Physics I Lesson 12: Redox Reactions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
CRB To help keep Oxidation and Reduction straight, students often remember one of two acronyms. What does each of the following stand for?
- OIL RIG
- LEO [the lion says] GER
- Oxidation Is Loss [of electrons] Reduction Is Gain [of electrons
- Lose Electrons [=] Oxidation Gain Electrons [=] Reduction
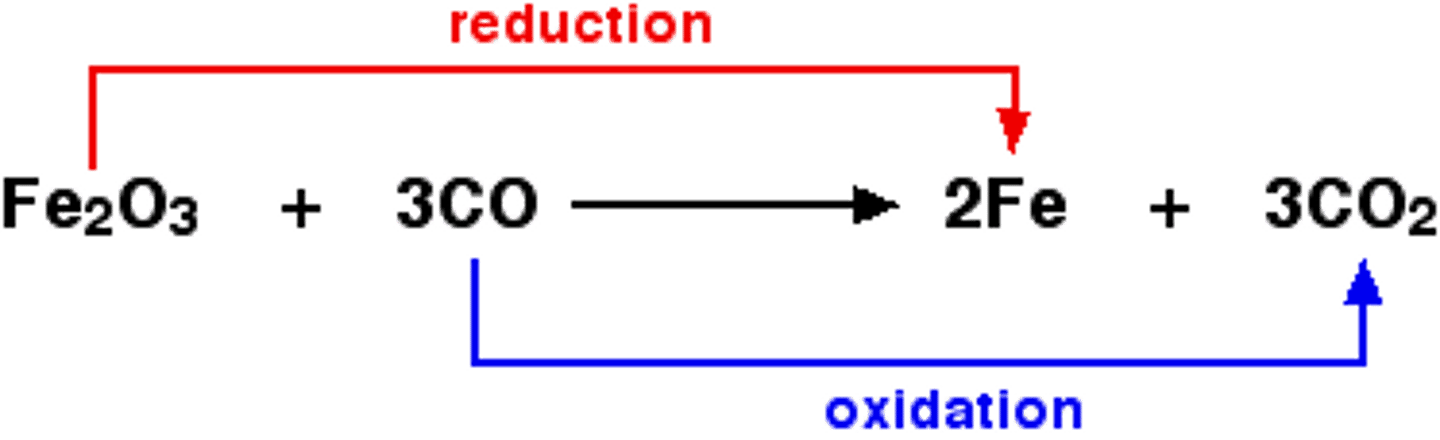
What is oxidized and what is reduced in the following chemical reaction?
Fe2O3 + 3CO -> 2Fe(s) + 3CO2
Fe is reduced as it gains electrons.
C is oxidized as it loses electrons, going from a +2 to a +4 oxidation state.
CRB Sort each of the following compounds as either Oxidizing or Reducing Agents:
-Nitric Acid (HNO3)
- KMnO4
- Hydrazine (N2H4)
- Zn(Hg)
- LiAlH4
- FADH2
-NAD+
- NaBH4
Oxidizing Agents:
-Nitric Acid (HNO3)
- KMnO4
- NAD+
Reducing Agents:
- Hydrazine (N2H4)
- Zn(Hg) [Often used with HCl]
- LiAlH4
- FADH2
- NaBH4
CRB True or false? Biochemical redox reagents, like NAD+ and FAD++, can act as oxidizing and reducing agents at different stages of biochemical pathways, making them useful carriers.
True. Biochemical redox reagents, like NAD+ and FAD++, can act as oxidizing and reducing agents at different stages of biochemical pathways, making them useful carriers.
What is the oxidizing agent and what is the reducing agent in the following reaction?
Cu2+ + Zn(s) -> Cu(s) + Zn2+
Cu2+ is the oxidizing agent because it oxidizes Zn(s), taking away its electrons.
Zn(s) is the reducing agent because it reduces Cu2+ by giving it electrons.
