Physics All Y9 Notes & Flashcards [end of years revision]
1/88
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Where is chemical energy stored
food, fuel, batteries
Where is kinetic energy stored
moving objects
Where is thermal energy stored
hot objects
Where is strain/elastic energy stored
stretched, squashed, twisted materials
Where is atomic/nuclear energy stored
atoms
Where is gravitational energy stored
objects in high places
System
something in which we are studying changes
Law of conservation of energy
energy can’t be created or destroyed
Units for energy
Joules (J)
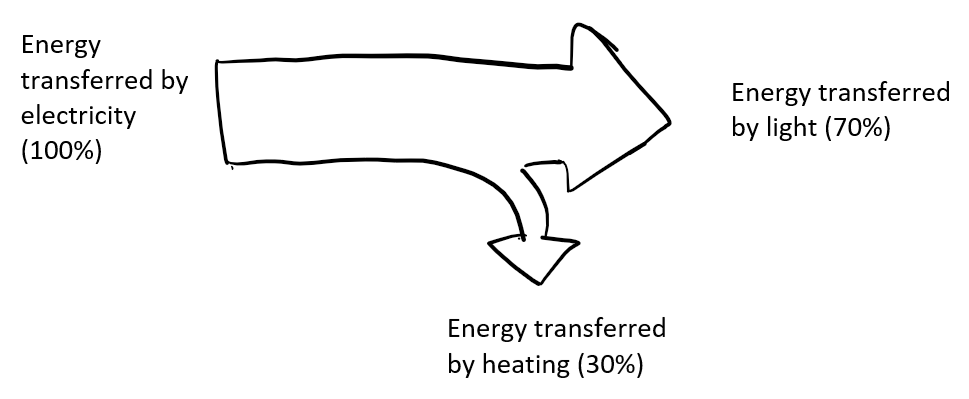
Sankey diagram
shows the amount of energy transferred and where to
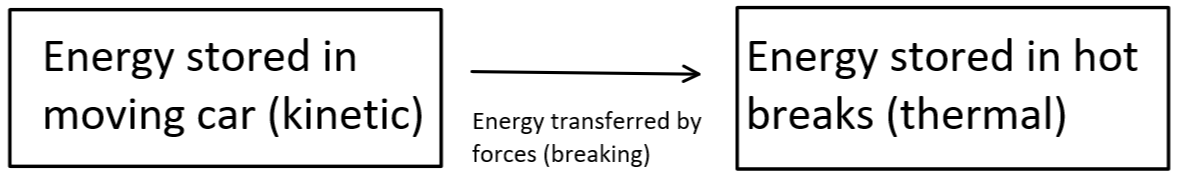
Energy transfer diagram
shows energy stores and transfers
Dissipated
spread out into the surroundings
How do mechanical processes become wasteful
when they cause a rise in temperature - energy dissipates through heating to the surroundings
Energy efficiency definition
how good a machine is at transferring energy into useful forms
given in a number between 0 and 1 or a percentage
Energy efficiency formula
useful energy transferred by device
total energy supplied to device
How can you reduce friction
lubrication - making a surface smooth so things can move easily on it
Insulation
slows the pace at which energy is transferred out of a place
Conduction
vibrations passed between particles in a solid
Convection
part of a fluid is warmer (less dense) and rises up, on the other side it is colder (more dense) and sinks down.
