exercise 37 KTTK: Starch hydrolysis (Micro. lab)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Starch is complex polysaccharide composed of α-glucose polymers in one of two forms
linear (amylose) and branched (amylopectin) - predominant
linear
amylose
branched
amylopectin - predominant
Know whether starch can pass through the bacterial cell membrane or whether it must be digested extracellularly
starch too large to pass through bacterial cell membrane. Therefore, it must first be broken down extracellularly.
• Must be broken down outside plasma membrane
• 3 enzymes involved in starch hydrolysis
three enzymes involved in starch digestion are
α-Amylase
β-Amylase
α-1,6-glucosidase
α-Amylase
breaks starch polymer into
• α-Glucose
• α-Maltose
β-Amylase
breaks starch polymer into β-maltose
α-1,6-glucosidase
• Breaks down small, branched molecules referred to as limit dextran after amylase activity since neither α- or β-amylase can break down branch points
• Produces short, linear oligosaccharides broken down by α-amylase into α-glucose and α-maltose
Know what limit dextran is, where it comes from, and which enzyme
can be used to break it down
breaks down small branched carbohydrate molecule after amylase activity. α-1,6-glucosidase breaks these down into short
Produces short, linear oligosaccharides broken down by α-amylase into α-glucose and α-maltose
oligosaccharide is
breaks down limit dextrin into short, linear oligosaccharides that α-amylase then hydrolyzes to α-glucose and α-maltose
enzymes referred to as
exoenzymes
exoenzymes
• Secreted outside of cell
• Mono and disaccharides produced absorbed through bacterial cell membrane
