NSCI 2001 Exam 1 Part 1 (2-4)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Glia
Have no axons
Myelin formation (Oligodendrocytes and Schwann Cells)
Tracts
Bundles of axons (CNS)
Ganglia
Groups of neuronal somata
Nerves
Bundles of axons (PNS)
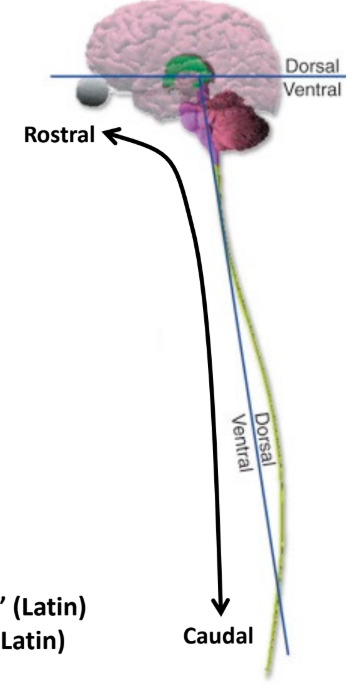
Dorsal
“Back”
“Top” of the brain, “back or behind” of the spinal cord
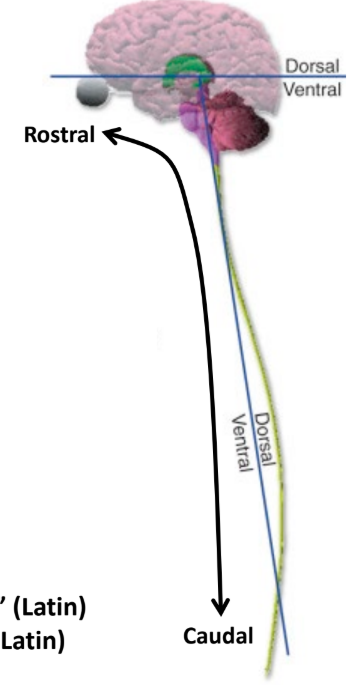
Ventral
“Belly”
“Bottom” of the brain, “stomach or front” of the spinal cord
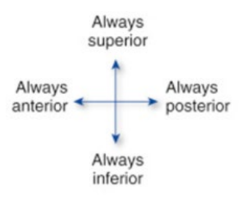
Always Superior
Up
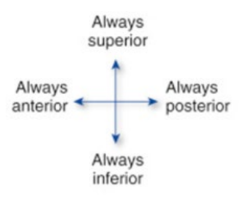
Always Inferior
Down
Always Anterior
Front
Always Posterior
Behind
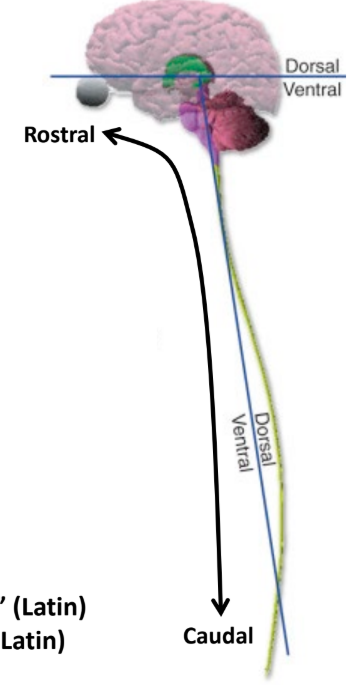
Rostral
“Towards the beak”