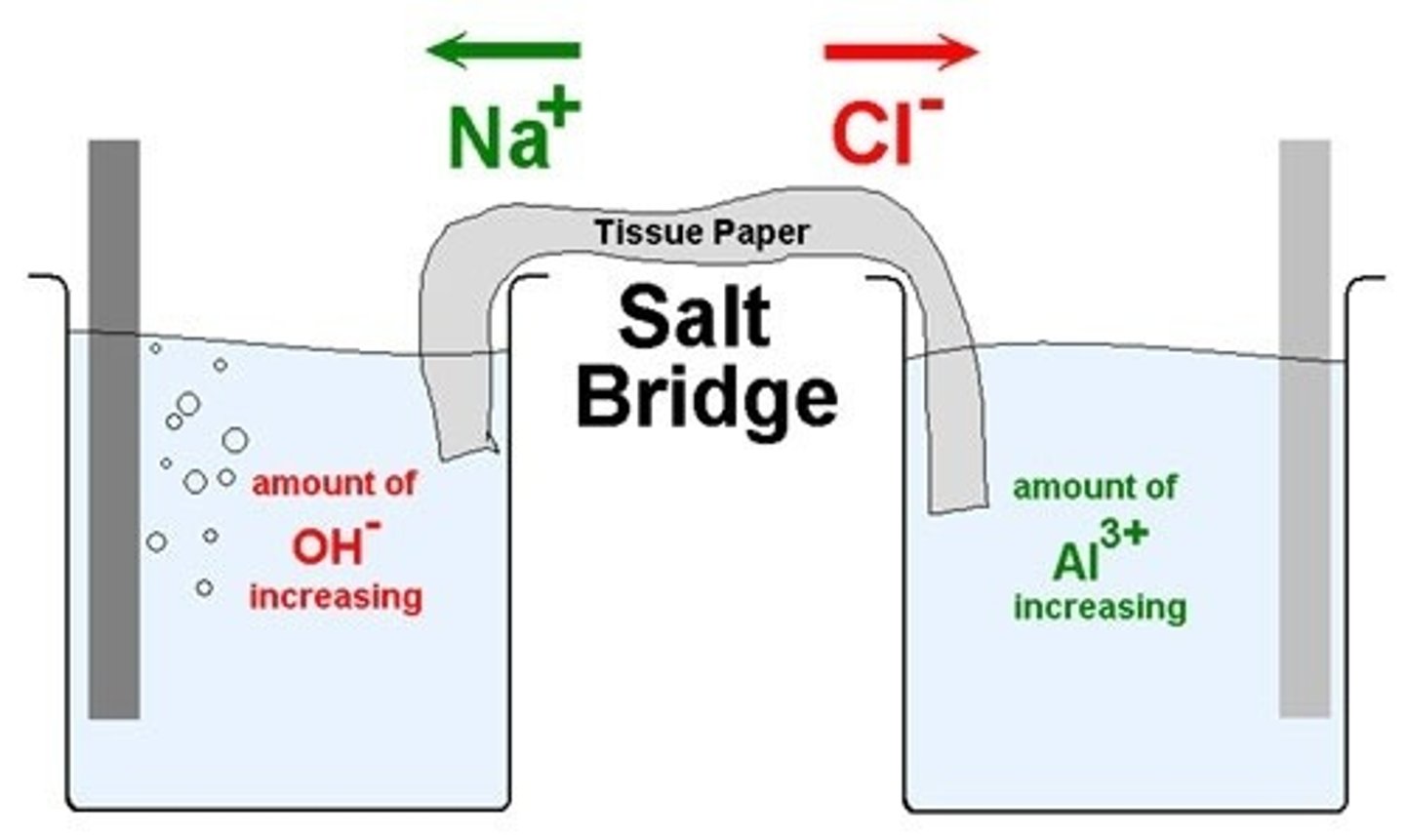
What is the purpose of a salt bridge?
The purpose of a salt bridge is to neutralize the charges in the solutions that are either becoming positive or negative as the reaction proceeds. This allows the reaction to continue moving forward.
