Physical chemistry
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
June 2022 v1
1) a) The solubility of the Group 2 sulphates decreases down the group. Explain this trend. [3]
[1] Lattice energy and enthalpy change of hydration both become less exothermic
[2] Lattice energy becomes less exothermic by a smaller extent OR enthalpy change of hydration changes by a larger extent
[3] So enthalpy change of solution becomes less exothermic OR more endothermic OR Hsol = Hhyd - Hlatt
June 2022 v1
1) b) Describe what is observed when magnesium and barium are reacted separately with an excess of dilute sulphuric acid [1]
Magnesium: Fizzing
Barium: fizzing AND white precipitate forms
Solubility product equation
C (s) ⇌ aA+ (aq) + bB- (aq)
Ksp = [A+ (aq)]^a [B- (aq)]^b
1) d) ii) Suggest how the lattice energy of BaSO4 differs from the lattice energy of Cs2SO4. Explain your answer. [2]
[1] BaSO4 is more negative as Ba2+ is smaller/has a larger charge
[2] Stronger force of attraction between ions
Equation for Gibbs free energy
ΔG = ΔHr - TΔS
Where ΔS is in kJ
ΔG = -nFEcell
F = 96500C
n = moles of electrons transferred within the reaction
Ideal gas equation
pV = nRT
p = Pressure (Pa)
V = Volume (m3)
R = Gas constant (8.31 J K-1 mol-1)
n = moles of gas
T = Temp (Kelvin)
Percentage yield equation
Percentage yield = actual yield / theoretical yield x 100
Calorimetry equation
Q = mcΔT
Q = energy change
m = mass (g)
c = specific heat capacity (4.18 J/gC° for water)
ΔT = temp change
Entropy change equation
ΔS = Sproducts - Sreactants
Equilibrium constant equation
Kc = [C]^c [D]^d / [A]^a [B]^b
for reaction aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
(same for partial pressures Kp except replace concentrations with partial pressure of substance)
Partial pressure equation
Partial pressure = mole fraction x total pressure
Partition coefficient equation
Kpc = [A(organic)]/[A(aqueous)]
Stability constant equation
Same as equilibrium constant except conc of water = 1 in all cases
Rate equation
rate = k[A]^x [B]^y [C]^z
x,y,z = orders with respect to A, B and C
k = rate constant
Rate constant equation
k = 0.693 / t1/2
t1/2 = half-life
Acid dissociation constant equation
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
pKa equation
pKa = -log10Ka
Ionic product of water
Kw = [H+][OH-]
Kw = 1x10^-14 at 298K
pH equation
pH = -log10[H+]
Ecell equation
Ecell = Reduction - Oxidation
Faradays constant equation
F = Le
F = 96500 C mol-1
L = Avogadros constant
e = charge of an electron (1.6x10^19)
Nernst equation
𝐸 = 𝐸0 − (0.059/z) log [oxidised species]/[reduced species]
E = electrode potential (V)
𝐸0 = standard electron potential (V)
z = moles of electrons transferred
Mass spectrometry equation
n = 100 x abundance of M+1 ion / 1.1 x abundance of M+ ion
n = number of carbon atoms
June 2022 v1
2) a) Define transition element [1]
[1] An element that forms one or more stable ions with an incomplete d sub-shell
June 2022 v1
2) b) Sketch the shape of a 3dz^2 orbital [1]
Infinity loop on z axis
Donut across y and x
June 2022 v1
2) c) i) Explain what is meant by a heterogenous catalyst [1]
[1] A catalyst that is in a different phase from the reactants
June 2022 v1
2) c) ii) Describe the mode of action of a heterogenous catalyst in a reaction [3]
[1] Adsorption of reactants to the surface of the catalyst
[2] Bonds within the reactants weaken (lowering the activation energy)
[3] Reaction occurs and the products are desorbed
June 2022 v1
2) d) ) Manganese(VII) oxide, Mn2O7, can be made by treatment of KMnO4 with concentrated sulfuric acid (reaction 1).
Mn2O7 readily decomposes at room temperature to form manganese(IV) oxide and a colourless diatomic gas (reaction 2).