Follows the CNS, towards the brain (head)
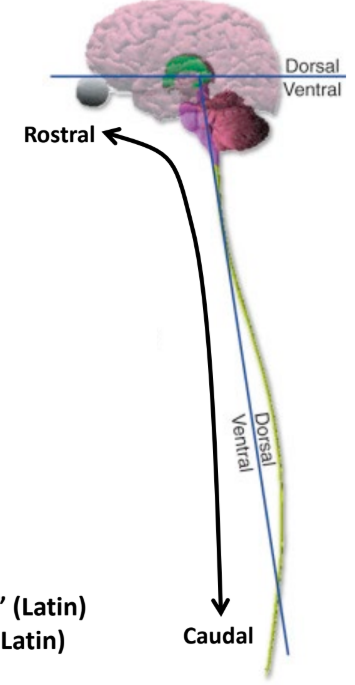
Caudal
“Towards the tail”
Follows the CNS, towards the bottom of the spinal cord (feet)
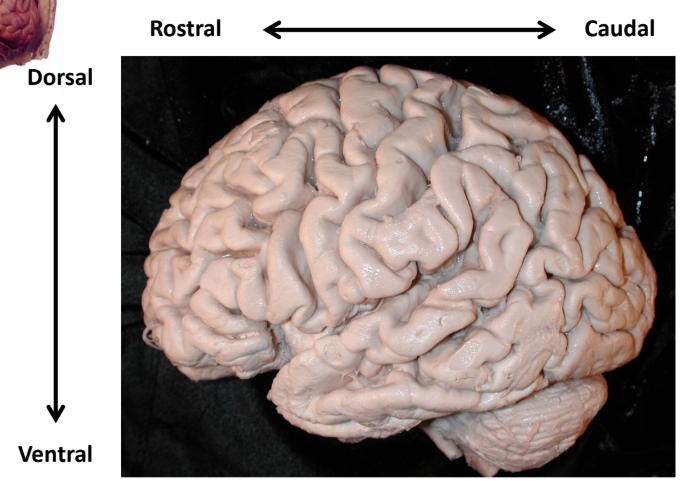
Orientation of the Human Brain
“X” Space - Rostral/Anterior, Caudal/Posterior
“Y” Space - Dorsal/Superior, Ventral/Inferior
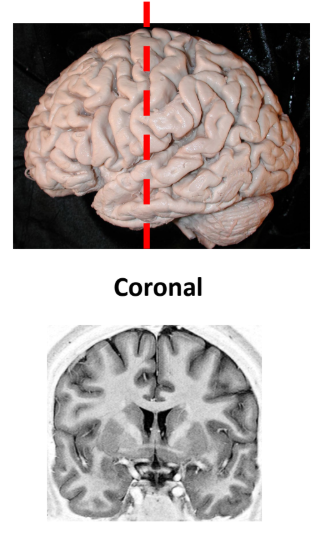
Coronal sectioning
Cross sectional
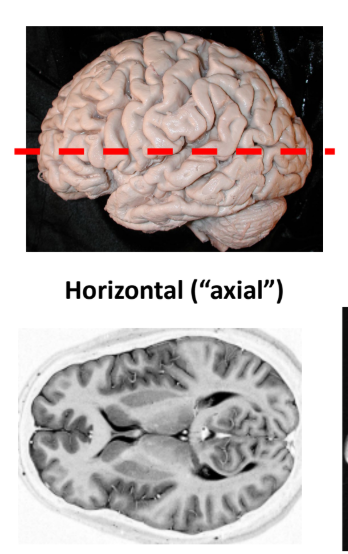
Horizontal sectioning
Axial
Most clinical scans are done this cut
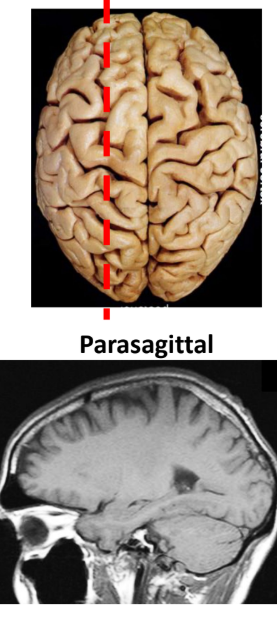
Parasagittal
Sideview
Diencephlon (Midbrain area)
“Quiets” sensory neurons
Medial Longitudinal
Runs Rostral/Caudral
Separates left and right hemispheres
Gyrus and Sulcus
