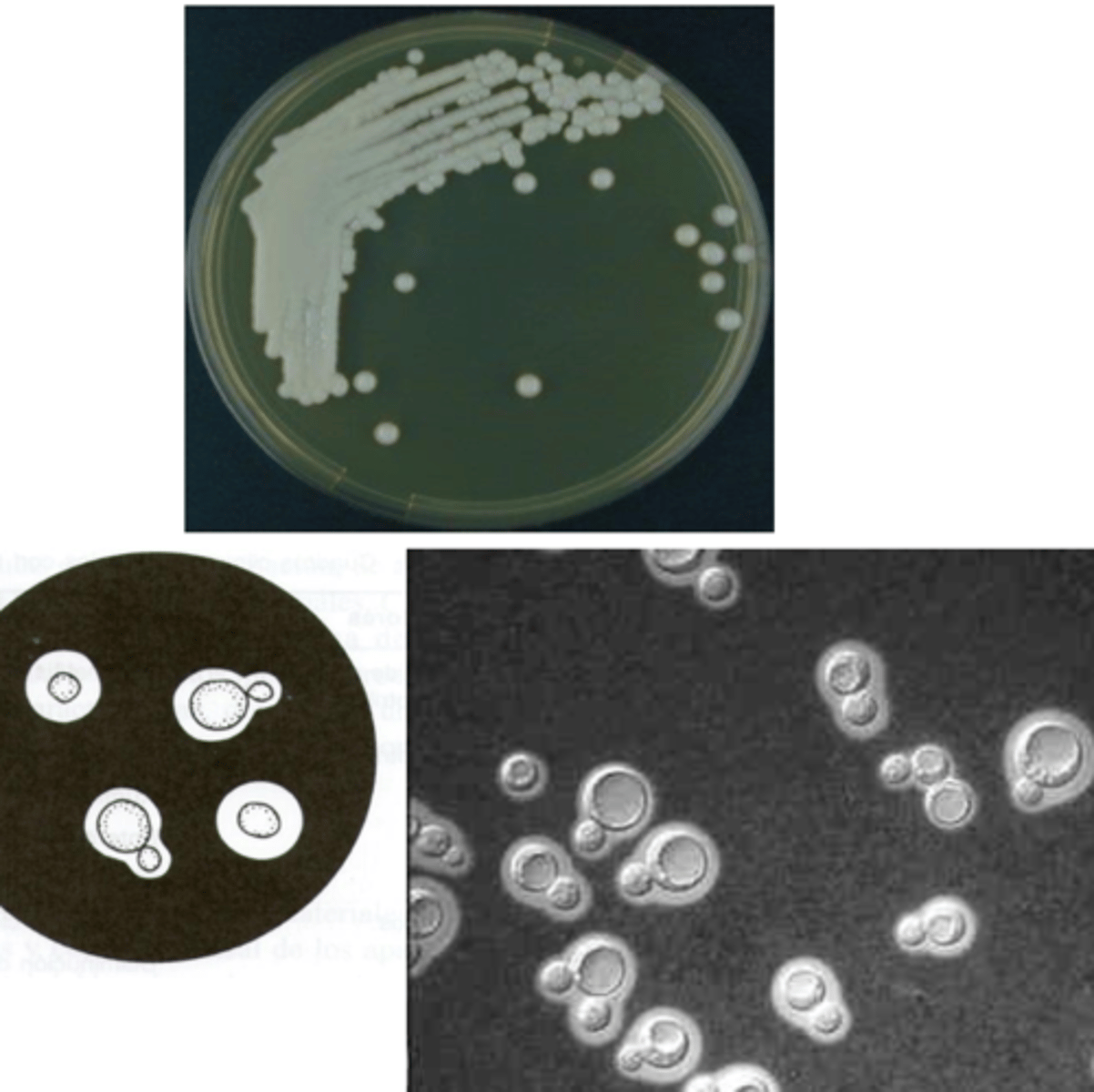
it is a part of the normal microbiota of the animal, but certain conditions can cause an overgrowth
how is an animal infected by Candida albicans?
Candida albicans and Malassezia pachydermatis
which species is normally existing in the animal, but can cause an infection if certain conditions cause an overgrowth?
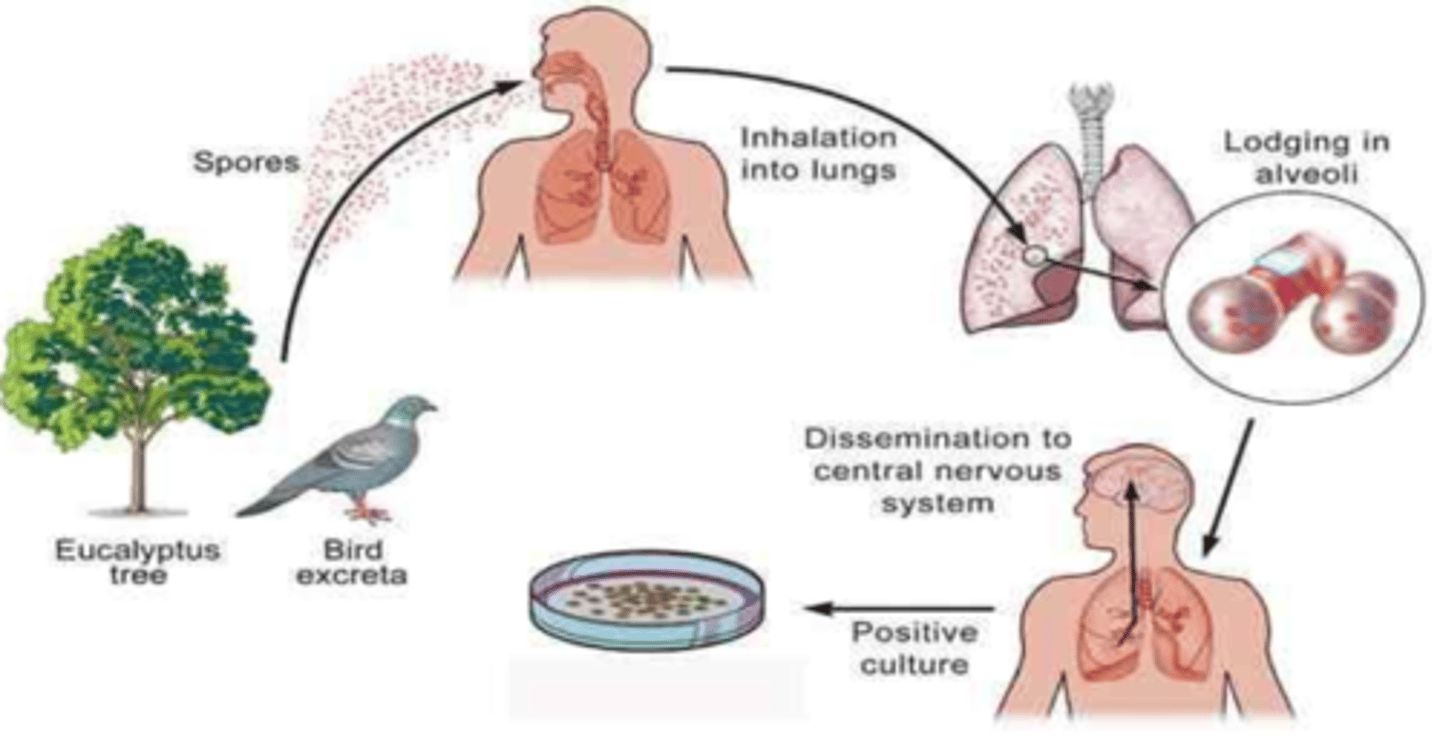
spore (blastoconidia) inhalation
how is an animal infected by Cryptococcus neoformans?