this creates a convection current going round in a circle
Radiation
energy transferred through waves, some types (infrared) can pass through solid objects
Thermal conductivity
how well a material allows heat to move through it
can depend on thickness and temperature difference
a good insulator needs low thermal conductivity
Solar energy
heating and lighting from the sun used with solar panels
Wind energy
using wind turbines, kinetic energy of wind turns a turbine
Hydroelectric energy
flowing water turns a turbine
Wave energy
kinetic energy of sea’s waves turned into electricity
Nuclear energy
energy in uranium nuclei is transferred into heating, creates steam and turns a turbine
Fossil fuels
chemical energy in coal, oil, gas transferred into heating, creates steam and turns a turbine
Biomass energy
chemical energy in things that were once alive burned and turned into heating
Geothermal energy
rocks underground are very hot, heat produces steam which turns a turbine
Tidal energy
water trapped behind a dam at high tide is released, turning a turbine
Wave definition
an oscillation (vibration) that transfers energy and information (not matter) from one place to another
Wavelength definition
length of a full cycle e.g. crest to crest
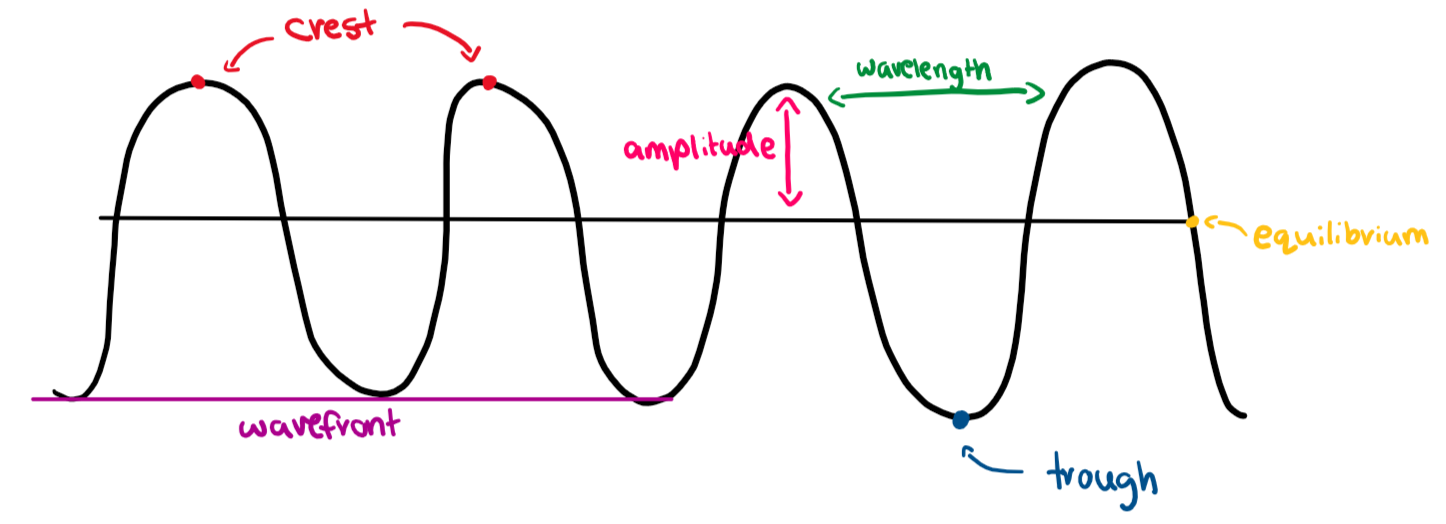
Amplitude
size of wave (1/2 crest to trough)
Frequency definition
number of complete waves to pass a point per sec
Period definition
time taken to move through one complete cycle
Velocity definition
speed in a stated direction
wave speed (with frequency and wavelength)
speed = frequency x wavelength
Transverse wave
Vibrations are perpendicular to direction of transfer
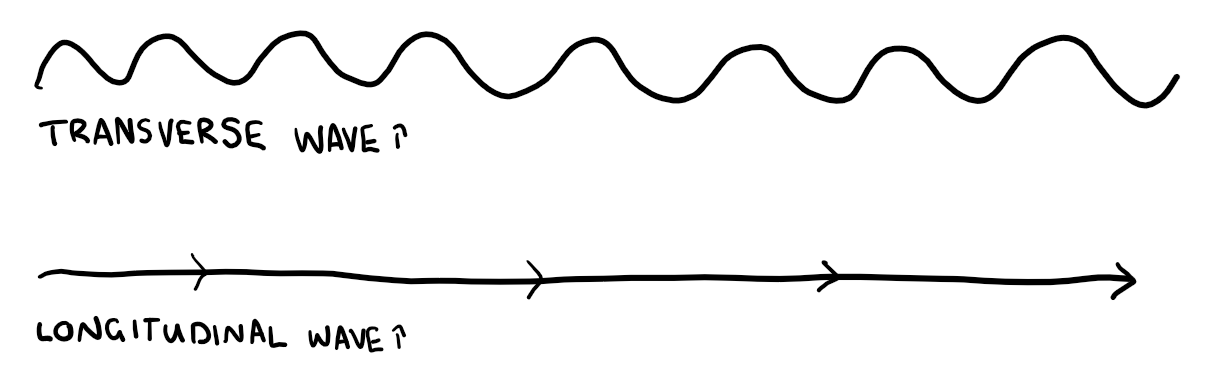
Longitudinal wave
Vibrations are parallel to direction of transfer
Crest
highest point of wave
Trough
lowest point of wave
Equilibrium
middle point of wave
Wavefront
all locations where wave is in the same phase e.g. all troughs
Period equation
1 / frequency
Frequency equation
1 / period
Reflection
when a wave bounces off a surface at an angle and changes direction
Refraction
when light changes speed between different media
Transmission