G - Bump or ridge
S - Groove (deep fissures)
What creates the embryo
Inner cell mass filled with fluid
Embryonic age
Time after fertilization
Biologists (Use this age in class)
Gestational age
Time after last menstral period (E.A. + ~2 weeks)
Clinicians
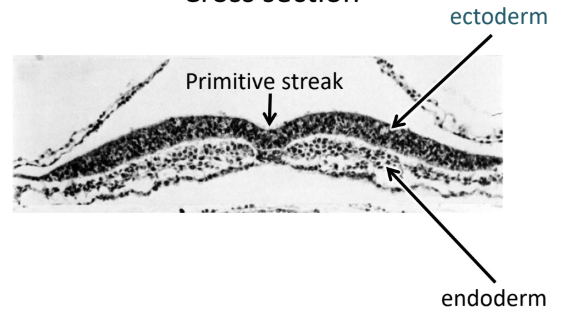
Primitive streak
Cells migrate to here
Splits right and left half
Allows generation of mesoderm
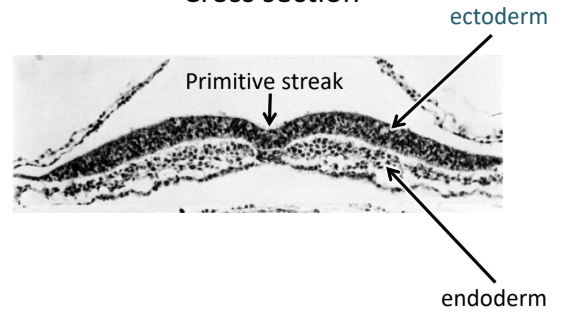
Ectoderm
Top layer (Dorsal)
Skin and nervous system
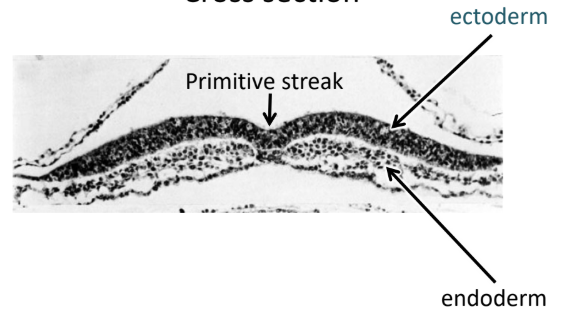
Endoderm
Bottom layer (Ventral)
Gut, glandular organs, and liver

Mesoderm
Middle space
Bone, muscle, and some organs
Induces ectoderm to become neural plate (CNS and PNS creation)
Dividing cells move…