Cryptococcus neoformans
which species can germinate throughout the entire respiratory tract?
Cryptococcus neoformans
which species lives in the environment in bird droppings?
in the environment in bird droppings
where does Cryptococcus neoformans usually live?
they are normal microbiota in the mucous membranes of animals
where does Candida albicans normally live?
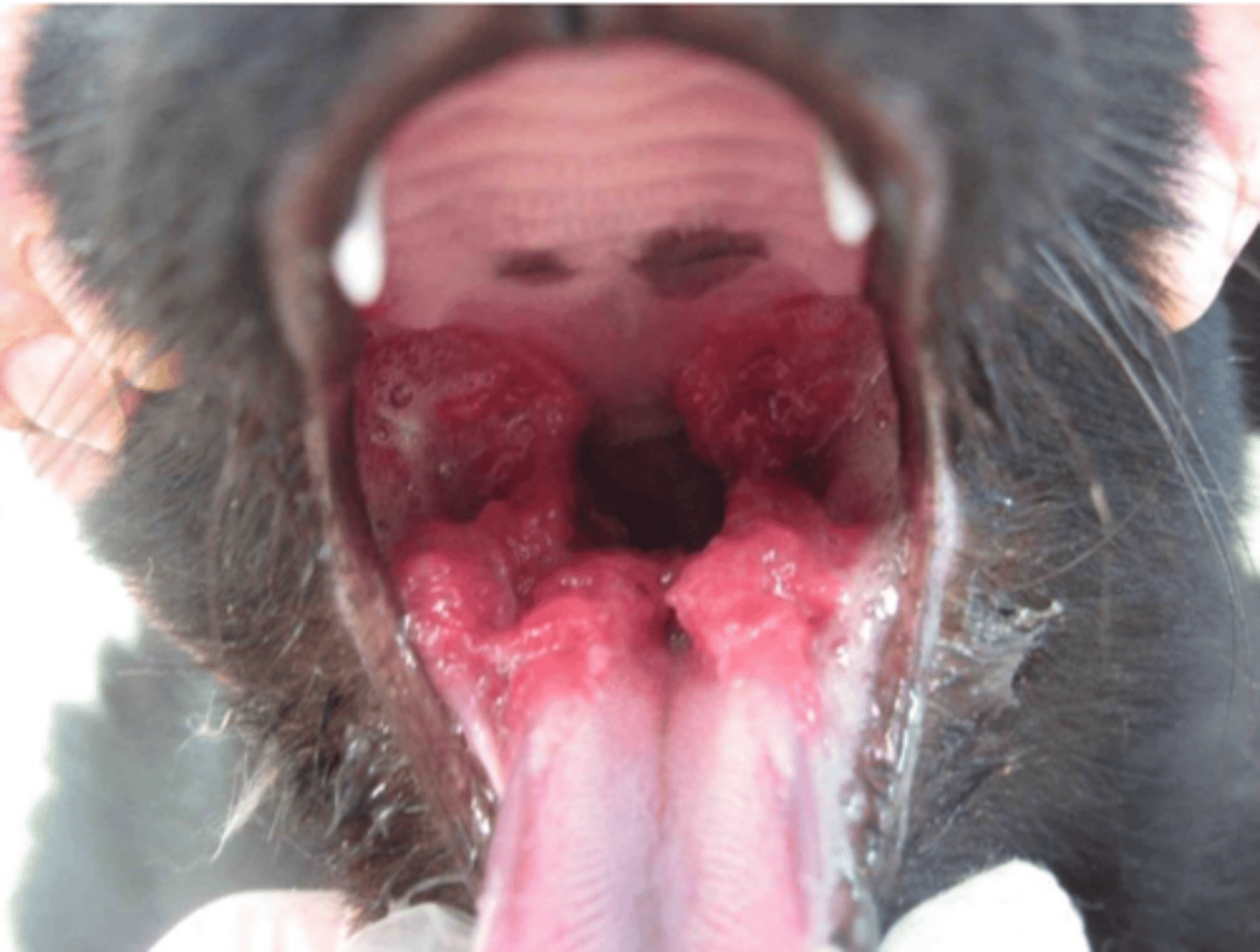
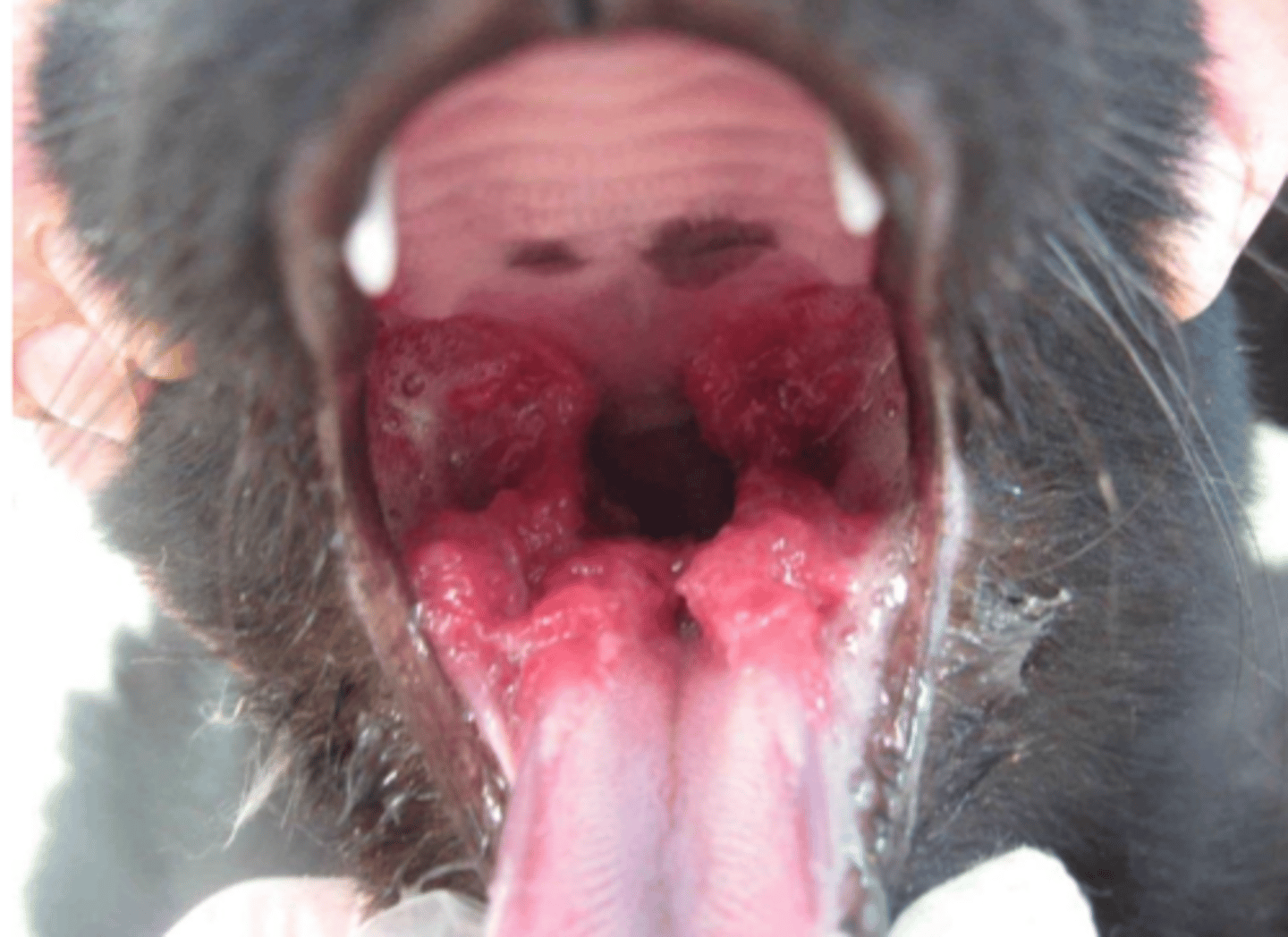
granulomas- tumor-like myxomatous masses
what lesions does Cryptococcus neoformans cause?
the brain, meninges, and bone
a Cryptococcus neoformans infection can spread from the respiratory tract to ____________
it resists phagocytosis
what is the function of the mucoid capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans?
Body temperature