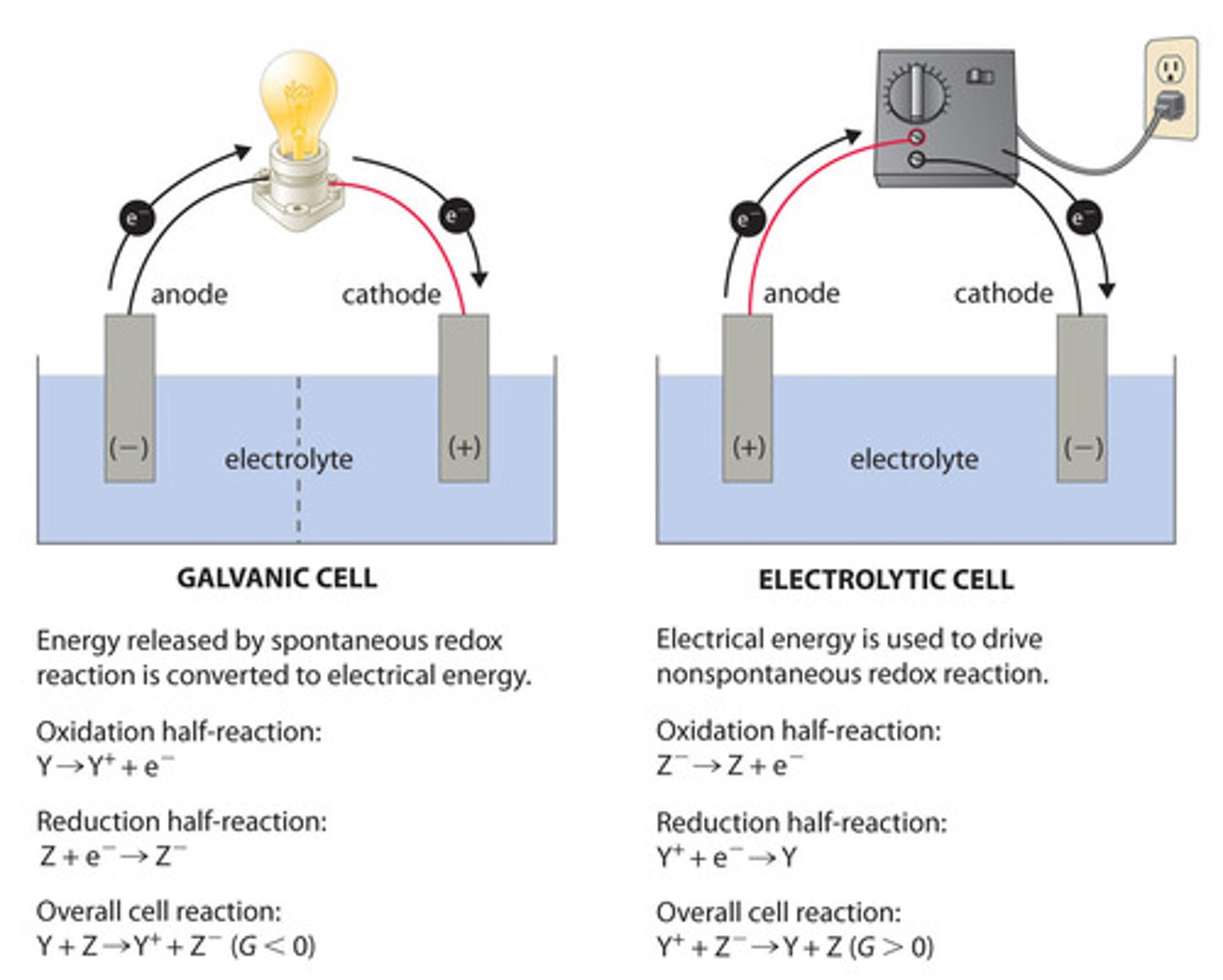
Oxidation occurs at the _________. Reduction occurs at the ___________.
(A) anode, anode
(B) anode, cathode
(C) cathode, cathode
(D) cathode, anode
(B) anode, cathode
Oxidation occurs at the anode. Reduction occurs at the cathode.
CRB Which of the following is NOT one of the three main types of Electrochemical Cells?
(A) Concentration Cell
(B) Galvanic Cell
(C) Magnetic Cell
(D) Electrolytic Cell
(C) Magnetic Cell
The three main types of Electrochemical Cells are Concentration, Galvanic/Voltaic, and Electrolytic Cells.