Rostrally to extend the embryonic disk
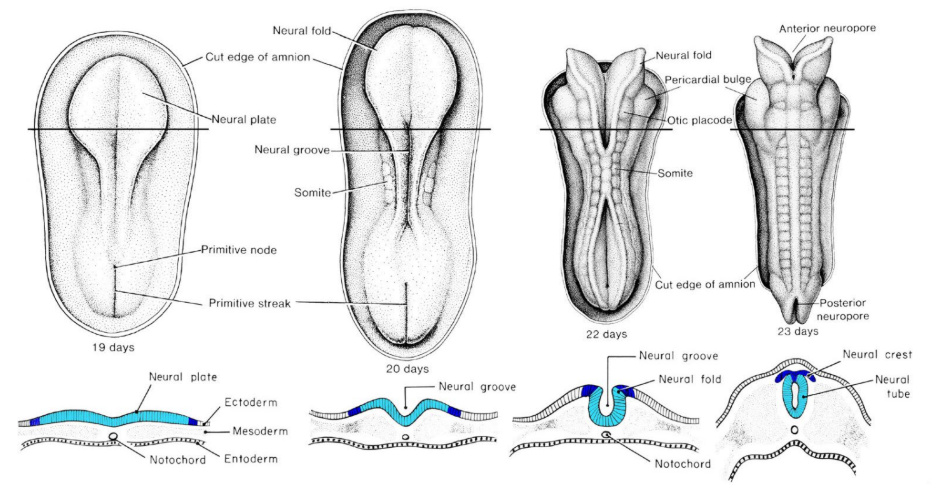
Neurulation
Neural plate → Neural groove → Neural tube/Neural Crest
Plate bulges out and up to develop the CNS
Neural Crest
Becomes the PNS (of the body)
Is made from the tissue when the tube is formed
Develops spinal column
Closure of neural tube…
Starts in the center
Moves both rostrally and caudally
Creates the CNS
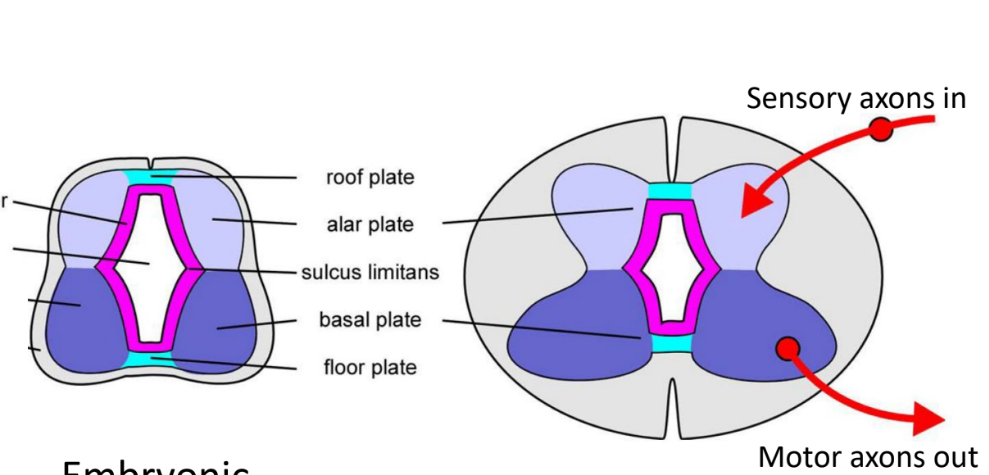
Alar plate
“Top wings”
Sensory
Sensory axons in
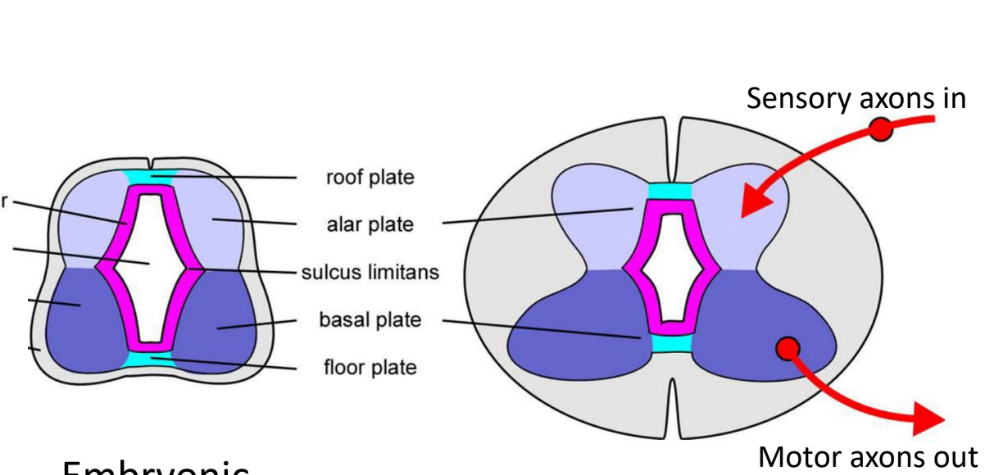
Basal plate
“Bottom wings”
Motor
Motor axons out
Sulcus limitans
Separates alar and basal plates
Visible in the brain stem
Becomes dorsal and ventral horn
Spina Bifida
Caudal