at what temperature do Cryptococcus neoformans grow?
Cryptococcus neoformans
which species produces phenoloxidase, which allows melanin accumulation in the cell wall, providing protection from the fungus against free radicals?
it produces phenoloxidase, which allows melanin accumulation in the cell wall
how is Cryptococcus neoformans protected from free radicals?
Cryptococcus neoformans
this represents the route of which yeast?
no
do Cryptococcus neoformans commonly infect domestic animals?
nose swab
infection by Cryptococcus neoformans. what sample would we appropriate?
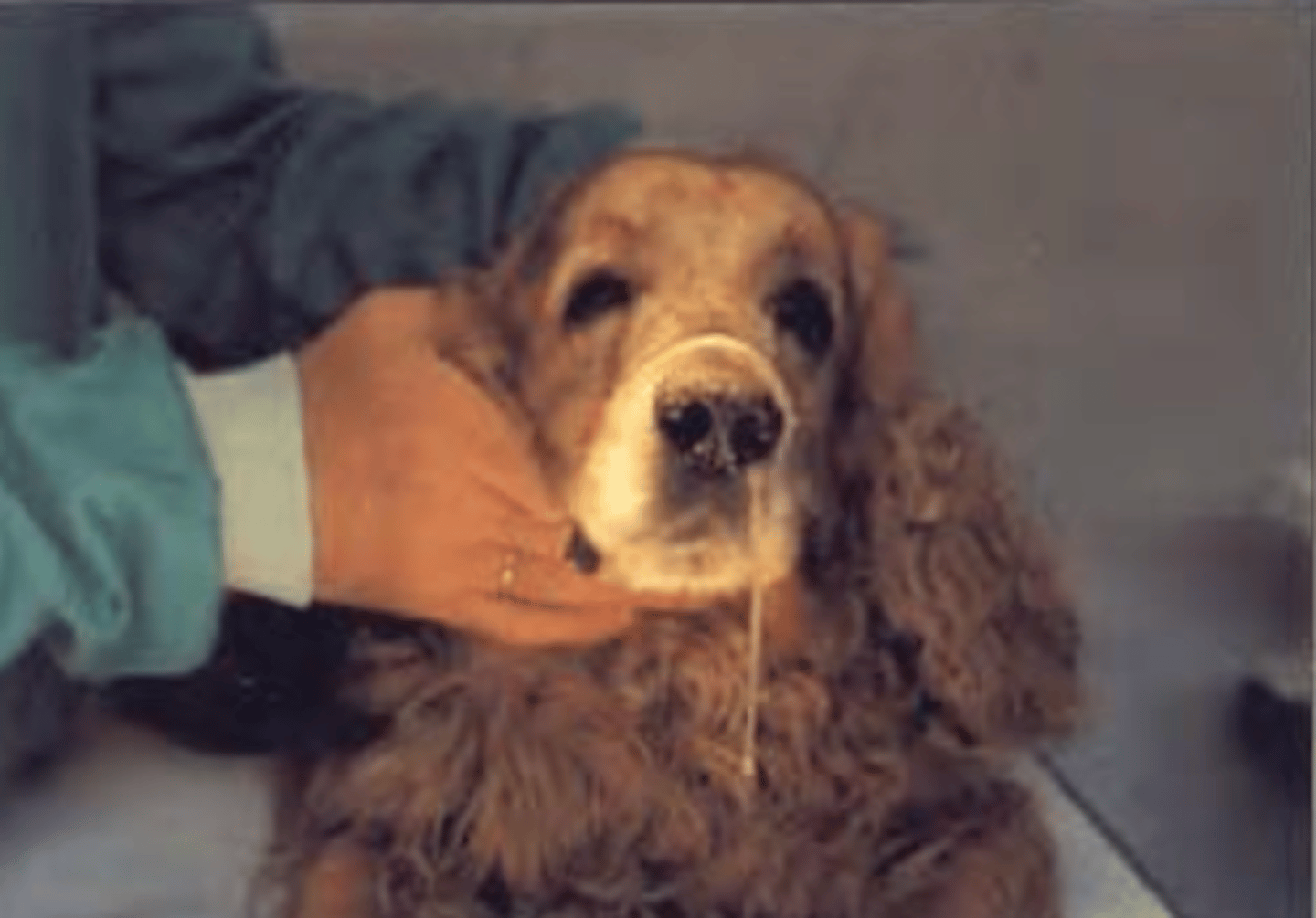

-exudates (fluids that leak from blood vessels)
-cerebrospinal fluid (if there are neurological signs)
-biopsy
-post mortem tissues
what are suitable specimens to collect from an animal infected by Cryptococcus neoformans?