CRB Which of the following statements about all Electrochemical Cells are true?
I. The movement of electrons is from anode to cathode.
II. The current runs from cathode to anode.
III. Temperature can influence the reactions in these cells.
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following statements about Electrochemical Cells are true:
I. The movement of electrons is from anode to cathode.
II. The current runs from cathode to anode.
III. Temperature can influence the reactions in these cells.
The anode is ___________ charged in a Galvanic Cell. The anode is ___________ charged in an Electrolytic cell.
(A) positively, positively
(B) positively, negatively
(C) negatively, negatively
(D) negatively, positively
(D) negatively, positively
The anode is negatively charged in a Galvanic Cell. The anode is positively charged in an Electrolytic cell.
Zn2+ has a Standard Reduction Potential (E°red) of -.76 V. What does that mean?
To say that Zn2+ has a Ered of -.76 V is to say that the reduction of Zn2+ has a voltage difference that is .76 V below the reference value, which is the reduction of H+.
CRB For a Redox Reaction to be spontaneous, which of the following must its voltage be?
(A) Positive
(B) Zero
(C) Non-Zero [positive or negative]
(D) Negative
(A) Positive
For a Redox Reaction to be spontaneous, the voltage must be positive.
CRB True or false? The Standard Hydrogen Electrode causes the reaction H2 +O2 ---> H2O, and is given the Reduction potential of 0 V.
True. The Standard Hydrogen Electrode causes the reaction H2 +O2 ---> H2O, and is given the Reduction potential of 0 V.
Cu2+ has a E°red of +.34 V, much higher than Li+ (E°red = -3.05). What is the significance of one ion having a much greater Standard Reduction Potential?
If an ion has a higher E°red, it means that that ion is much more likely to be reduced. The E°red is like the desire of an ion to be reduced. The higher E°red, the greater the desire/likelihood of that ion getting reduced.
What equation can be used to determine the Standard Cell Potential for a Galvanic Cell?
E°cell = E°red (cathode) - E°red (anode)
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/

Cu2+ (Ered = .34) and Cd metal (Ered = -.40) are used to create a Galvanic Cell. What is the Standard Cell Potential (Ecell) in this case?
(A) -.74
(B) -.06
(C) .06
(D) .74
(D) .74
E°cell = .34 - (-0.40)
E°cell = .74
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
Consider the following Galvanic Cell: https://fthmb.tqn.com/YUma5BLsDaaZLT7X3iw5SureRVY=/735x0/battery-56a128375f9b58b7d0bc8c92.gif
Write out the shorthand notation for this galvanic cell.
Zn(s) | Zn2+ || Cu2+ | Cu
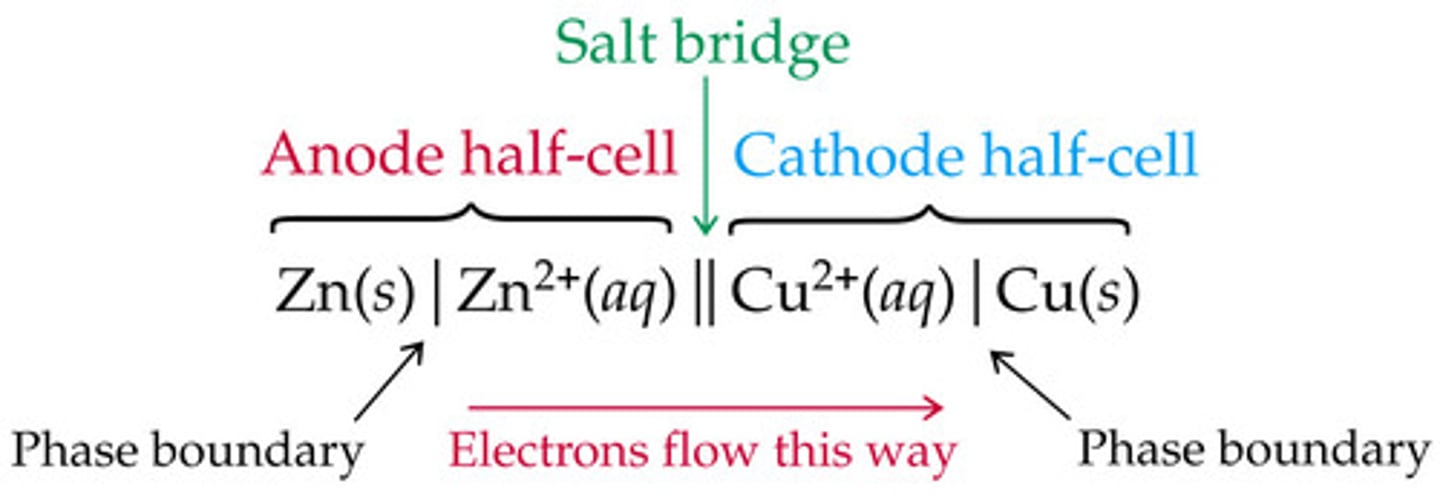
CRB The Galvanic cell in the previous card is the classical Daniell Cell. Which of the following descriptions about the Daniell cell are true?