Incomplete closure of the spinal tube or spine
Most often of no consequence
Anecephaly
Rostral
Incomplete closure of the brain end of the spinal cord
Rare and lethal
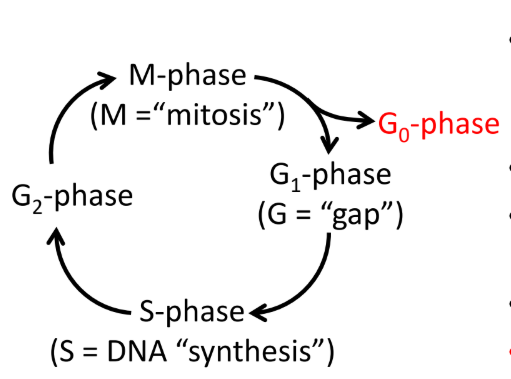
Cell cycle
G1, S, G2, M
When a cell differentiates into a neuron, mitosis ends and the cell enters G0 (terminal differential)
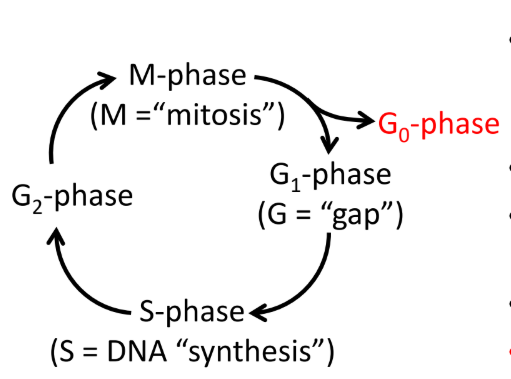
G1 Phase (gap)
Pause: factors that initiate or block cell division are expressed
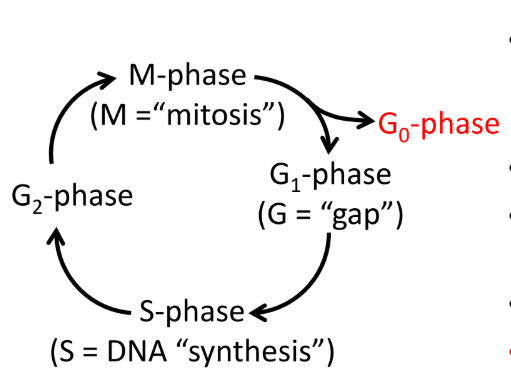
S Phase
DNA synthesis
DNA is replicated
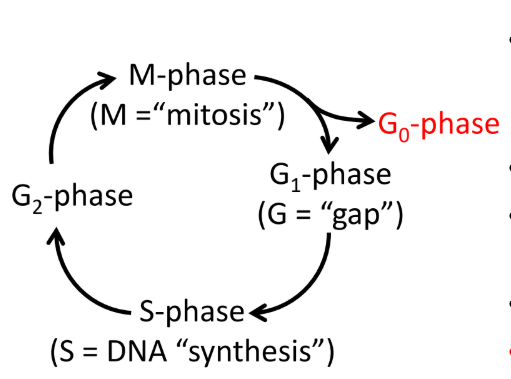
G2 Phase (gap)
Pause: proteins needed for mitosis are expressed
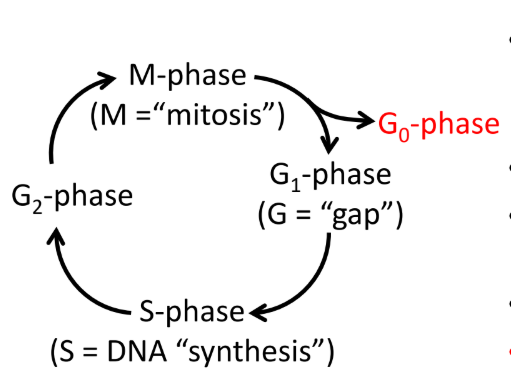
M Phase
Mitosis
Cell divides into two
PNS derives from…