yes, very easily- so it is necessary to isolate using a safety cabinet
can humans be infected by Cryptococcus neoformans?
Cryptococcus neoformans
what species is this, isolated on bird seed agar?
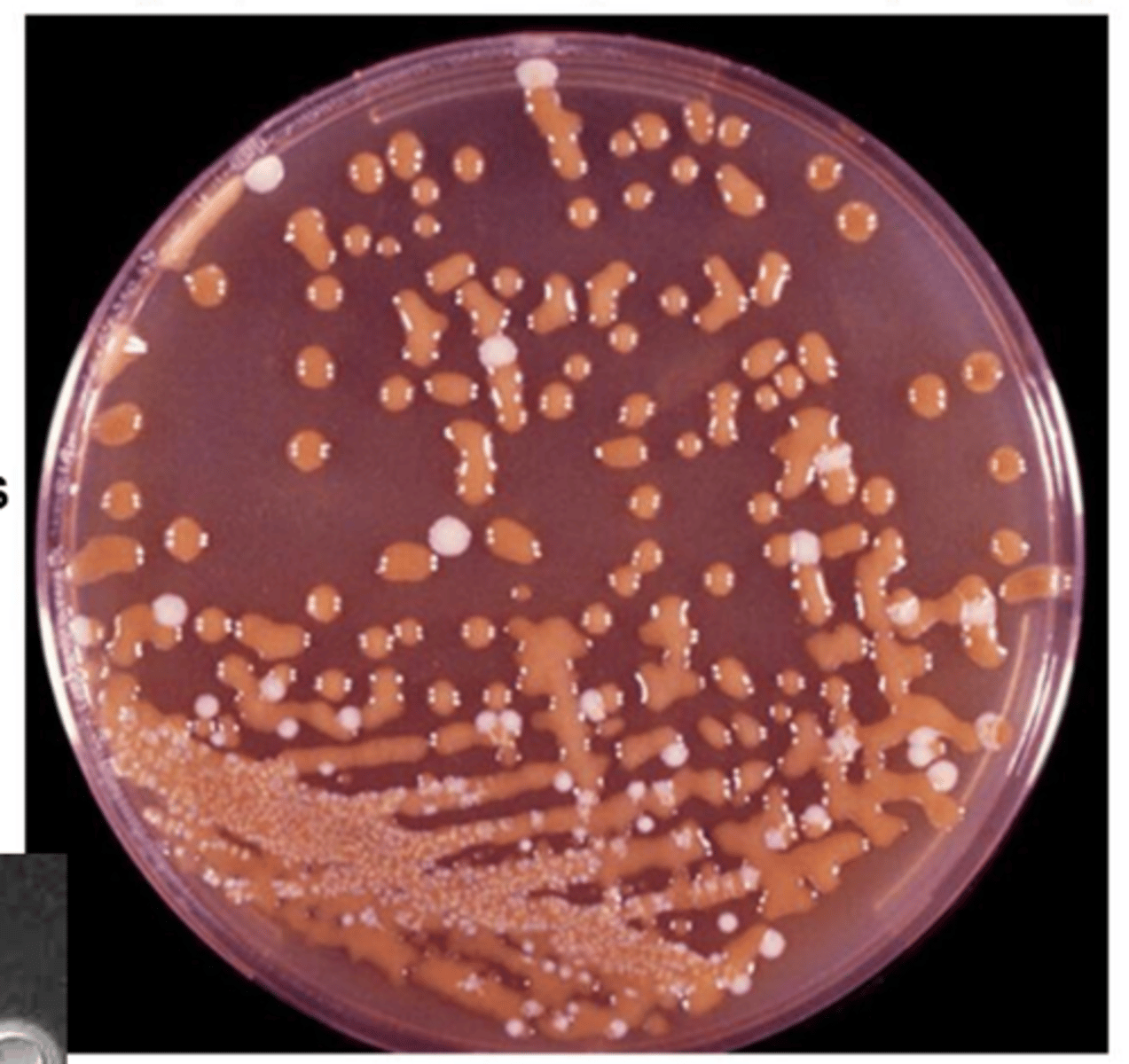
bird seed
Cryptococcus neoformans produces brown/orange colonies on __________ agar
Malassezia pachydermatis
what is the important yeast species in the genus Malassezia?
monopolar budding
Malassezia pachydermatis reproduce by......
Malassezia pachydermatis
which species reproduces by monopolar budding?
Malassezia pachydermatis and Candida albicans
which species are part of the normal microbiota of the animal, so cause infection only when external factors trigger an overgrowth?
it is a normal microbiota, so needs external factors to cause an overgrowth. this overgrowth is usually associated with immunosuppression and other predisposing factors that alter the microclimate of the skin or ear canal
how does Malassezia pachydermatis cause an infection in the animal?
Malassezia pachydermatis
which species commonly infects the skin and/or ear canal of the animal?
skin of mammals and birds- areas rich in sebacious glands (anal region, external ear canal, lips, interdigital skin)
the normal habitat of Malassezia pachydermatis is.........
Malassezia pachydermatis
which species lives in the areas of the animal that are high in sebacious glands?
Malassezia pachydermatis
which species?