Know what the starch hydrolysis (amylase) test indicates about the organism
To test for organisms that can hydrolyze starch and produce exoenzymes such as a-amylase, b-amylase and oligo-1, 6-gluosidase.
Know what is in the starch agar which allows for testing of the
presence of amylase
beef extract, soluble starch and agar
Know what substance needs to be added to the starch agar plate
to be able to visualize whether an organism produces amylase or not
Iodine
Know what color the starch agar turns after iodine is added to it
If starch is present, will turn blue-black or dark brown color
Know what it means if a clear zone appears around the growth of
an organism on the starch agar plate after iodine is added to it
If starch has been hydrolyzed and consumed will see cleared zone around
organism
It means the organisms were able to hydrolyze the starch
Know why (application) the starch hydrolysis (amylase) test is used
• Originally designed for cultivating Neisseria
• No longer used for this
• With pH indicators, can be used to isolate and presumptively identify Gardnerella vaginalis
• Helps to differentiate between members of the genera Corynebacterium, Clostridium, Bacillus, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, and Enterococcus which have both amylose-positive and amylose-negative species
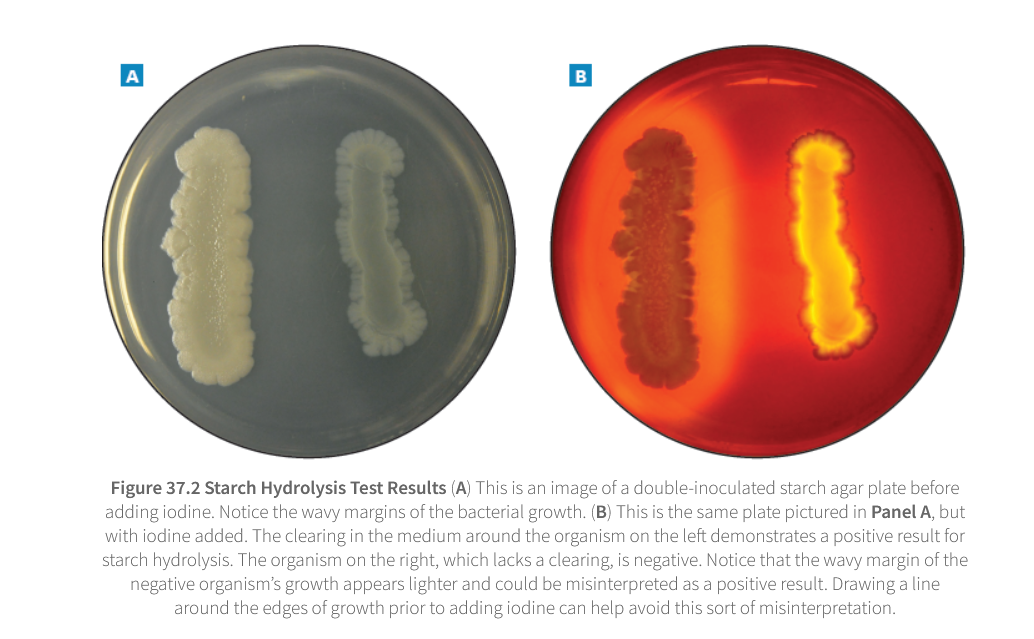
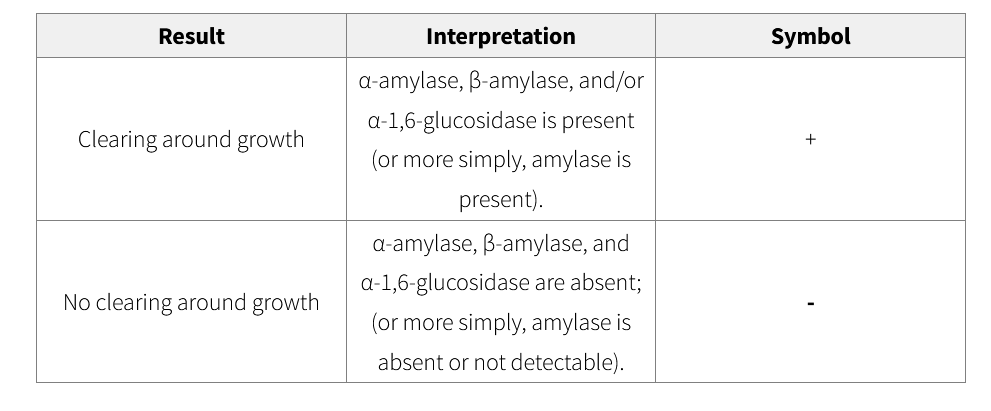
Starch Hydrolysis Test Results and Interpretations
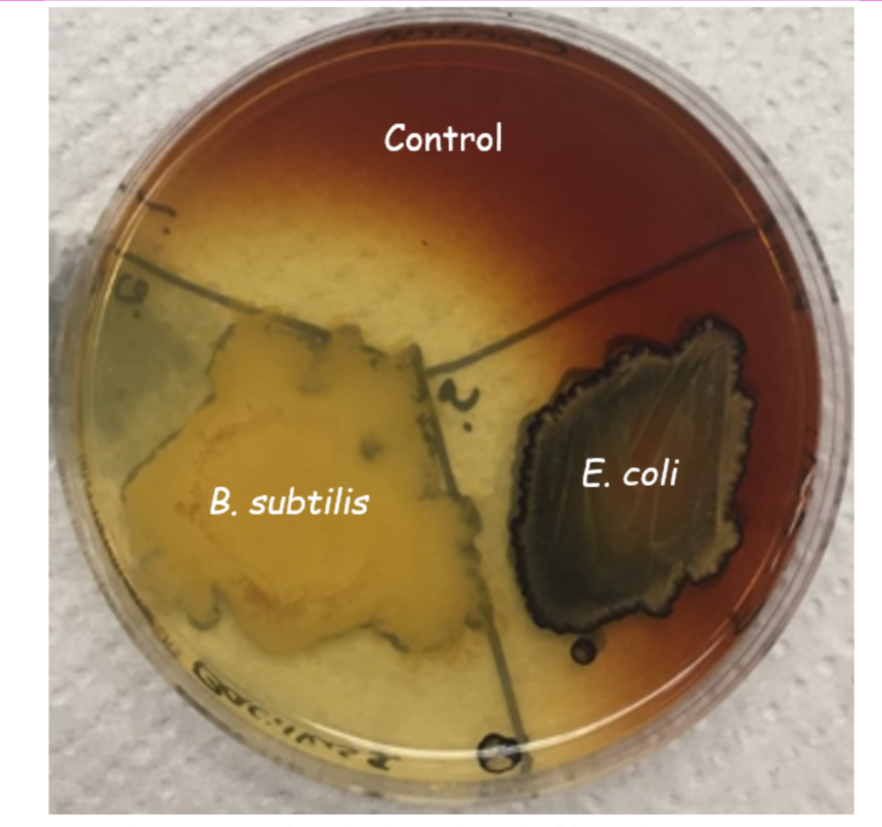
Starch Agar – Results #1
control: no clearing around growth (-). α-amylase, β-amylase, and α-1,6-glucosidase are absent; (or more simply, amylase is absent or not detectable).