Neural crest
Neural placodes
Neural Placodes
Develops and becomes the PNS (of the head)
Lens Placode
Lens
Lens placode
Eye
Retina
Brain tissue
Olfactory placode
Sense of smell
From both placode and crest
Placodes can also…
Induce changes in neighboring cells and tissues
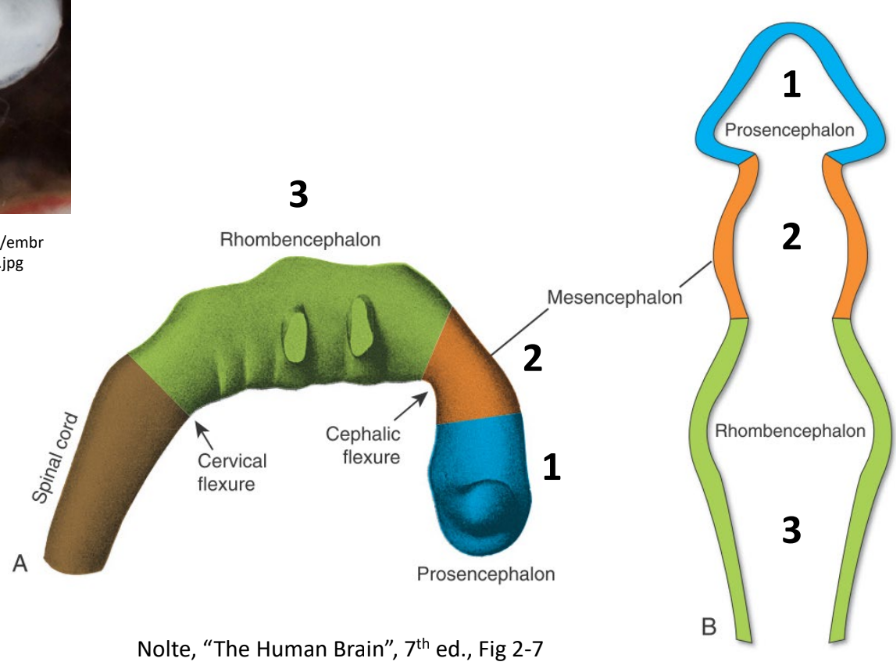
Three primary vesicles
Prosencephalon (Blue, Rostral)
Mesencephalon (Orange)
Rhombencephalon (Green, Caudal)
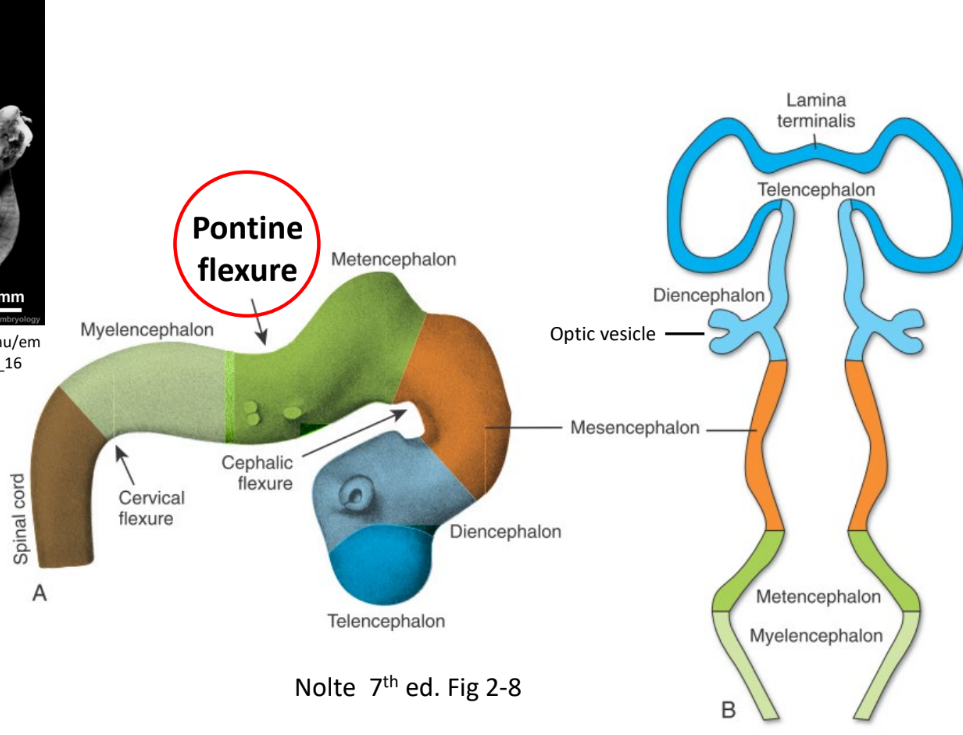
Secondary neural vesicles
Myelencephalon
Metencephalon
Mesencephalon
Diencephalon
Telencephalon
Pontine flexure
Marks the boundary between the Myelencephalon and the Metencephalon
Opens the 4th Ventricle
Becomes the brain stem
Prosencephalon becomes..