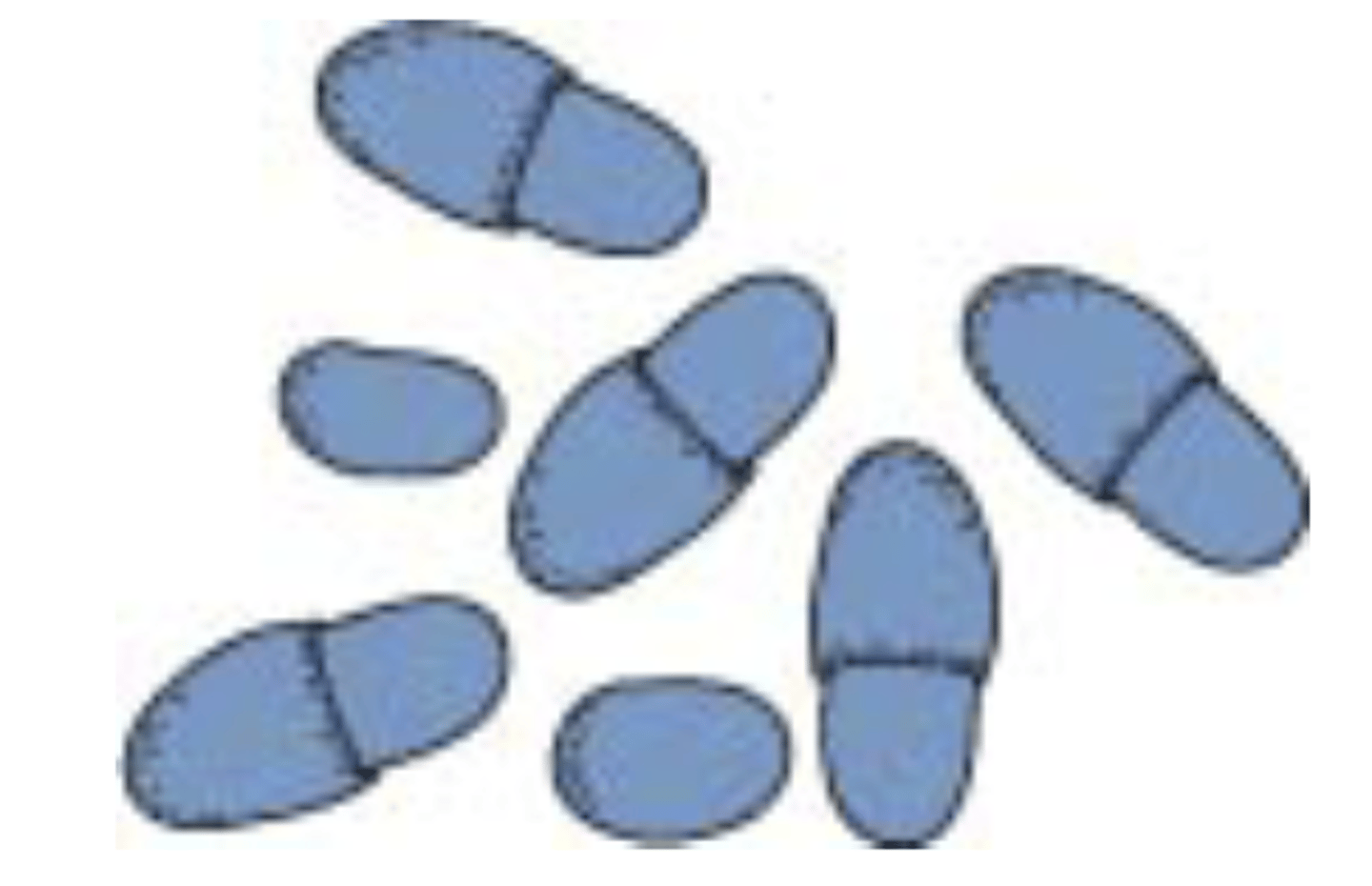
Malassezia pachydermatis
otitis externa and dermatitis are the common clinical conditions of what yeast species?
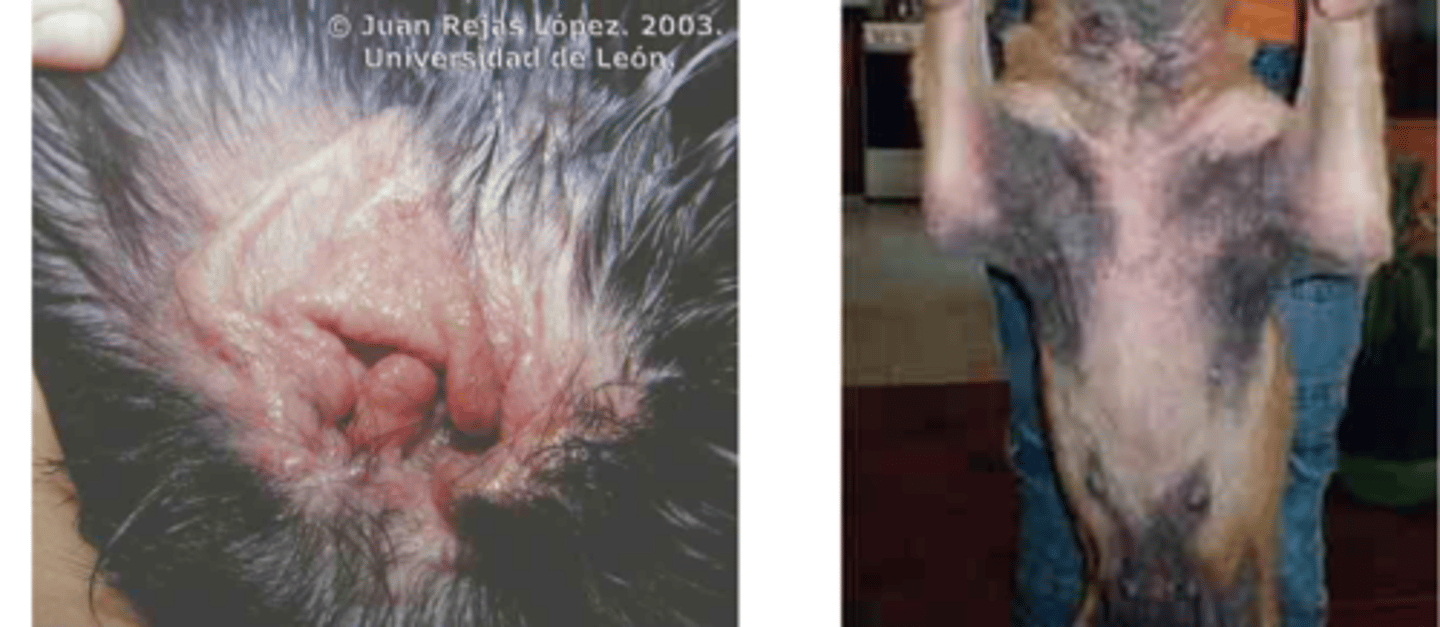
wax overproduction and enzymes that damage the mucosa- because they cause inflammatory changes, inflammatory exudate, and necrotic debris accumulation in the ear canal
otitis externa is caused by Malassezia pachydermatis when these conditions are present:
Malassezia pachydermatis
these clinical signs are common of what yeast infection?