Construct equations for both the reactions described. [2]
[1] Reaction 2: 2KMnO4 + H2SO4 → Mn2O7 + H2O + K2SO
[2] Reaction 2: Mn2O7 → 2MnO2 + 1.5O
June 2022 v1
2) e) i) Write the ionic equation, and state the type of reaction, for the reaction of [Mn(H20)6]2+ with NaOH (aq) [2]
[1] [Mn(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH– → Mn(OH)2 + 6H2O
[2] Acid-base
June 2022 v1
2) e) ii) Write the ionic equation, and state the type of reaction, for the reaction of [Mn(H20)6]2+ with concentrated HCl [2]
[1] [Mn(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl– → [MnCl4]2– + 6H2O
[2] Ligand substitution
What does a more negative cell potential indicate
Stronger reducing agent and more likely to be oxidised
June 2022 v1
3) c) i) Define standard electrode potential [1]
[1] Potential difference when a half-cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode under standard conditions
June 2022 v1
3) c) ii) A salt bridge is used in an electrochemical cell. State the function of the salt bridge. Explain your answer. [1]
[1] Ions move to maintain charge balance / to complete the circuit
June 2023 v2
1) a) ii) Describe the variation in the thermal stability of Group 2 carbonates. Explain your answer. [3]
[1] Thermal stability increases down the group
[2] Ionic radius of group 2 ion increases, reducing charge density
[3] So less polarisation/distortion of carbonate ion
June 2023 v2
1) b) i) Define lattice energy [2]
[1] Enthalpy change/energy released when one mole of an ionic solid/compound is formed
[2] From its gaseous ions
![<p>June 2023 v2</p><p></p><p>2) b) ii) [3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/18da305f-e8b9-45d1-b716-0b64070ffc99.png)
June 2023 v2
2) b) ii) [3]
[1] ΔHdecomp becomes more positive down group
[2] Ionic radii of oxide ions are smaller than carbonate ions
[3] So ΔHlatt of oxides becomes less exothermic faster (changes more down grp)
June 2023 v2
2) a) State two properties of a transition element [1]
Two from:
Have variable oxidation states
Behave as catalysts
Form complex ions
Form coloured ions/compounds
June 2023 v2
2) b) i) Define complex ion [1]
[1] Molecule formed by a central metal ion surrounded by ligands
June 2023 v2
2) c) i) Explain what is meant by a bidentate ligand [2]
[1] Species that donates/uses two lone pairs
[2] To form two dative covalent bonds to a central metal ion
June 2023 v2
3) a) Define enthalpy change of atomisation [2]
[1] Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is produced
[2] From its element in its standard state
June 2023 v2
3) f) The standard enthalpy change of solution ΔHsol of AgNO3(s) in water is +22.6kJ mol-1. Suggest how the feasibility of dissolving AgNO3(s) in water changes with temperature. Explain your answer [2]
[1] Feasibility increases as temperature increases
[2] ΔS is positive and -TΔS becomes more negative, so ΔG is negative and becomes more negative
June 2023 v2
4) a) i) Explain what is meant by the overall order of reaction [1]
[1] Sum/total of the powers to which a concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate equation
Nov 2022 v2
2) b) iv) Explain why a reaction can have zero order kinetics when the amount of reactant is large and the amount of catalyst is small [1]
[1] All active sites on the surface of the catalyst are occupied
Nov 2022 v2
3) a) i) Define standard electrode potential. Include details of the standard conditions used. [2]
[1] The voltage produced by a half cell compared with a standard hydrogen electrode
[2] 1 mol dm^-3, 298K, 1 atm
Nov 2022 v2
4) b) i) Define conjugate acid-base pair [1]
[1] Two species that differ by one H+ ion
Nov 2022 v2
5) b) ii) In an isolated Cu2+ ion, the d-orbitals are all degenerate. In a complex ion such as [Cu(H2O)6]2+, the d-orbitals are non degenerate.
Define degenerate and non=degenerate in this context [1]
[1]
Degenerate = of the same energy
Non-degenerate = not of the same energy
Nov 2022 v2
6) b) i) Define stability constant [1]
[1] Equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from its constituent ions
OR
[2] Equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion in a solvent
March 2022
1) c) i) Identify a suitable indicator for a reaction producing iodine [1]
[1] Starch
March 2022
1) c) Sketch the shape of a 3dxy orbital
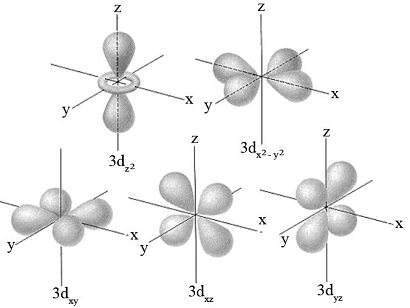
March 2022
3) b) i) TiO2- is a colourless ion. Suggest why [2]
[1] Ti is in a 4+ oxidation state, so no d electrons
[2] So cannot absorb photons
March 2022
3) c) ii) Explain, in terms of d-orbitals, why Ti³+ is able to form complex ions.