when a wave passes through a material
Absorption
when a wave is taken in and the energy is transferred to the material
Refraction: when the wave gets faster…
it bends away from the normal
Refraction: when the wave gets slower…
it bends towards the normal
Range that humans can hear
20Hz - 20,000Hz
Ultrasound definition
very high sounds humans can’t hear above 20,000Hz
Infrasound
very low sounds humans can’t hear below 20Hz
Auditory nerve
electrical signals carry messages along this to the brain
Eustachian tube
tube that connects ear and nose
Ear canal
tube that carries sound to the inner ear
Pinna
visible part of the ear, collects sound waves and funnels them into the ear
Eardrum
thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves hit it
Ossicles
made up of the stirrup, anvil and hammer
they help transmit vibrations to the inner ear
Semi-circular canals
help you balance
Cochlea
snail shaped and full of cilia (tiny hairs) that convert vibrations into electric signals (aka nerve impulses)
The base is thicker and stiffer than the apex, and vibrates at higher frequencies.
Measuring waves in a ripple tank practical
Count how many waves are formed in 10secs
Put a ruler against the tank and use it to measure the length of the waves (easier to take a photo and measure off that)
Measure the distance between two points and see how long it takes waves to go from one part to another
To get frequency divide the number of waves in 10s by 10 (step 1)
To get speed divide the distance by the time (both from step 3) OR Multiply the wavelength (step 2) by frequency (above)
Ultrasound sonar
Ship emits ultrasound wave downwards
Wave reflects off seabed and returns to the ship
Speed = distance/time is used to calculate depth of seabed (distance) as instruments on the ship measure the speed & time of the wave
Ultrasound scanning
Transducer (or probe) is placed against skin
Gel is used to stop waves reflecting off skin
Transducer emits ultrasound waves and measures how long it takes for them to bounce off something and come back
Shorter time = closer object
Speed = distance/time used for exact distance calculations
An image can also be made if you know how far away lots of things are