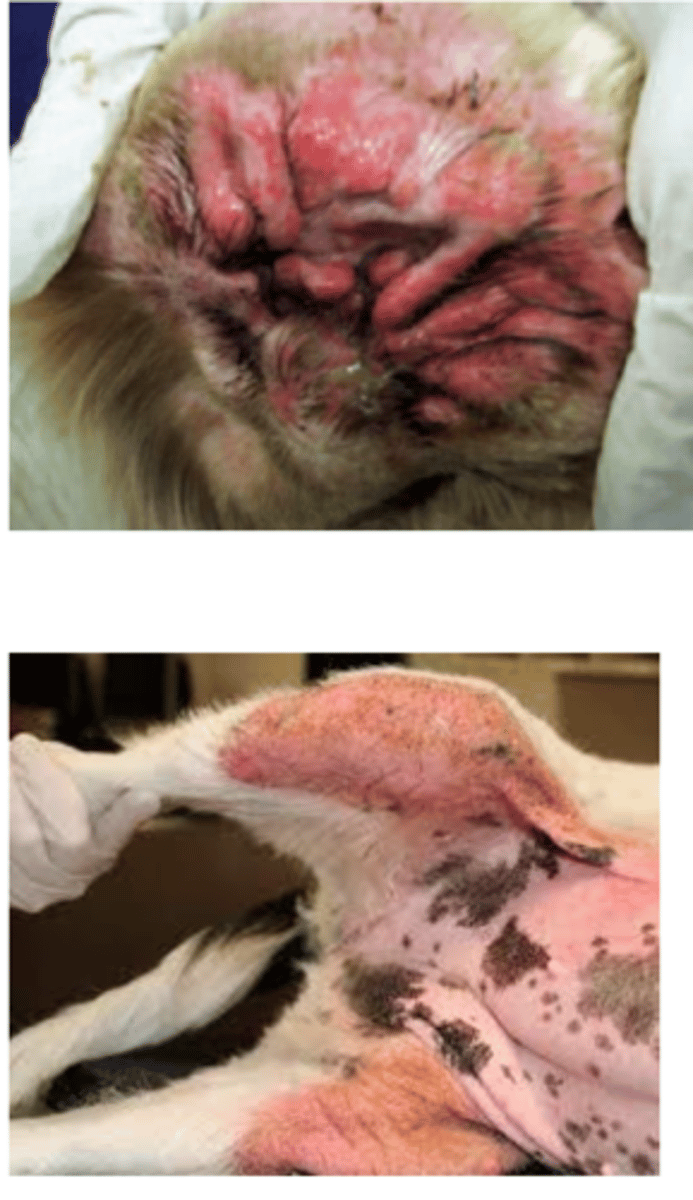
it is the excessive sebacious secretion caused by the lipases produced by yeast cells. typical of Malassezia pachydermatis
what is seborrheic dermatitis? what yeast species typically causes this?
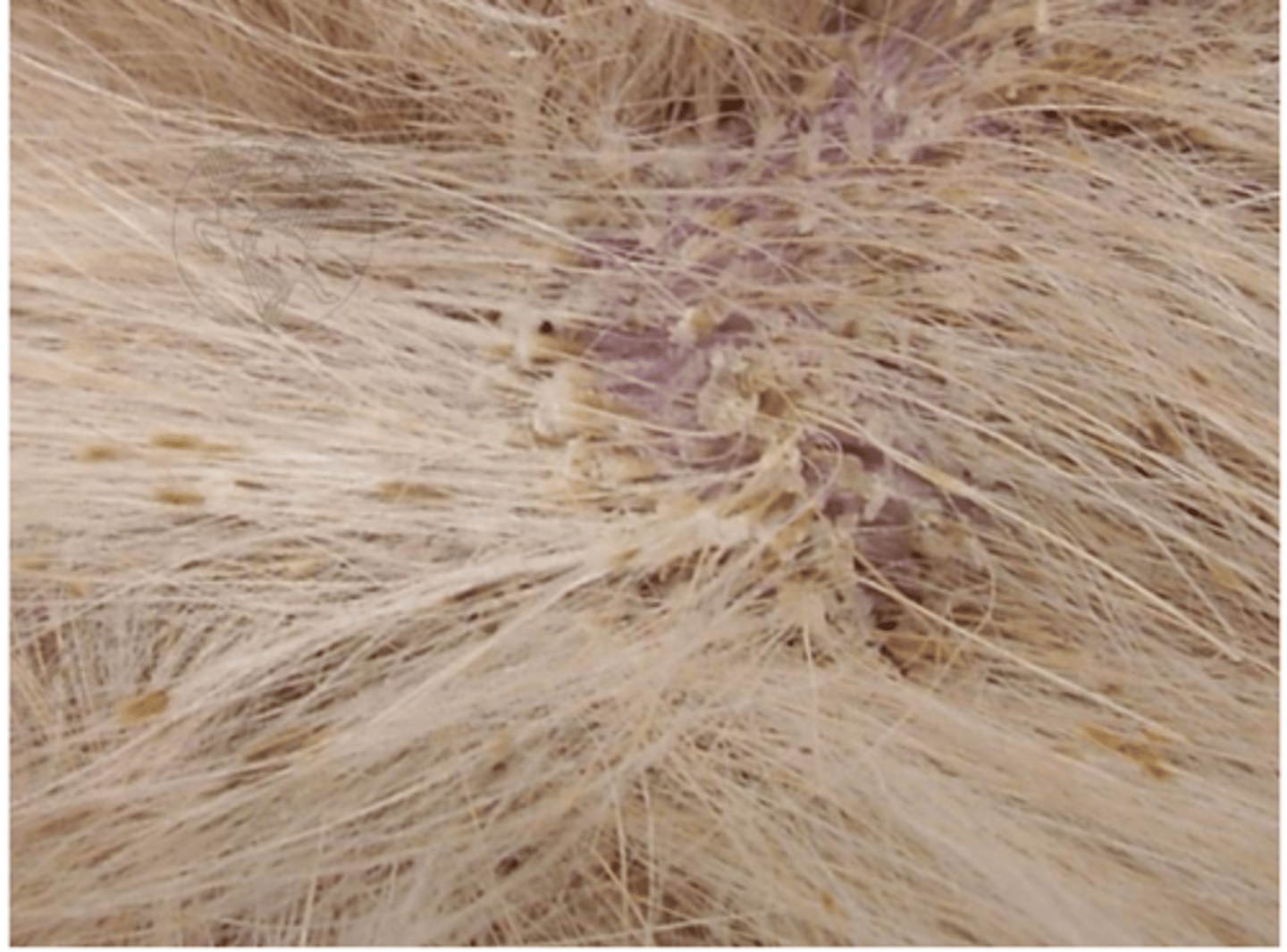
canine seborrheic dermatitis, caused by Malassezia pachydermatis, use a skin scraping sample
what is this condition called? what yeast species causes it? what sample would we take?