The Forebrain (Rostral)
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Optic Vesicles
Telencephalon becomes…
The most of the brain
“C” shaped
Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
Diencephalon becomes…
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Optic Vesicles becomes…
Retina
Mesencephalon becomes…
Midbrain
Rhombencephalon becomes…
The Hindbrain (Caudal)
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Metencephalon becomes…
Cerebellum
Pons
Myelencephalon becomes…
Medulla
The main meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Falx cerebri
Stabilizes and prevents the brain from force and cerebral hemispheres from moving laterally (side to side)
Dural folds
Stabilizes the posterior part of the brain
Tentorium cerebelli is above the cerebellum
Lateral ventricles
One in each hemisphere
Within telencephalon
Third ventricle
Ventral to the Lateral ventricles
Lies on the midbrain
Separates thalamus and hypothalamus
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects the third and fourth ventricles together
(Diencephalon to pons)
Fourth ventricle
Rostral to the cerebellum
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Extracellular fluid (plasma like)
High Na, Low P, and little protein
Made by the choroid plexus
500 ml produced each day
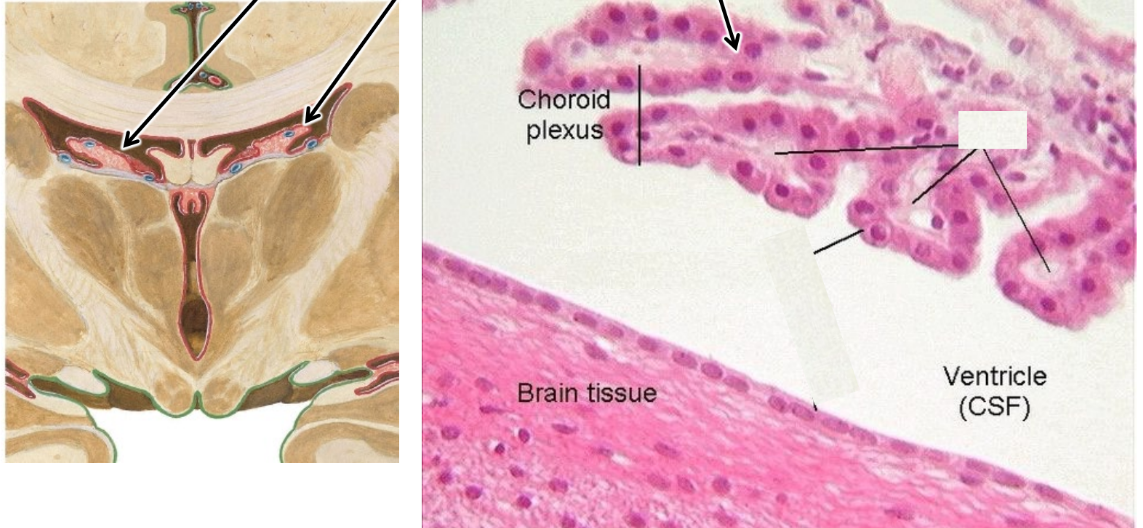
Choroid plexus
Found in all ventricles
Total volume of ventricles
200 ml
Excess CSF drains through
Subarachnoid space to veins (arachnoid granulations/ Fourth ventricle)
Hydrocephalus (in newborns)
CSF doesn’t drain
Not fatal if treated correctly (Shunting to the abdomen)
Doesn’t become severe
Hydrocephalus (in adults)
Critical condition
Pressure onto the brain stem can cause death
Shunting for treatment
Menigitis
Cloud or foggy CSF
Changes in proteins or glucose
Lumbar Puncture
To sample CSF
Diagnose CSF diseases like meningitis