I. Each electrode is in an electrolyte solution with the cation form of the same element the electrode is made of.
II. To balance the charges of the electrolyte solution, Sulfate ions are also dissolved.
III. Because the Electrolyte solution has a balanced charge at the beginning, there is no need for a Salt Bridge.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
Each of the following statements about the Daniell Cell are true:
I. Each electrode is in an electrolyte solution with the cation form of the same element the electrode is made of.
II. To balance the charges of the electrolyte solution, Sulfate ions are also dissolved.
CRB True or false? The deposition of the metal from the electrolyte solution onto the cathode is called Galvanization, explaining the alternate name for these cells.
True. The deposition of the metal from the electrolyte solution onto the cathode is called Galvanization, explaining the alternate name for these cells.
What equation allows you to calculate the Gibb's Free Energy for a Galvanic Cell based on the Cell Potential (Ecell)?
∆G = -nFEcell
∆G = Gibb's Free Energy
n = Number of Electrons
F = 96,500 C/mol
Ecell = Cell Potential
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
What equation allows you to calculate the Standard Gibb's Free Energy for a Galvanic Cell based on the Standard Cell Potential (E°cell)?
∆G° = -nFE°cell
∆G° = Standard Gibb's Free Energy
n = Number of Electrons
F = 96,500 C/mol
E°cell = Standard Cell Potential
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Li- (E°red = -3.05) and Zn2+ (E°red = -.76) are both part of a Galvanic Cell. What is the Standard Gibb's Free Energy (in J) for this cell?
(A) -54,978
(B) -110,574
(C) -221,453
(D) -441,970
(D) -441,970
E°cell = E°red (cathode) - E°red (anode)
E°cell = -.76 - -3.05
E°cell = 2.29
∆G° = -nFE°cell
∆G° = -(2)(96,500)(2.29)
∆G° = approx. -400,000 J (actual: -441,970)
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
You are reducing copper, and decide to double the number of moles of copper that you are reducing. If you do so, the:
I. ∆G° will double
II. E°red for copper will double
III. K will double
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I and III Only
(A) I Only
You are reducing copper, and decide to double the number of moles of copper that you are reducing. If you do so, the ∆G° will double and n will double, leaving the E°red as the same value according to the relationship ∆G° = -nFE°cell. K will not change according to the relationship -nFE°cell = -RTlnK.
If ∆G° = 441,970 J, what is the value of the Equilibrium Constant K?
(A) 2.33⋅10^-26
(B) 6.78⋅10^-34
(C) 2.80⋅10^-56
(D) 3.36⋅10^-78
(D) 3.36⋅10^-78
∆G° = -RTlnK
441,970 = -(8.314)(298)lnK
lnK = - 441,970 / (approx. 2500 (actual: 2477.57))
lnK = approx. - 180 (actual: - 178.39)
K = approx. 1⋅10^-78 (actual: 3.36⋅10^-78)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What equation simplifies the relationship -nFE°cell = -RTlnK, allowing us to compare the E°cell
E°cell = (.0592 / n)logK
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Cu2+ (E°red = .34) and Zn2+ (E°red = -.76) are both part of a Galvanic Cell. What is the equilibrium constant K for this cell?