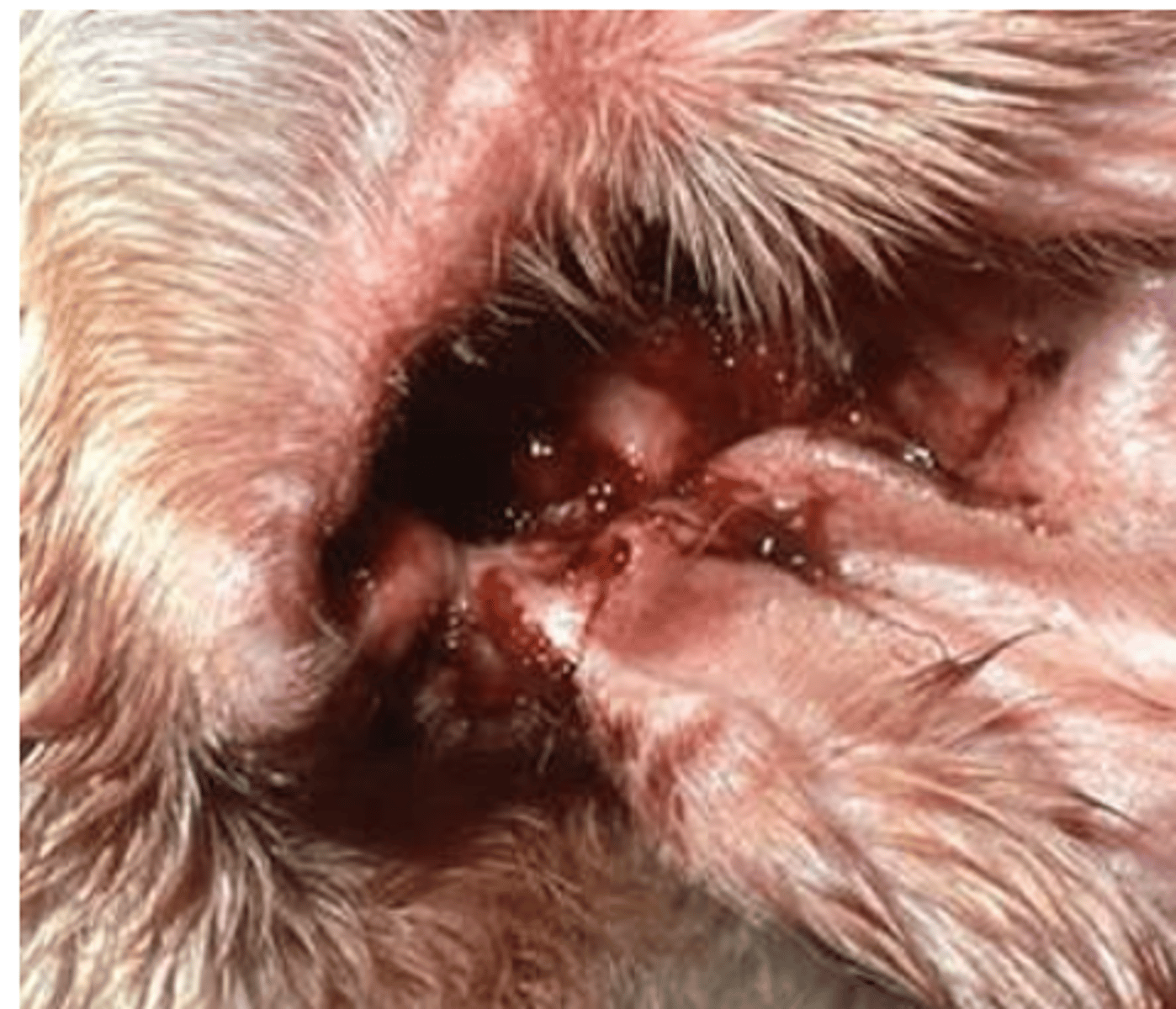
canine otitis externa, caused byMalassezia pachydermatis, use an ear canal swab
what is this condition called? what yeast species causes it? what sample would we take?