B. subtilis: Clearing around growth (+). α-amylase, β-amylase, and/or α-1,6-glucosidase is present (or more simply, amylase is present).
E. coli: no clearing around growth (-). α-amylase, β-amylase, and α-1,6-glucosidase are absent; (or more simply, amylase is absent or not detectable)
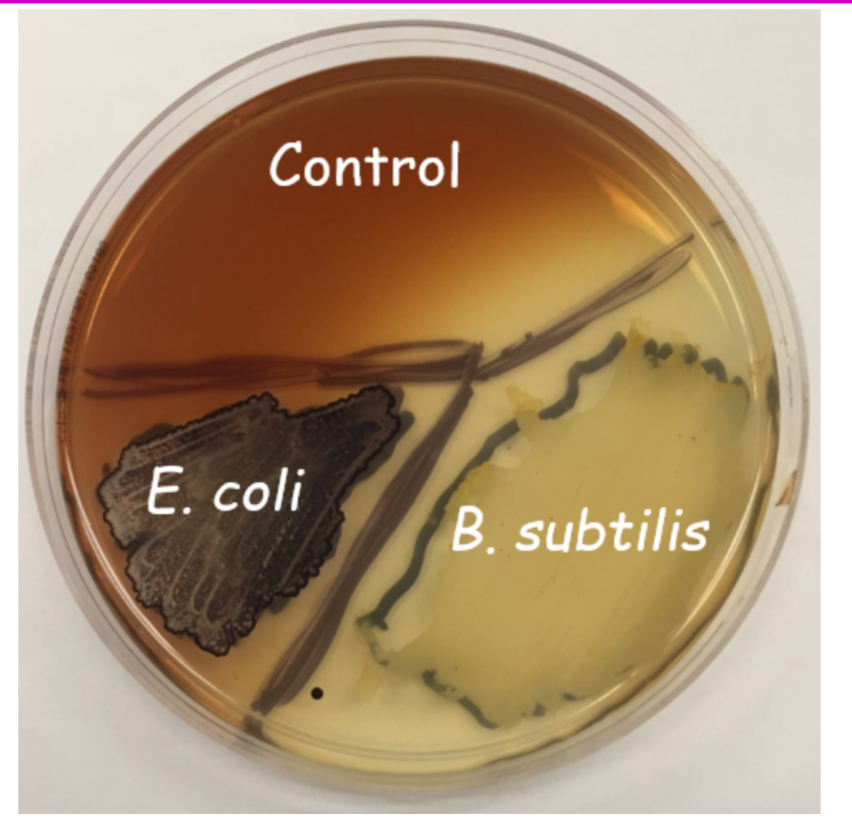
Starch Agar – Results #2
control: no clearing around growth (-). α-amylase, β-amylase, and α-1,6-glucosidase are absent; (or more simply, amylase is absent or not detectable).
B. subtilis: clearing around growth (+). α-amylase, β-amylase, and/or α-1,6-glucosidase is present (or more simply, amylase is present).
E. coli: no clearing around growth (-). α-amylase, β-amylase, and α-1,6-glucosidase are absent; (or more simply, amylase is absent or not detectable).
Starch Hydrolysis Test Results