(A) 3.05⋅10^6
(B) 8.90⋅10^14
(C) 6.03⋅10^33
(D) 1.59⋅10^37
(D) 1.59⋅10^37
E°cell = E°red (cathode) - E°red (anode)
E°cell = .34 - -.76
E°cell = 1.10
E°cell = (.0592 / n)logK
1.10 = (.0592 / 2)logK
logK = approx. 40 (actual: 37.2)
K = approx. 1⋅10^40 (actual: 1.59⋅10^37)
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
The Nernst Equation allows us to relate E°cell to Ecell. Write out this equation.
Ecell = E°cell - (.0592 / n)logQ
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Cu2+ (E°red = .34) with a concentration of 3.2⋅10^-3 M and Zn2+ (E°red = -.76) with a concentration of 4⋅10^-5 M are both part of a Galvanic Cell. What is Ecell for this cell under these conditions?
(A) .54
(B) .95
(C) 1.06
(D) 1.16
(D) 1.16
E°cell = E°red (cathode) - E°red (anode)
E°cell = .34 - -.76
E°cell = 1.10
Ecell = E°cell - (.0592 / n)logQ
Ecell = 1.1 - (.0592 / 2)log(4⋅10^-5 / 3.2⋅10^-3)
Ecell = 1.1 - (.0296)log(approx. .01 (actual: .0125)
Ecell = 1.1 - (.0296)(approx. -2 (actual: -1.903))
Ecell = 1.1 - (.approx. -.05 (actual: -.056))
Ecell = approx. 1.15 (actual: 1.156)
CRB Fill in the blanks: _________ Cells are driven by spontaneous reactions, whereas __________ Cells require Electrolysis (energy from an external voltage source) for the reaction to occur.
(A) Voltaic, Galvanic
(B) Galvanic, Concentration
(C) Electrolytic, Concentration
(D) Galvanic, Electrolytic
(D) Galvanic, Electrolytic
Galvanic Cells (and Concentration Cells) are driven by spontaneous reactions, whereas Electrolytic Cells require Electrolysis (energy from an external voltage source) for the reaction to occur.
CRB Which of the following types of cells do not need to be separated into different compartments?
(A) Concentration Cell
(B) Galvanic Cell
(C) Magnetic Cell
(D) Electrolytic Cell
(D) Electrolytic Cells
This is because the reaction is not spontaneous, so there is no fear of the reaction proceeding to completion too quickly or in an uncontrolled manner.
CRB One laboratory technique commonly used to separate amino acids by charge is Isoelectric Focusing. The gel has a gradient of pH's, and the amino acids will migrate to the portion where the pH is equal to the isoelectric point (pI) of the amino acid. Which of the following types of cells would power this technique?
(A) Concentration Cell
(B) Galvanic Cell
(C) Magnetic Cell
(D) Electrolytic Cell
(D) Electrolytic Cell
Again, this reaction can be finely controlled by the voltage source, making it the best option to power a controlled experimental technique.
CRB Which of the following types of cells uses the same elements in both the anode and cathode, and the reaction is only driven by the concentration gradient between the two solutions around the electrodes?
(A) Concentration Cell
(B) Galvanic Cell
(C) Magnetic Cell
(D) Electrolytic Cell
(A) Concentration Cell
Also note that the Nernst Equation must be used here to calculate the voltage as a function of concentrations.
CRB True or false? Concentration cells often overshoot their equilibrium point where concentrations are equal, reversing which electrode is the cathode and anode and reversing the current.
False. Concentration Cells will work until equal concentrations in each compartment is achieved, and then there is no Electrical Potential Energy or the ability to do further work.
CRB Fill in the Blanks: Rechargeable batteries can function as _____________ Cells when they are discharging and ______________ Cells while they are charging.
(A) Electrolytic, Galvanic
(B) Galvanic, Electrolytic
(C) Concentration, Electrolytic
(D) Electrolytic, Concentration
(B) Galvanic, Electrolytic
Rechargeable batteries can function as Galvanic Cells when they are discharging and Electrolytic Cells while they are charging.