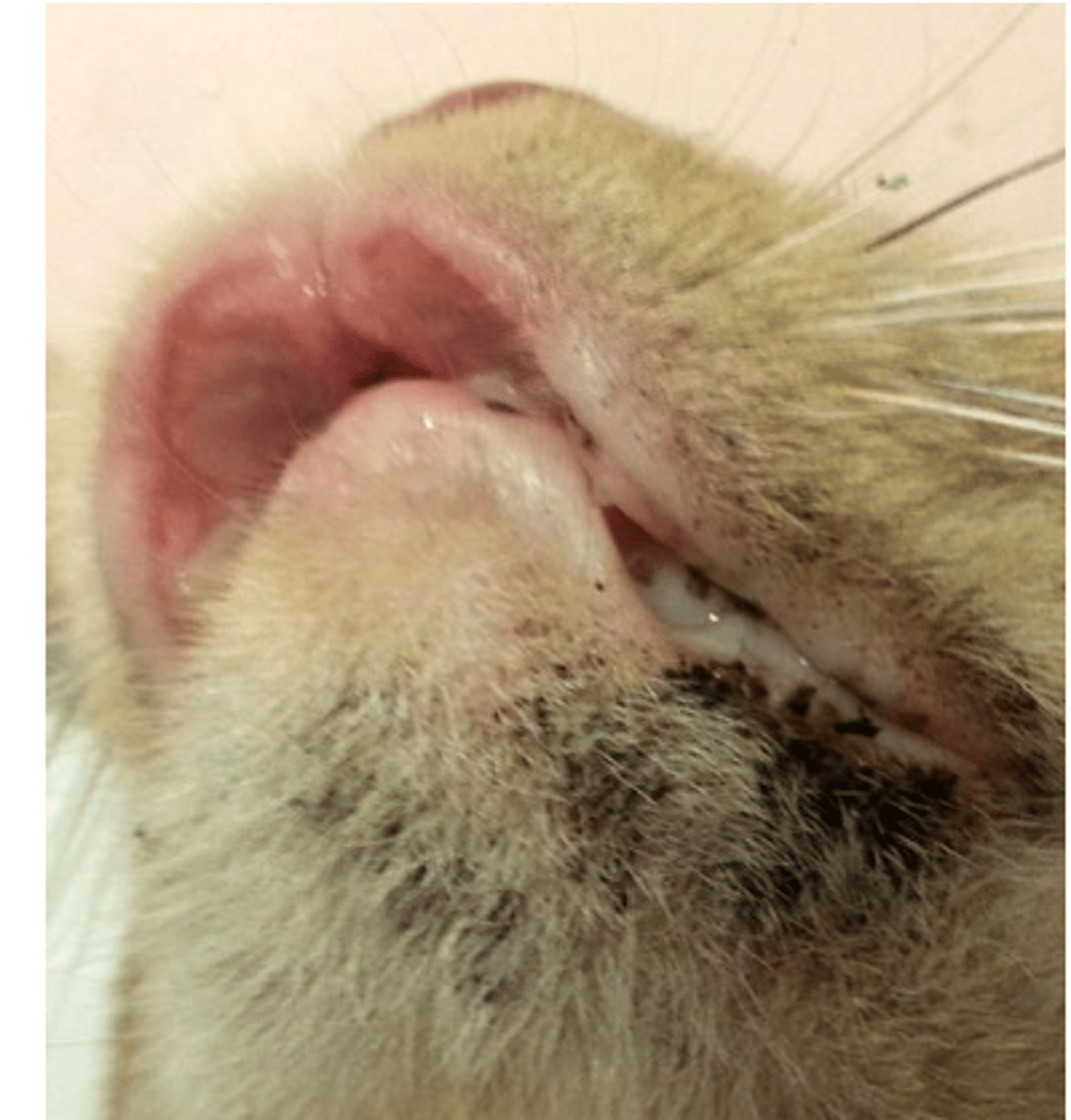
Malassezia pachydermatis, skin scraping or adhesive tape sample
feline chin acne is a common clinical sign of what yeast infection? what sample would we take?
-exudate from ear canals and impression smears
-rigorous skin swabbing
-superficial skin scraping
-biopsy (for severe subcutaneous dematitis)
what specimens are appropriate for the diagnosis of an Malassezia pachydermatis infection?
Malassezia pachydermatis
what species caused this infection?
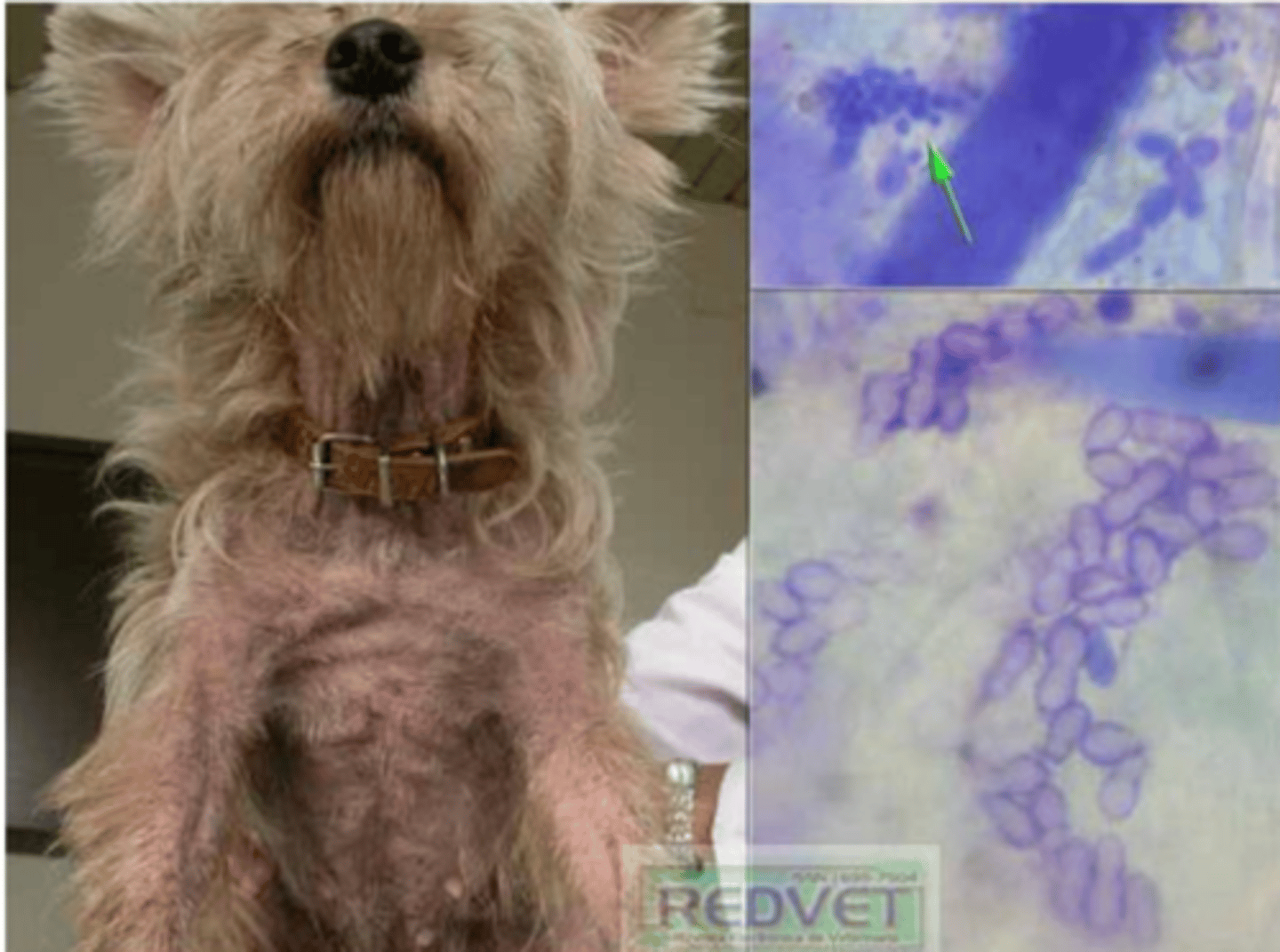
Malassezia pachydermatis
what species?