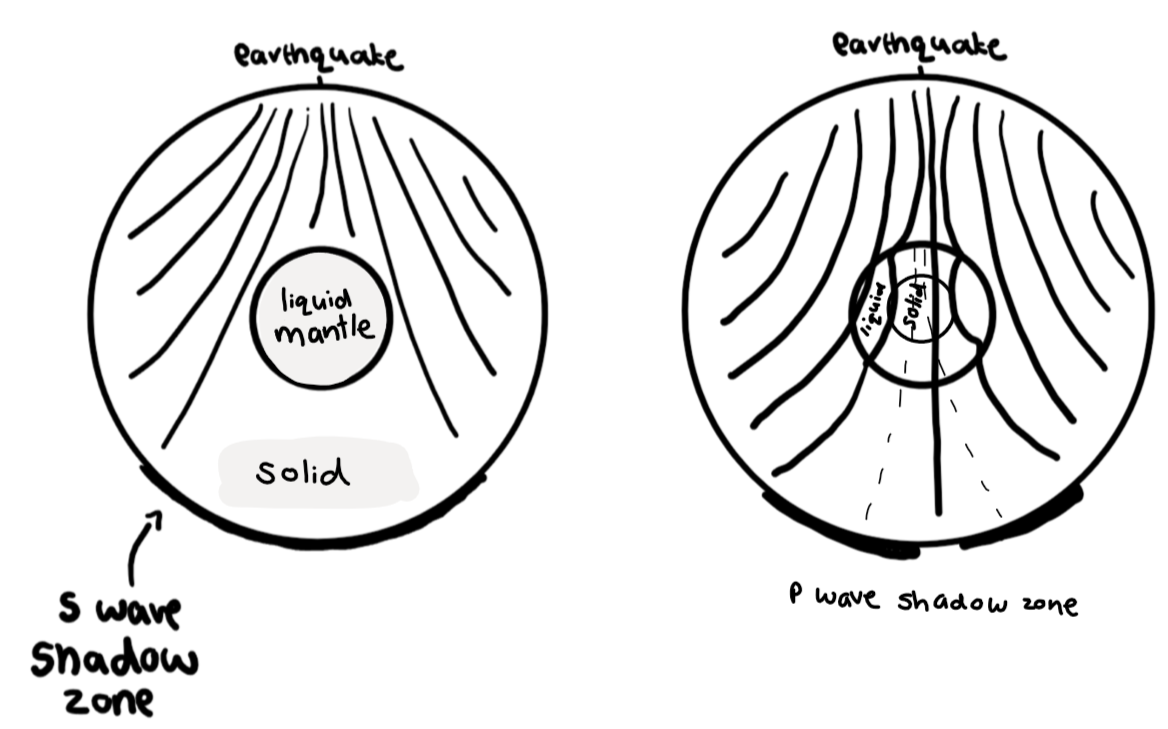
P waves
longitudinal waves, travel through both solids and liquids
S waves
transverse waves, only travel through solid
Infrasound and the earth’s core
The properties of the earth change as you go deeper
The S wave shadow zone means that there is something liquid in the centre of the earth stopping the S waves going through, as they can’t travel through liquids (the mantle)
When P waves pass in and out of the liquid mantle, the refract and change direction
The few weak waves received in the P wave shadow zone are because of the solid inner core
This happens no matter where the earthquake is
Seismic waves
waves produced by earthquakes
Seismometers
instruments that detect/measure seismic waves
Scalars
Have just a magnitude (size)
Examples:
Speed
Distance
Time
Mass
Speed with distance & time
distance / time
Velocity equation
displacement / time
Acceleration definition
rate of change of velocity (doesn’t have to be getting faster)
Acceleration equation with time
a = acceleration
t = time
u = starting velocity
v = ending velocity
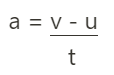
Acceleration in a free fall
10m/s2
Instantaneous speed
speed at any given moment throughout the journey
Average speed
speed averaged taking into account the whole journey
Gradient on a distance/time graph
speed
steeper gradient = more speed
Straight line on a distance/time graph
constant speed
Horizontal line on a distance/time graph
stationary
aka constant speed of 0
Area bounded on a distance/time graph
no meaning
Gradient on a velocity/time graph
acceleration
line sloping up = acceleration
line sloping down = deceleration (negative acceleration)
Straight line on a velocity/time graph
constant acceleration
Horizontal line on a velocity/time graph
constant velocity
Area bounded on a velocity/time graph
Distance travelled
Gradient equation
rise / run
Pick two points on a line
Find the vertical distance between points (rise)
Find the horizontal distance between points (run)
Divide the rise by the run
Example of a longitudinal wave
sound wave
Example of a transverse wave
Visible light wave